BIOL 3350 EXAM 2
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Essential fatty acids/lipids
Small intestine aka - midugt
Large intestine aka - hindgut
A state where the inside of the cell is negative, typically associated with excitatory signals.
voltage gated ion channels open and allow sodium ions to flow into the cell, making the inside more positive.
Brain structure that receives neural input about smells from the nasal cavity olfactory epithelium.
dendrites extend to mucous layer and ends to dendritic knob to the sensory cilia
axons connect to olfactory bulb in forebrain
Elephant, bear, wolf, raccoon, mouse
Arrange animals from lowest mass-specific metabolic rate to highest: elephant, raccoon, wolf, bear, mouse
bile salt
____ aids in the digestion of lipids by emulsifying
lipids
Energy reserves in the body are stored mainly as:
what are immune cells?
microglia
increase speed of action potential
what is the function of myelin sheaths on the axon?
the peripheral nervous system is made of the:
brain
spinal cord
none of the above
What facilitates the slowest form of communication at a synapse?
metabotropic receptors
Small-molecule neurotransmitters are synthesized in the ___ while neuropeptides are synthesized in the ___.
axon terminals, cell body
autonomic nervous system
The pancreas is controlled by the
Skeletal muscle movement is controlled by the:
somatic nervous system
sympathetic nervous system
Which uses norepinephrine as a neurotransmitter?
why do animals need nitrogen
they are essential building blocks of amino acids, which are required for most bodily functions
how does the body absorb lipids?
brokedown by lipidase → fatty acids emulsified by bile salts into small droplets → carried to cell membranes by micelle
Vitamins
compounds that can’t be synthesized, must be consumed by plants
once consumed vitamins are released, and we adapt to needing them
lipid soluble in vertebrates, water soluble for general functions
responsible for breaking down ingested food with bacteria in the gut microbe
what is beneficial about symbiotic microbes in digestion?
ruminants
consume plant material with regurgitation to imporve digestibility
hindgut fermenters
use microbes in the cecum/colon for further digestion
what can cause gut microbiome across species?
varies due to genetics, diet, and environmental factors
4 factors of a neruon:
dendrite
soma
axons
presynaptic
dendrite
recieves input from other neurons
soma
integrates input signals, filled with cargo packaged to be carried and released at other end of the neurons
axons
carries signals from cell body to synaptic terminals
presynaptic
neurotransmitters are released here
repolarization
Na+ channels close, K+ channels open
neuroplasticity structural benefits
physical changes including growth of new neurons and/or dendritic modeling
neuroplasticity nureotransmitters
physical adjustments, can go from electrical to chemical synapses and vice versa
electrical synapses pros and cons
pros:
high-speed transmission
direct current flow from neuron
con:
signal weakens transmitted to next cell
chemical synapses pros and cons
pros:
amplification of post-synaptic neuron responses
communication is modifiable “synaptic plasticity”
con:
slower than direct electrical passage
triggering of neuropeptide release
depolarization opens calcium channels → calcium binds protein synaptotagmin → activation of complex fusion cell membranes
results in exocytosis/recycling and release from synaptic terminals
small-molecule neurotransmitters
amino acids and/or their derivative, synthesized in axon terminal, packaged into synaptic vesicles by transport molecules
neuropeptide neurotransmitters
short chains of amino acids, produced & released by neurons that act as chemical messengers
synthesized as larger molecule
carried to vesicles
requires high action potentials & broken peptidase
long-term potentiation
After stimulation, long-lasting enhancement of synaptic transmission. Axon projections are stimulated, resulting in amplified and prolonged response to electrical stimulation
mechanoreception
response to mechanic stimulus
chemioreception
response to chemical stimulus
photoreception
response to light
salty/sour taste cells
include ionotropic receptors
sweet/bitter/umami cells
cells including metabotropic receptors
light interaction with photopigment receptors?
GCPRs specialized receptors with chromophore used to absorb light inducing conformational change within opsin (retinals)
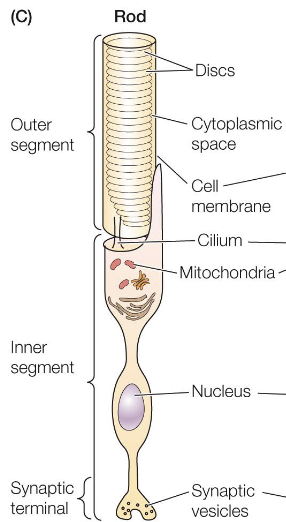
Rods
response to dim light using rhodopsin as opsin in the receptor
discs are non-continuous
no outer membrane
cyclic GMP (cGMP) usage
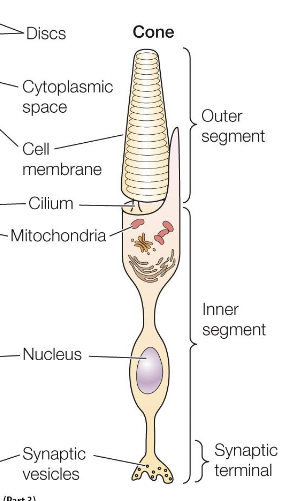
Cones
respond to bright light using 2+ opsin types
connected by modified cilium
membrane with photopigments in flattened disks
Central Nervous System (CNS)
integrative controller - primarily the brain & spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
connection to the rest of the body to the CNS
autonomic (sympathetic & parasympathetic)
somatic (sensory & motor)
Sensory Somatic Nervous System
communication through spinal nerves to areas below the neck
project from dorsal root ganglion (DRG) of spinal cord to skin
sensory nerve endings for mechanosensory input
Motor Somatic Nervous System
somatic neurons directly innervate muscle cells and communicate via acetylcholine s a neurotransmitter that
what is a nerve made of?
axons of multiple neurons in PNS bundle together
dendrite → soma → axon → node of Ranvier
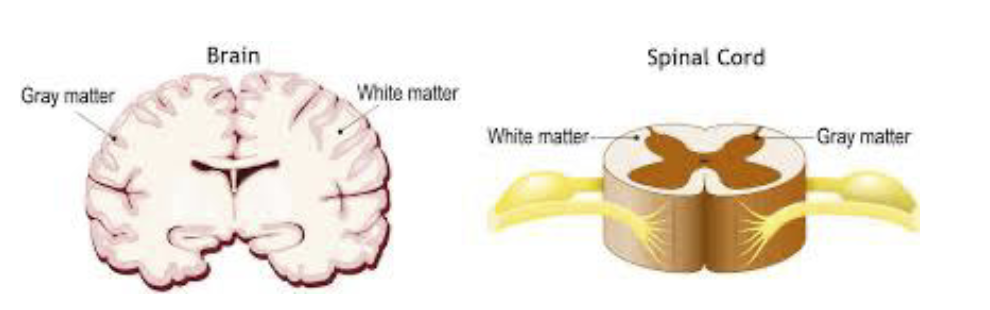
Grey matter
cell bodies & synapses
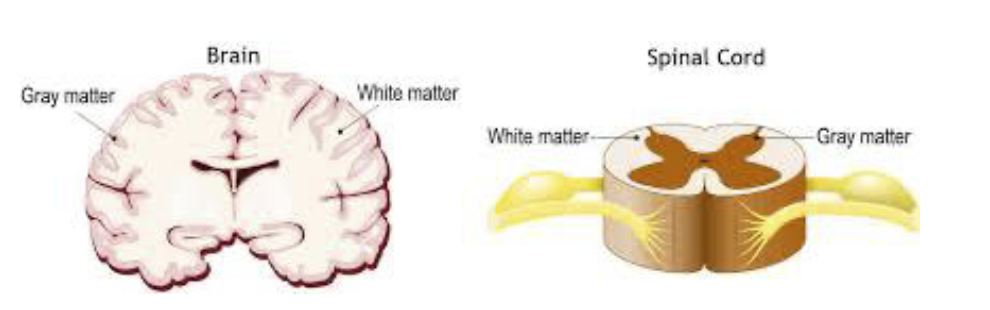
white matter
tracts of myelinated axons wrapped around oligodendrocytes = many lipids & fats
Somatic Nervous System
response to sensory system
coordination of skeletal muscles/motor control
Parasympathetic Autonomic System
response to calming system
balances sympathetic sytems
Enteric Autonomic System
gut mobility - gut nerves communicated to brain via vagus nerve
Vagus Nerve
responsible for 90% of connections from the gut to the brain
composition influences brain/behavior
Somatic Nervous System
signals projected from dorsal root ganglion of spinal cord to the skin
sensory nerve endings with specialized endings for mechanosensory
cranial nerves in the head and neck
motor control, direct innervated muscle cells
communicate via acetylcholine
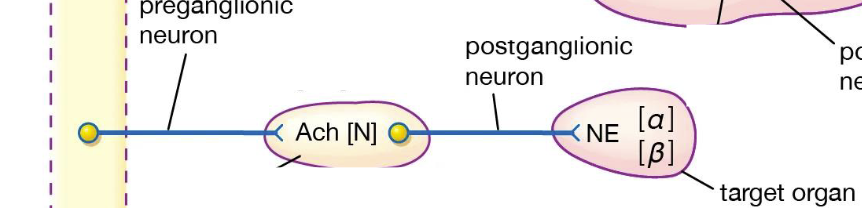
Sympathetic Somatic Nervous System
two neuron communication
short preganglionic neuron
longer postganglionic
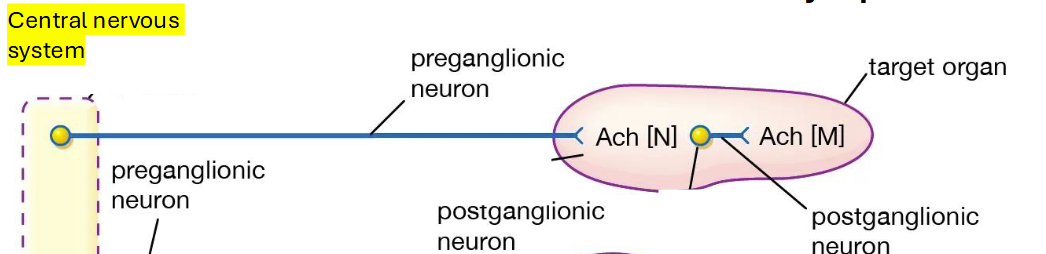
Parasympathetic Somatic Nervous System
two neuron communications
long preganglionic neuron
short postganglionic inside the target organ
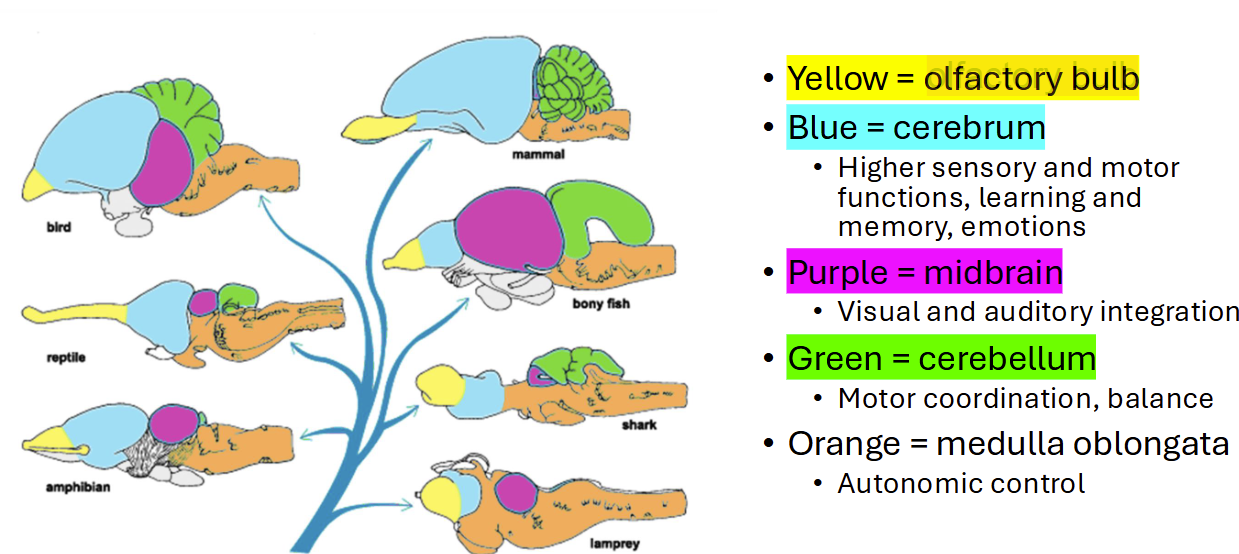
Cerebrum
high sensory and motor functions, learning, memory, & emotions
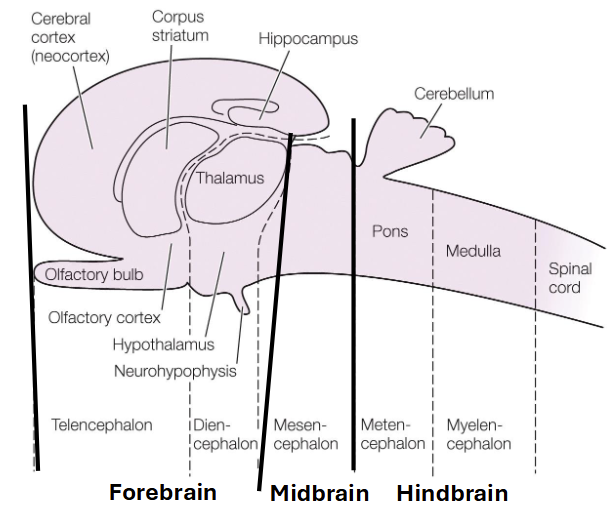
cerebellum
motor coordination
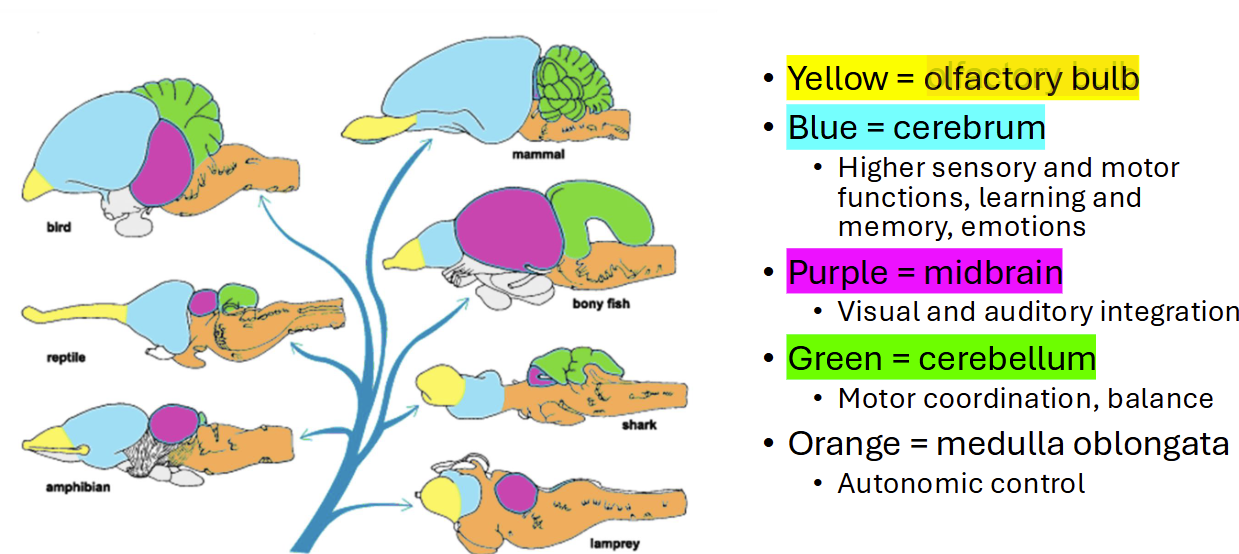
medulla oblongata
autonomic and respiratory control
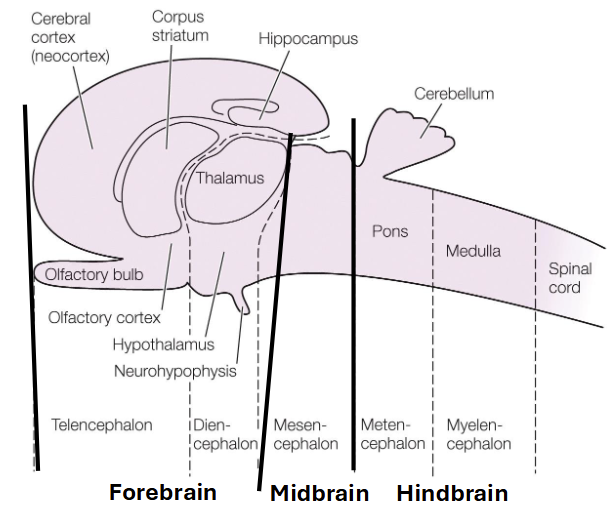
olfactory bulb
receives neural input about smells from nasal cavity