Ch. 7 PP - The Wealth of Nations and Economic Growth
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Economic wealth brings
wealth, which increases societal well-being
Wealthier nations have
Higher interest rates, life expectancy, nutrition, education opportunities, leisure, entertainment, fewer conflicts (civil wars and riots), and more material goods
1st Key fact about the wealth of nations and economic growth
GDP per capita varies enormously among nations
2nd Key fact about the wealth of nations and economic growth
Everyone used to be poor
3rd Key fact about the wealth of nations and economic growth
There are growth miracles and disasters
GDP per capita
is the total economic output of a country divided by its population, indicating the average income per person. (average about the distribution of wealth within each country)
Richer countries have
higher GDP per capita
In 2019, 10% (or 760 million) of world’s population
lived in a country with a GDP per capita of less than $4,000
In 2019, 70% of world’s population
Lived in a country with a GDP per capita equal to or less than $14,000
In 2019, 76% (or 5.8 billion) of world’s population
lived in a country with a GDP per capita of less than average
The distribution of world income states that poverty is
normal
Wealth is
unusual
GDP per capita in year 1 is estimated to be
$700 - $1,000 per year, which was the same in all major areas of the world
For most of human history
there was no long-run growth in real GDP per capita
GDP per capita today is
50 times larger in the richest countries than in the poorest
Economic growth
Measured as the growth rate of real GDP per capita
Large differences in growth or real GDP per capita
slow growth sustained over long periods of time.
Exponential growth or compounding
Growth that builds on top
Economic growth is measured as
(Original real GDP per capita - final real GDP per capital) divided by final real GDP per capita times 100
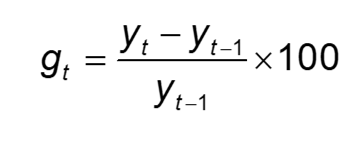
economic growth
growth rate of real GDP per capita
Growth rate
percentage change in real GDP per capita over time.
Measuring growth
Rule of 70 approximates the length of time needed for a growing variable to double
Rule of 70
doubling time = 70/ growth rate percent
Growth miracles
phenomena where countries experience rapid economic growth, often doubling their GDP per capita in a short period.
The U.S. is 1 of the worlds wealthiest countries because
It grew slowly but consistently for more than 200 years
From 1950 to 1970 Japan grew
at an average annual rate of 8.5%, transforming into one of the world's leading economies.
In 1950, South Korea had about the same as
Nigeria
From 1970 to 1990 South Korea GDP per capita
grew at a rate of 7.2% per year and is now on par with many European economies
Growth disasters
refers to periods when economies fail to achieve potential growth, often due to factors like conflict, poor governance, or economic mismanagement.
Nigeria has barely grown since 1950
It was poorer in 2005 than in 1974, when high oil prices briefly bumped up its per capita GDP.
In 1900, Argentina was one of the richest countries in the world, with GDP per capita almost as large as that of the United States.
By 1950 GDP per capita had fallen that of the U.S. By 2000 it’s GDP per capita was less than 1/3 of the U.S.
Bad news of economic growth
Most of the world is poor, more than 1 billion people live on incomes of less than $3 per day which leads to reduced prospects of health, happiness, and peace
Good news economic growth
Economic growth has lifted millions out of poverty, improved living standards, and increased access to education and healthcare.
Causes in GDP per capita include factors of
production, incentives, and institutions
Physical capital
The stock of tools that include machines, structures, and equipment.
Human capital
The productive knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience.
Countries with higher GDP per capita have a lot of factors of production
physical capital, human capital, and technological knowledge.
More and better physical capital
Makes workers more productive and take advantage of more sophisticated tools
Make Wokers more productive
Greater quantities of physical and huma capital per worker
Increase human capital
Education
Technological knowledge
The understanding and skills necessary to produce goods and services efficiently, often leading to innovations and improvements in productivity.
Improved technological knowledge
leads to enhanced production methods and increased efficiency in creating goods and services (potentially boundless)
Better technological knowledge has allowed U.S. farms
increase their output two and a half times since 1950, and while using less land.
Increase technological knowledge
research and development
organization of factors of production
Depends on incentives and institutions
Institutions
are the rules and norms that structure social interactions, influencing economic performance and growth.
Institutions include laws and regulations, but also
customs, practices, organizations, and social mores
Institutions that promote growth
create incentives that align self-interest with the social interest
Wealthy countries have institutions that make it
in people's self-interest to invest in physical capital, human capital, and technological knowledge.
Institutions of economic growth include
Property rights, Honest government, Political stability, A dependable legal system, Competitive and open markets
Property rights
are legal rights that individuals or firms have to use their property as they see fit, which encourages investment in physical and human capital
free ride
is a situation where individuals benefit from resources or services without paying for them, leading to underinvestment in those resources.
communal property
is a type of property ownership where resources are owned and managed collectively by a group, often leading to shared benefits and responsibilities.
When China switched from communal to individual farms
food production increased by 50%, and 170 million people were lifted above the lowest poverty line.
Savers won’t invest if
they don't expect that they will receive a return for their savings and investment.
Property rights encourage
technological innovation
Companies will not undertake research and development unless
they expect to profit from it
Corpution
involves the abuse of power for personal gain, undermining economic growth and trust in institutions.
Corruption is like
a tax that bleeds resources away from productive entrepreneurs.
Resources invested in bribing
cannot be invested in machinery and equipment
Few people want to be entrepreneurs when corruption is high because
They know their wealth will be stolen
In many nations, civil war, military dictatorships, and anarchy
have destroyed the institutions necessary for economic growth.
Good legal system
facilitates contracts and protects private parties from expropriating one another.
Poorly protected property rights
stem from either too much or too little government.
Some legal systems are of such low quality
no one knows for certain who owns what.
difficult to borrow money
lenders aren't sure they will get their money back.
the differences in per capita income across countries are explained by
differences in the amount of physical and human capital. Additionally, not being able to use capital efferently
Competitive and open markets are one of the best ways
encourage the efficient organization of resources.
reasons for inefficient organization
Inefficient and unnecessary regulations, Red tape, or the time and cost to do tasks such as starting a business or enforcing a contract in a court of law, Barriers to free trade
Economies of scale
The advantages of large-scale production that reduce average cost as quantity increases.
Natural resources help explain
the differences in economic growth between countries, as access to accumulate physical and human capital
Transport is cheaper
over water than over land, so countries with access to water are more open to trade.
Landlocked countries
Lower GDP per capita than countries with access to a coast
Important to economic growth
History, ideas, geography, culture, and luck
economic growth
raised billions of people out of poverty
Poor countries
catch up to rich countries, and in a surprisingly short period.
Countries with a high GDP per capita
lots of physical and human capital per worker, organized using the best technological knowledge.
Countries with a high GDP per capita have institutions
encourage investment in physical capital, human capital, technological innovation, and the efficient organization of resources.
Institutions for increasing economic growth
property rights, honest government, political stability, a dependable legal system, and competitive and open markets.
red tape
The time and cost to do tasks such as starting a business or enforcing a contract in a court of law.