Topic 2 - Thermodynamics - Biology 241 - University of Calgary
5.0(4)
Card Sorting
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:46 PM on 10/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
1
New cards
• Biochemical Reactions
• Cells
• Organisms
• Ecosystems
• Cells
• Organisms
• Ecosystems
What can systems be? (4)
2
New cards
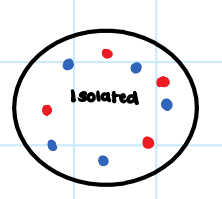
• No exchange of energy or matter with surroundings.
Isolated System
3
New cards
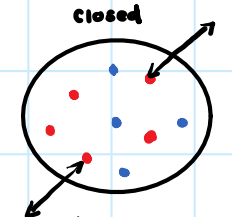
• Exchanges energy with surroundings.
Closed System
4
New cards
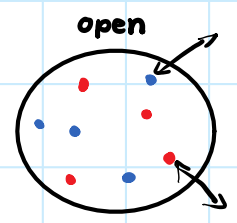
• Exchanges energy and matter with surroundings.
Open System
5
New cards
C) Open
Biological systems are...
A) Isolated
B) Closed
C) Open
A) Isolated
B) Closed
C) Open
6
New cards
• Must absorb needed and remove unneeded molecules.
Why are biological systems open systems?
7
New cards
• The ability to cause change.
Energy
8
New cards
• Change that requires energy.
Work
9
New cards
Any of these answers are correct:
• DNA Replication
• Protein Synthesis
• Metabolism
• Mobility
• Reproduction
• Transport
• Cell Division
• DNA Replication
• Protein Synthesis
• Metabolism
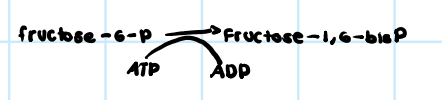
• Mobility
• Reproduction
• Transport
• Cell Division
List three types of work that cells/organisms perform.
10
New cards
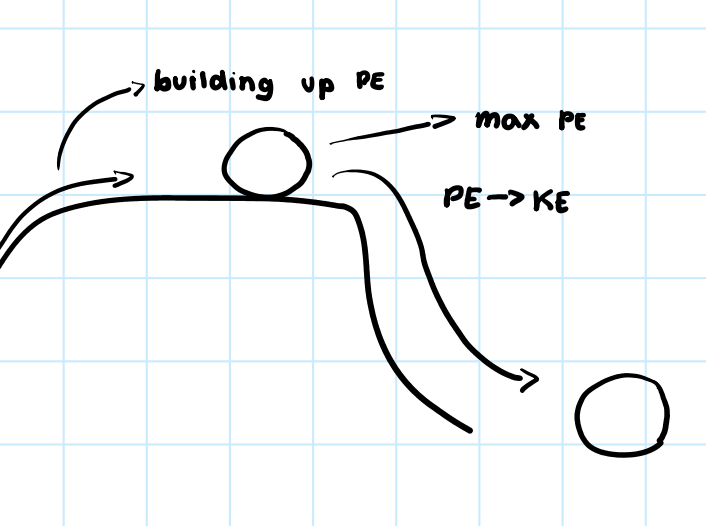
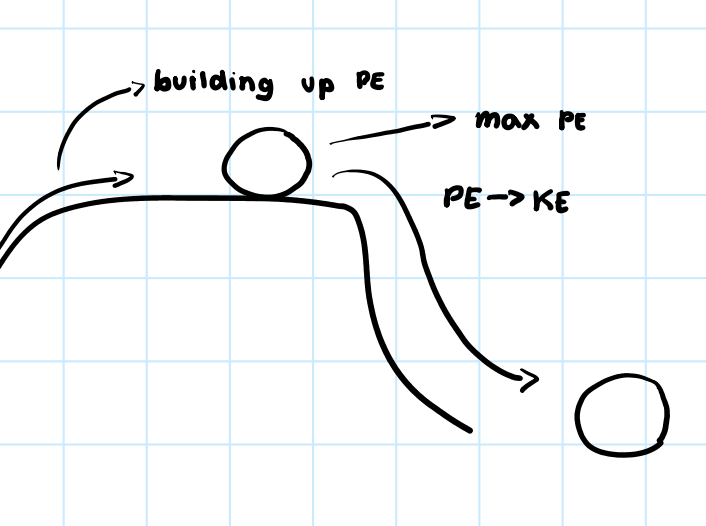
• Stored energy of an object due to its position or chemical structure.
Potential Energy
11
New cards
• Energy of motion or change.
Kinetic Energy
12
New cards
B) High Potential Energy
A molecule with lots of non-polar covalent bonds has...
A) Low Potential Energy
B) High Potential Energy
A) Low Potential Energy
B) High Potential Energy
13
New cards
• The arrangement of electrons in its bonds.
What changes the potential energy within a molecule?
14
New cards
• Energy is neither created nor destroyed.
The First Law of Thermodynamics
15
New cards
• Changes location or changes forms.
What happens to the energy within a system according to the first law of thermodynamics? (2)
16
New cards
• Sum of potential energy and kinetic energy of a system.
Enthalpy
17
New cards
Yes, due to the energy change in the system.
Does the enthalpy change when work occurs?
18
New cards
• Delta H (∆H)
What is the symbol for change in enthalpy?
19
New cards
• Exothermic
If heat is released, the ∆H is...
20
New cards
• Endothermic
If heat is absorbed, the ∆H is...
21
New cards
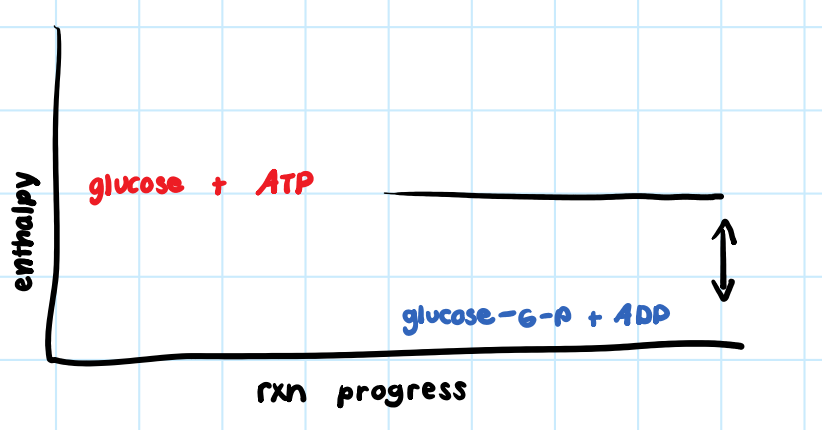
• Products have less enthalpy than reactants.
• Heat released to surroundings.
• Heat released to surroundings.
What are the two characteristics of an exothermic reaction?
22
New cards
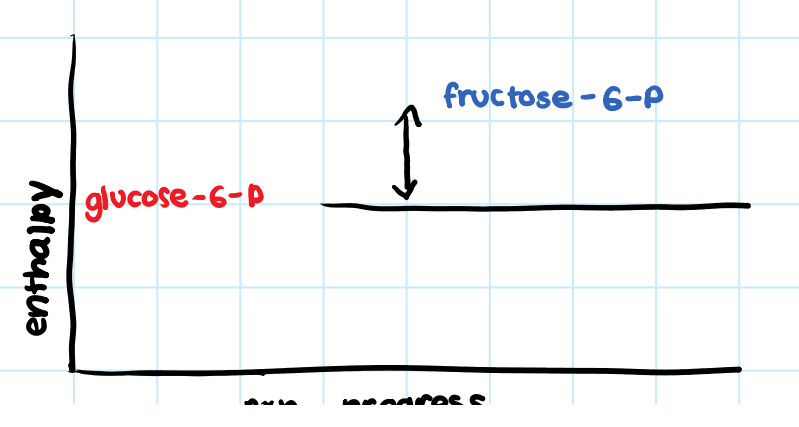
• Products have more enthalpy than the reactants.
• System absorbs heat from surroundings.
• System absorbs heat from surroundings.
What are the two characteristics of an endothermic reaction?
23
New cards
• A reaction that is able to occur under current conditions.
Spontaneous
24
New cards
Yes.
Is an ice cube to liquid water a spontaneous reaction?
25
New cards
No, since it requires sunlight to begin the process.
Is photosynthesis a spontaneous reaction?
26
New cards
• Instantaneous
Spontaneous reactions are not...
27
New cards
• Nonspontaneous
If a reaction is spontaneous, then it is ___________________ in the reversed direction.
28
New cards
• A reaction that cannot occur under the current conditions.
Nonspontaneous
29
New cards
No.
Is liquid water to an ice cube a spontaneous reaction?
30
New cards
Yes.
Can exothermic and endothermic reactions both be spontaneous?
31
New cards
• How dispersed the energy of the system and surroundings is.
Entropy
32
New cards
• Delta S (∆S)
What is the symbol for change in entropy?
33
New cards
• Positive
If energy has higher dispersion, then ∆S is...
34
New cards
• Negative
If energy has a lower dispersion, then ∆S is...
35
New cards
• The total entropy of the universe if always increasing.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
36
New cards
• Spontaneous
Entropy determines if a reaction is...
37
New cards
• ∆Stotal = ∆Ssystem + ∆Ssurroundings
What is the equation for total entropy?
38
New cards
• Measure of energy in a system that is free to do work.
Free Energy
39
New cards
• The amount of energy that was used to make the change.
The change in free energy in a reaction is measured as...
40
New cards
• More
For work to occur, energy must be available to carry out the change and reactants must have ______ free energy than the products.
41
New cards
• Delta G (∆G)
What is the symbol for free energy?
42
New cards
• Positive
If energy is available, the change in free energy is...
43
New cards
• Negative
If energy is not available, the change in free energy is...
44
New cards
• Negative free energy.
• Spontaneous.
• Spontaneous.
What are the characteristics of exergonic reactions? (2)
45
New cards
• ∆G = -T∆Stotal
What is the equation that relates free energy to the total entropy of a system and its surroundings?
46
New cards
• Positive free energy change.
• Nonspontaneous.
• Nonspontaneous.
What are the characteristics of an endergonic reaction? (2)
47
New cards
• Enough energy available to change the system and the total entropy of the universe increases.
What causes exergonic reactions?
48
New cards
• Not enough energy to change the system, total entropy of the universe decreases.
What causes endergonic reactions?
49
New cards
∆G = ∆H - T∆Ssystem
What is the equation that relates free energy, entropy, and enthalpy?
50
New cards
• Exergonic
Are biological reactions exergonic or endergonic?
51
New cards
• The rate of the forward reaction = the rate of the reverse reaction.
Chemical Equilibrium
52
New cards
• The reverse reaction is spontaneous.
What does a positive tabulated standard free energy mean?
53
New cards
∆G = ∆G° + RT(ln(product/reactant))
What is the equation that involves standard free energy?
54
New cards
• Chemical reactions in the cells that change food into energy.
Metabolism
55
New cards
• Breaking down of complex molecules.
Catabolism
56
New cards
• Amino acids
If a protein undergoes catabolism, what is the product?
57
New cards
• Building up of complex molecules.
Anabolism
58
New cards
• Protein
If an amino acid undergoes anabolism, what is the product?
59
New cards
• A series of connected reactions.
Biochemical Pathways
60
New cards
• Biochemical Pathways
In cells, metabolic reactions are linked to...
61
New cards
• Endergonic
Is anabolism endergonic or exergonic?
62
New cards
• False, it is exergonic.
Catabolism is endergonic, true or false?
63
New cards
• When the second reaction contains the first reactions product as a substrate.
Connected Reactions
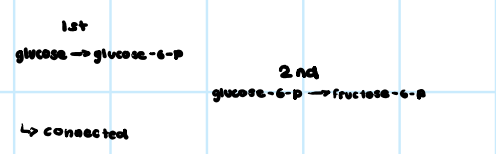
64
New cards
• Nitrogenous Base (Adenine)
• Ribose (Sugar)
• Ribose (Sugar)
What is adenosine made up of?
65
New cards
• Potential Energy
What type of energy does ATP store?
66
New cards
• Negative compressed charges.
Where does the potential energy in ATP come from?
67
New cards
• Reaction of the interaction of chemicals with water, leading to their decomposition.
Hydrolysis
68
New cards
• A single reaction with two things happening, which occur at the same time and same place.
Coupled Reactions

69
New cards
• Coupled
What is the first reaction of glycolysis considered?
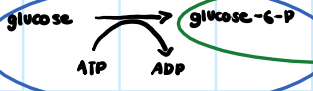
70
New cards
• No, since it only has one thing occurring.
Is the second reaction of glycolysis considered coupled?

71
New cards
• Yes.
Is the third reaction of glycolysis a coupled reaction?