Matrix and Wedge
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
what is the proximal contact area?
area on a mesial or distal surface of a tooth crown that contacts the adjacent tooth in the same arch
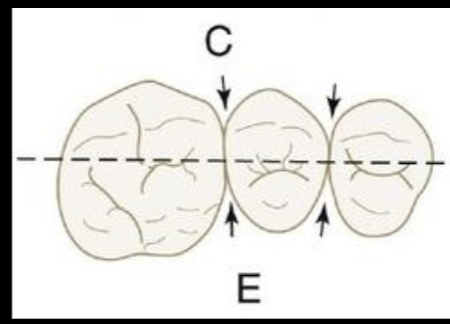
why are proximal contact areas important?
promote normal healthy interdental papillae
improper contacts = food impaction
increased risk of periodontal disease, caries, tooth movement
maintain integrity of dental arches
what is the system made of?
matrix
matrix retainer
wedge
what is the strip or band made of metallic or plastic material that works as a type of a tray, inside which the restoration will be made?
matrix
To keep the matrix in position around the tooth structures during the restorative procedure, several different types of instrument can be used, commonly called
matrix retainer
When the matrix is placed in position on the interproximal region, it must be stabilized and better adapted to the remaining tooth structure. To reach this goal, what is inserted into the interproximal space?
a small wedge with triangular cross section
what are 2 types of matrices that are used?
metallic → resotring contact point in posterior teeth cavities
polyester (mylar strip) →
protecting adjacent teeth during acid etching (anterior or posterior)
restoring anterior teeth
what are circumferential metallic matrix?
metallic bands with a V or boomerang shape, known as Tofflemire matrix band
tofflemire matrix bands are __ cm long with various widths for different crown sizes
7
what kind of preps would indicate using a matrix?
compound class I cavitieis
simple, compound or complex Class II cavities.
Class III cavities
Class IV cavities
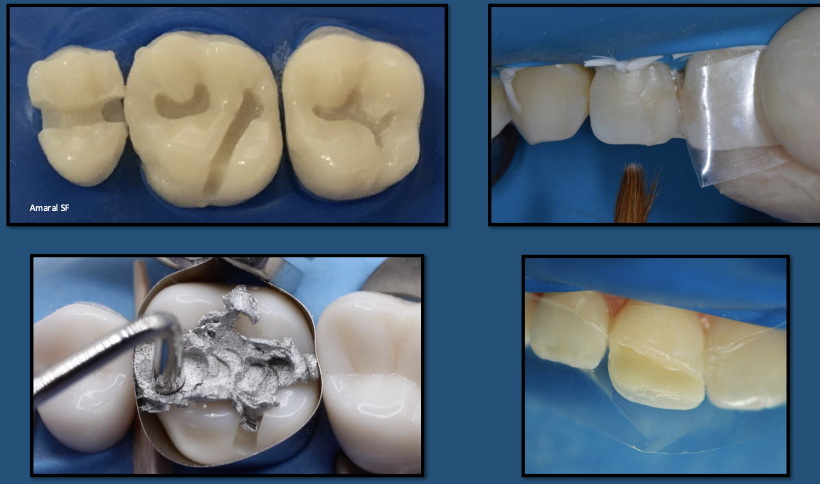
The boomerang-shaped matrix must be assembled on the retainer with the internal edge of its curvature facing the _______ region
cervical
what are the devices intended to hold the matrix in position and to adjust it around the tooth that will be restored?
matrix retainer
t/f: Polyester matrices are not suitable for use in matrix holders or for restoring posterior teeth
true
a matrix must extend slightly below the _____ wall and about __mm above the cavosurface angle.
gingival
1
requirements of a matrix
easy to place/remove without compromising contour to be obtained in restoration
resistance to pressure during condensation of restorative material
extend slightly below gingical wall and 1 mm above cavosurface angle
easy adaptation/fixation to tooth
have a smooth and polished surface
what are the purposes of using a matrix?
provide protection to adjacent tooth
replace missing walls of cavity and allow condesnation of restorative material
enable construction of lost contour
restore contact relationship correctly
what does a sectional metallic amtrix do?
Surround only one proximal surface during the restoration