NETWORK TOPOLOGIES, ARCHITECTURES, AND TYPES - Unit 1
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
physical topology
actual layout of cables and network devices
network topology
way in which network appears to devices that use it
point-to-point connection (P2P)
direct network connection between exactly two devices where data travels across a dedicated link without being shared with other devices
star/hub and spoke topology
all computers and network devices connect to central device called hub or switch
Each connected device requires a cable to be connected to hub, creating point-to-point connection
Easiest to expand in terms of number of devices connected to network
star/hub and spoke advantage
easily expanded without disruption to network
cable failure only affects single user
easy to troubleshoot and implement
star/hub and spoke disadvantage
needs more cables than most topologies
central connection device allows for single point of failure
needs additional networking equipment to create network layout
mesh topology
each computer on network connects to every other, creating P2P connection between devices on network
provides redundancy so better fault tolerance
mesh advantage
provides redundant paths between LAN topologies
network can be expanded without disruption to current users
mesh disadvantages
needs more cables than other topologies
implementation is complicated
hybrid topology
creates redundant P2P network connection between specific network devices
spine and leaf topology
2-tier data center network design using spine switches (core) and leaf switches (access) for high scalability and performance; used in data centers
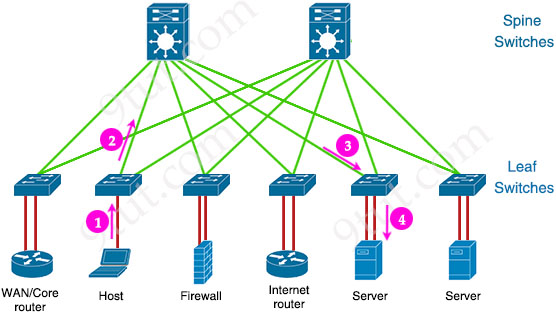
latency
typical amount of time it takes for packets of data to travel from one computer or system to the next; high is bad
equal latency
traffic always crosses the same number of devices (consistent hop count)
high redundancy
if a spine fails, only minor performance loss due to multiple alternate paths
collapsed core architecture
two tier network design that combines core and distribution layers from 3 tier model; commonly used in datacenters and medium sized enterprise networks
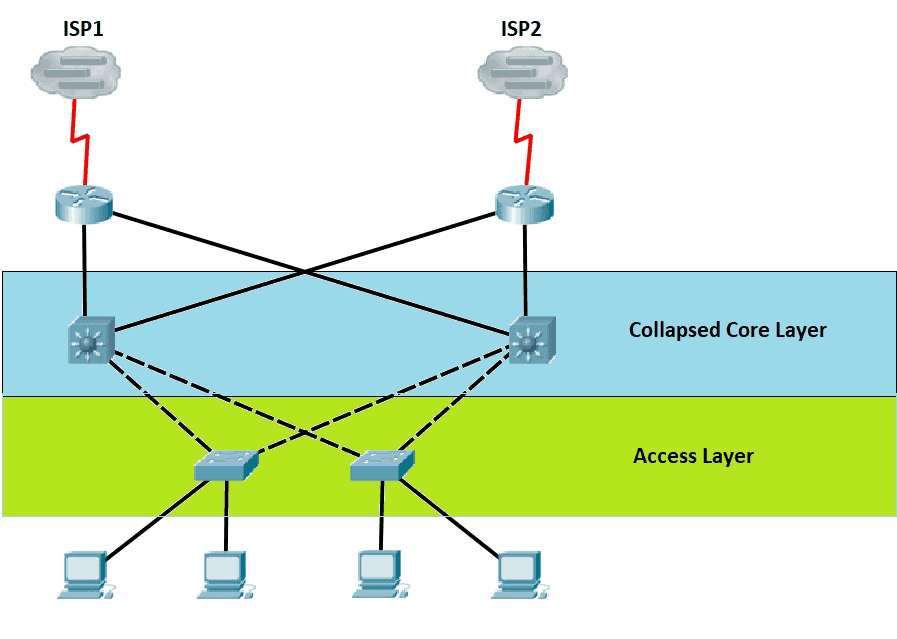
collapsed core benefits
simple design, cost effective, lower latency, scalable
collapsed core disadvantages
failure at collapsed core can impact entire network, scalability limits, design can cause congestion
North-South traffic flow
traffic flow between a client and external resources
exs: internet browsing, accessing cloud services
East-West traffic flow
relates to flow between internal resources within a network
exs: inter-server communication, database queries
Three-Tier Hierarchical Model
a structured approach to network design that breaks the network into three distinct layers; Each layer is designed to serve a specific purpose, optimizing scalability, performance, and maintainability
Core Layer (3 tier hierarchical model)
backbone of network
handles high-speed packet switching across entire network
fast and reliable routing of data
has high redundancy and fault tolerance
Distribution Layer (3 tier hierarchical model)
intermediary layer between core and access layer
manages routing, filtering, and WAN access
aggregates data received from access layer switches
Access Layer (3 tier hierarchical model)
network’s point of entry for devices and end users, connecting them to network
includes switches and access points that provide connectivity to network devices