AP Psychology: Topic 4.6 -Motivation
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Drive-reduction theory
states that motivation comes from biological needs or drives that cause people to act in ways that restore balance

Homeostasis
the tendency of the human body to seek balance, equilibrium, and stability
Arousal theory
people's tendency to maintain a balance of arousal and excitement to avoid boredom and apathy with each person having their own optimal level of arousal

Optimal level of arousal
the psychological state where a person feels alert and engaged--but not stressed--and is able to perform at their best
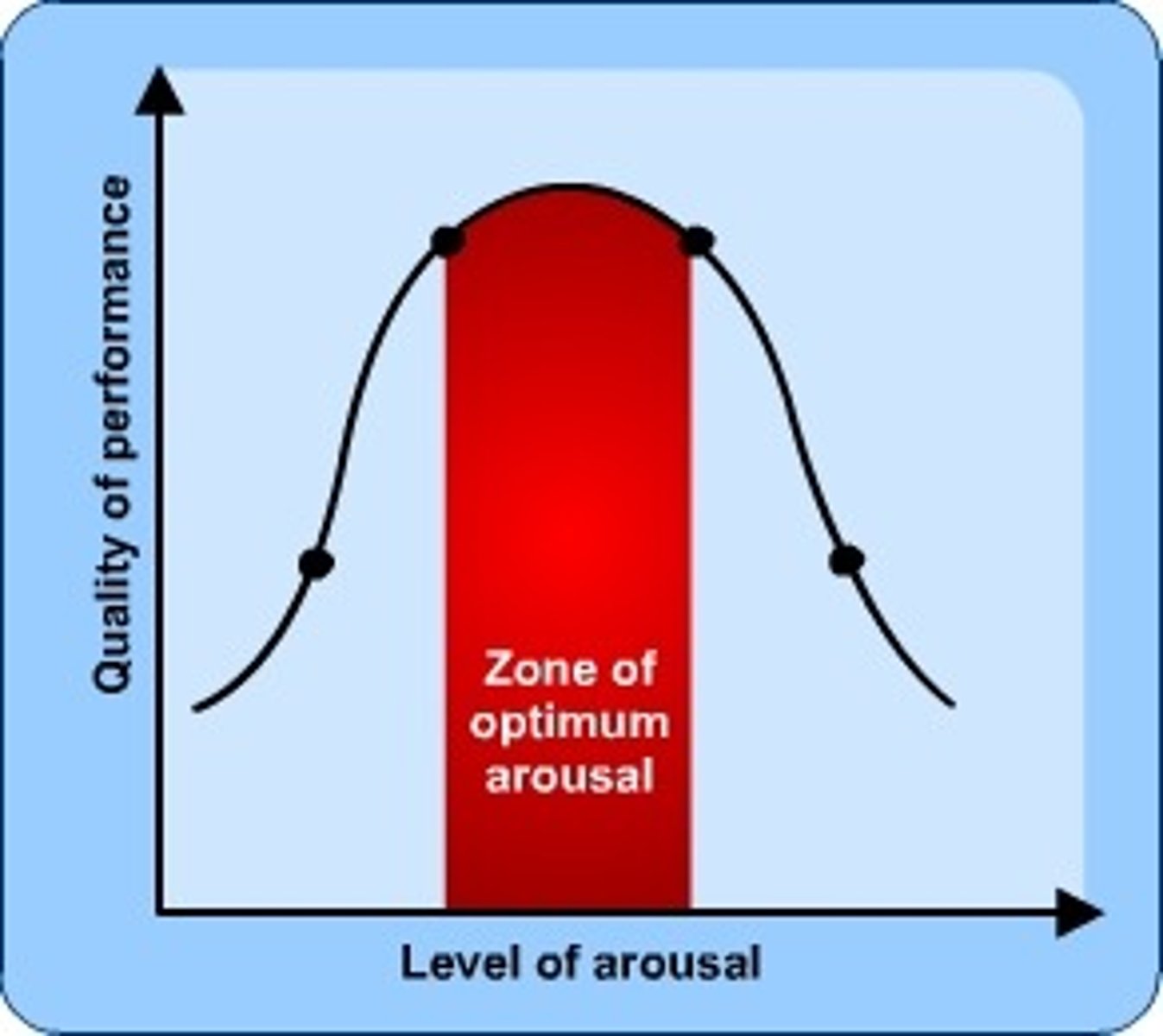
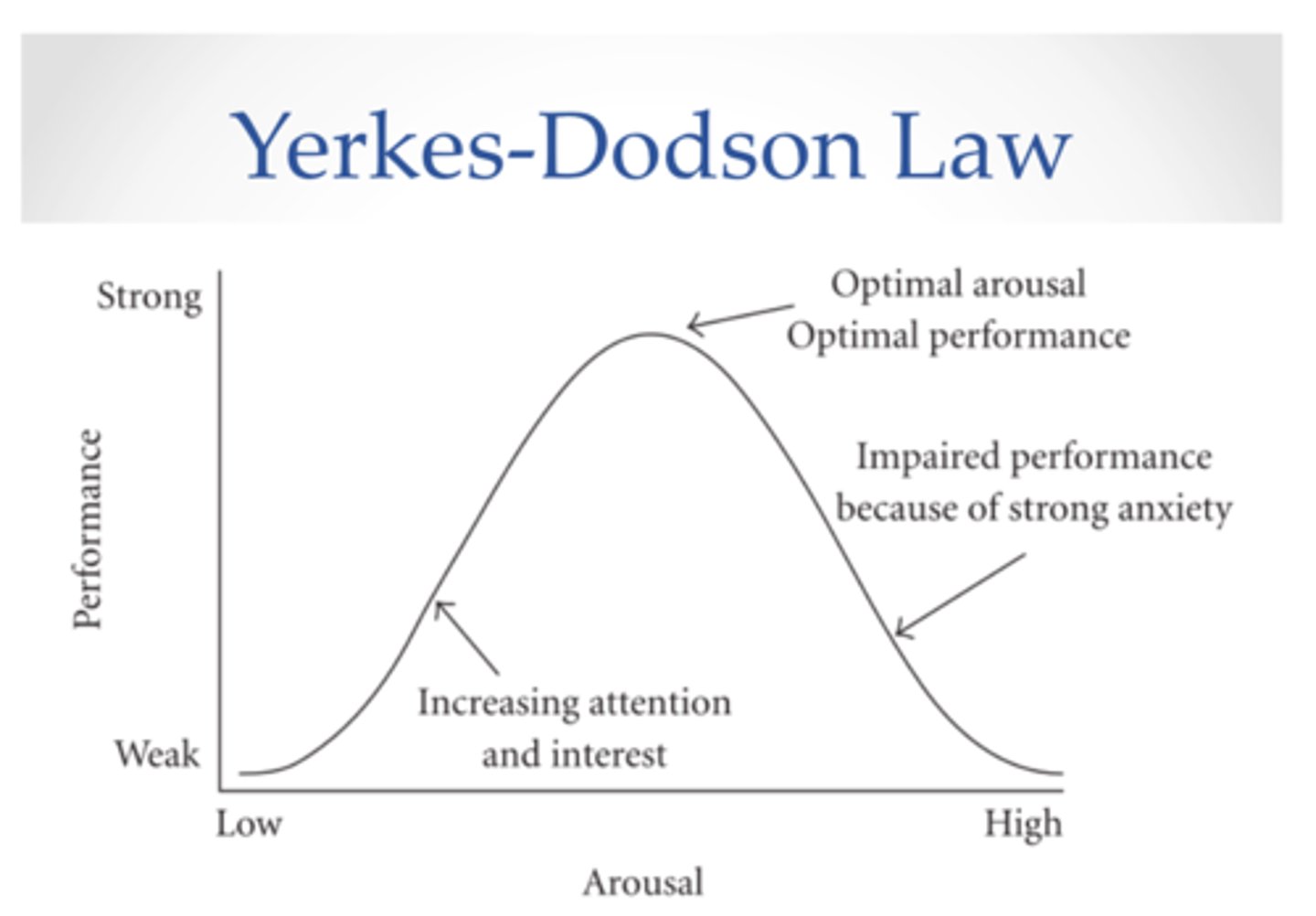
Yerkes-Dodson Law
states that performance improves with arousal, but only up to a certain point
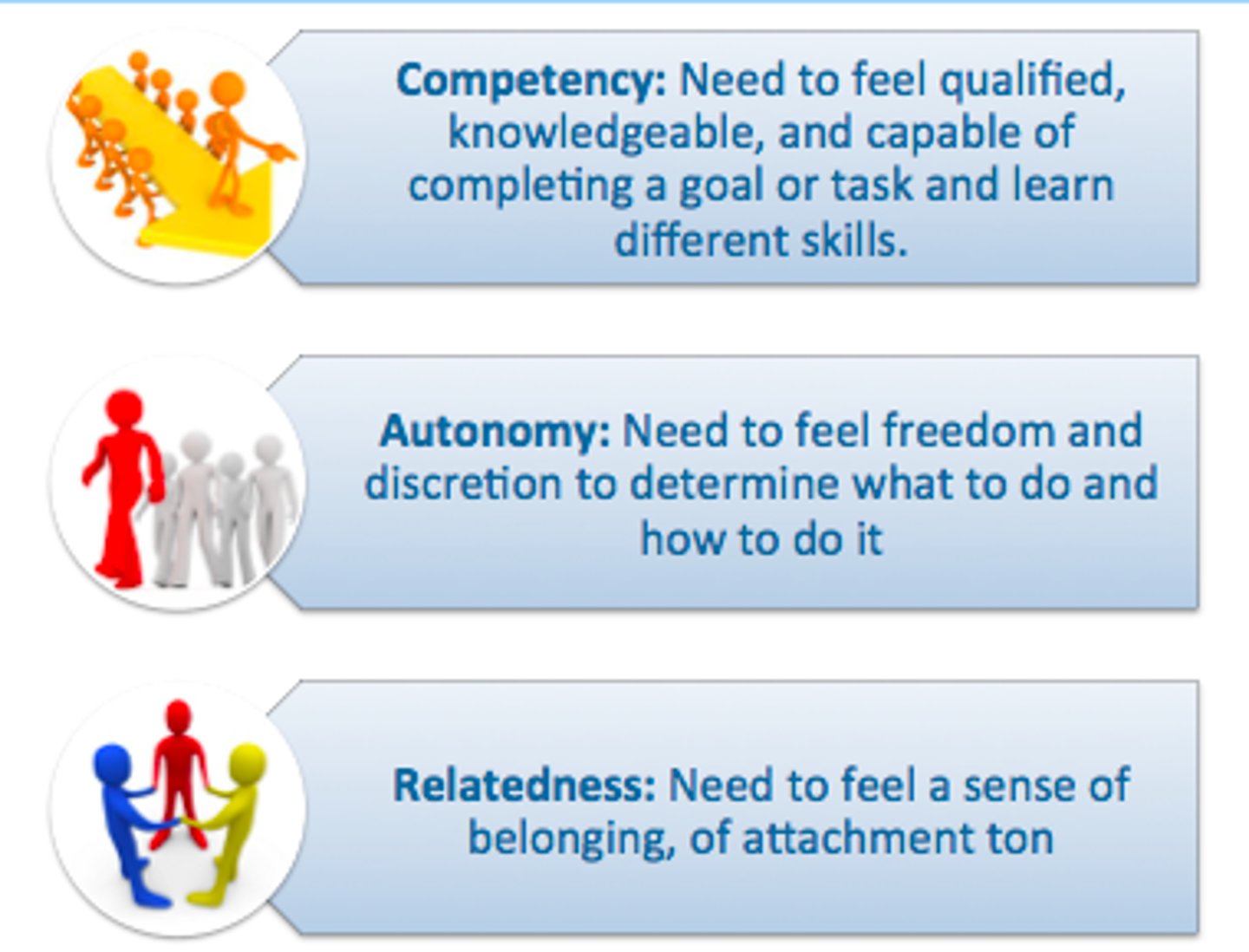
Self-determination theory
suggests that all humans have three basic psychological needs—autonomy, competence, and relatedness—and that people feel more motivated to take action when they believe their choices will have an effect on the outcome
Intrinsic motivation
the drive to complete a task because it is personally rewarding and internally satisfying
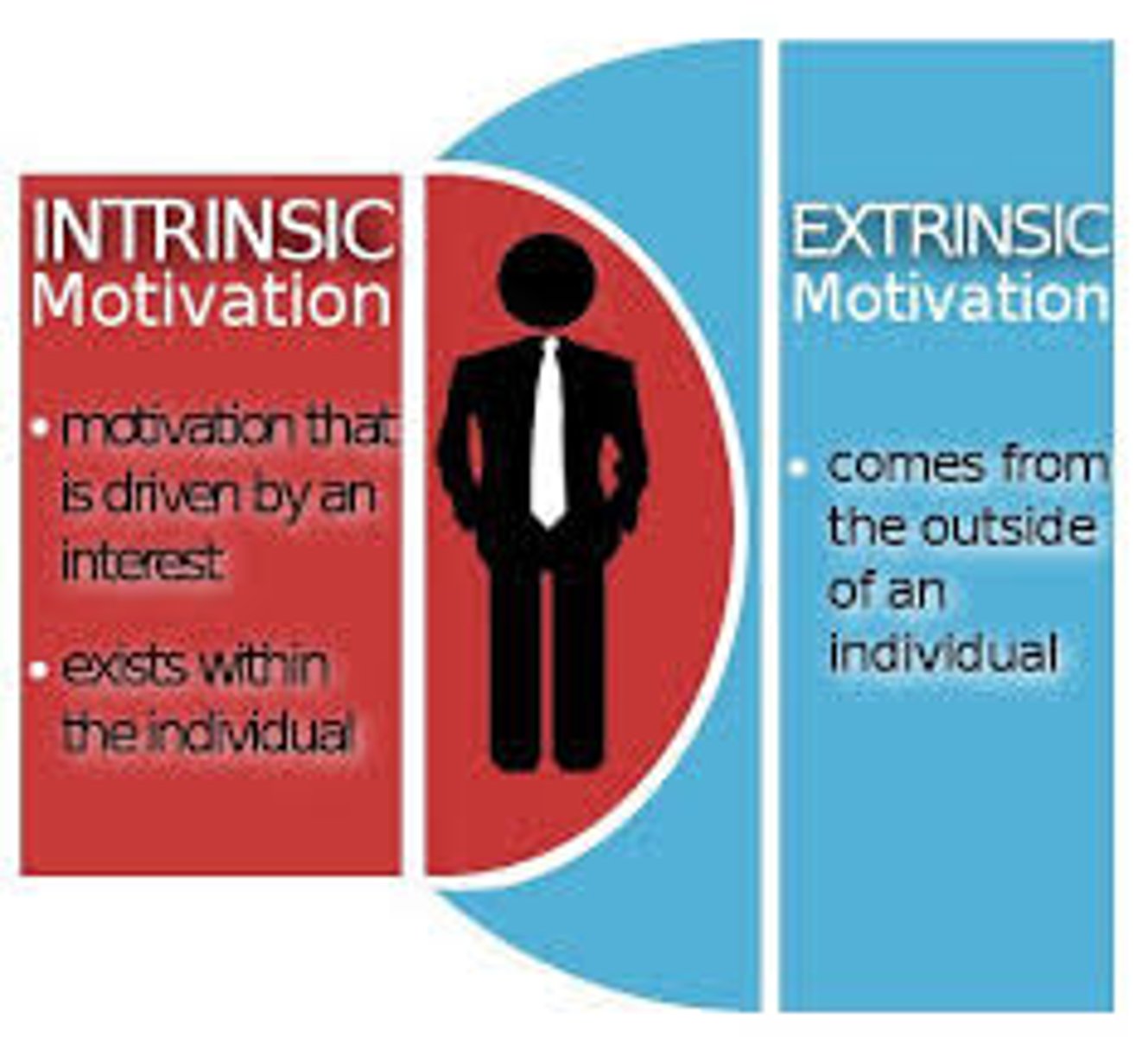
Extrinsic motivation
the drive to participate in an activity in order to achieve an external goal, such as receiving a reward or avoiding punishment

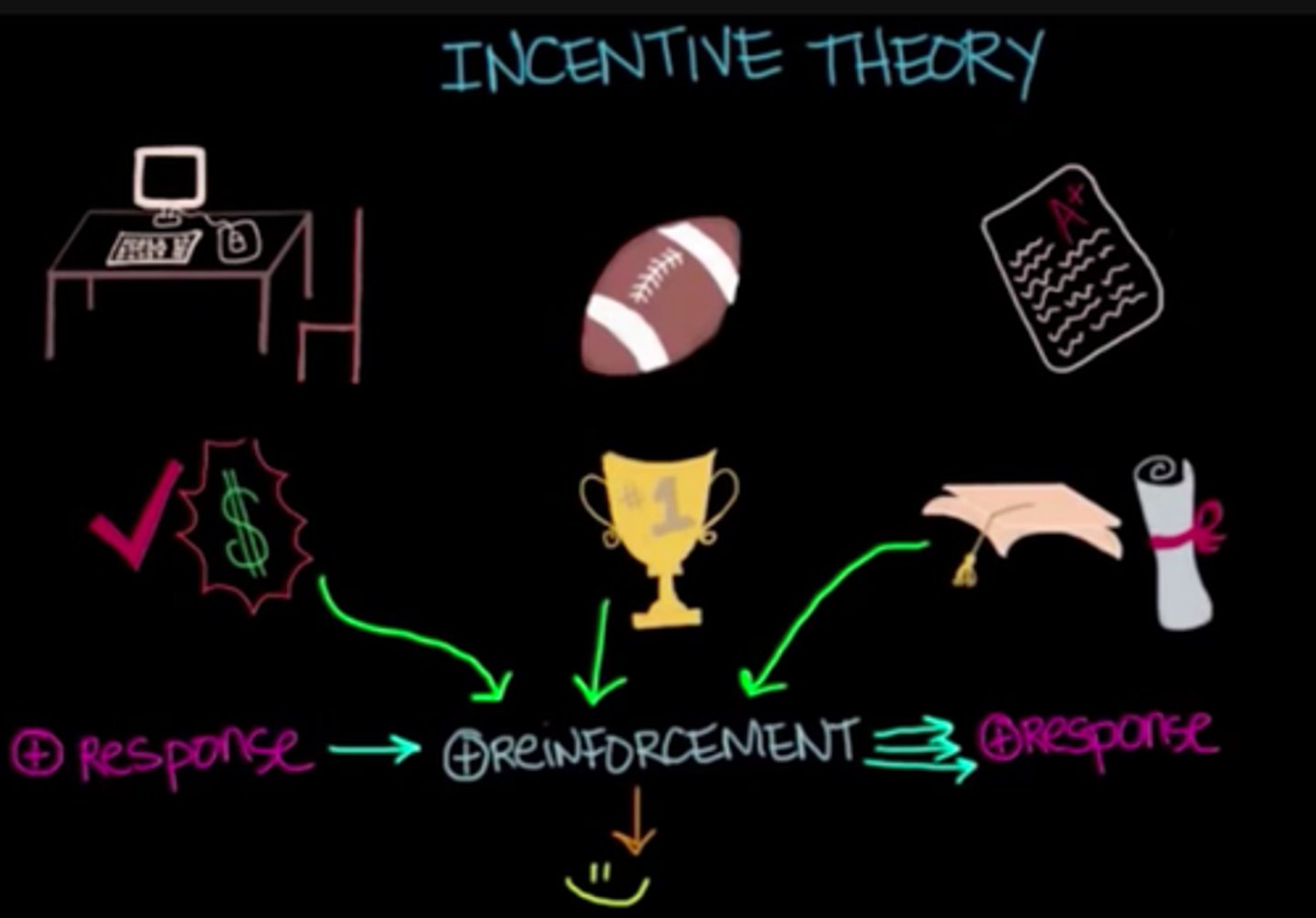
Incentive theory
a theory of motivation stating that behavior is motivated by the desire to attain rewards and avoid punishments
Instincts
inborn, fixed patterns of behavior in response to certain stimuli; don't require conscious thought

Lewin's motivational conflicts theory
states that conflicts between undesirable alternatives are more difficult to resolve than conflicts between desirable alternatives

Approach-approach conflicts
these conflicts occur when a person must choose between two equally appealing options

Approach-avoidance conflicts
these conflicts occur when a goal has both positive and negative aspects (there are advantages and disadvantages to both approaching and avoiding the goal)

Avoidance-avoidance conflicts
these conflicts occur when a person must choose between two undesirable options

Sensation-seeking theory
explains a tendency to seek out novel, complex, and intense experiences and sensations, and to take risks to satisfy this desire

Thrill seeking
the tendency to pursue new and different sensations, feelings, and experiences which often involve a degree of risk

Adventure seeking
the tendency to participate in an unusual, exciting, and potentially dangerous journey or series of events

Disinhibition
a lack of restraint that involves impulsivity, poor risk assessment, and a disregard of social conventions

Boredom susceptibility
an aversion to repetitive experiences, routine work, and predictable people with a reaction of restless discontent when exposed to such situations

Hunger
a natural physical drive to avoid starvation that is controlled by hormones, such as ghrelin and leptin (regulated by the hypothalamus via the pituitary gland)

Satiety
the state of being satisfactorily full and unable to consume more food (controlled by hormones such as ghrelin and leptin and regulated by the hypothalamus via the pituitary gland)
