Scrotum & Prostate
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Verumontanum
The junction of the ejaculatory ducts with the urethra
Peripheral Zone
The largest zone in the prostate, containing 70% of the glandular tissue; the most lateral portions of the prostate; found lateral and and posterior to the urethra; Most cancers arise here
Central Zone
Forms about 20% of the prostate bordering seminal vesicles
Transition Zone
Located on the lateral sides of the proximal urethra; where BPH occurs
Ejaculatory ducts
descend inferiorly through the posterior portion of the gland and open into the prostatic urethra
BPH
Benign prostatic hypertrophy; common in older men; constricts the urethra
Seminal fluid
Produced by the prostate, seminal vesicles, and Cowpers gland
PSA
Serum prostatic specific antigen; used to evaluate the function of the prostate; levels nearing 10 are always suspicious for pathology
*levels will rise with the age of the pt.
Adenocarcinoma
The most common malignant neoplasm of the prostate
Seminal vesicles
Superior and slightly posterior to the prostate
NL size of the prostate
4 × 3 × 4cm
PSA density formula
= PSA/ gland volume
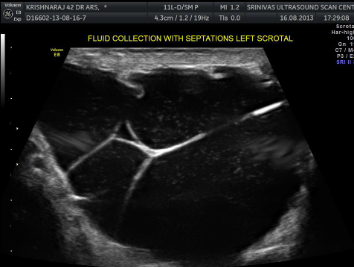
Hydroceles
Located between the two layers of tunica vaginalis; SA: anechoic fluid filled in the scrotal sac surrounding testicles and epididymis, may contain debris or septations
CI: Asymptomatic or pt. c/o of scrotal enlargement
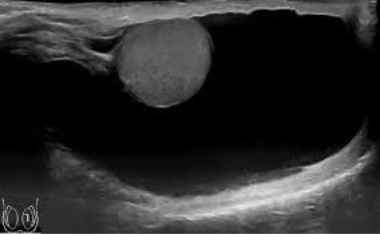
Cryptorchidism
Undescended testicle, typically seen in newborns; cannot be brought into the scrotum with external manipulation; 80% of cases, the testis is found in the inguinal canal; high risk for cancer and infertility
SA: smaller and less echogenic, oval and homogenous, mediastinum usually not seen
CI: Asymptomatic or palpable mass in the pelvic/ groin region
Epididymitis
infection of the epididymis
SA: enlargement, hypoechoic gland, increased vascularity
CI: scrotal pain/ possible discharge
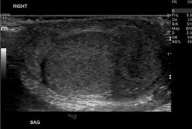
Normal appearance of the testis
smooth, homogeneous, echogenic, ovoid shape
Best scanned from superior to inferior
Normal appearance of the epididymis
Normal finding: shows little flow with color doppler
Undescended testis
SA: smaller and less echogenic than the normal testis
*more likely to develop cancer
Lymphoma
SA: decreased echogenicity; patchy-looking; “liver that’s focal sparing”
CI: Pt. may experience wt. loss, anorexia, & weakness
Testicle may become enlarged
Diffuse orchitis
SA: decreased echogenicity, and vascularity throughout entire testicle
CI: pain, fever, nauseas, vomiting
*almost always occurs secondary to epididymitis
Infarction
Tissue death due to lack of blood flow
SA: hypoechoic wedge shaped area
CI: decreased or complete absence of doppler
*if entire testis in infarcted, findings cannot differentiate from testicular torsion
Hydrocele image
Can have a “snow globe” like appearance, or largely septated loculations
Germ Cell Tumors
Type of testicular tumor that is typically highly malignant
Associated with elevated HCG & AFP levels
Seminoma
SA: solid/homogeneous, hypoechoic masses with a smooth border
*The most common germ cell tumor
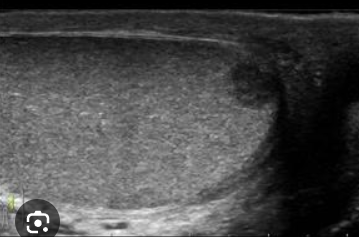
Embryonal cell tumor
Second most common germ cell tumor; more aggressive than seminomas, invading the tunica albuginea
SA: heterogeneous, poorly circumscribed *may contain echogenic areas/ calcifications
Teratocarcinoma
Third most common germ cell tumor, MALIGNANT
teratomas
lesser common germ cell tumor; benign in children; may show dense foci that produce acoustic shadowing
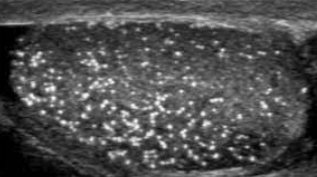
microlithiasis
An uncommon condition characterized by tiny calcifications within the testis; typically smaller then 3mm; occurring bilaterally
SA: multiple tiny echogenic foci throughout the testicle, w/ or w/o shadowing “speckling”
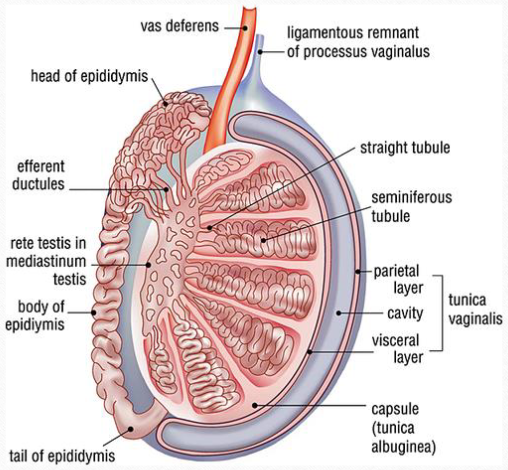
rete testis
Tiny tubular structure in the mediastinum, located at the hilum of the testis; drains into the head of the epididymis through the efferent ducts
epidiymis
Tubular structure beginning superiorly and courses posterolateral to the testis; the head is the largest part; reservoir for sperm
mediastinum testis
vertical septum; supporting structure for vessels
SA: thin echogenic line
spermatic cord
contains the vas deferens, testicular arteries, venous pampiniform plexus (veins), & lymph vessels
tunica albuginea
Dense/ fibrous tissue that completely covers the testicle
tunica vaginalis
Lines the inner walls of the scrotum, covering each testis and epididymis; consists of two layers
Parietal & Visceral layers
Two layers that comprise the tunica vaginalis:
visceral- surround the testis and epididymis
Parietal- inner layer of the scrotal wall
*hydroceles form between these two layers; it is normal to see a small amount of fluid here
testicular arteries
Both LT and RT arteries arise from the abdominal AO just below the renal arteries; primary source of blood flow to the testis
Vascular flow
Lobules—> tubules—> straight tubules—> rete testi (in the mediastinum)—> efferent ducts—> epididymal head/body/tail—>vas deferens (spermatic cord)
Pampiniform plexus
venous drainage of the scrotum
optimal pt positions for exam
Supine
upright position used to check for varicoceles
**or valsalva maneuver
Performing an exam
It is best to perform a brief survey scan to determine what abnormalities are present; each testis is scanned from superior to inferior
Varicoceles
Abnormal dilation of the veins within the spermatic cord; caused by incompetent venous valves; more commonly on the left due to drainage of the spermatic vein into the left renal vein; LRV can become compressed between SMA and AO
Hernnia
occur when bowel, omentum, or other structures herniate into the scrotum; the bowel is the most common herniated structure; peristalsis of the bowel confirms the diagnosis of a scrotal hernia
Rare varicoceles
rare in the testicle
mediastinum
posterior portion of the tunica albuginea
Testicular microlithiasis
tiny echogenic foci throughout testis; with or without shadowing
Abscess
Increased WBC, fever, variable mass with irregular borders
Labeling testicle