AP Calc AB Formulas
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
sin²x + cos²x =
1
1 + tan²x =
sec^2 x
1 + cot²x =
csc^2 x
sin(A + B) =
sinA cosB + cosA sinB
sin(A - B) =
sinA cosB - cosA sinB
cos (A + B) =
cosA cosB - sinA sinB
cos (A - B)
cosA cosB + sinA sinB
sin(2x) =
2sinx cosx
cos(2x)
cos^2 x - sin^2 x
sin(-x) =
-sinx
cos(-x) =
cosx
tan(-x) =
-tanx
Definition of |x|
|x| = {
x if x >= 0
-x if x < 0
distance between two points
sqrt( (x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2 )
midpoint formula
((x1 + x2) / 2, (y1 + y2) / 2)
ln(ab) =
lna + lnb
ln(a/b) =
lna - lnb
ln(a^n) =
n * lna
ln(1/a) =
-lna
sec(x) =
1 / cos x
csc(x) =
1 / sin x
tan(x) =
sin x / cos x
cot(x) =
cos x / sin x
Definition of a limit
lim x -> a f(x) = L iff lim x -> a^- f(x) = L = lim x -> a^+ f(x)
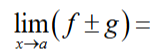
lim x -> a f +- lim x -> a g
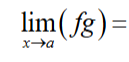
lim x -> a f * lim x -> a g
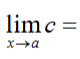
c
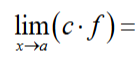
c * lim x -> a f
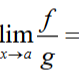
lim x -> a f / lim x -> a g for lim x -> a g != 0
Definition of Vertical Asymptote:
The line x = a is called a vertical asymptote iff lim x -> a^- f(x) = +-infinity or lim x -> a^+ f(x) = +-infinity
Definition of Horizontal Asymptote: (use “a” and f(x) to answer)
The line y = a is called a horizontal asymptote iff lim x -> -infinity f(x) = a or lim x -> infinity f(x) = a
Limits of the ratios of two functions
Consider these:
x^c
ln a
x^c * ln a
a^x
x!
x^x
x^(c + d)
ln a < x^c < x^c * ln a < x^(c + d) < a^x < x! < x^x
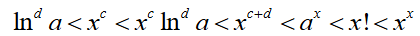
if f grows faster than g, then
lim x -> infinity
g(x) / f(x) = 0
f(x) / g(x) = infinity
Definition of continuity
a function f is continuous at x = a iff
1. f(a) exists
2. lim x -> a f(x) exists
3. lim x -> a f(x) = f(a)
Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT): If, then
If
1. f is continuous on the closed interval [a,b]
2. f(a) != f(b)
3. k is between f(a) and f(b)
Then there exists a number c between a and b for which f(c) = k
Squeeze Theorem
if f(x) <= g(x) <= h(x) and as x -> a, f(x) -> L and h(x) -> L, then g(x) -> L
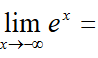
0
lim x -> infinity e^x =
infinity
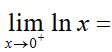
-infinity
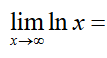
infinity
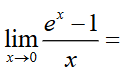
1
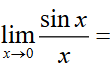
1
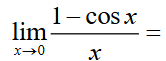
0
e^c = (2 equations of common limits)
lim x -> +- infinity (1 + c/x)^x
lim x -> 0^+ (1 + cx)^(1/x)
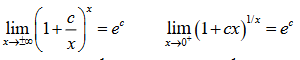
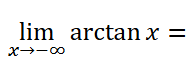
-pi / 2
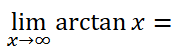
pi / 2
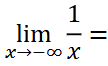
0
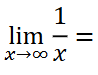
0
derivative standard formula/ limit of the difference quotient
f’(x) = lim h -> 0 ( f(x + h) - f(x) ) / h
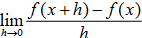
Derivative alternative formula
f’(x) = lim x -> c ( f(x) - f(c) ) / (x - c)
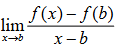
Normal Line
The line perpendicular to the tangent line at the point of tangency.
Average rate of change of f from x = a to x = b is (definition and equation)
the slope of the secant line between the 2 points
( f(b) - f(a) ) / ( b - a )
average rate of change =
delta f / delta x
delta y / delta x
( f(b) - f(a) ) / (b - a)
Three reasons a function, f, will not be differentiable at a point x = a
1. f is not continuous at x = a
2. The graph of f has a “corner” or “cusp” at x = a
3. The graph of f has a vertical tangent at x = a
s(t) =
position
v(t) =
velocity = s’(t)
|v(t)| =
speed
a(t) =
acceleration = v’(t) = s’’(t)
particle at rest when v(t) =
0
speed is increasing if
v and a have the same sign
speed is decreasing if
v and a have opposite signs
average velocity is the same as
average rate of change of the position
differentiation rules (for things like chain rule, product, and quotient rule) (functions f and g, and what c is)
f and g are functions of x
c is a constant
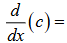
0
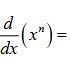
n * x^(n-1)
![<p>or d/dx [cf(x)] = </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/614956ef-1d06-4cac-b6e2-04f87eb3810b.png)
or d/dx [cf(x)] =
c * d/dx f(x)
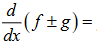
d/dx f(x) +- d/dx g(x)
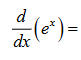
e^x
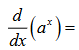
a^x * ln(a)
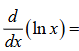
1/x
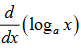
1/(x * lna)
Chain Rule: if h(x) = f(g(x), then
h’(x) = f’(g(x) * g’(x)
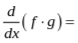
Product Rule
f’ * g + f * g’
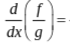
Quotient Rule
(f’ * g - f * g’) / g^2
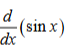
cosx
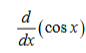
-sinx
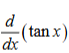
sec^2 x
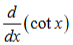
-csc^2 x
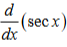
secx * tanx
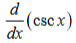
-cscx * cotx
The equation for Linear approximation of f for values of x near x = a
y = f(a) + f’(a) (x - a)
Linear approximation of f for values of x near x = a
What is a?
a is the x-value at the point of tangency
(tangent line at x = a)
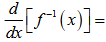
Inverse Function (if then equation)
f must be differentiable and one-to-one on the interval, then
1 / ( f’(f^-1(x)) )
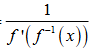
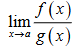
L’Hospital’s Rule (When, then)
This rule can only be used directly when the limit evaulates to the indeterminate forms 0/0 and infinity / infinity.
lim x -> a f’(x) / g’(x)
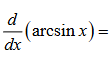
1 / sqrt(1 - x^2)

-1 / sqrt(1 - x^2)
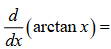
1 / (x^2 + 1)
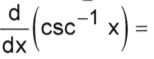
-1 / |x| sqrt(x^2 - 1)
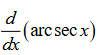
1 / ( |x| * sqrt(x^2 - 1) )
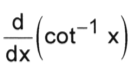
-1 / (x^2 + 1)
Extreme Value Theorem (EVT)
If f is continuous on a closed interval [a,b]
Then f has an absolute max and an absolute min on the interval [a,b]
Definition of critical points: A critical point of f is a number c (x value) such that either
f’(c) = 0 or DNE
Candidates Test for extreme values on a closed interval
1. Find the y-values of critical points in the interval (a,b)
2. Find the y values of endpoints, a and b
3. The largest y-value is the maximum and the smallest y-value is the minimum
Rolle’s Theorem
If
1. f is continuous on [a,b]
2. differentiable on (a,b)
3. f(a) = f(b)
Then there is at least one number c on (a,b) such that f’(c) = 0
Mean Value Theorem
If
1. f is continuous on [a,b]
2. differentiable on (a,b)
Then there exists a number c between a and b such that f’(c) = ( f(b) - f(a) ) / (b - a)
Test for increasing and decreasing respecitively
f’ > 0 means increasing
f’ < 0 means decreasing
Relative Extrema
relative (or local) mins/maxes must occur at critical points
1st derivative test for relative extrema ( f(c) must exist)
1. if f’ changes from positive to negative at c, then f(c) is a relative max
2. if f’ changes from negative to positive at c, then f(c) is a relative min
3. if f’ does not change signs at c, then f(c) is neither a max or a min
Test for concavity
f’’ > 0 means f is concave up
f’’ < 0 means f is concave down
Definition of point of inflection (POI)
A point on the graph of f where the concavity of f changes