IB Geography Periglacial Landforms and Processes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:23 AM on 5/20/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
1
New cards
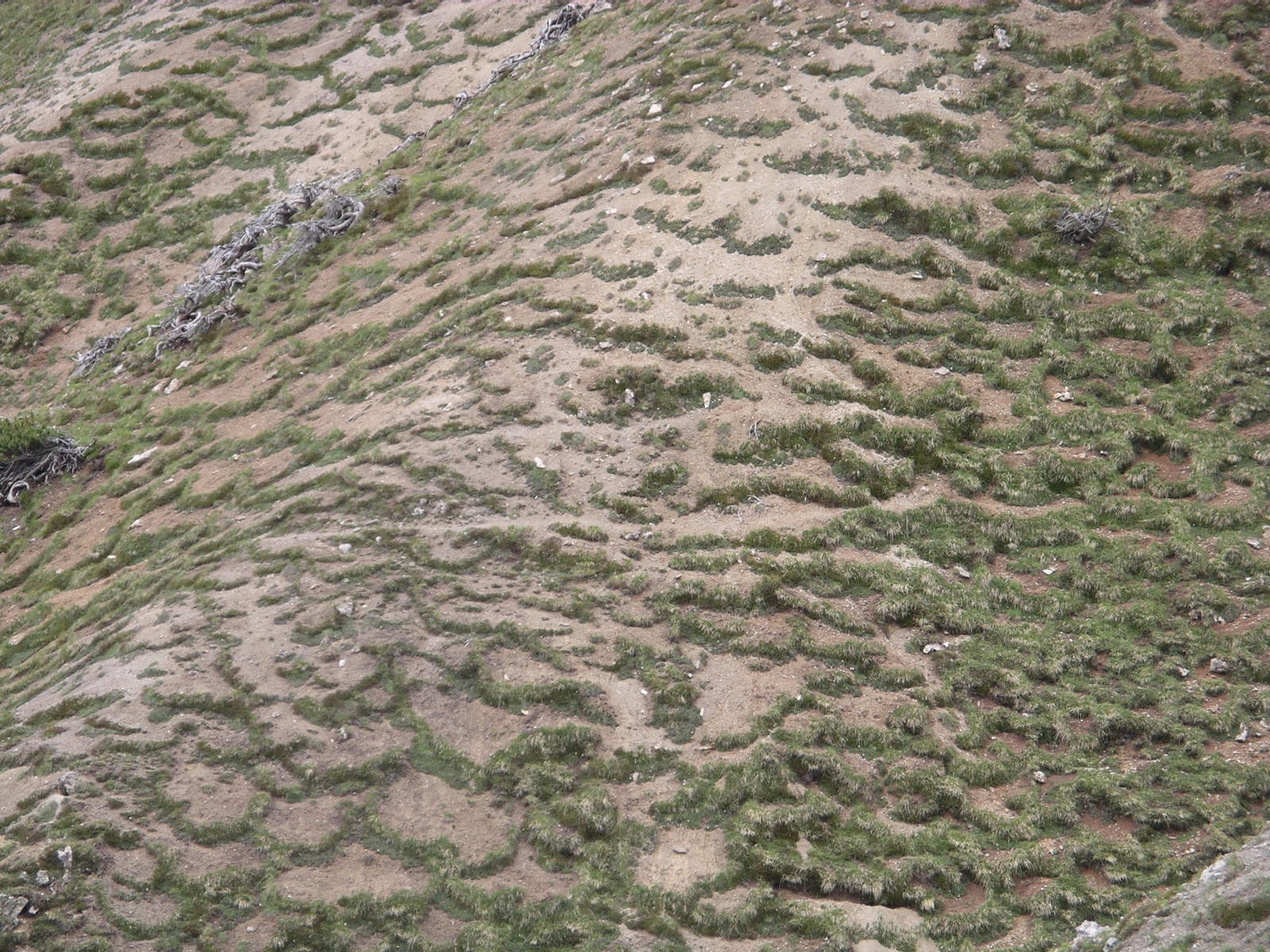
Solifluction
Slow downslope movement of soil in cold regions due to freezing and thawing, forms lobes

2
New cards
Ice Heave
Ice crystals expand and force soil up
3
New cards
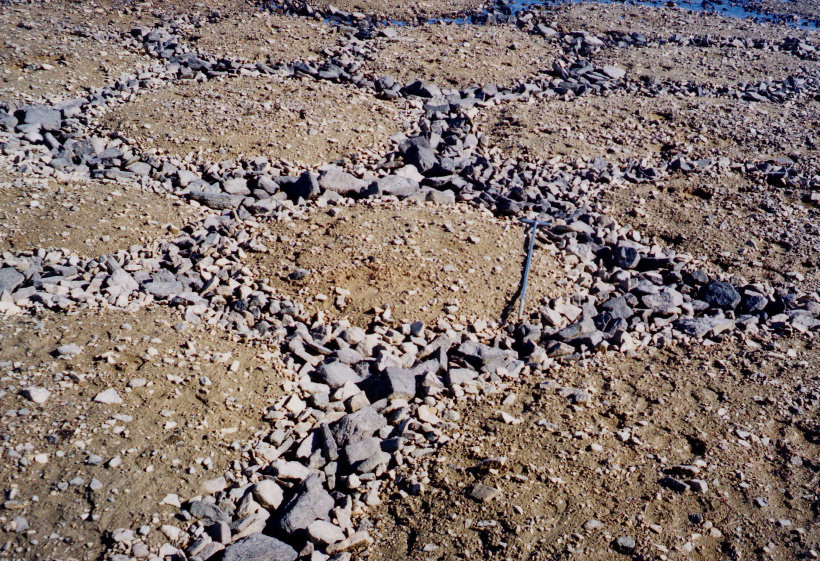
Ice Wedges
Water gets into a small crack, expands and grows every year with freeze-thaw, forms ice-wedge polygons
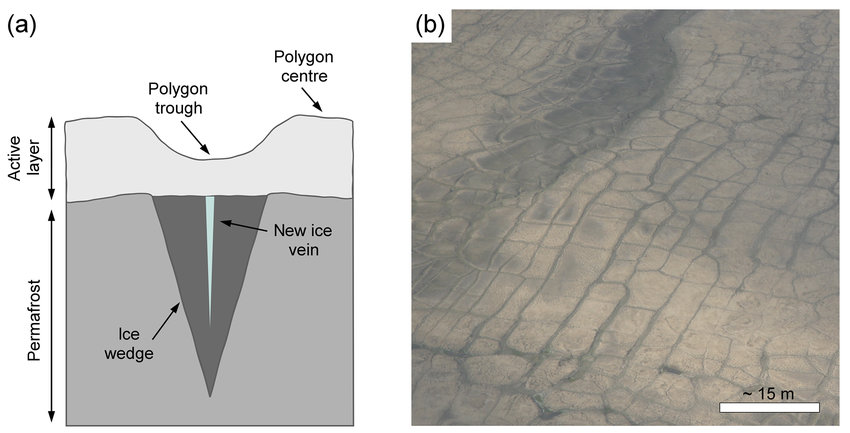
4
New cards
Thermokarst
Thawing of ice-rich permafrost or the melting of massive ice blocks, irregular pits and depressions develop by thaw settlement
5
New cards
Permafrost
Soil, regolith, bedrock that is below 0°
Continuous, discontinuous, or sporadic
25% of exposed land in the Northern Hemisphere
Active layer that freezes and thaws with seasons
Continuous, discontinuous, or sporadic
25% of exposed land in the Northern Hemisphere
Active layer that freezes and thaws with seasons
6
New cards
Impacts of Melting Permafrost
* Ecosystem damage → habitats, lakes disappear
* Infrastructure damage → roads, houses, pipes
* Landslides → loose debris
* Coastal erosion
* Methane
* Infrastructure damage → roads, houses, pipes
* Landslides → loose debris
* Coastal erosion
* Methane
7
New cards
Pingos
* Conspicuous conical mound or circular hill, with a core of ice, found on tundra where permafrost is present
* Form under initially frozen lakes (closed system) or by groundwater forcing through permafrost (open system)
* Form under initially frozen lakes (closed system) or by groundwater forcing through permafrost (open system)
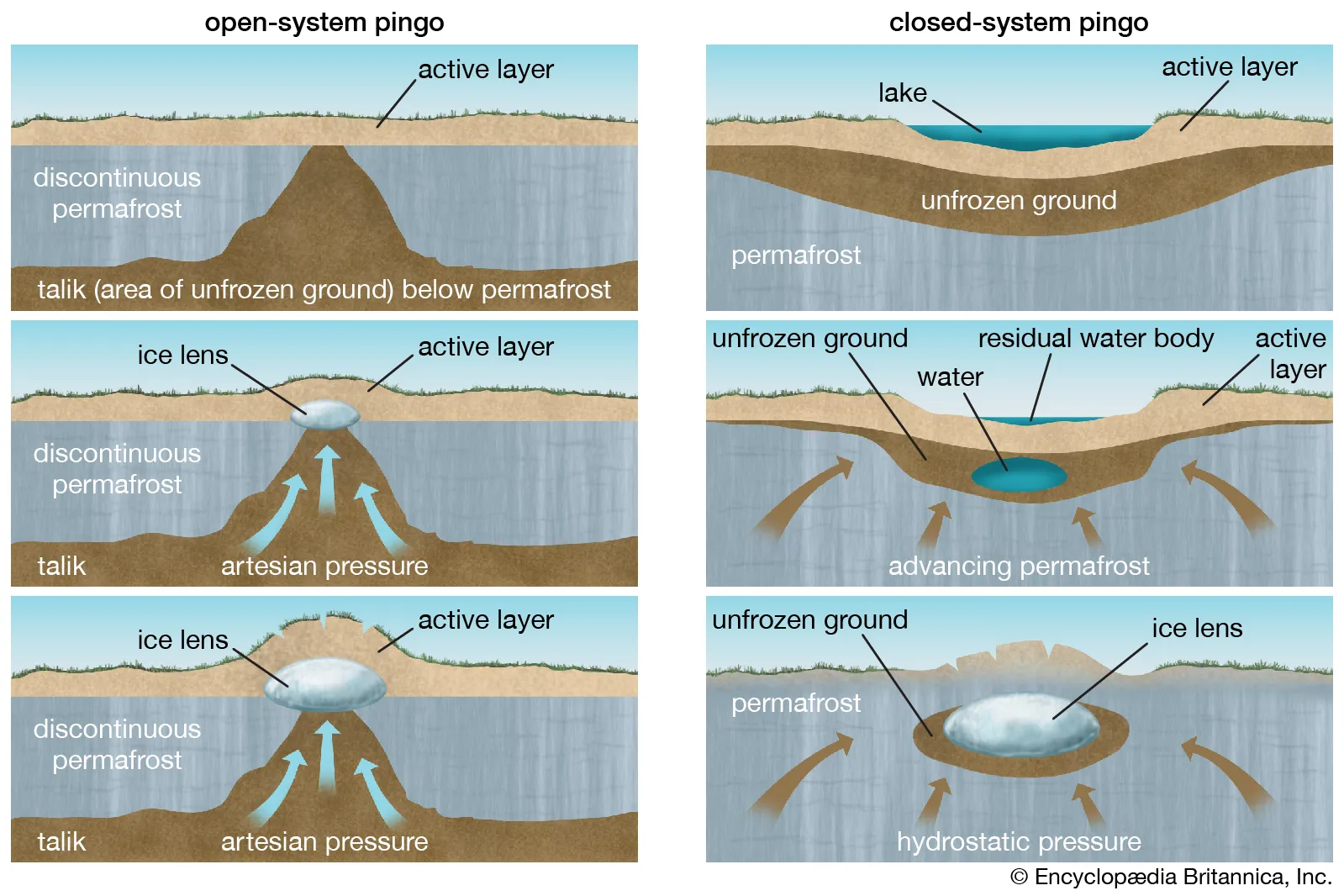
8
New cards
Patterned Ground
* Polygons, stone circles, stripes
* Freeze-thaw cycles → frost heave
* active layer freezes → ice crystals develop → increases volume of soil → frost heave (hydrostatic pressure) → forms small domes on surface
* stones → lower specific heat capacity → expand further → push up → fall forming circles or stripes
* Freeze-thaw cycles → frost heave
* active layer freezes → ice crystals develop → increases volume of soil → frost heave (hydrostatic pressure) → forms small domes on surface
* stones → lower specific heat capacity → expand further → push up → fall forming circles or stripes
