BIOL1111 (General Biology 1) Exam 1 Mary Sue Potts Santone
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Defining Life
All living things are comprised of the same chemical elements and obey the same physical and chemical laws as nonliving objects
3 Things for Life
Hereditary material, raw material, energy inputs
Biological Evolution
Descent with modification (the process by which the characteristics of organisms change over generations, by means of genetic variation and natural selection)
Unity
The theory of evolution is a unifying concept in Biology and shows how all living organism descended from a common ancestor
Diversity
The the theory of evolution also explains the vast amount of diversity in living species
Natural Selection
The process whereby organisms better adapted to their environment tend to survive and produce more offspring
Adaptation
Any modification that makes an organism suited to its way of life
Aristotle
Author of Scala Naturae (scale of life) that classified organisms and non living objects from least to most complex
(Carolus) Linnaeus
Author of Systema Naturae and creator of binomial nomenclature
(Charles) Darwin
Creator of the theory of evolution based on natural selection
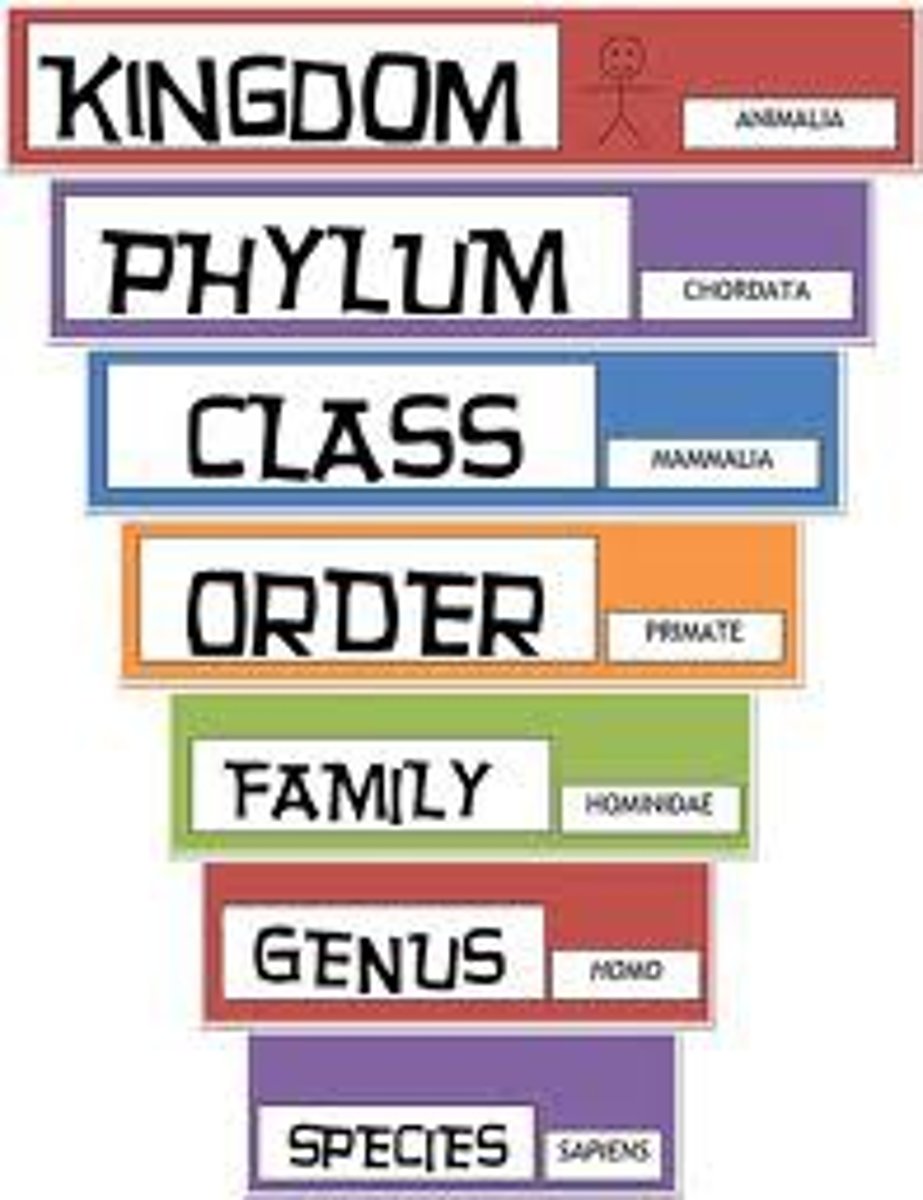
Taxonomy
Science of identifying and classifying organisms according to evolutionary relationships
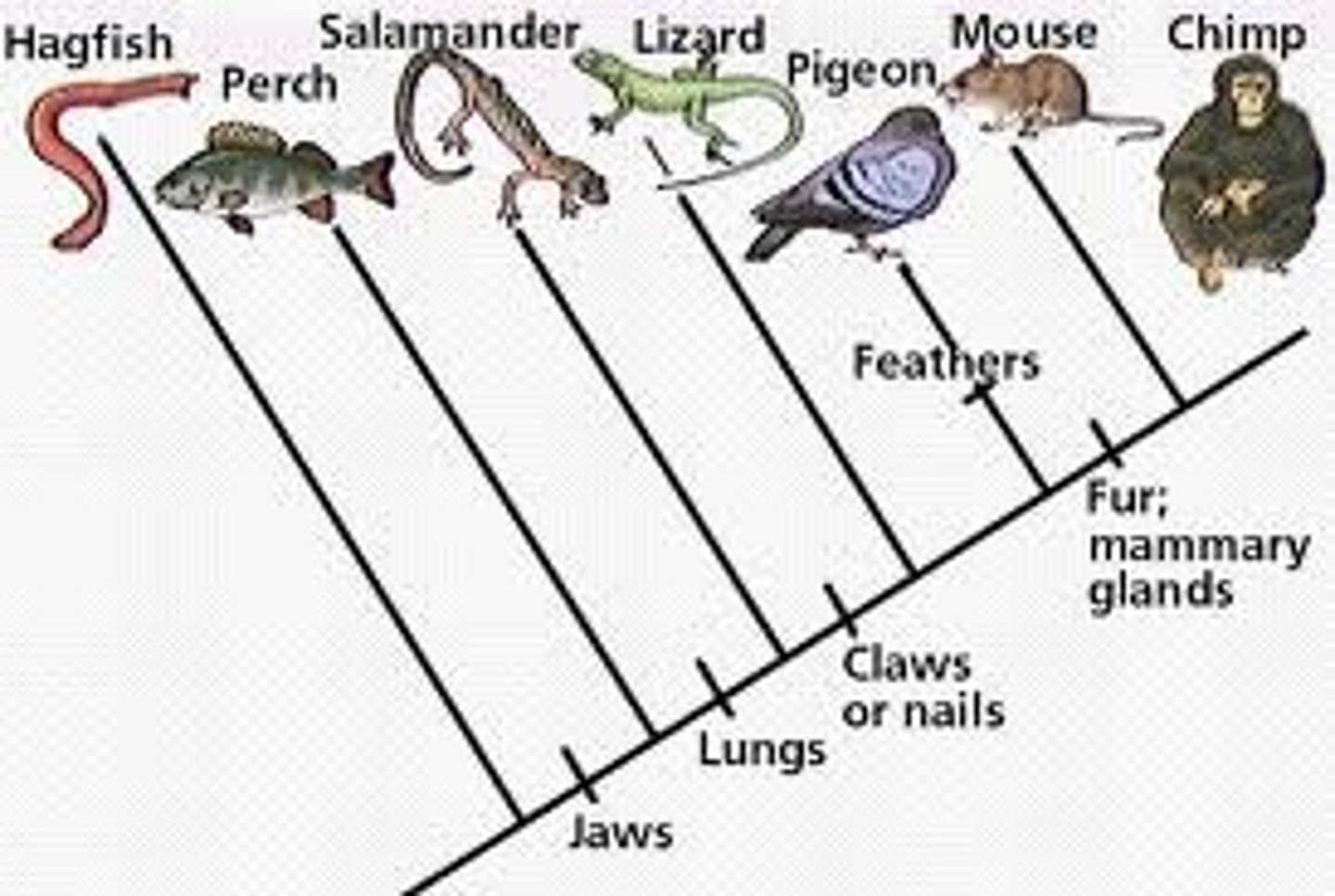
Phylogeny
Tree of life
Scientific Name
Binomial Nomenclature (Genus species), universal, Latin-based
Levels of Biological Organization
Cell->Tissue->Organ->Organ System->Organism(species)->Population->Community->Ecosystem->Biosphere
Cell
Most basic unit of life
Materials and Energy
Energy is the capacity to do work, energy flows through the biosphere in nutrient cycles
Metabolism
All chemical reactions in a cell
Anabolism
The synthesis of more complex substances from simpler ones (constructive metabolism)
Catabolism
The breaking down of more complex substances into simpler ones, with the release of energy (destructive metabolism
Homeostasis
Maintenance of internal conditions within certain boundaries
Dynamic Equilibrium
A state of balance between continuing processes
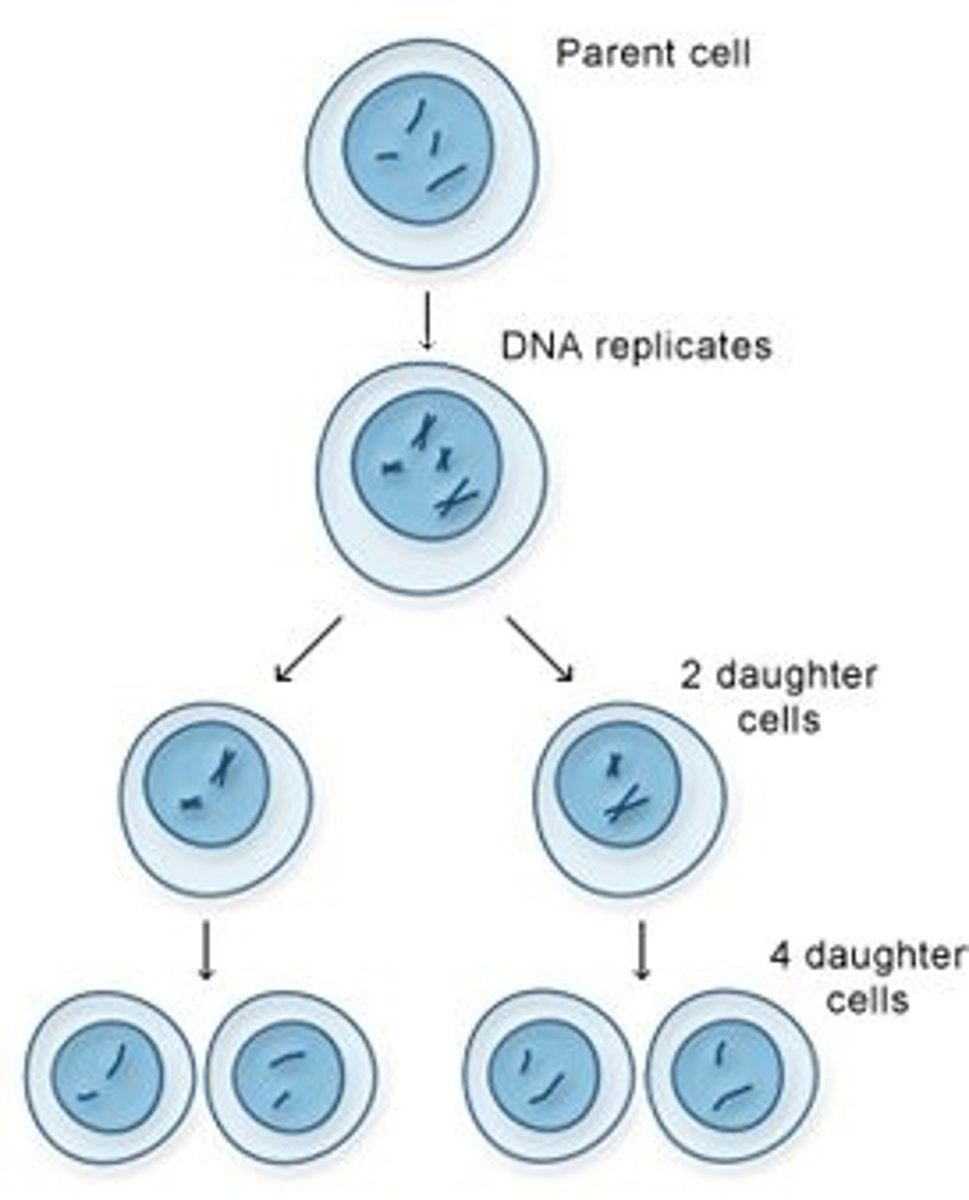
Mitosis
Cell division that results in two daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth.
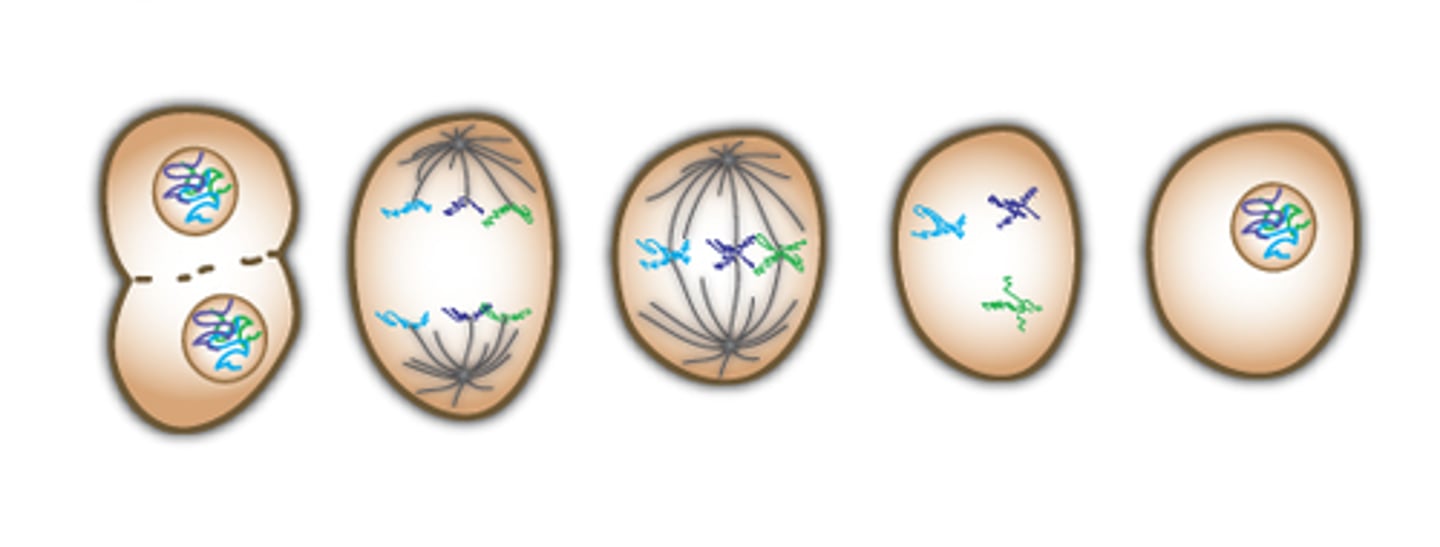
Meiosis
Cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes
Stimuli
Stim->receptor->control center->response(usually movement)->prompts survival
Behavior
Responses collectively constitute behavior and are examples of adaptations
Science
Obeys natural laws, explained in reference to natural law, it is tentative and falsifiable
Discovery (Descriptive) Science
Science that begins with observation and has conclusions based on inductive reasoning (qualitative)
Inductive Reasoning
Reasoning where specific observations lead to a general principle
Deductive (Scientific) Method
Scientific method where general principles are applied to specific circumstances so that one may form hypotheses
Deductive Reasoning
Reasoning in which a conclusion is based on the multiple principles that are generally assumed to be true (quantitative)
Hypothesis
Tentative, testable explanation for what was observed
Scientific Theory
Related to well-supported hypotheses that for a broad ranging testable explanation about fundamental aspects of the natural world; complex and dynamic; regarded as true by scientific community
Scientific Law
Statement of fact that concisely describes an action; often expressed as a mathematical equation; universally true
C, H, O, N, P, S
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur; organisms 98% composed of these elements
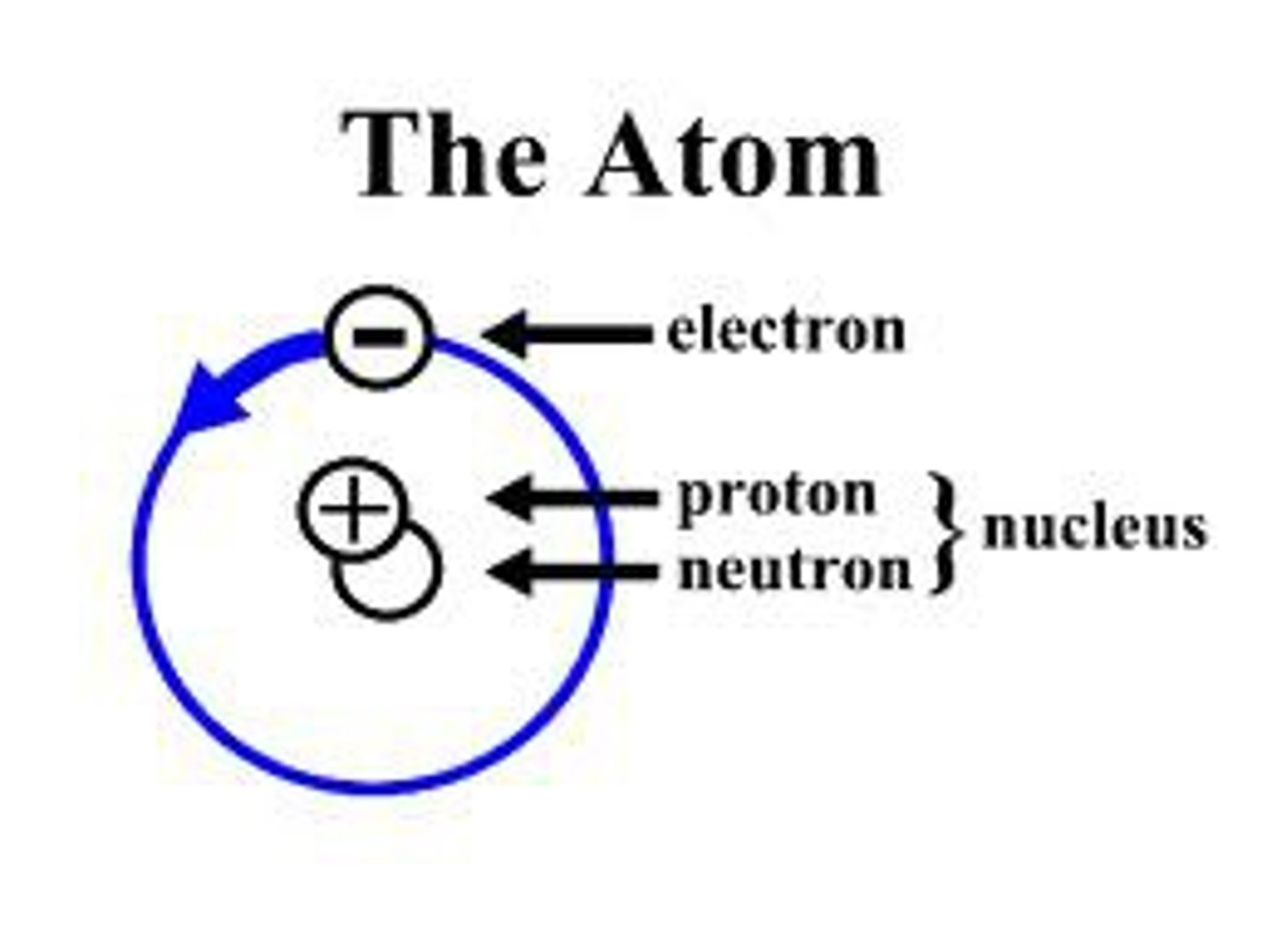
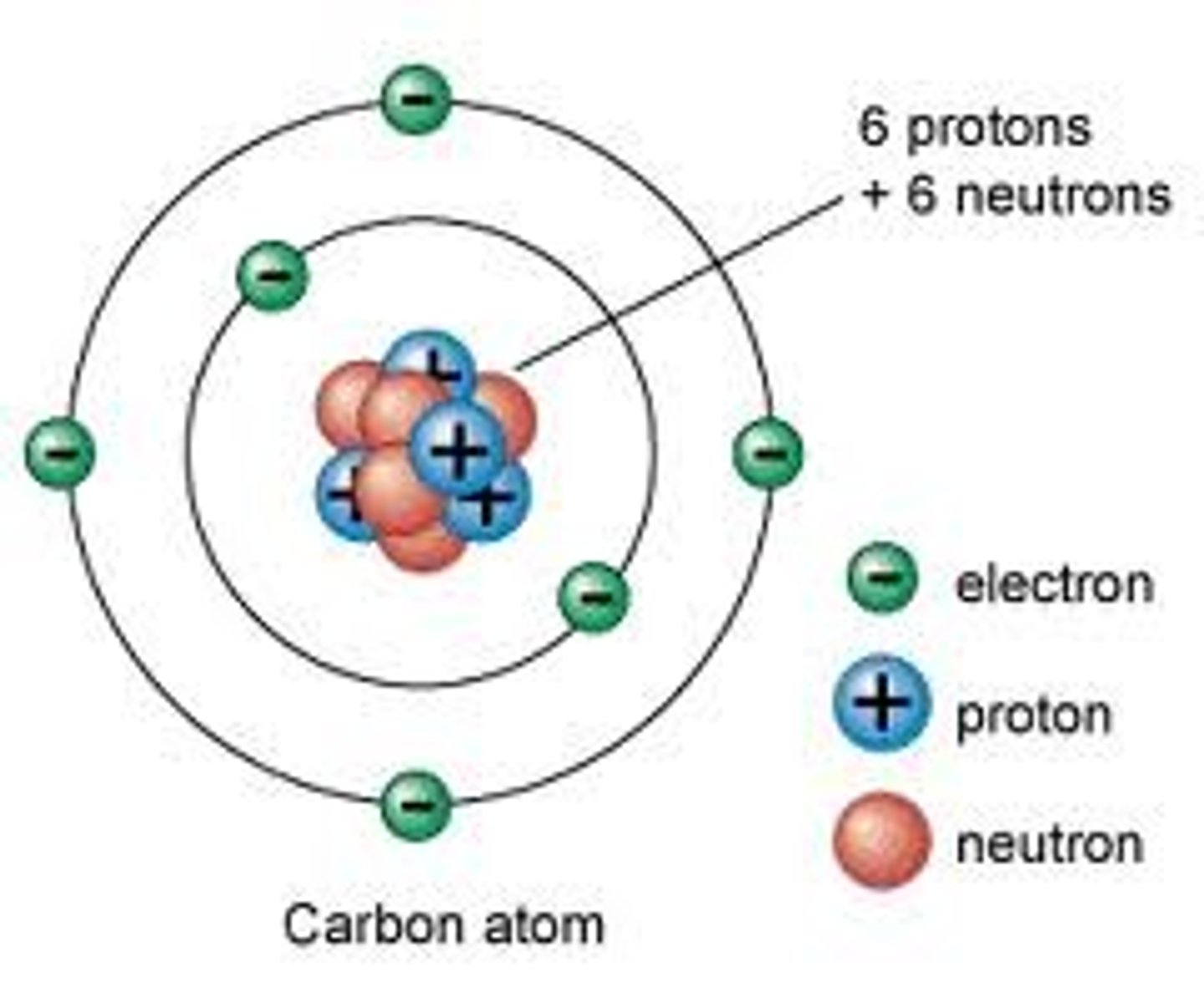
Atom
Smallest functional unit of matter that form all chemicals
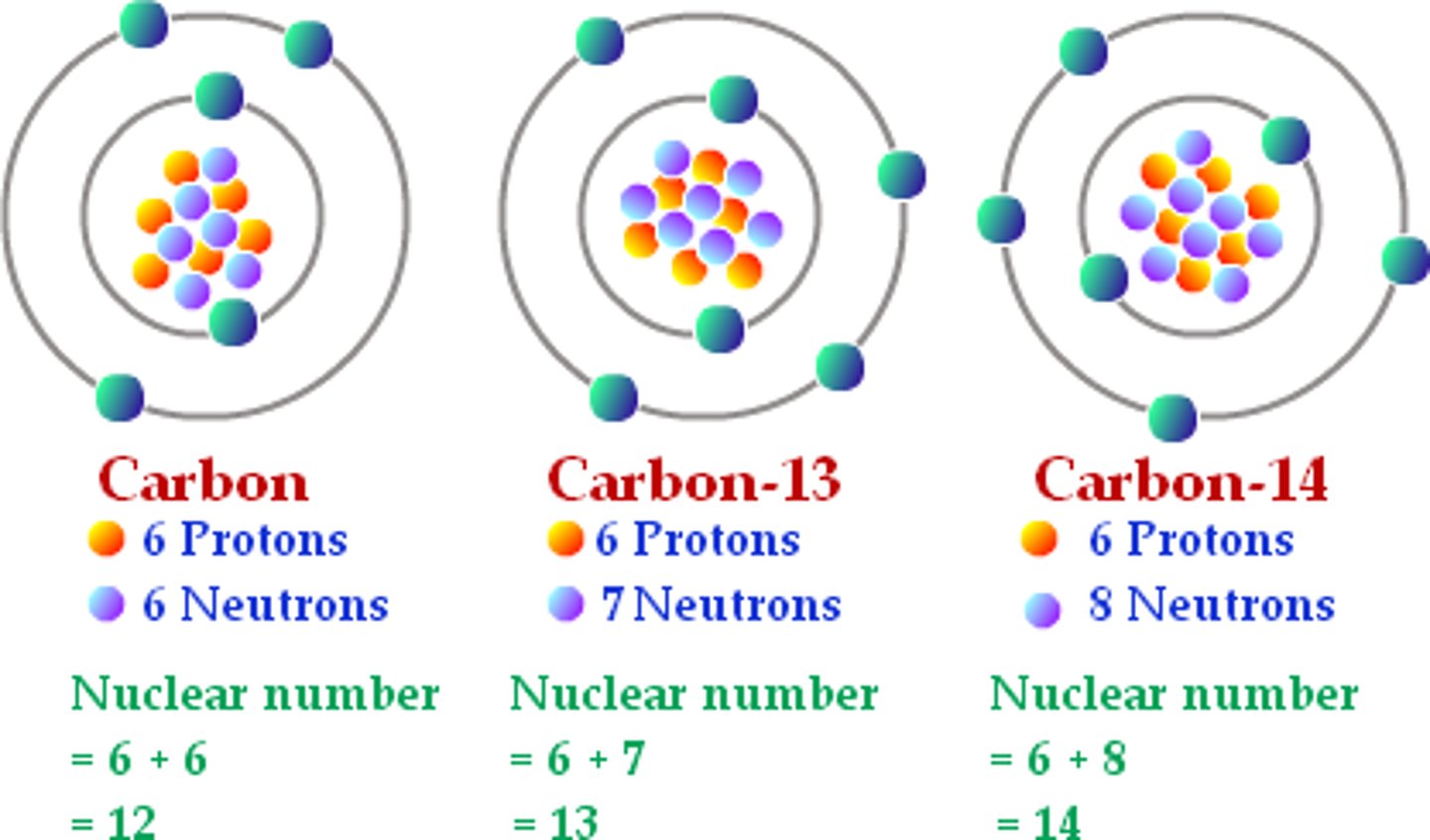
Isotope
Same element with different numbers of neutrons
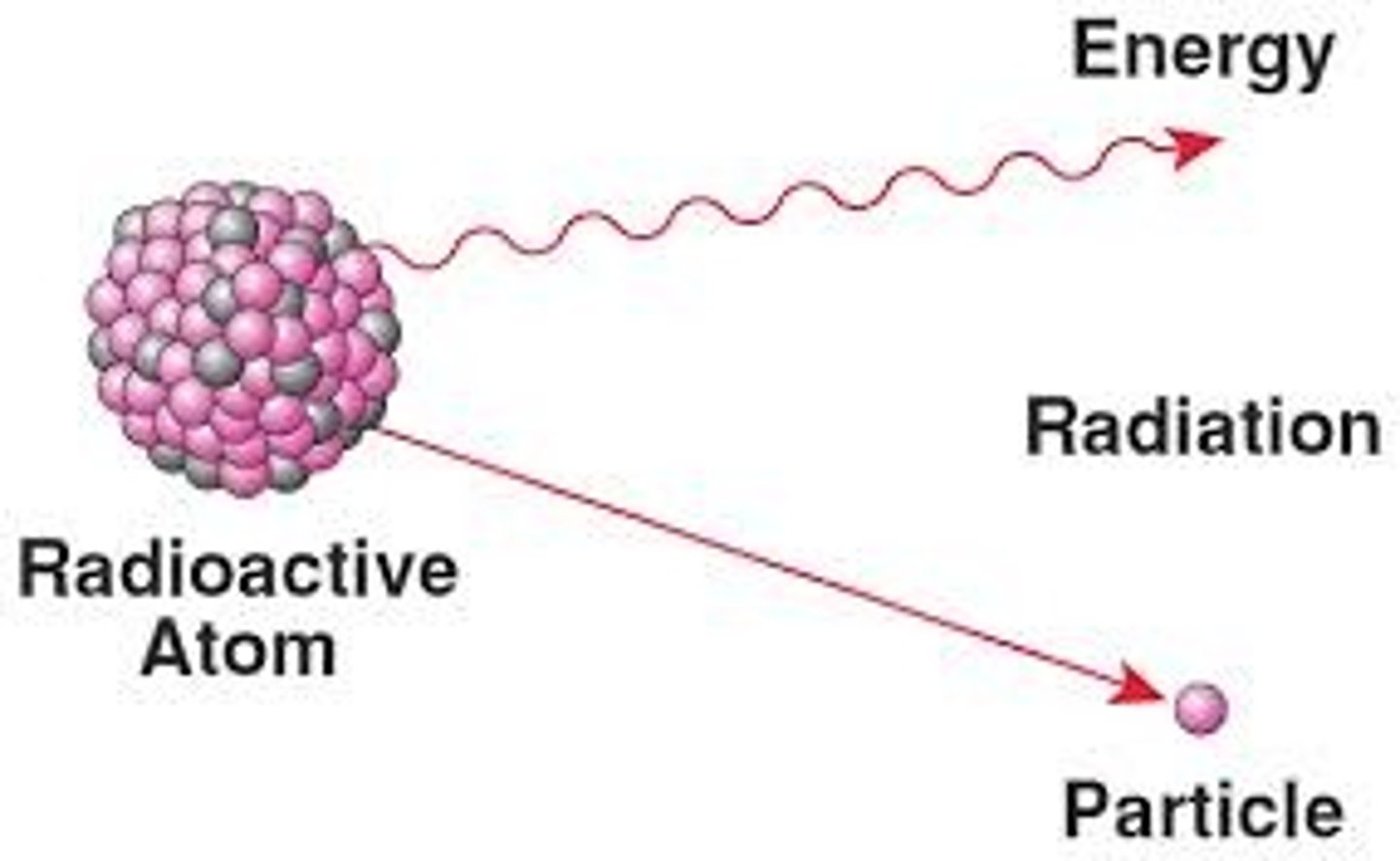
Radioisotope
Isotopes that spontaneously decay; give off energy in the form of rays (gamma) or subatomic particles (alpha, beta)
Bohr Model
Electron shells as concentric circles around nucleus
Octet Rule
Atoms tend to combine in such a way that each atom has eight electrons in its valence shell
Molecule
Two or more atoms bonded together.
Compound
A substance formed from two or more elements
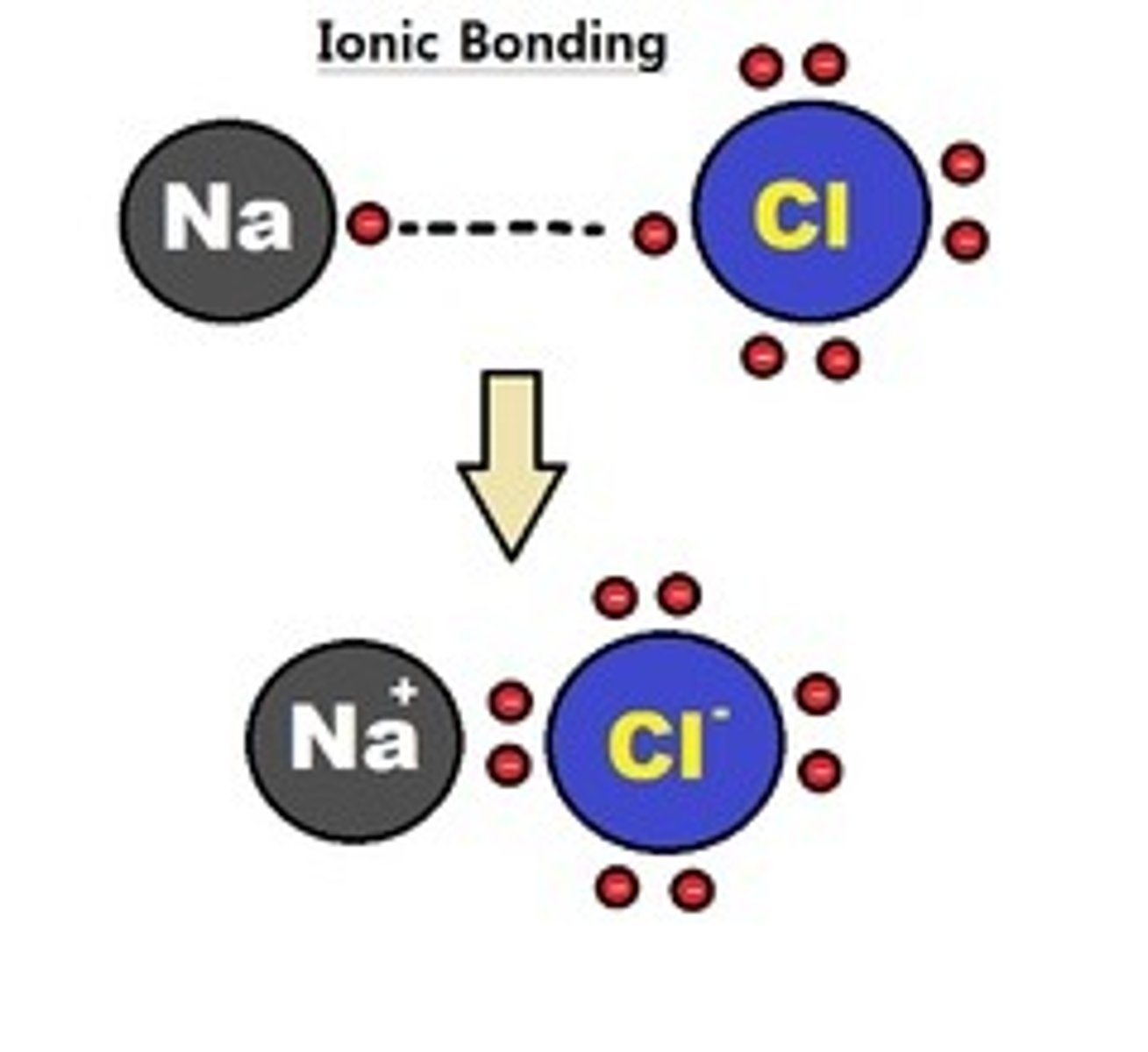
Ionic Bond
Type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions; complete transfer of valence electrons between atoms
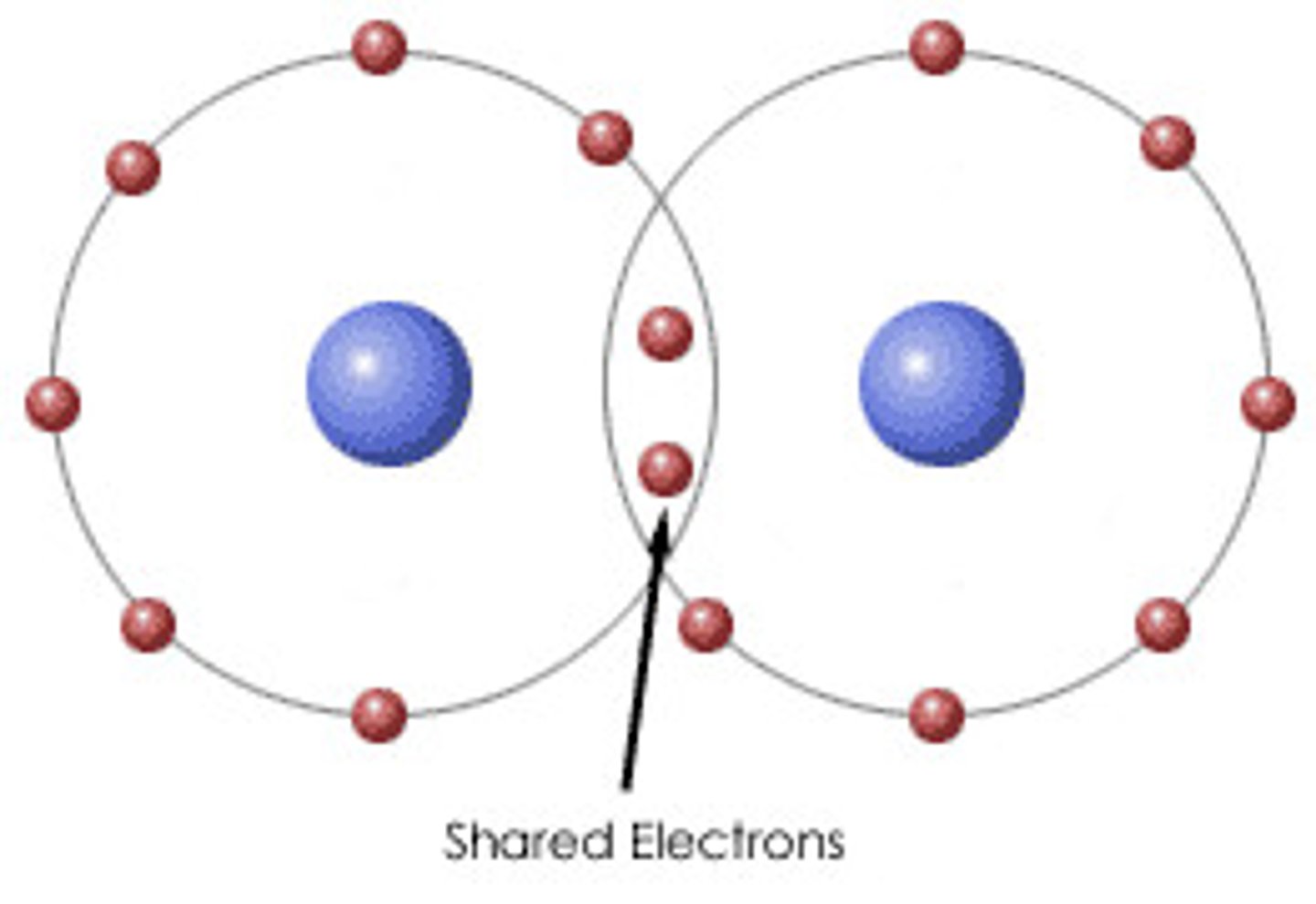
Covalent Bond (Polar v Nonpolar)
Chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms
Electro - negativity/positivity
N: Measure of the tendency of an atom to attract an electron
P: Measure of the tendency of an atom to donate an electron
Free Radicals
Atoms with a single unpaired electron in outer shell
Hydrogen Bond
H atoms in one molecule are attracted to the O or N atoms in other polar covalently bonded molecules, between molecules or between parts of large molecule
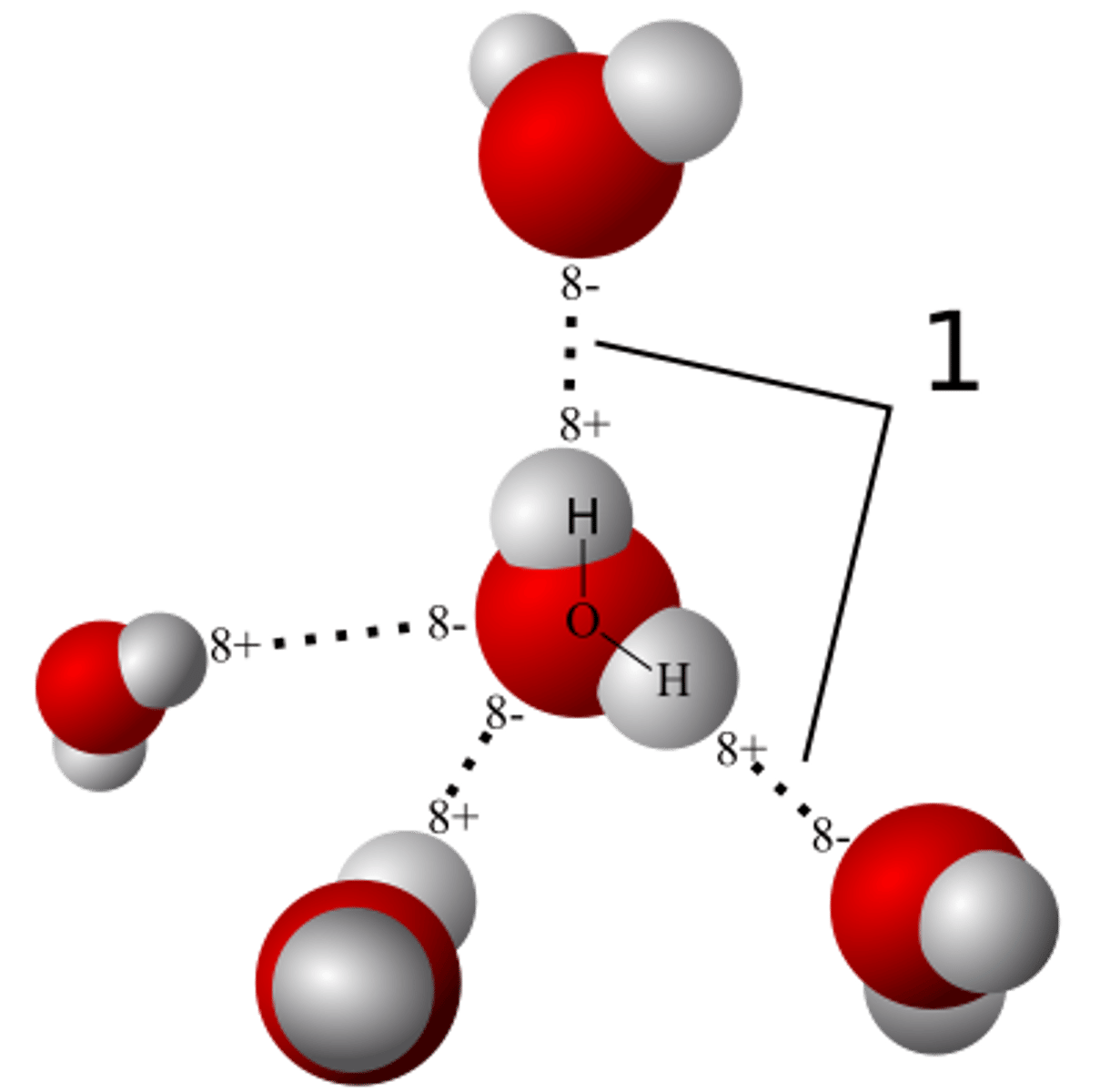
Water
Hydrogen bonding; high heat capacity; high heat of vaporization; cohesive; adhesive; high surface tension
Ice
unique solid; less dense than liquid state; insulation
Acid
Dissociate in water to release hydrogen ions; pH < 7
Base
Dissociate in water to release hydroxide ions; pH > 7
Neutralization Reaction
When an acid and a base react to form water and a salt
pH scale
Measure of acidity/basicity in a solution; logarithmic scale

Buffer
Solution that resists changes in pH when acid or base is added to it
Organic Compound
Type pf compound with carbon and hydrogen; each carbon can bond with up to 4 different atoms; covalent bonds; large
Inorganic Compund
Any compound that is not organic; ions; ionic bonding; few atoms
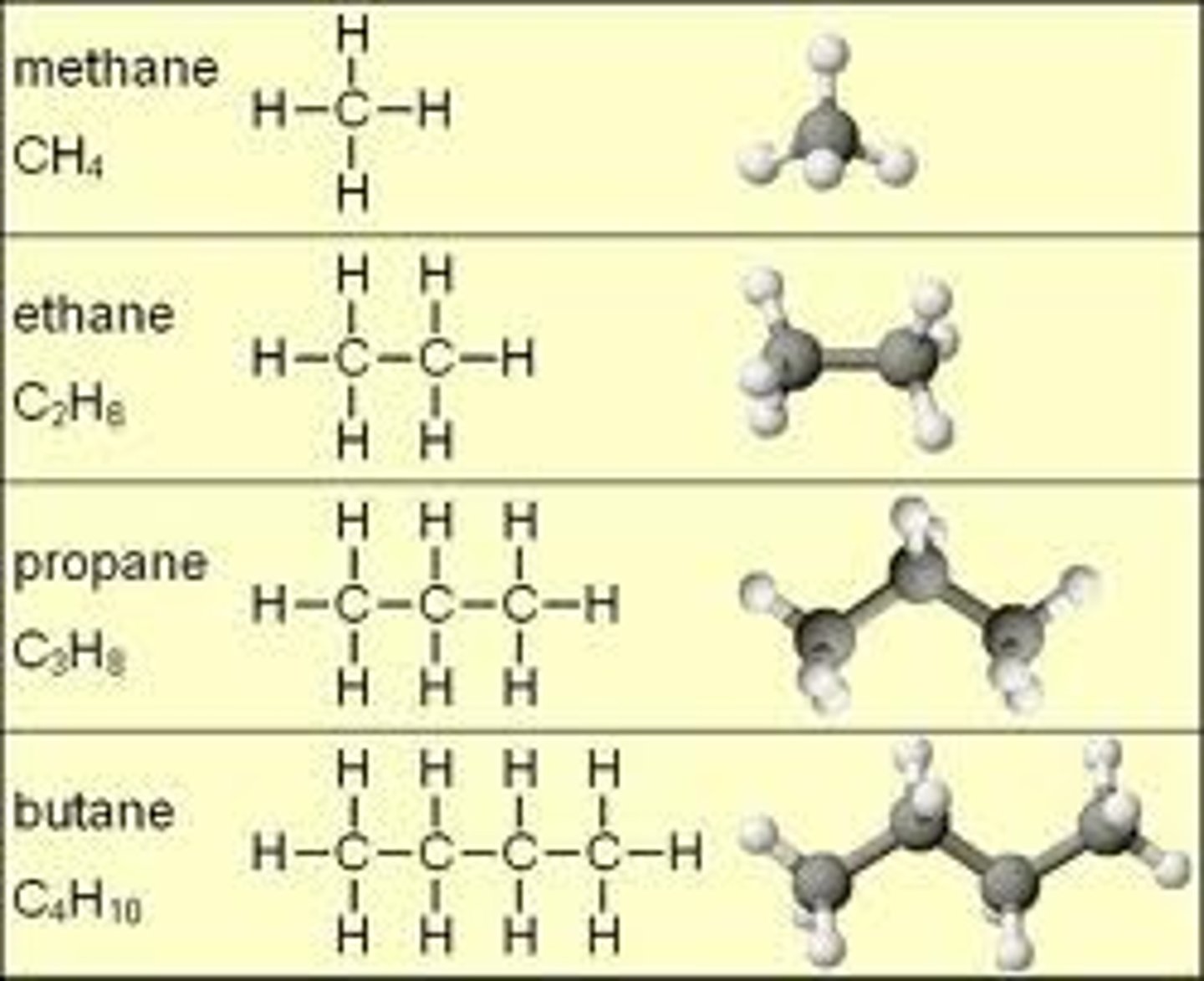
Hydrocarbon
Long carbon chains; usually skeleton/backbone of organic compounds; may be linear, ringed, or branched
Functional Group
Group of atoms responsible for the characteristic reactions of a particular compound (i.e. hydroxyl, carboxyl, phosphate, amino)
Hydroxyl Group
Alcohols (R-OH)
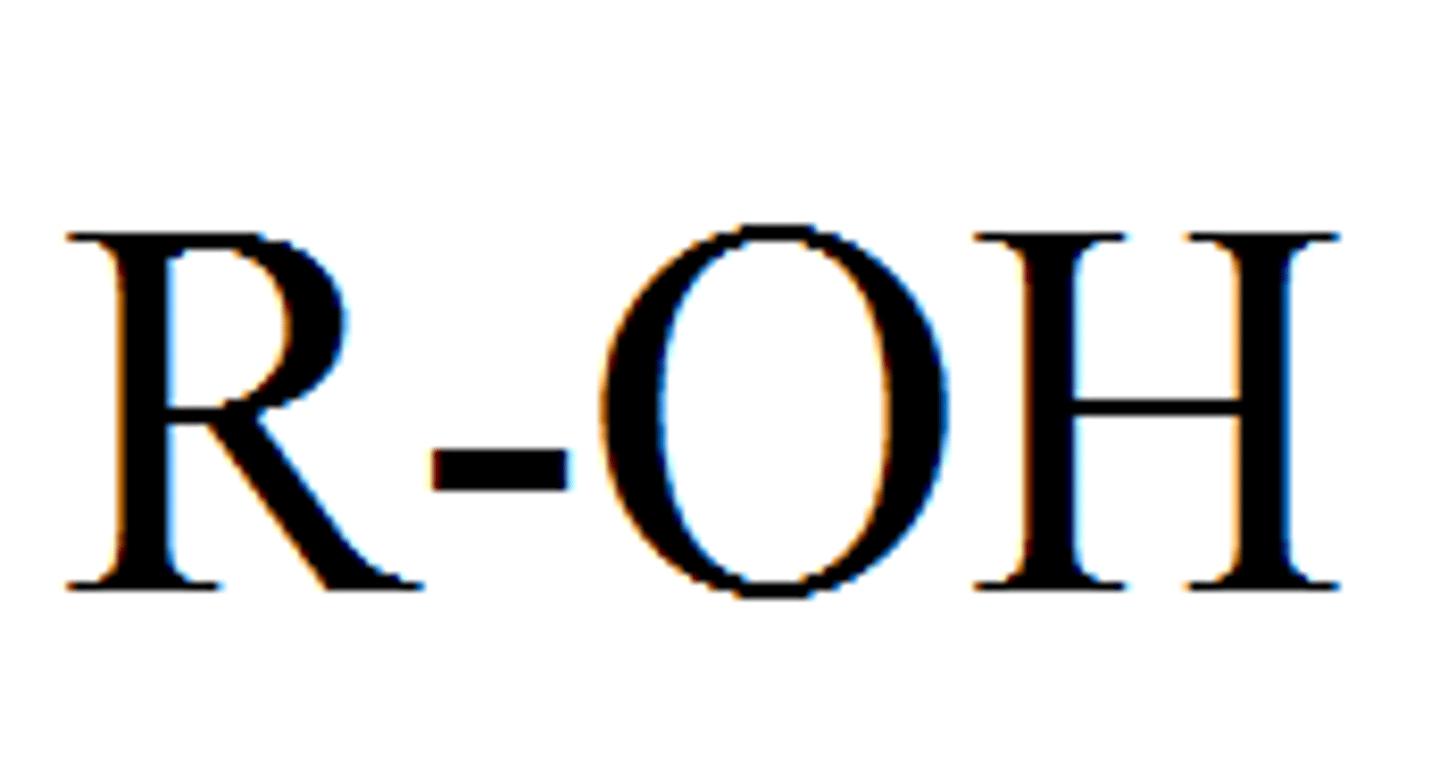
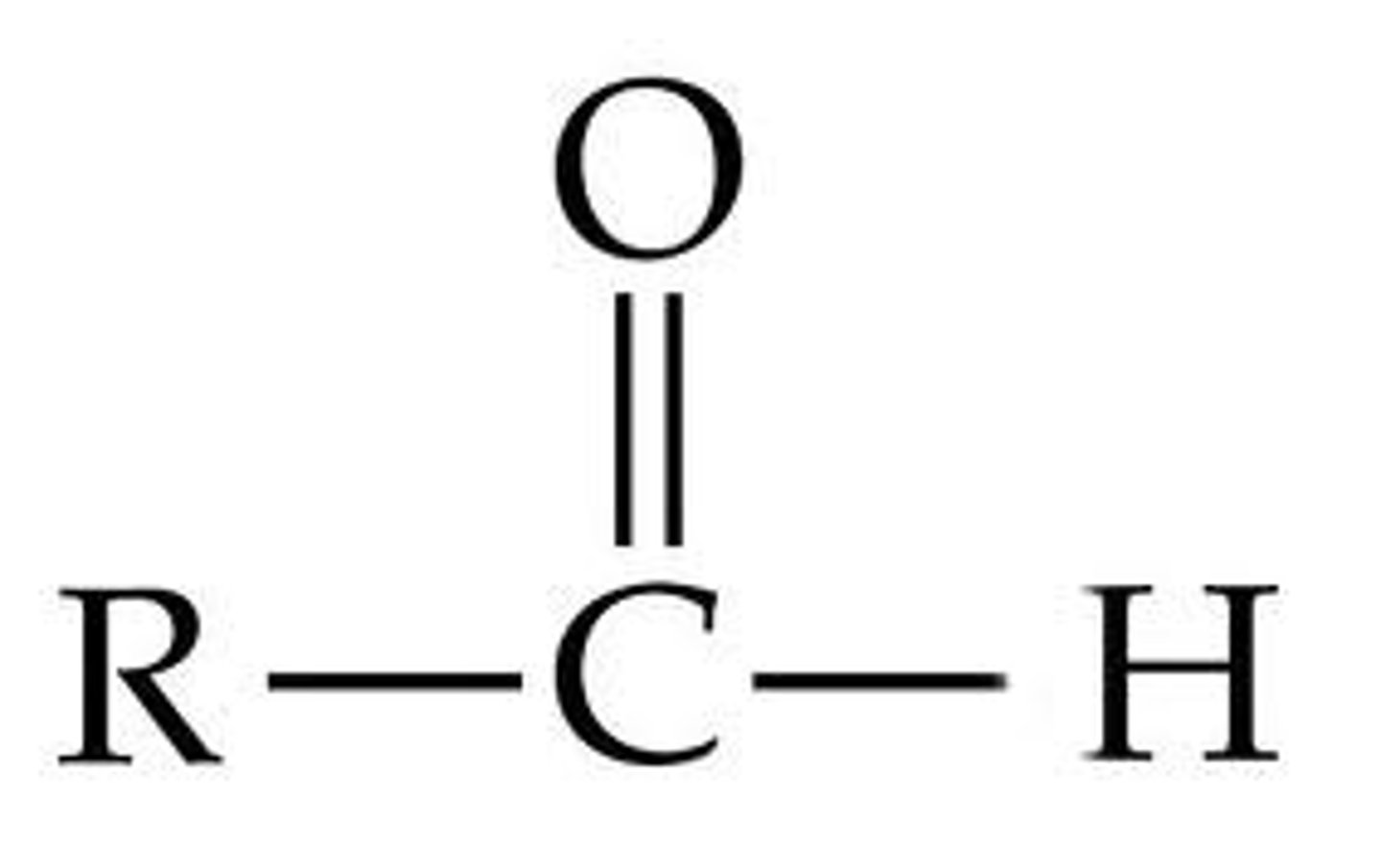
Carbonyl Group
Aldehydes (R-COH) and
Keytones (R-CO-R)
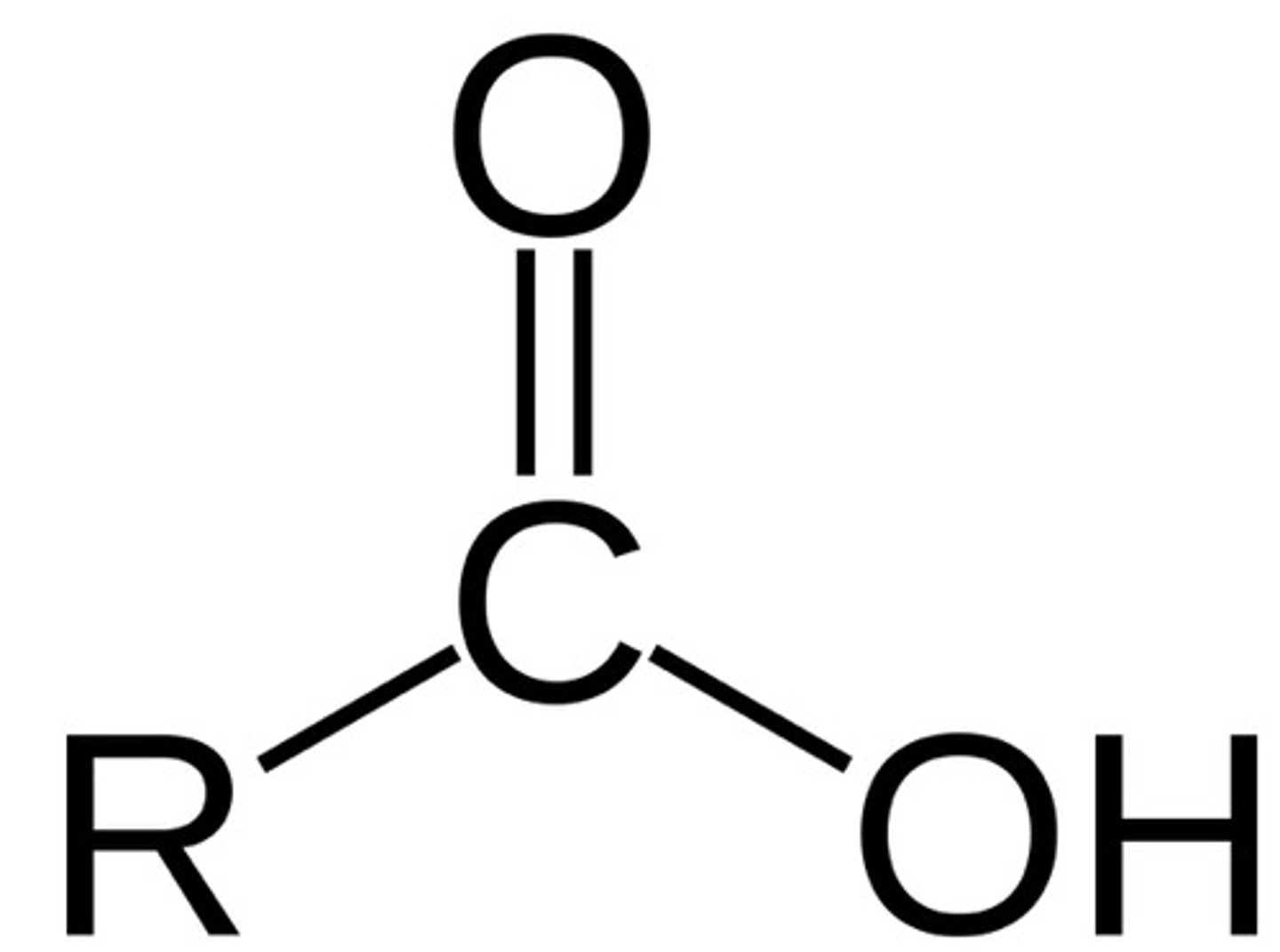
Carboxyl Group
Carboxylic Acids (R-COOH)
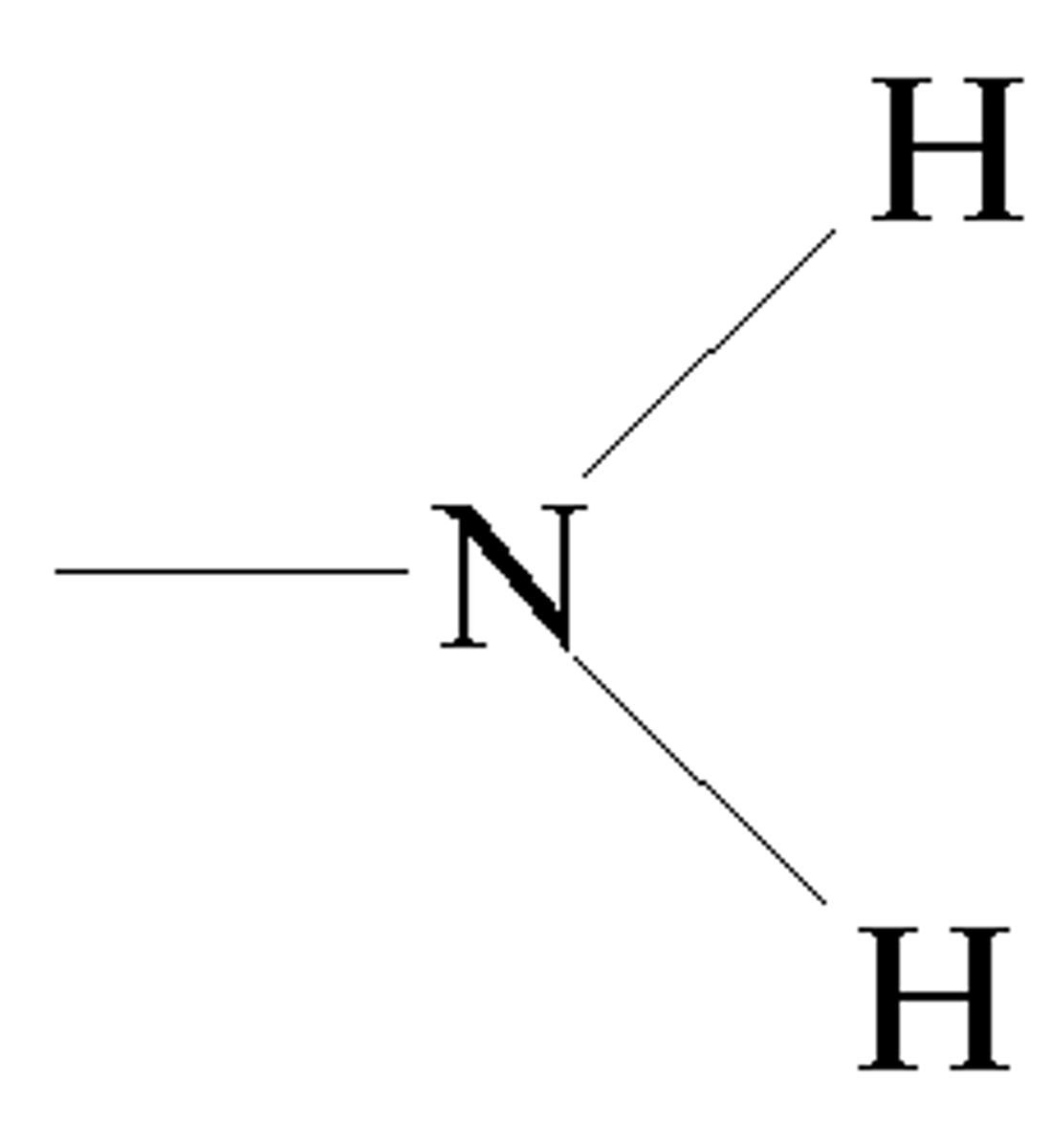
Amino Group
Amines (R-NH2)
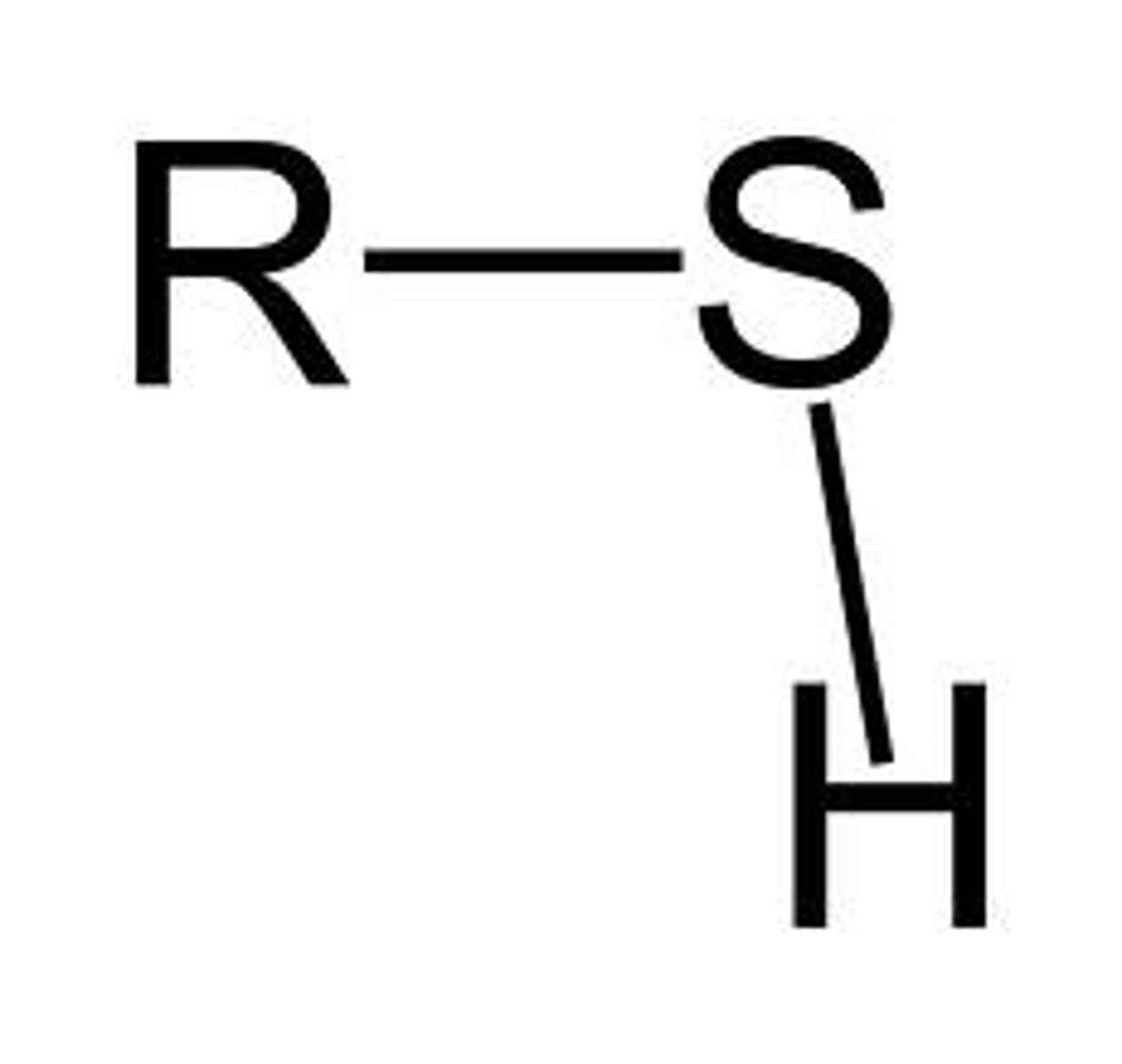
Sulfhydryl Group
Thiols (R-SH)
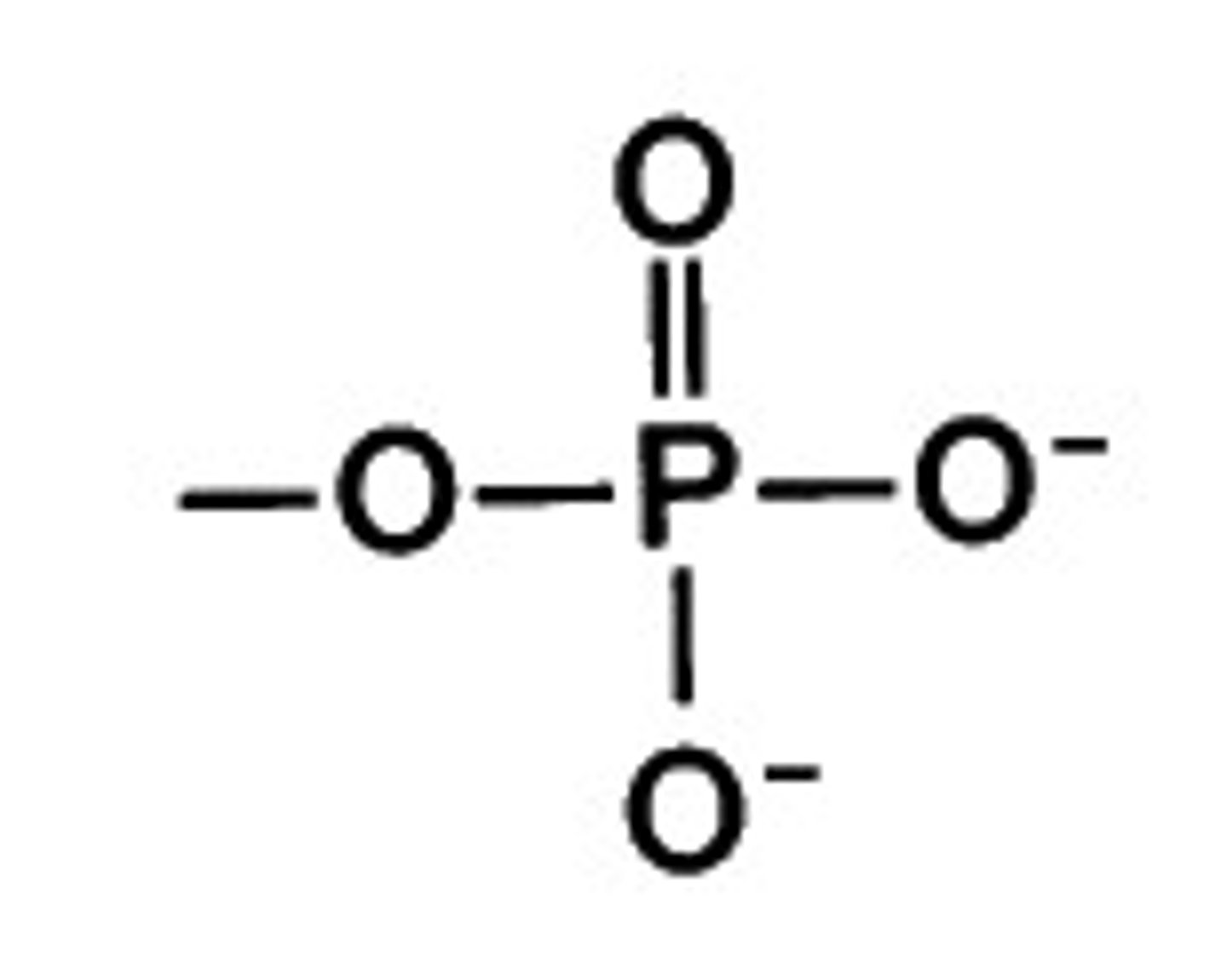
Phosphate Group
Organic Phosphates (R-OP=O(OH)2)
Monomer
Molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer
Polymer
Compound made up of a repeating chain of monomers
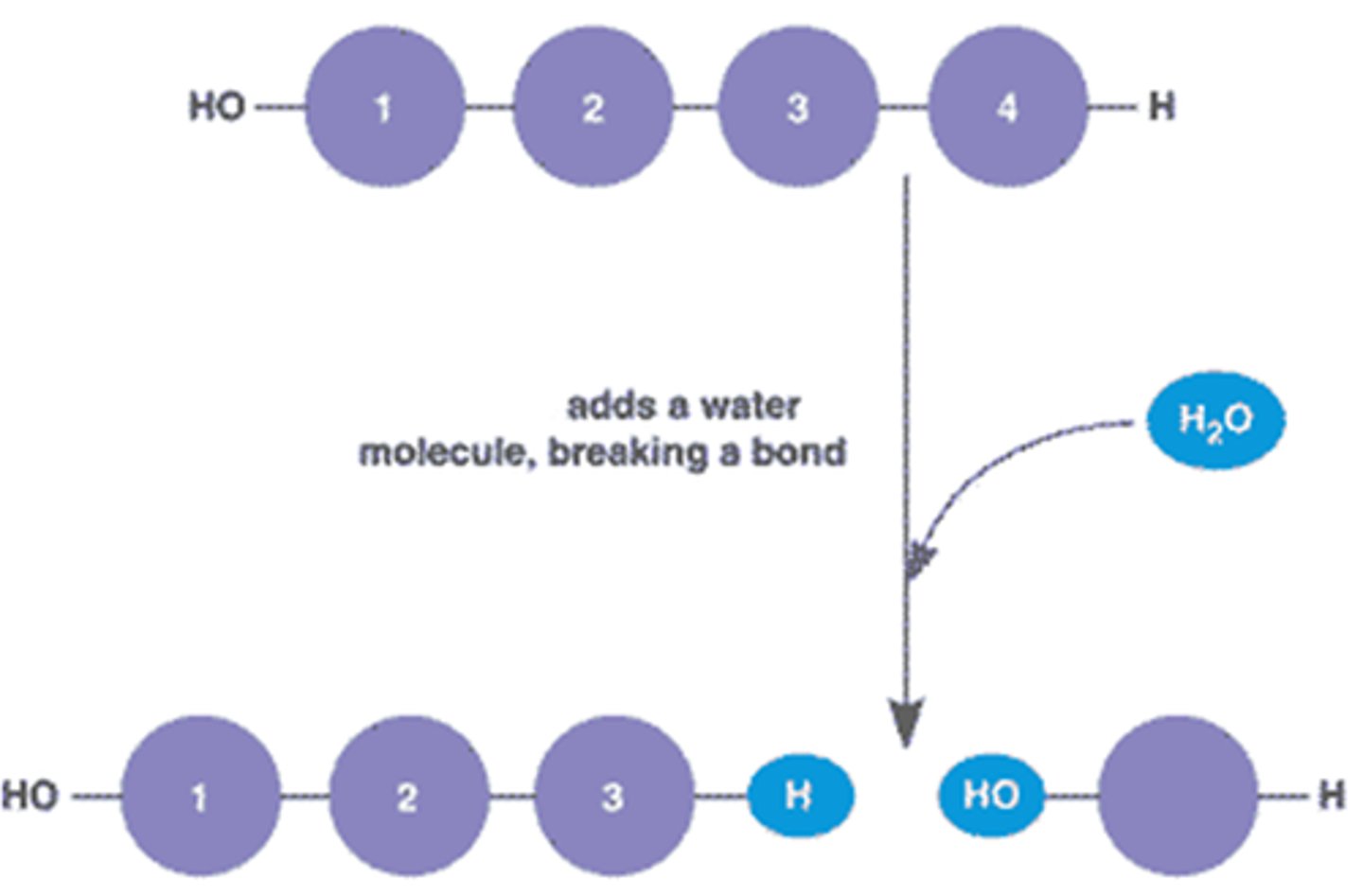
Hydrolysis
Chemical breakdown of a compound due to reaction with water (reactant)
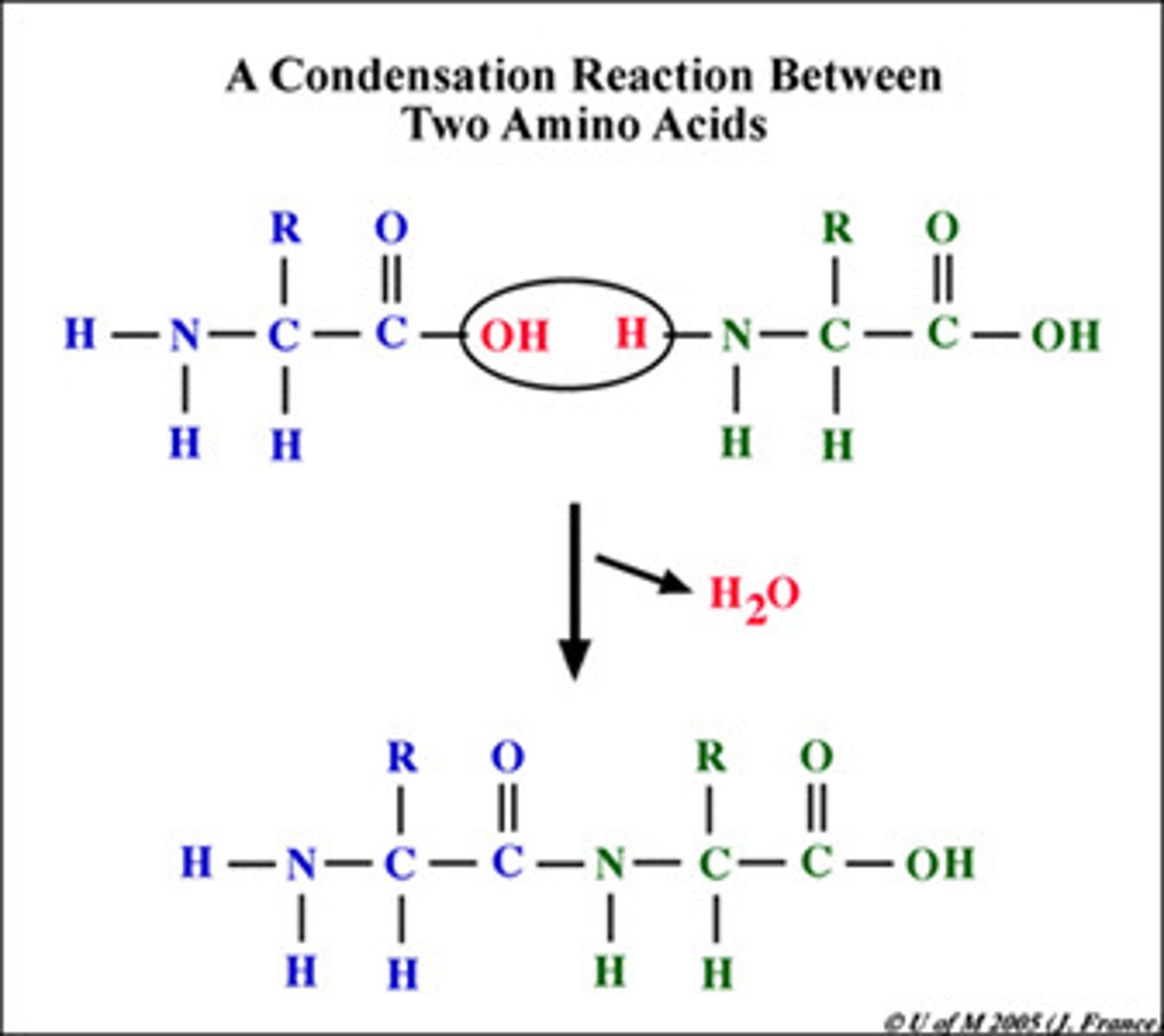
Dehydration Synthesis
Joining two molecules, or compounds, together via the removal of water (product)
Biomolecules
Biologically important molecules
Carbohydrates
Type of biomolecule C, H, O (1:2:1); universally used as an energy source and for energy storage; structural component of cells, most abundant MMs on Earth
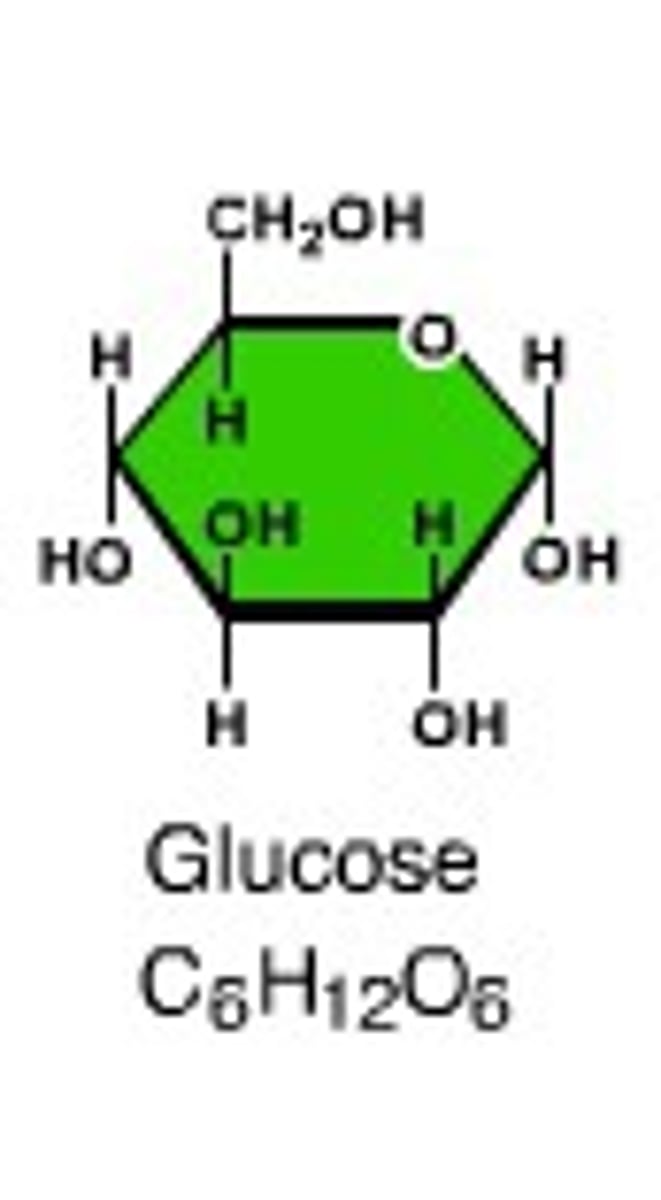
Monosaccharide
Simple sugars; single sugar molecule; quite soluble; sweet (i.e. glucose, fructose, galactose)
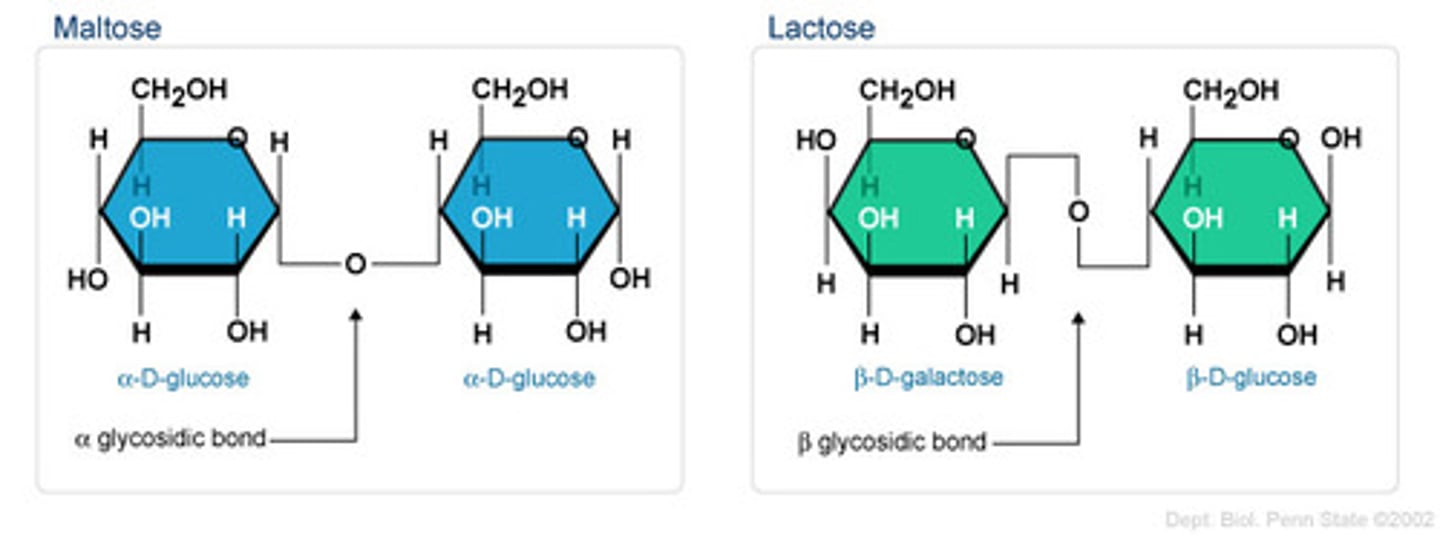
Disaccharide
Two monosaccharides joined by dehydration; soluble; sweet; important in transport of sugars (i.e. sucrose, lactose)
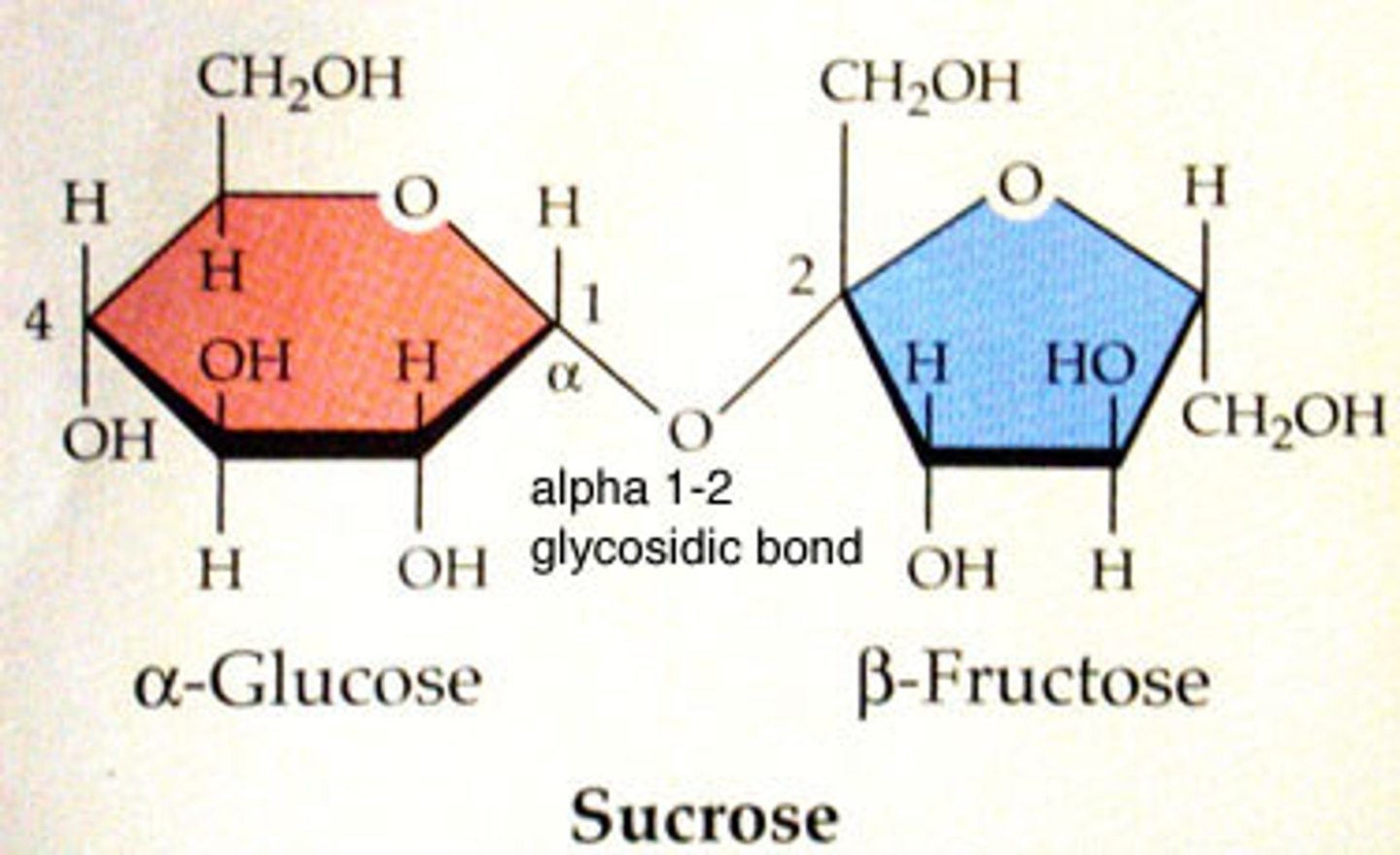
Glycosidic Bond
Type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group; alpha (above) or beta (below) linkages depend on where hydroxyl group is located
Polysaccharide
Polymers of monosaccharides; may be branched or unbranched; low solubility; not sweet; structural; short term energy storage
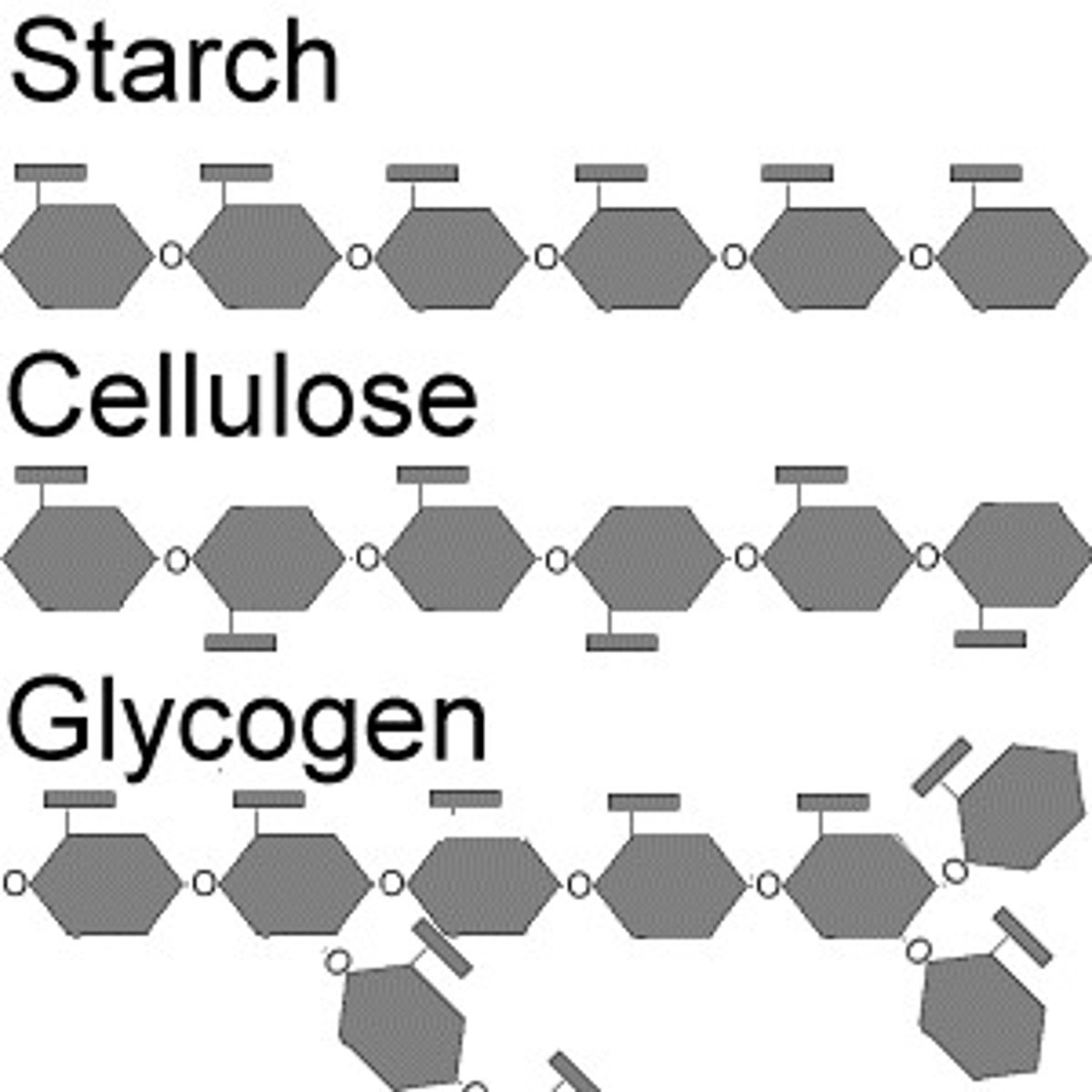
Carbs for Energy
Starch and glycogen
Starch
Polymer of glucose; moderately branched; short term energy storage; plants
Glycogen
Animal starch; highly branched; more soluble; muscle
Carbs for Structure
Cellulose, chitin, glycosaminoglycans
Cellulose
Long coiled glucose polymer; beta-linkages; unbranched; indigestible by most animals
Chitin
Polymer of glucose; each glucose with amino group; resistant to water and digestion; exoskeleton; fungal cell walls
Glycosaminoglycans
Sugar monomers with carboxyl and sulfide groups; structural in animals; abundant in cartilage;
Lipids
Type of biomolecule insoluble in water; not polymers; long chains of repeating CH2 units (also with O, P, N); renders molecule nonpolar
Functions of Lipids
Structural in cells; energy reserves; messengers; insulation; cushioning; protective coating
Types of Lipids
Fats, oils, phospholipids, steroids, waxes
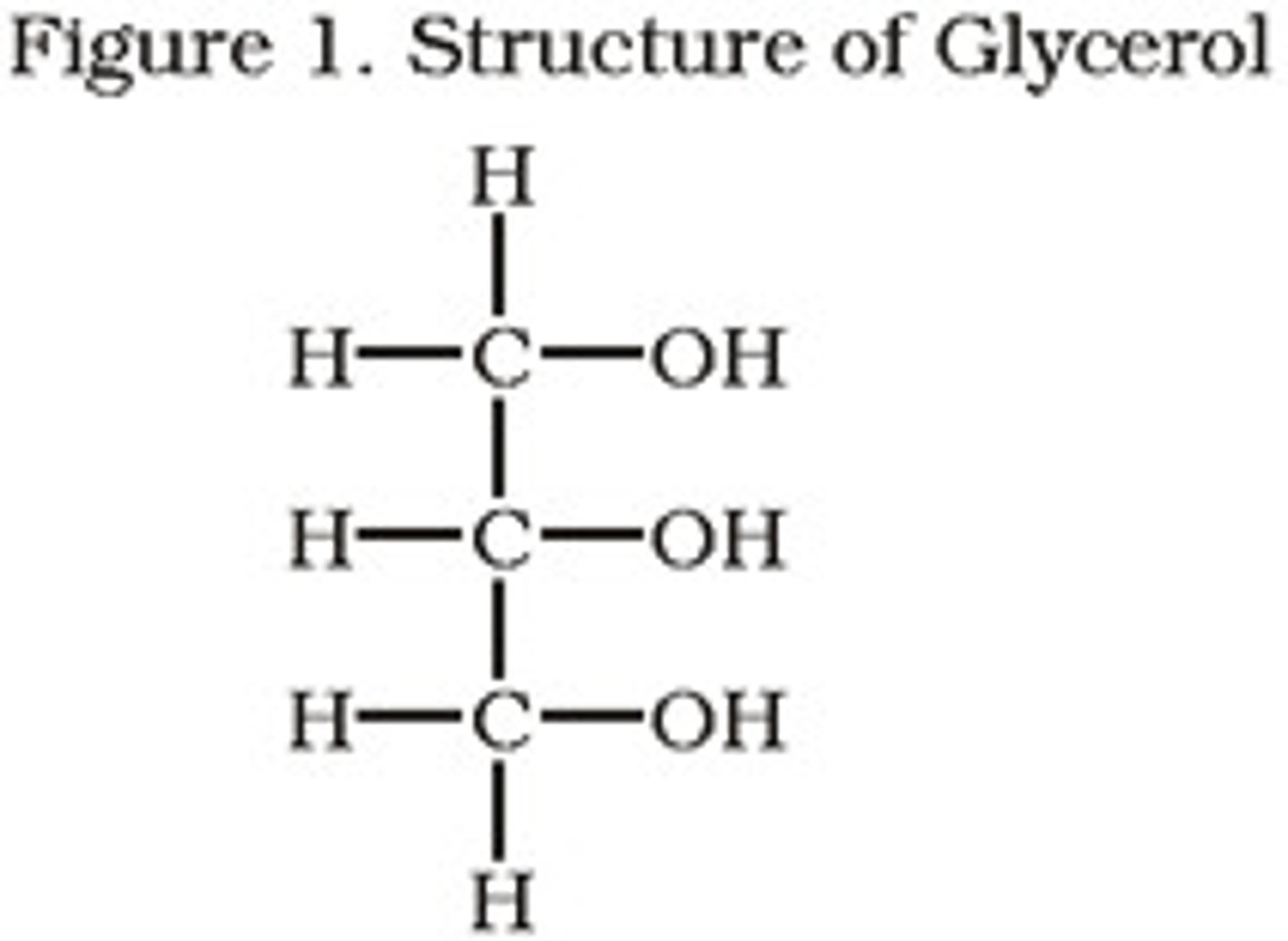
Glycerol
Three carbon alcohol (each C with hydroxyl group)
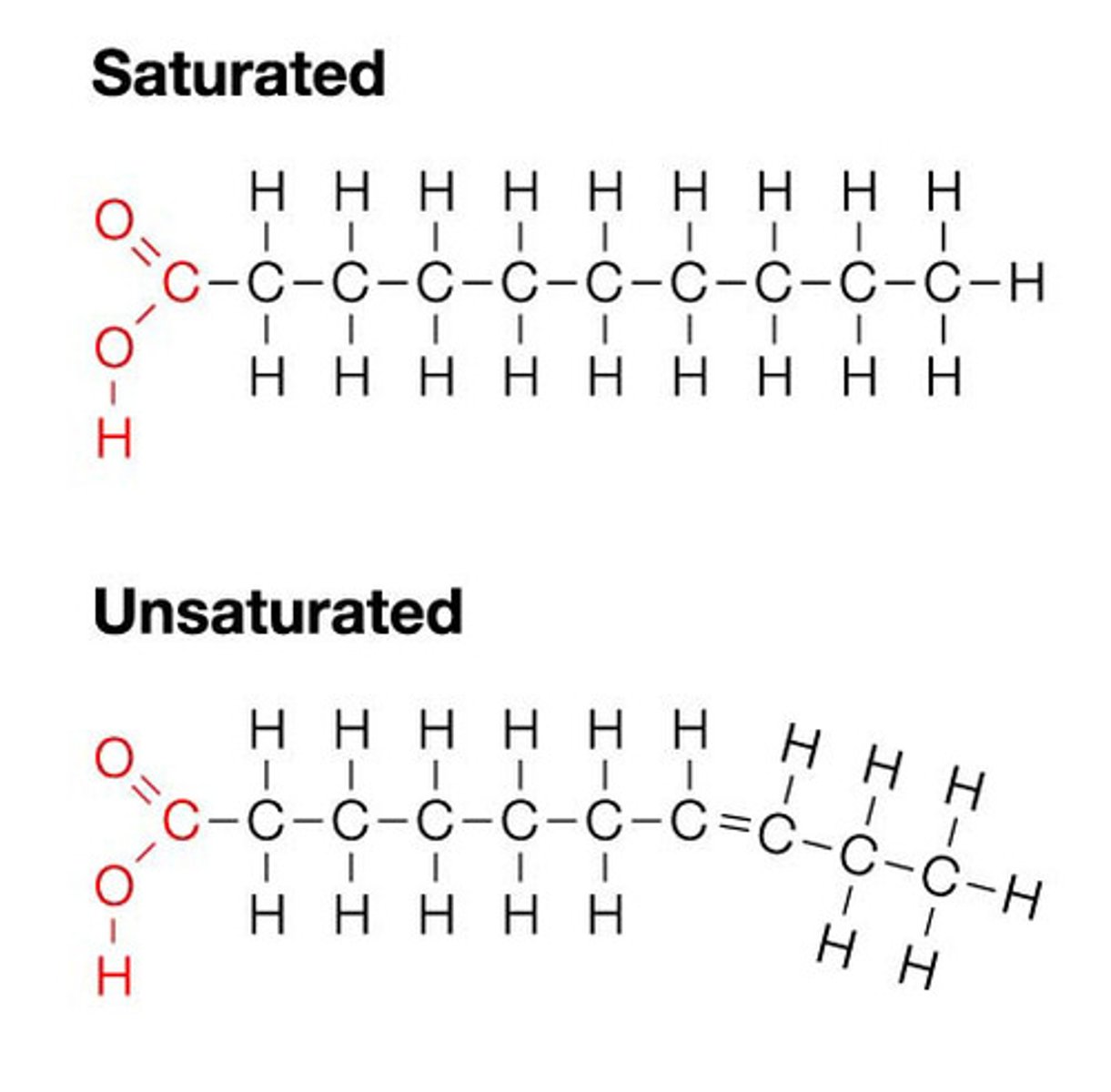
Fatty acid
Long hydrocarbon chain with carboxylic acid at one end (saturated or unsaturated); hydrophobic
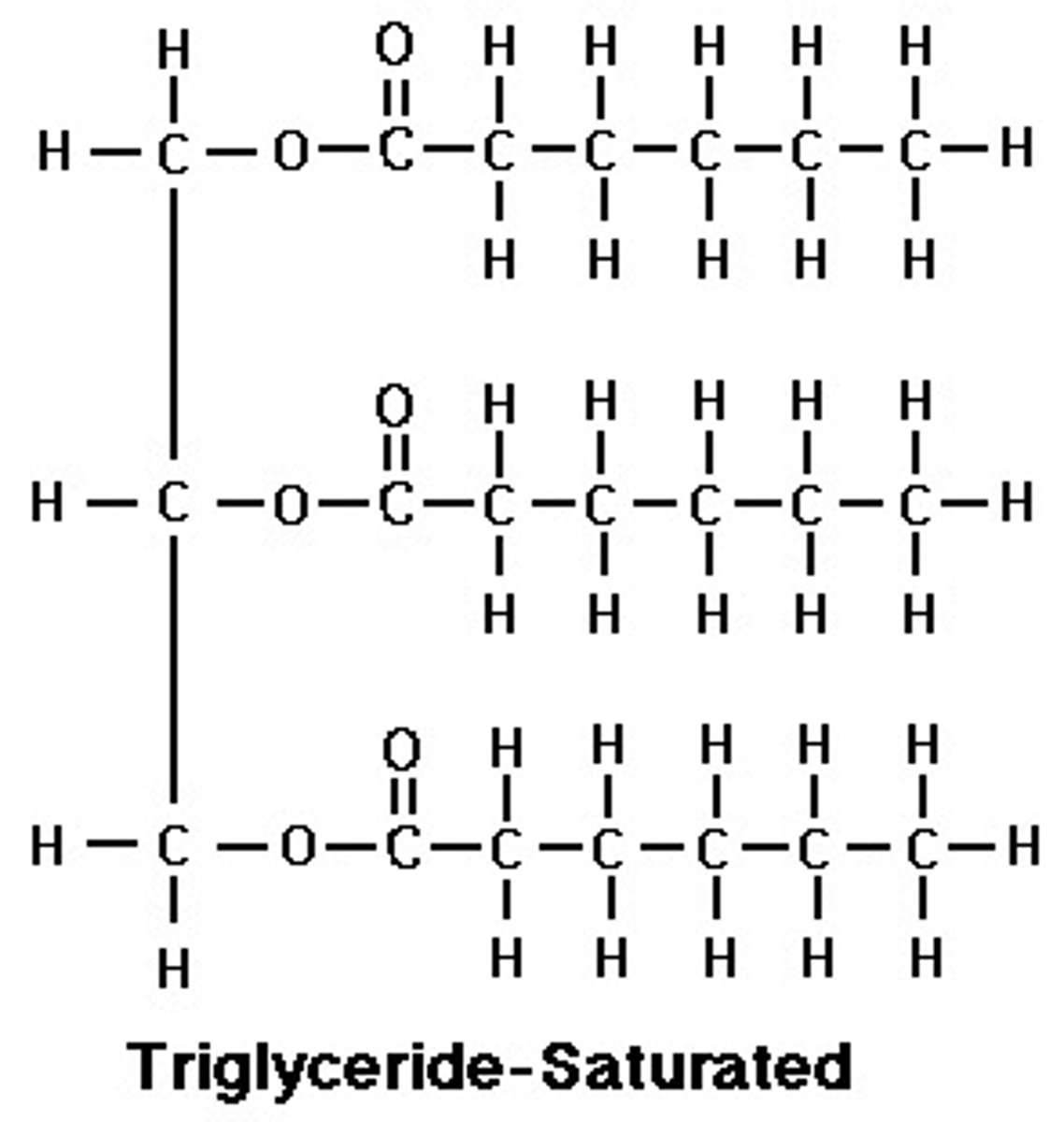
Triglyceride
Neutral fat; formed via dehydration synthesis of glycerol and 3 fatty acids connected by ester bond
Phospholipids
Derived from triglycerides; glycerol backbone with 2 fatty acids and 1 phosphate group (hydrophilic)
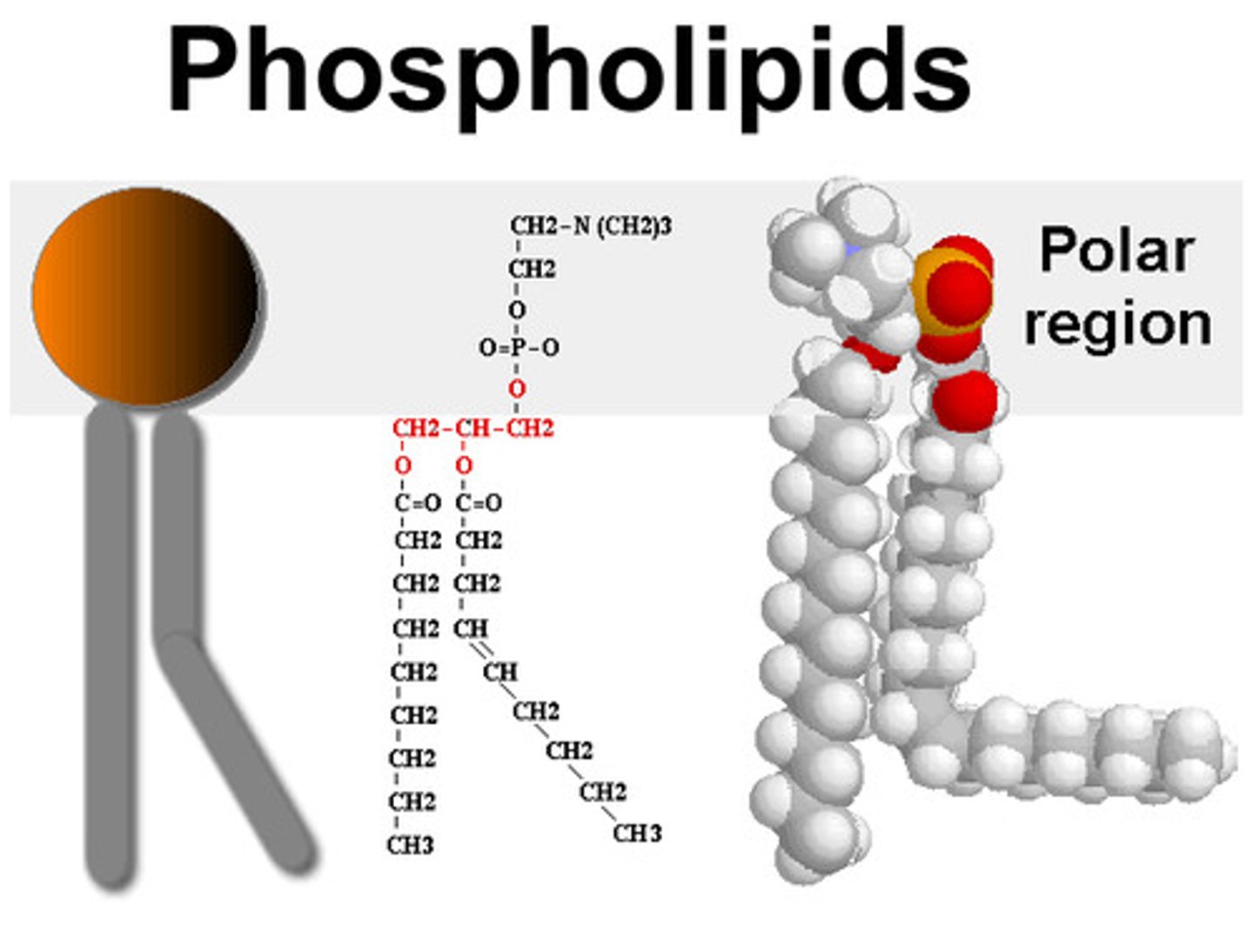
Phospholipids in Water
Polar phosphate "head" near water; non polar fatty acid "tails" overlap and exclude water; spontaneously form double layer & spheres
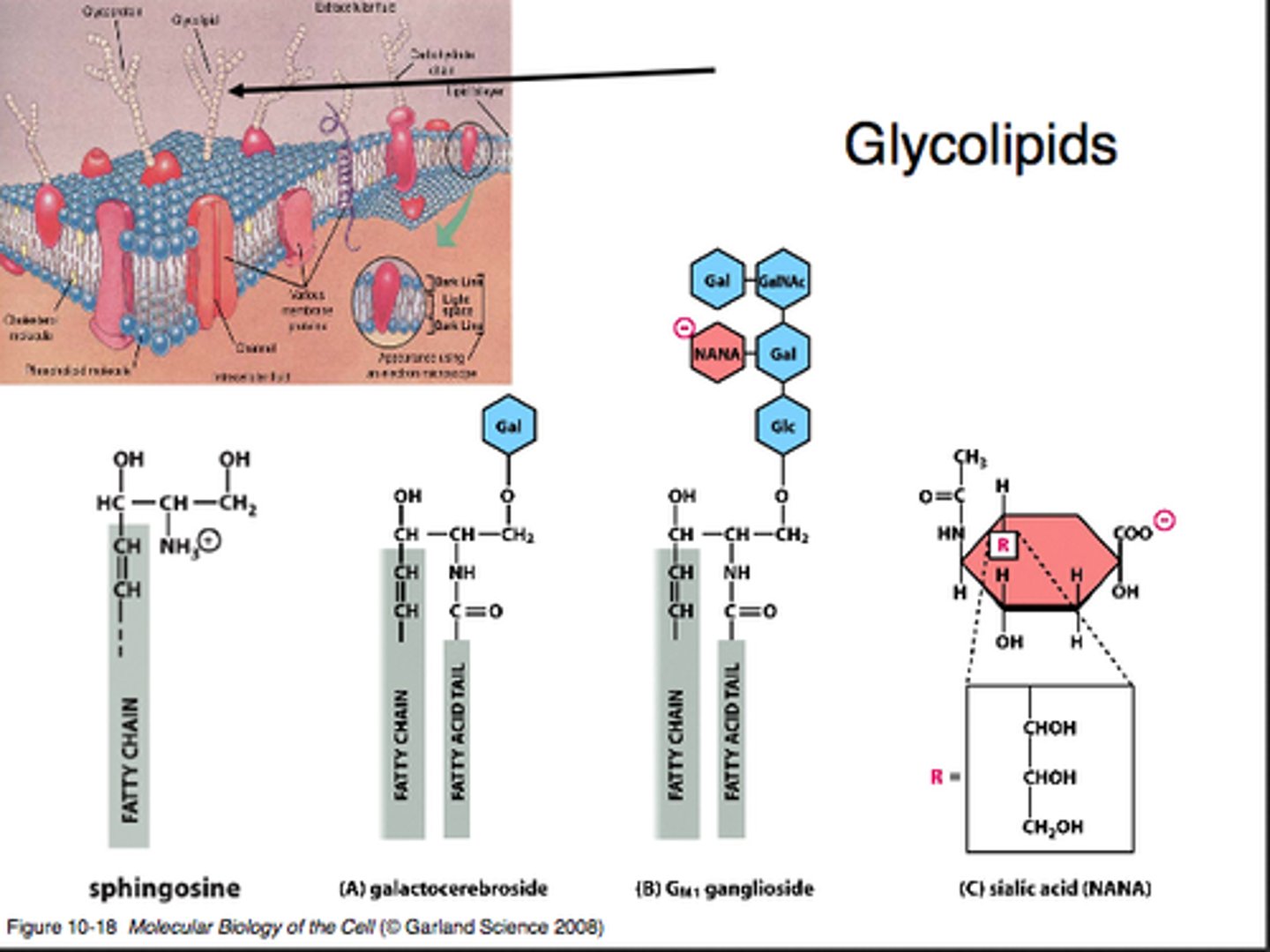
Glycolipids
Lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic bond; serve as markers for cellular recognition and to provide energy
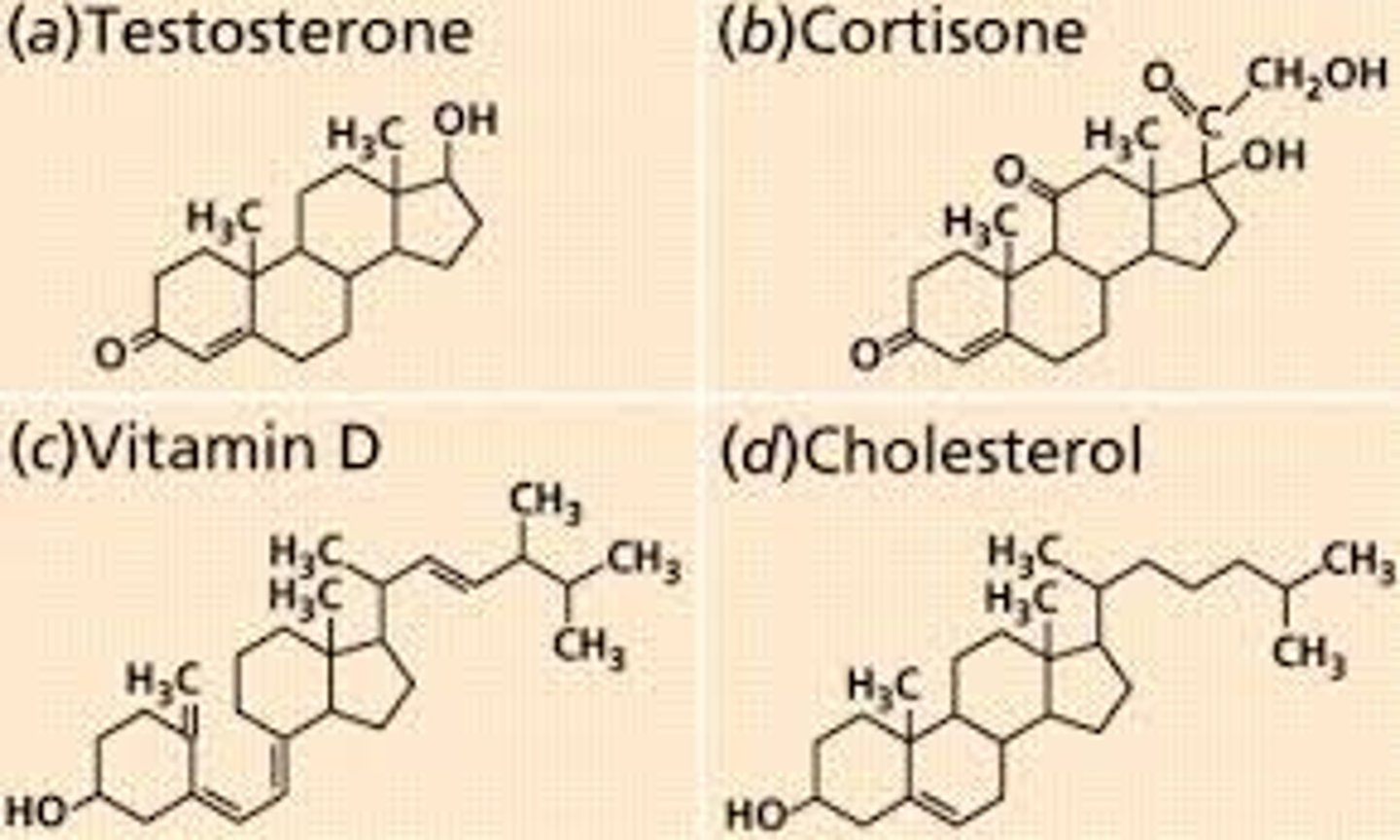
Steriod
Skeletons of 4 fused C rings + polar groups; Cholesterol: animal cell membranes; sex hormones
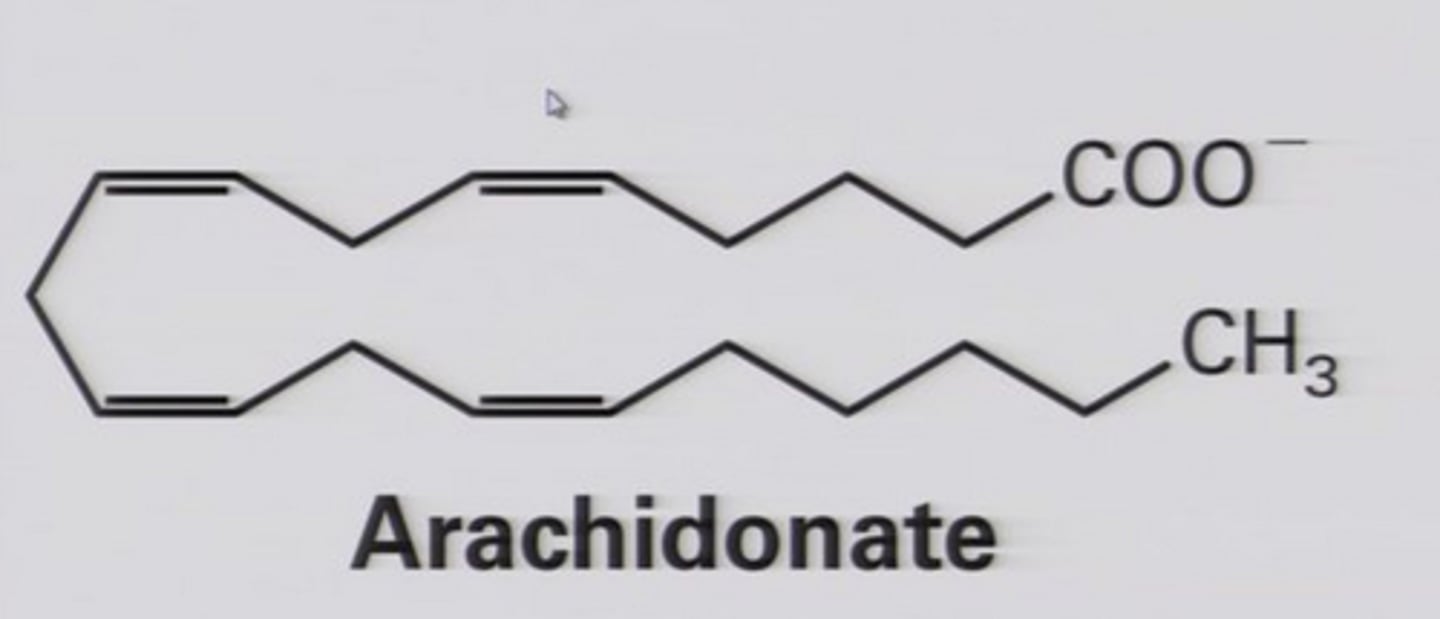
Eicosanoid
Based on arachidonic acid (20C); local hormones prod. by all cells of human body
Wax
Long chain fatty acid bonded to long chain alcohol; very nonpolar; high melting point; waterproof
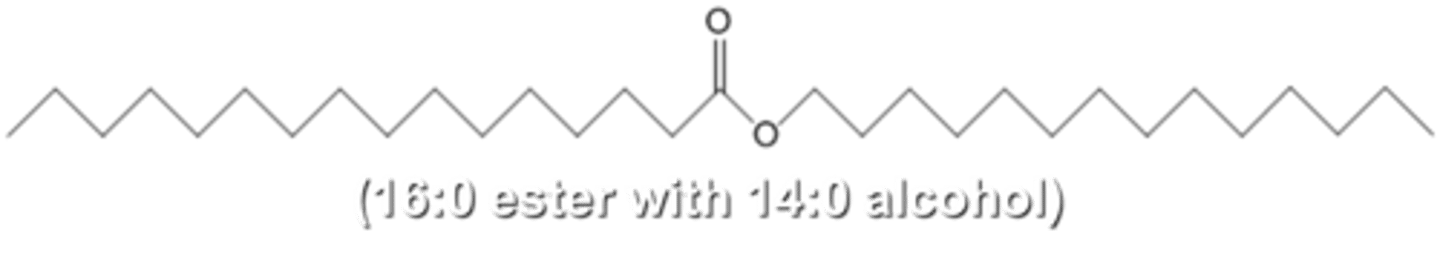
Protein
Nitrogenous biomolecul; large molecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acids; some of most abundant organic molecules in the human body; very diverse
Functions of Protiens
Metabolism, defense, cell recognition, transport, structure, motion, osmotic regulation, storage
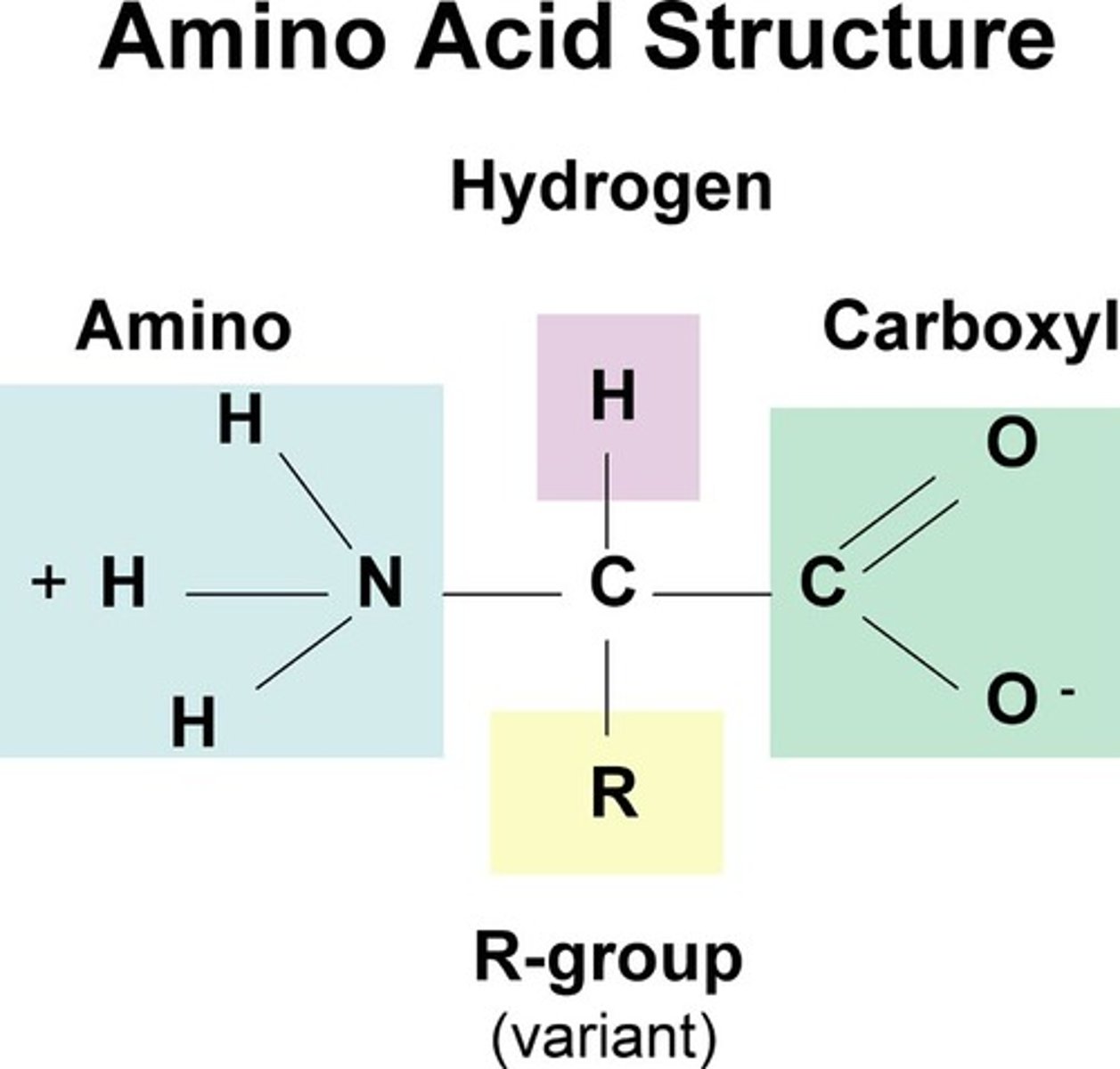
Amino Acid
Simple organic compound containing a carboxyl, amino, and R group attached to a central (alpha) carbon
Peptide Bond
Carboxyl group (C-terminus) of one AA attaches to amino group (N-terminus) of another AA
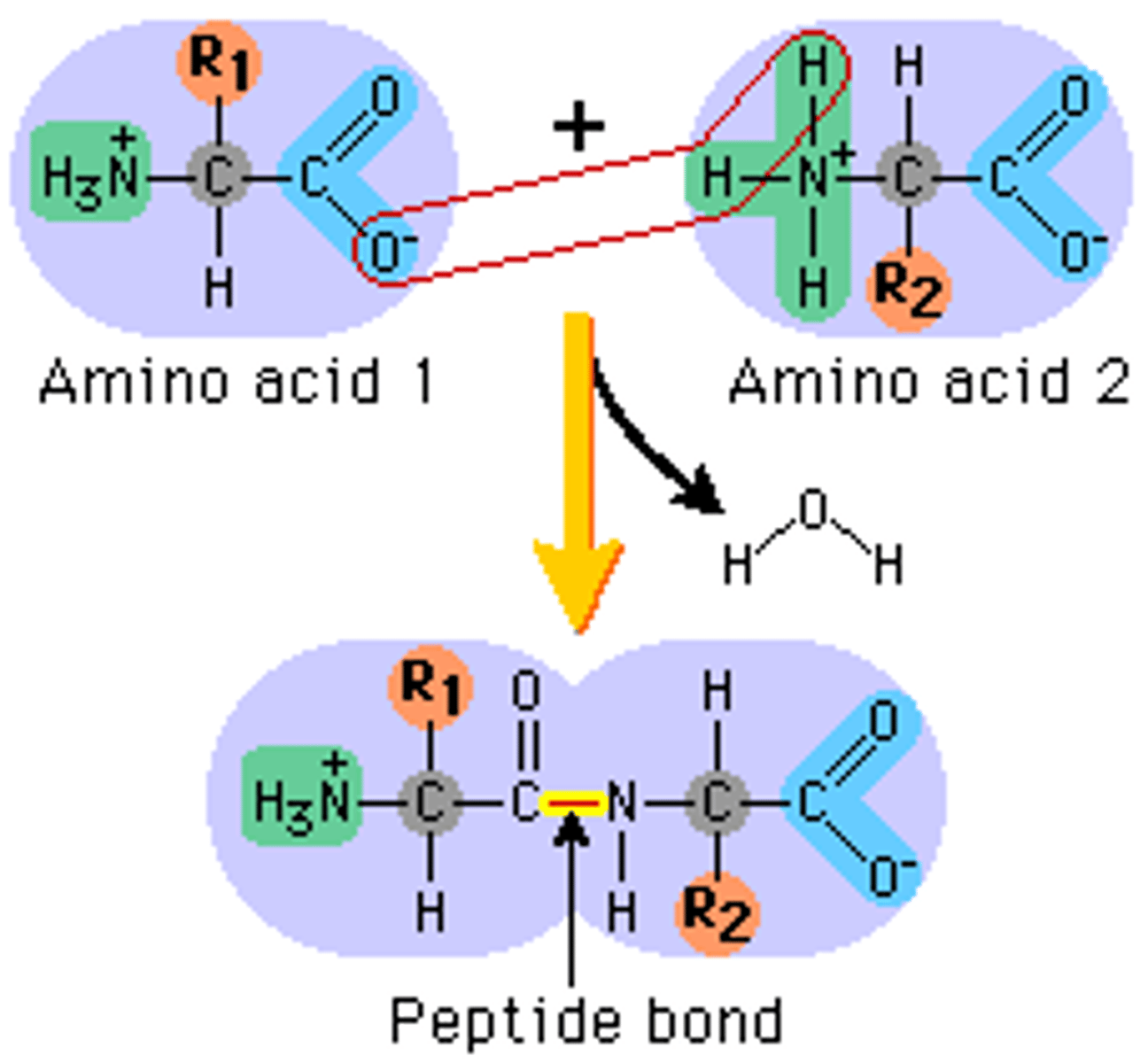
Polypeptide
Amino acids joined together end-to-end; only refers to structure NOT function
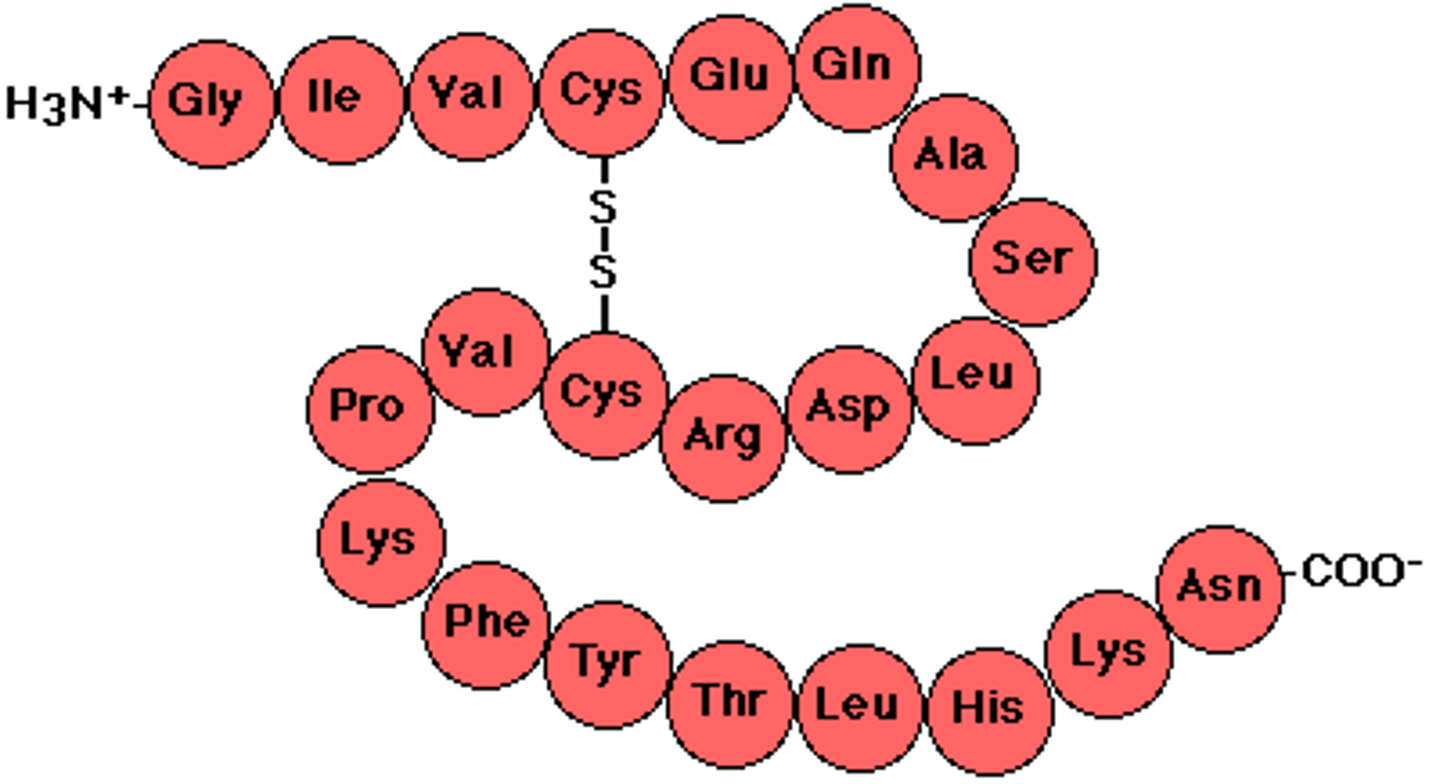
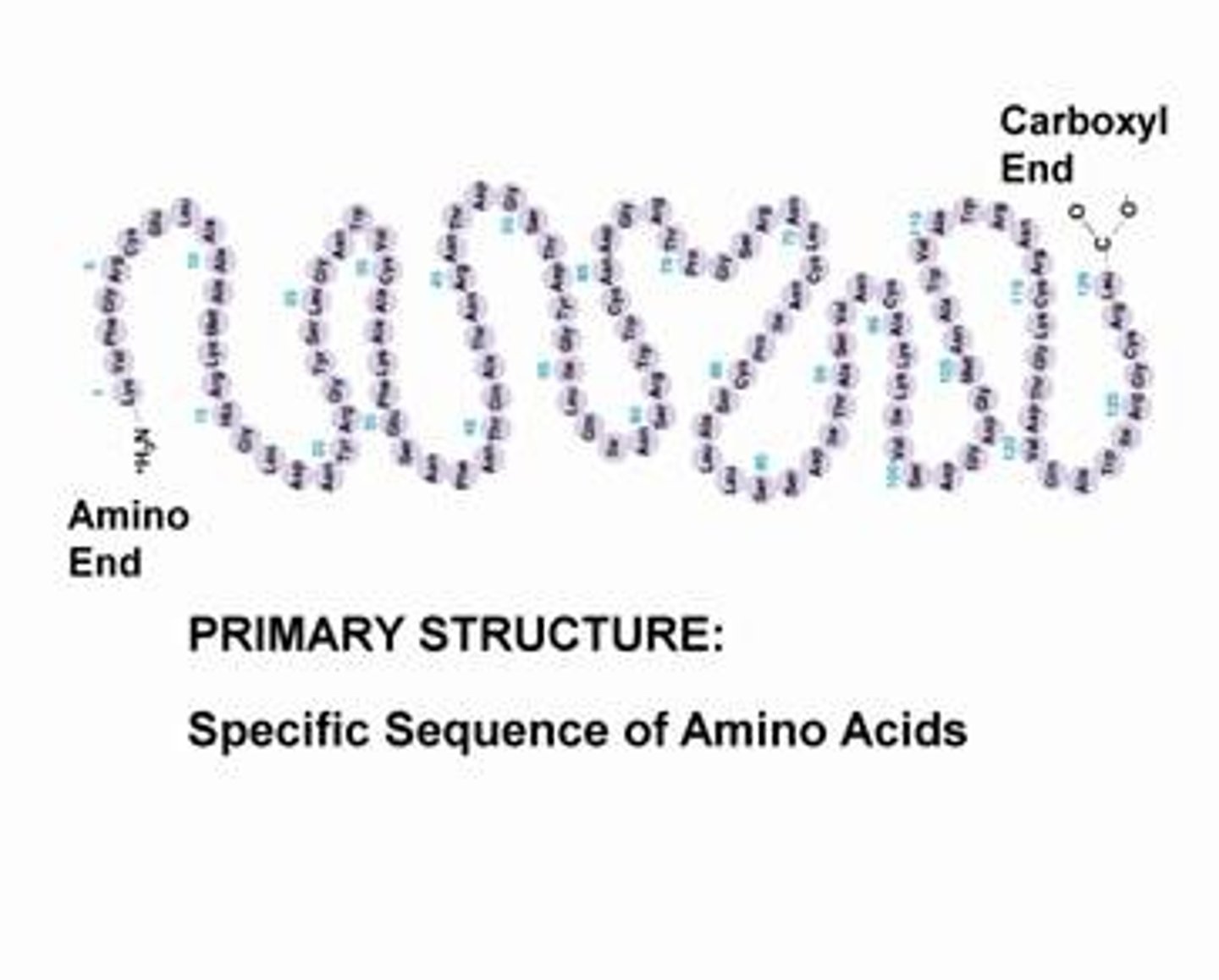
Primary Level (Protein)
Specific sequence of AAs; genetically determined
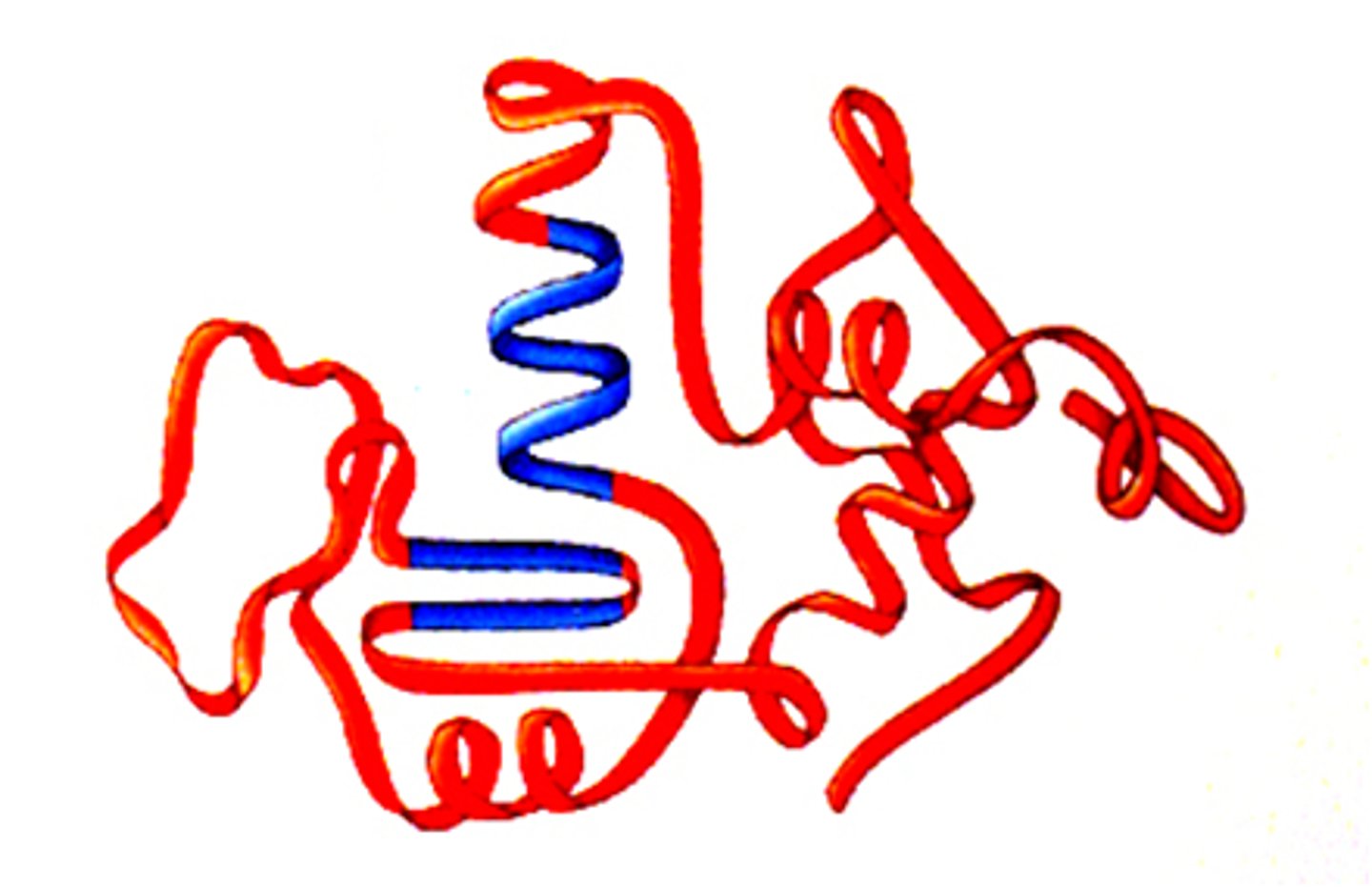
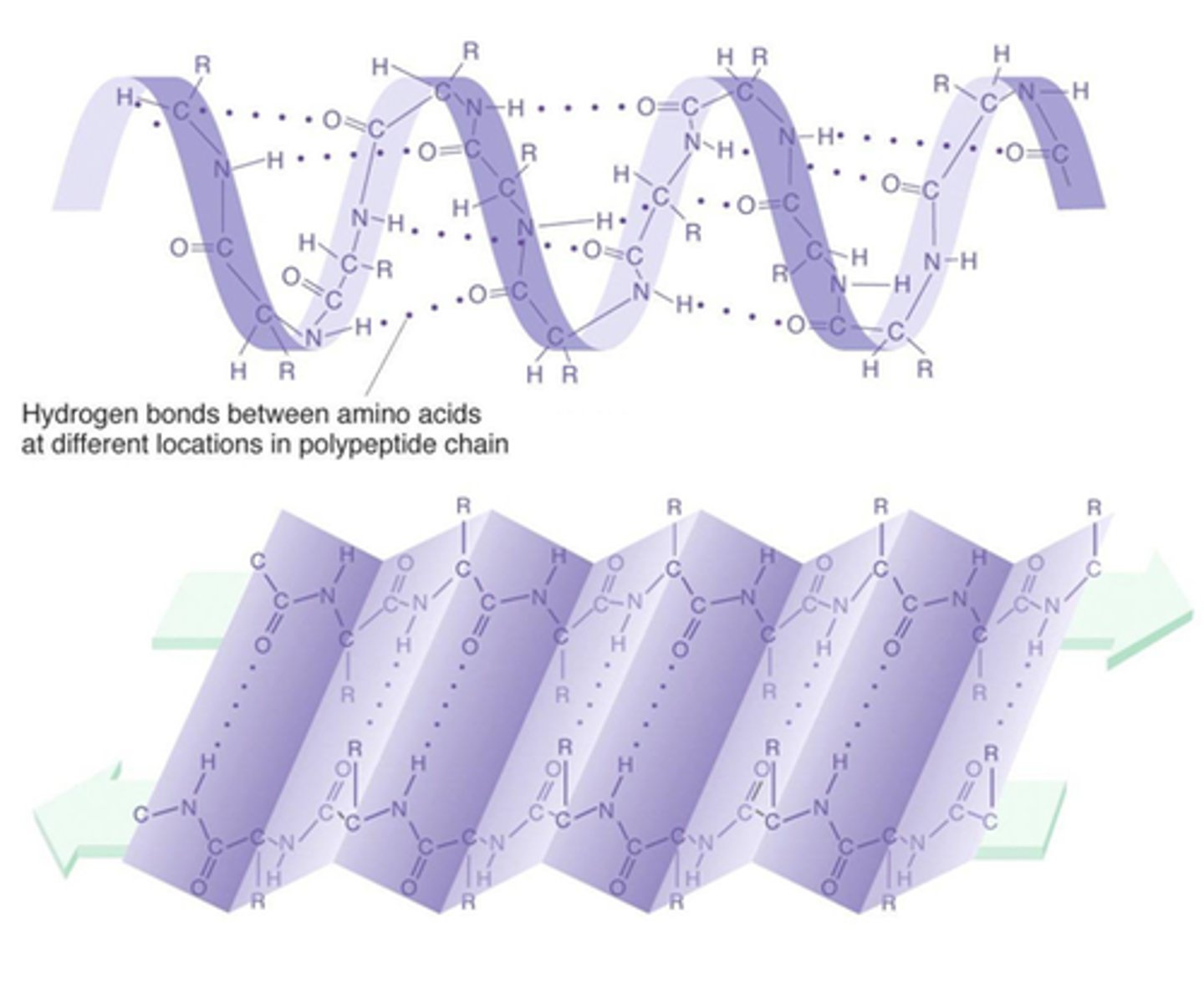
Secondary Level (Protein)
Way the AA chain coils or folds; result of H-bonding; random coiled regions
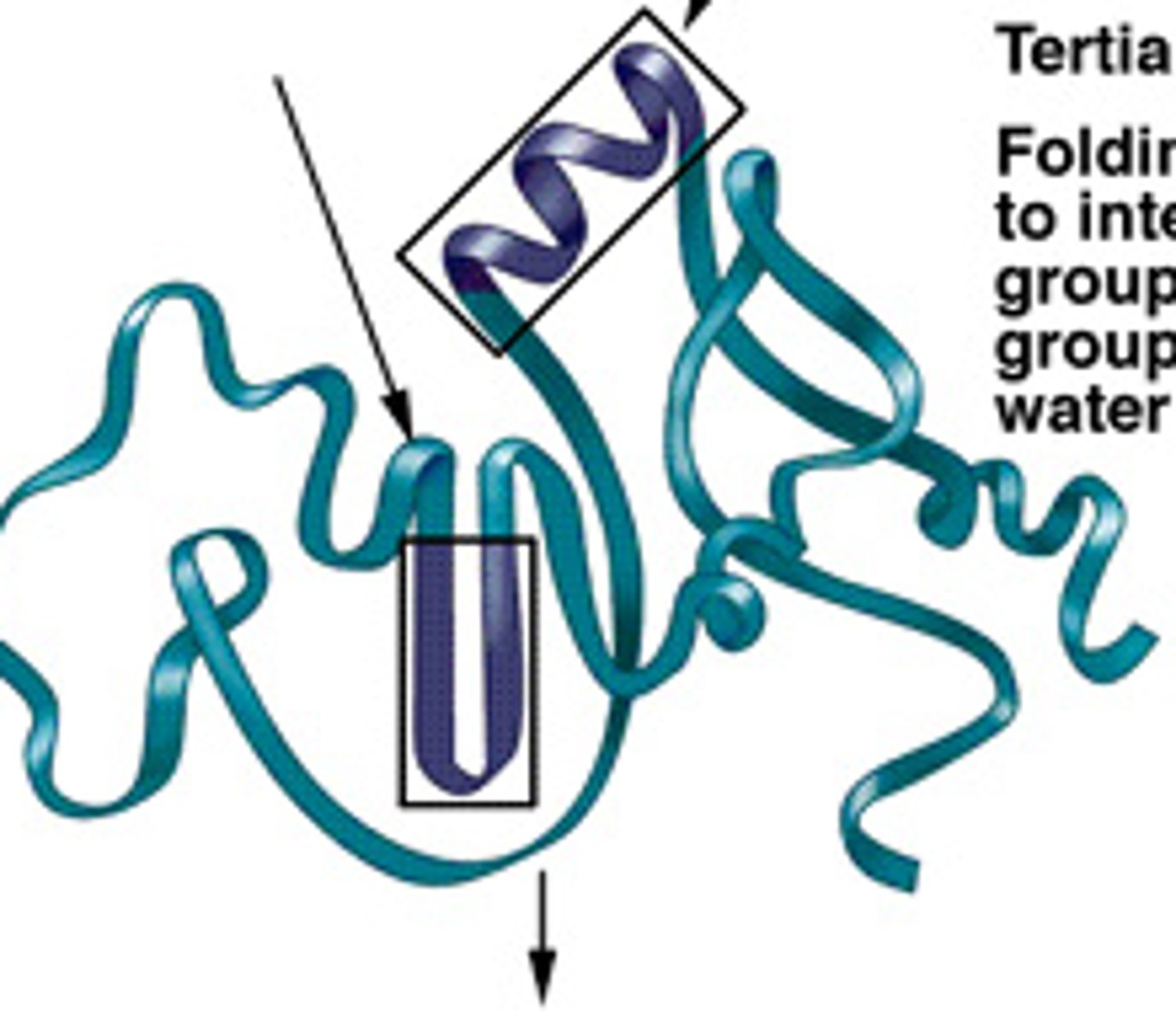
Tertiary Level (Protein)
3D shape of polypeptide; complex R-group interactions; H-bonding; disulfide bridges; ionic bonding; van der Waals forces