X-ray interaction w/ matter
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
rad elect
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Factors Affect Scatter
Patient thickness
Tissue density
kV Energy
Field Size
5 Types of Scatter Radiation
Classical
Compton
Photoelectric
Pair Production
Photodisentigration
Scatter Radiation - Classical
Interaction between low energy x-rays and entire atom
Below 10 kV
No ionization in this interaction
X-ray photon loses no energy
Wavelength of incident x-ray = wavelength of scattered x-ray (photon)
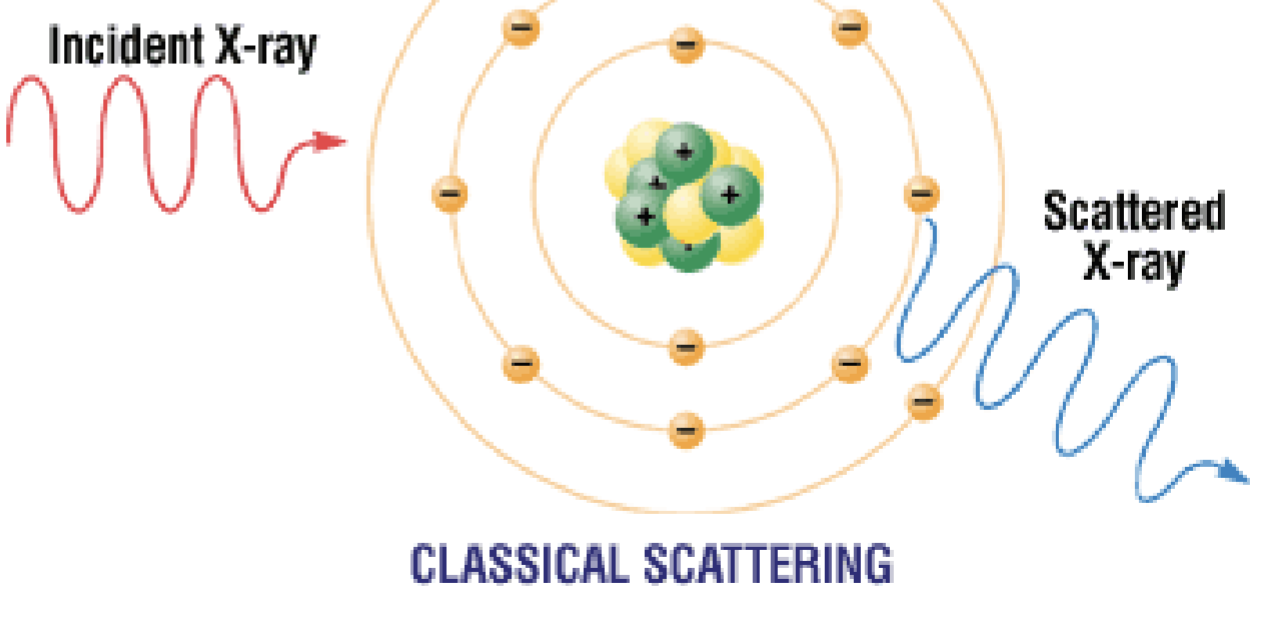
Scatter Radiation - Classical Also called 4 names:
– Coherent
– Rayleigh
– Unmodified
– Thompson
Scatter Radiation - Compton/Modified
Interaction between moderate energy x-rays and atom
Interacts with outer shell electrons
Ionization occur
Photon changes direction
– photon can be redirected back towards source
(backscatter)
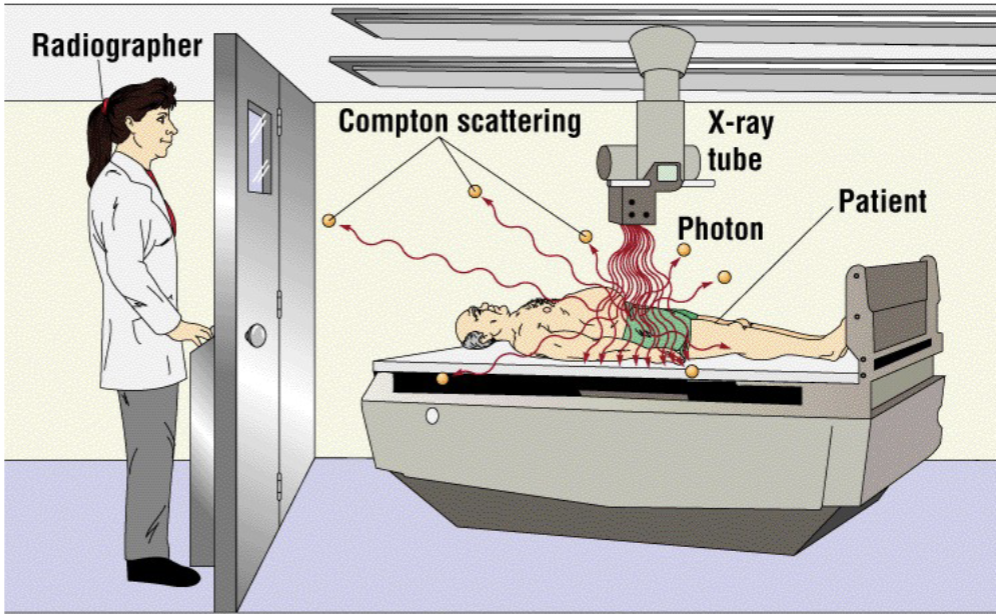
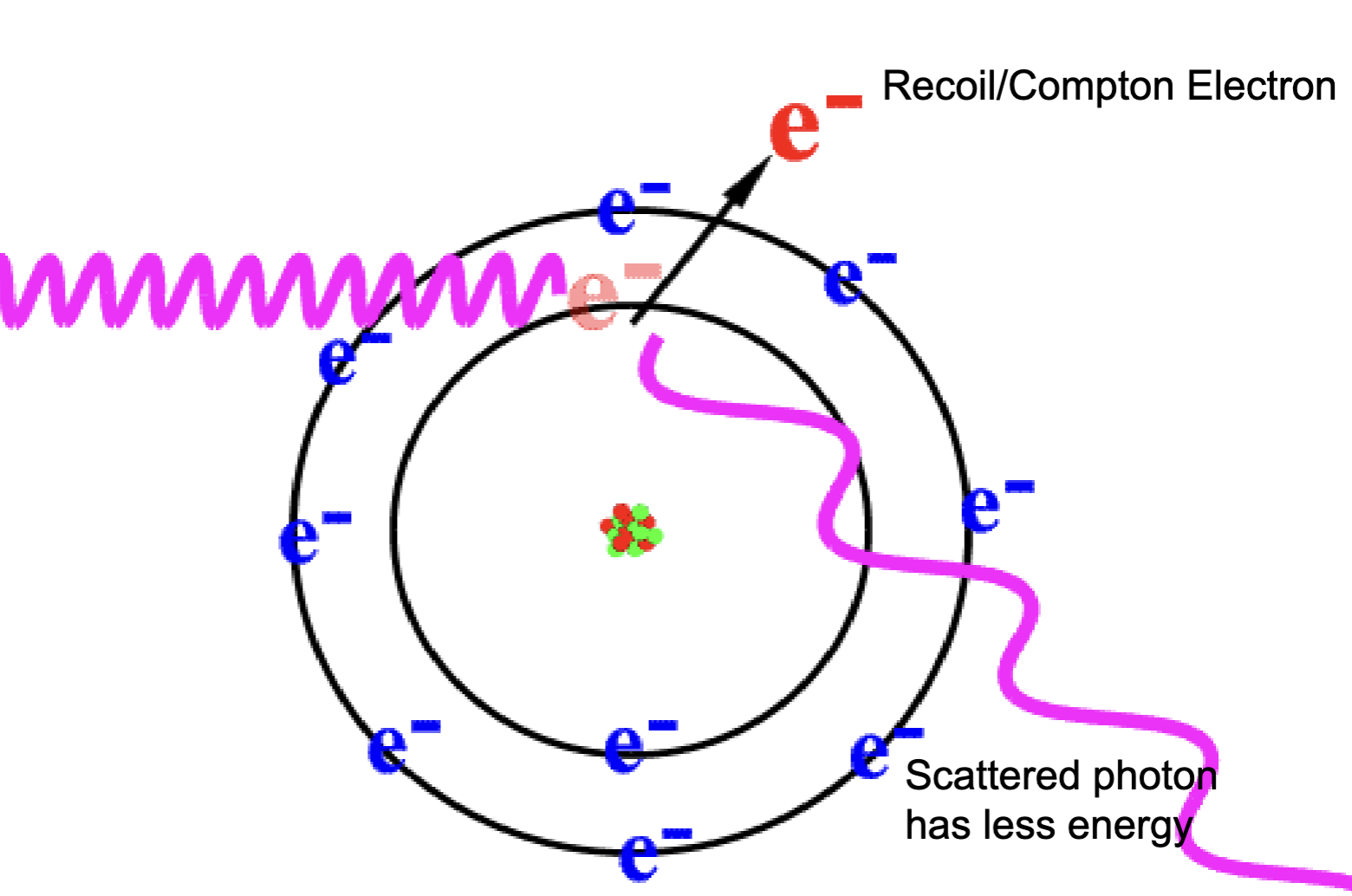
Scatter Radiation - Compton/Modified is responsible for…
majority of scatter radiation reaching image receptor (IR), contributes most to occupational exposure
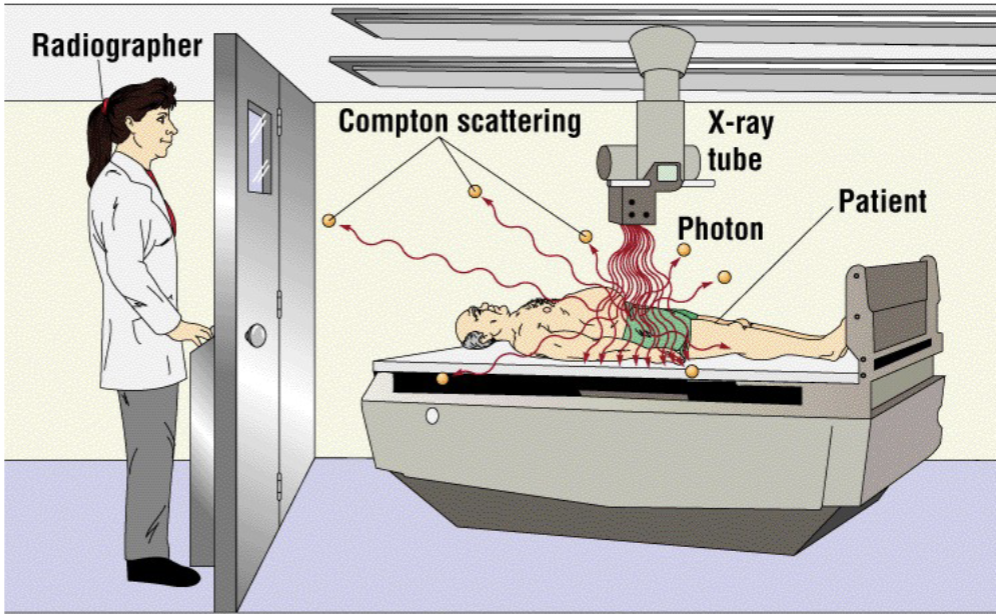
During Fluoro – the patient is the…
largest scattering object
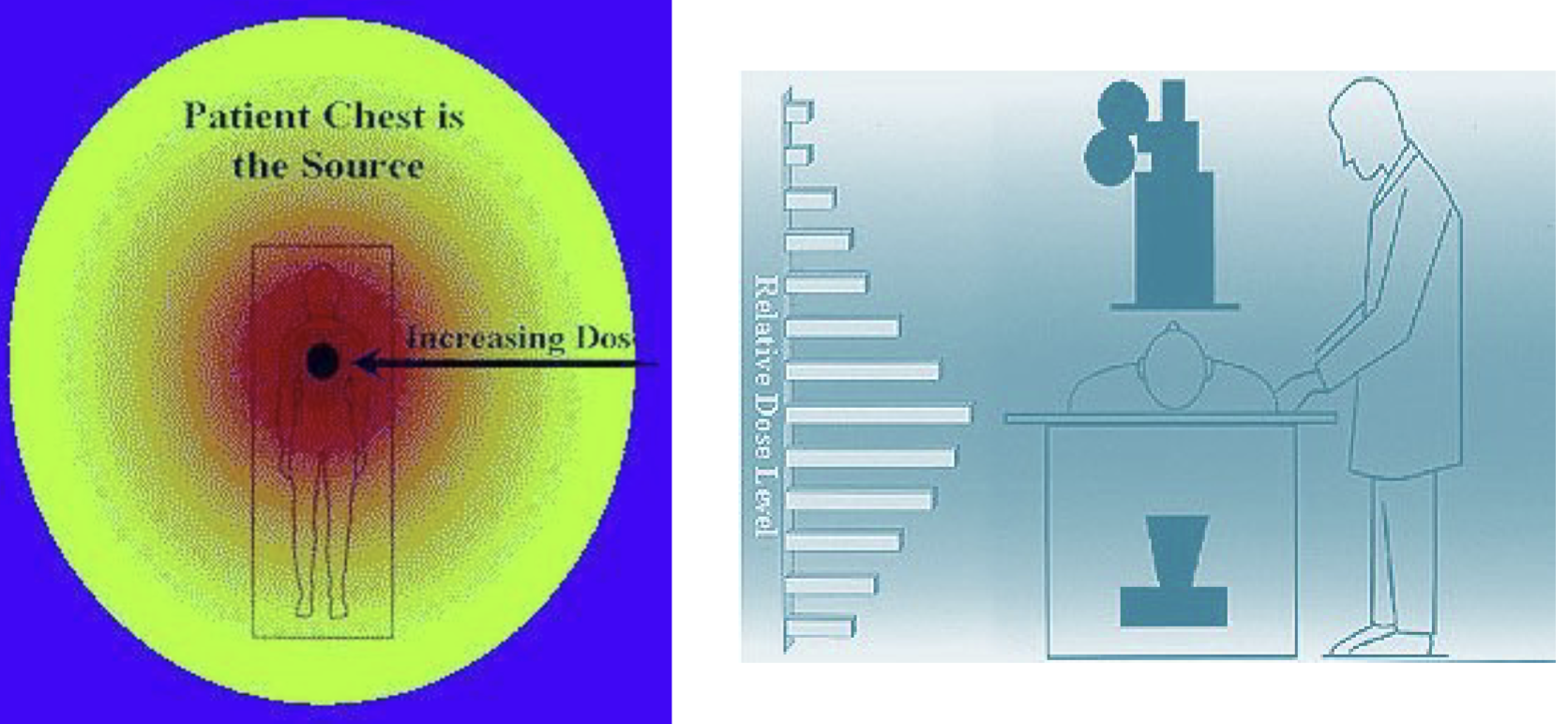
Compton scatter contribute to the increases in…
fog which decreases the contrast in the radiograph
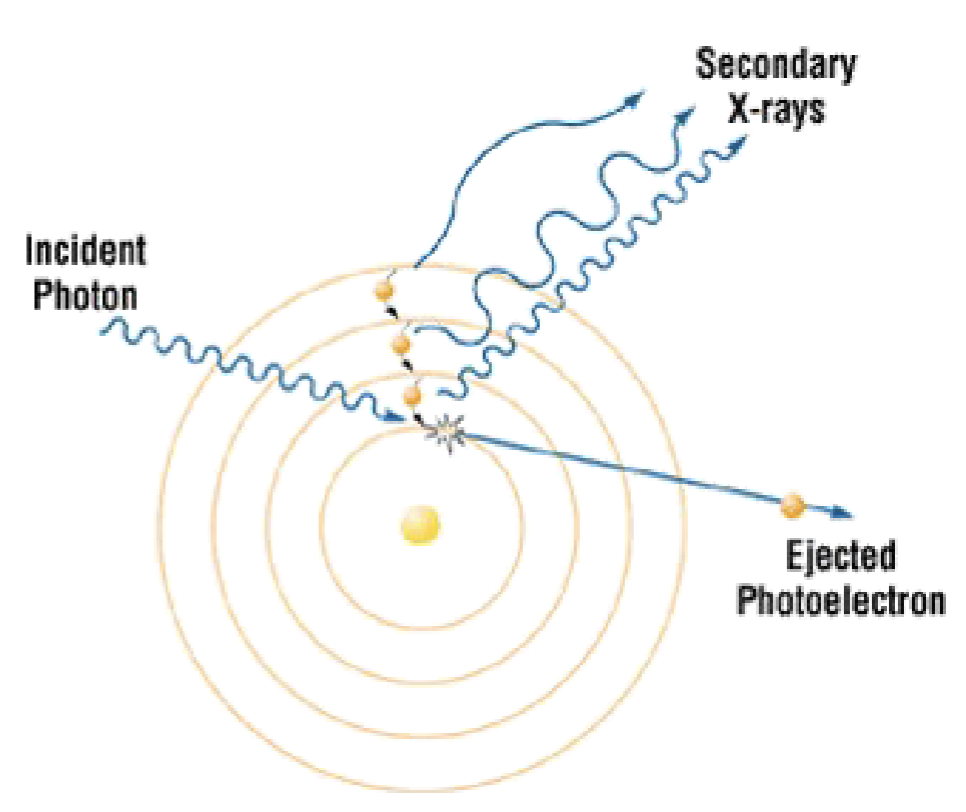
Scatter Radiation - Photoelectric
Ionization occurs when Incident photon disappears, photoelectron is ejected
Incident photon has to be greater than K shell electron energy
outer electron fills the orbit-producing characteristic radiation
Contributes significantly to patient dose
Metal or high atomic number elements will have…
more photoelectric absorption
Pair Production
Occurs at 1.02 MeV or higher
High energy photon nears nucleus and loses energy
negatron & positron are emitted
Pair Production 2
Negatron is absorbed
Positron combines with a free electron
When positron & electron combine, they annihilate each other
Births 2 photons of 0.51 MeV each
Photodisintegration
Occurs with photon energies of 10 M eV or higher
High energy photons strikes nucleus
Nucleus excited
Ejects a nuclear fragment
Importance of Interactions of X-rays w/ Matter
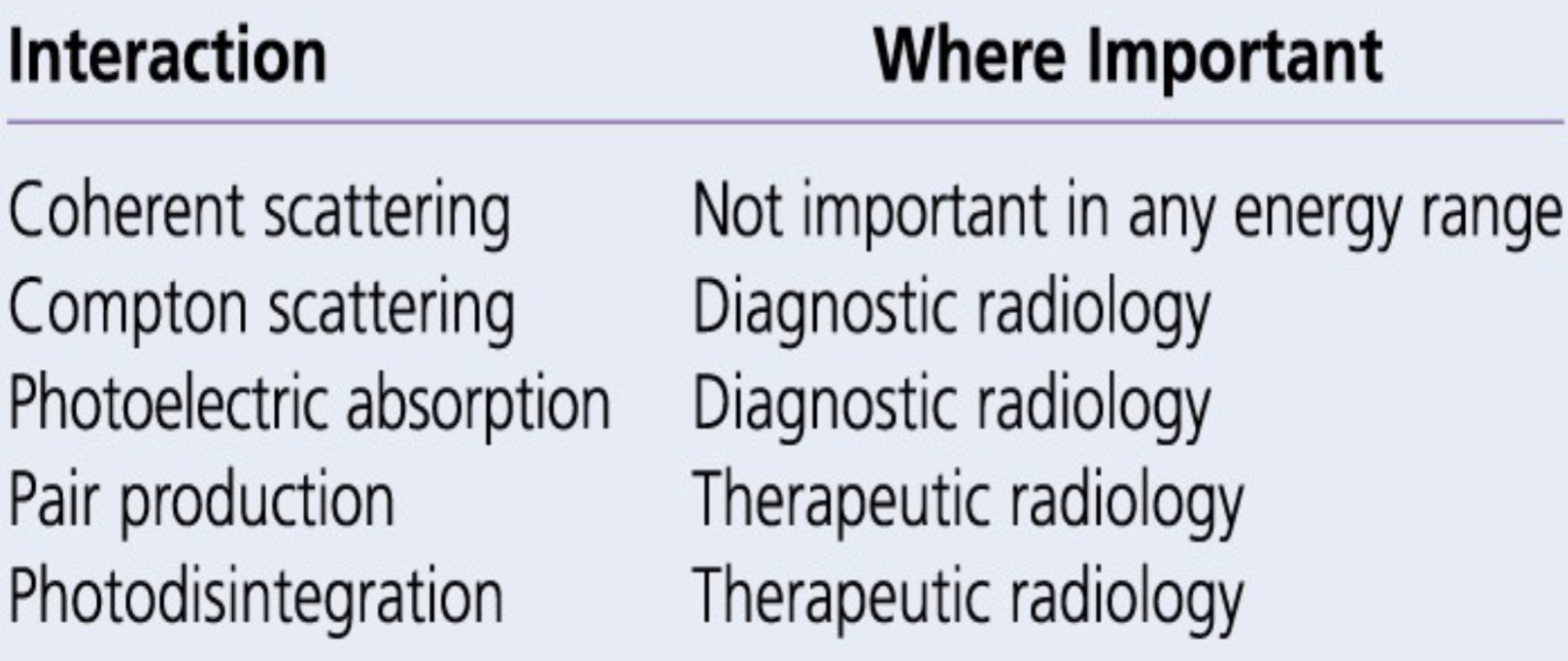
kVp determines type of interaction in the body
High kV decrease in photoelectric absorption and increases Compton interaction (more penetration and less body
interaction)
Low kV increase in photoelectric absorption, Increase in patient dose