C 205 - Exam A Prep
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
Information Systems
collects, processes, stores, analyzes, and disseminates information for a specific purpose
Information Technology (IT)
Any computer-based tool that people use to work with information and support the information and information-processing needs of an organization
What are the components of Information Systems
hardware (actors), software (intrusctors), data (bridge), procedures (instructors), people(actors)
Data
raw facts that describe the characteristics of an event or object
information
Data converted into a meaningful and useful context
knowledge
information that facilitates action
wisdom
The combination of knowledge and experience
tacit knowledge
strategies for success that are not explicitly taught but that instead must be inferred
explicit knowledge
knowledge that is easily communicated and available to everyone
Who are the people in IS?
Creators, Operators, Managers, Users
Creators
System Analysts, Programmers, Comp Engineers
Operators
Operations and Administrations - involved in the day to day operations. Computer operator
Capabilities of Information Systems
1. Perform high-speed, high-volume computations
2. Provide fast, accurate communication and collaboration
3. Store huge amounts of information in a small space
4. Allow quick and inexpensive access to info, worldwide
5. Interpret vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently
6. Automate business processes and manual tasks
Generation 1 - Vacuum Tubes
late 1930s - mid 1950s
Large, fragile, complex and expensive
One program at a time
Housed at universites
Gen 2 - Transistors
Mid 1950s - Mid 1960s
First digital computing machiens used in businesses and government
Lower power required and less heat
Simpler and smaller.
IMB 650
Gen 3 - Integrated Circuits
Mid 1960s - Early 1970s
Silicon Chips
Smaller, faster, cheper
Keyboard input, monitor output
Gen 4 - Microprocessors
Early 1970s - Present
CPU
GUI
Mouse
Floppy dirve
Gen 5 - AI
Early 2000s - Present
Nanotechnology
Natural language input
Siri
Networking Personal Computers
1985-Present
-Critical to the rapid adoption of personal computers and rise of
social networks
Local Area Networks (LANs)
-linking many personal computers together
-shared access to data, printers, and other peripheral devices
Wide Area Networks (WANs)
-the Internet
-web browsing
Cloud Computing
the practice of using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data, rather than a local server or a personal computer.
Mobile Computing
A real-time connection between a mobile device and other computing environments, such as the Internet or an intranet.
Hardware
The physical components of a computer.
Inputs --> Process --> Output
input hardware
Accept or capture data.
Direct:
keyboard, mouse, document scanner, bar code, microphones.
Indirect
Scanners, Digital Cameras, Biometric Systems
output hardware
Hardware that is used to create outputs, data flows out of the hardware (speakers, printers, Screen projections etc.)
Bits
binary digits (0s and 1s)
Bytes
8 bits
In 1024 - mostly rounded down to 1000 for simplicity.
discrete values
only occur in whole numbers (integers)
Motherboard
A circuit board that contains all of the computer system's main components.
What components must connect to the motherboard?
Socket for the CPU (Microprocessor)
Primary Memory
Buses
Ports and Expansion Slots
buses (computer)
Data channles within the motherboard that move data
CPU (Central Processing Unit)
The internal operating unit or "brain" of a computer.
cache
Very fast memory that keeps frequently used instructions.
Main Memory (RAM)
program instructions, operating system instructions.
What happens if I have too little RAM
Constant memory swapping, slows processing, needs more memory if processing many programs.
Primary Storage
The computer's immediate internal memory, RAM and ROM.
RAM
Random Access Memory
Volatile - Deleted when turned off
Working Memory
ROM
Read Only Memory
Non-Volatile
Stores Permenant instructions
Use to boot up machine
Secondary Storage Devices
Non Volatile - Hard disk, floppy disks, CD, DVD, jump drives
flash memory
Type of nonvolatile memory that can be erased electronically and rewritten.
SSD, Flash Memory Drive,
client computer
Computer on a network that uses services provided by a server.
Server Computers
provide access to information and application
-faster, larger, more powerful
-serve resources to client computers
-the Cloud is a term assigned to servers accessible anywhere and anytime (over the internet)
-dedicated: mail, file, web, applications, database, etc.
Firmware
Software that is permanently stored in a chip. The BIOS on a motherboard is an example of firmware.
BIOS
Basic Input/Output System
Required because all volitile memory is lost when the computer is turned off.
What are the 2 types of computer software?
OS and Application Software.
Operating Software
software that operates the computer
Applicaiton Programs
Perform Specific user tasks.
Buy off Shelf vs Custom Developed
proprietary software
Software that has been developed by a company and has restrictions on its use, copying, and modification.
open source software
noncommercial software shared freely and developed collectively on the internet
3 Types of Application Software
horizontal market application
vertical market application
custom application
Horizontal-market application
software provides capabilities common across all organizations and industries
Word Processing, spreadsheets.
Vertical Market Application Software
serves the needs of a specific industry
Appointment scheduling
Custom Software
For a specific need.
Moore's Law
the observation that computing power roughly doubles every two years.
Commoditization
Where competitive products become very hard to differentiate from each other.
Huang's Law
Huang's law is an observation in computer science and engineering that advancements in graphics processing units are growing at a rate much faster than with traditional central processing units.
Database
a collection of organized data that allows access, retrieval, and use of data
Self desicribing - contains within itself
relational database model
a structured collection of data acces and utilized by many different applications and users.
DBMS (Database Management System)
a product used for the storage and organization of data that typically has defined formats and structures
Flat file database
One large single table; used if the amount of data that is being recorded is fairly minimal
Field
A column in a database table.
record
A row in a database table.
Primary Key
A field (or group of fields) that uniquely identifies a given entity in a table.
Atomic Key or Composite Key (2 or more)
Foreign Key
A primary key of one table that appears as an attribute in another table and acts to provide a logical relationship between the two tables
A way to make a relationship between tables. Null FK are okay.
attributes (database)
Describing some aspect of the object or entity
Data Normalization
the reorganization of tables, and attributes within a database to reduce duplication is especially important during database redesign, but also when data is imported or merged.
Why do we normalize data?
To resolve undesirable dependencies, remove redundancies, eliminate repeating groups.
NoSQL
A new generation of database management systems that is not based on the traditional relational database model.
Database vs. Spreadsheet
database: stores more data, user-friendly interface, data linkage complex relationships, creates reports...
spreadsheets: small amount of data, cannot relate multiple tables, uncomplicated data relationships, good for calculation and visualization
ER diagram (ERD)
A graphical representation of database requirements; contains entities and relationships
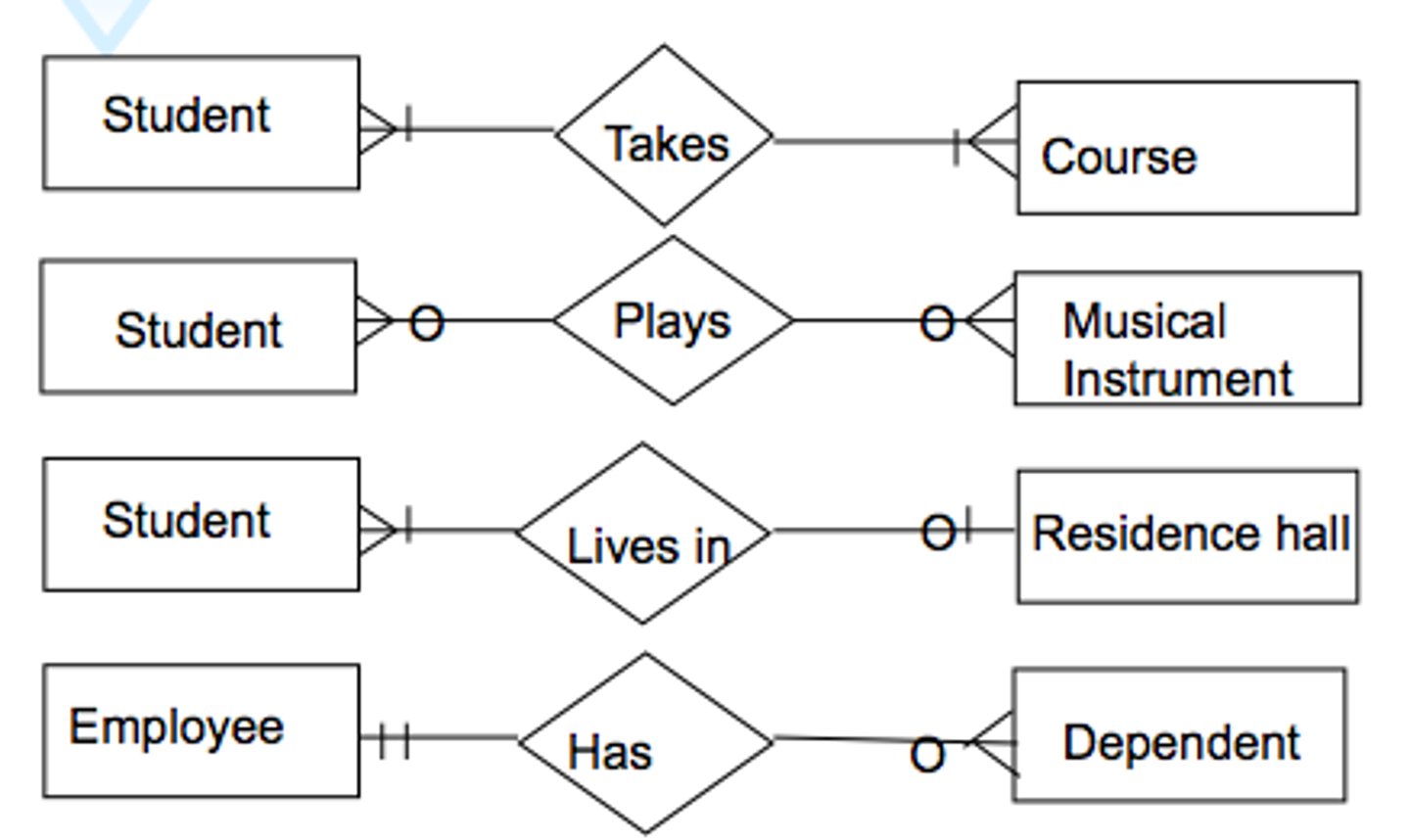
entities
Data contained in the database (students, course, grade)
4 types of cardinality
One to one (1:1) , one to many (1:M) , many to one (M:1) , many to many(M:N)
SQL (Structured Query Language)
A language that provides a standardized way to request information from a relational database system.
SELECT * (The attribute)
FROM (table to be used)
WHERE (speicify conditions)
Can dragging and dropping different fields.
QBE (query by example)
Using a grid to form queries where fields can be added, sorted, compared, etc.
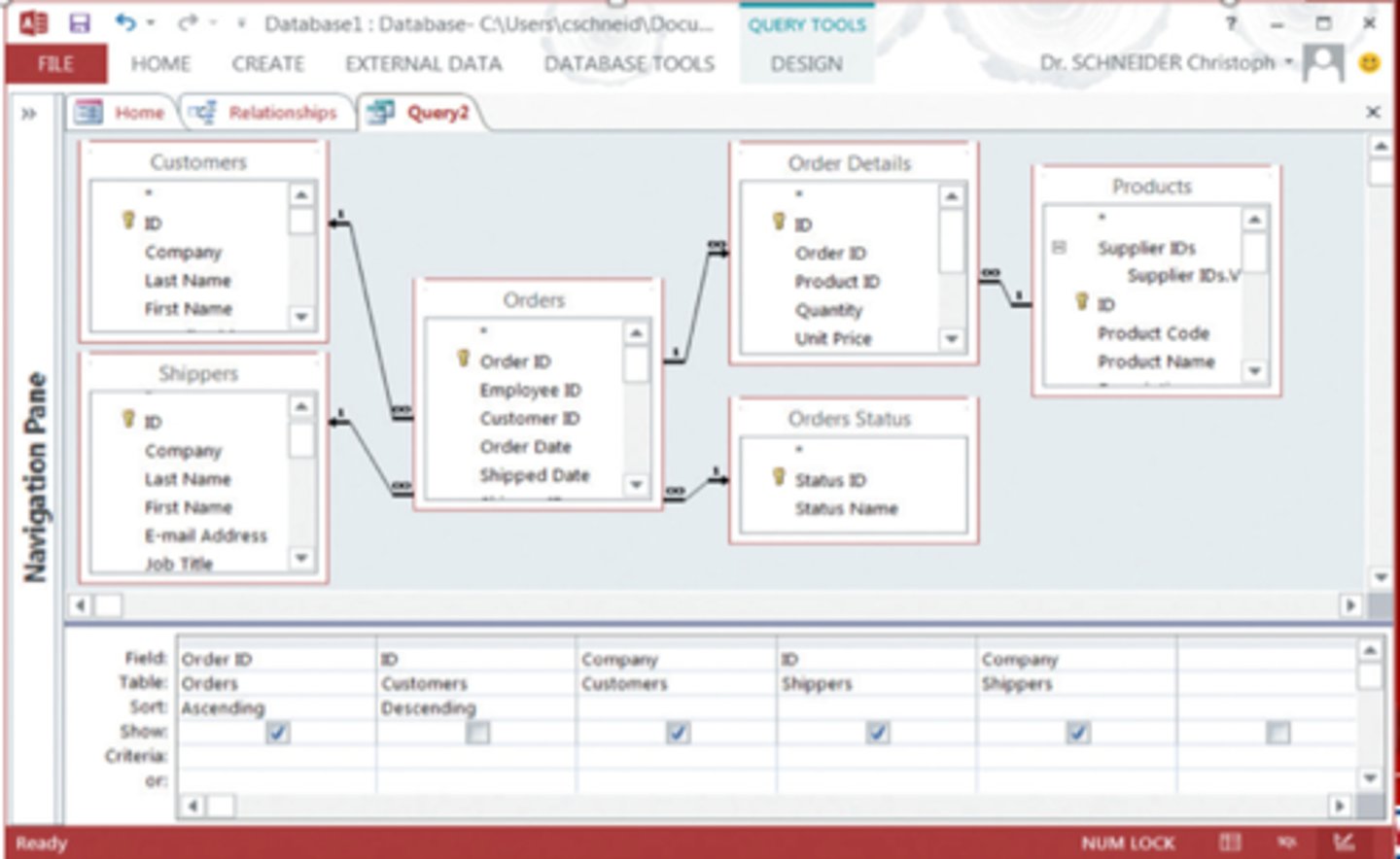
Parent table and child table
The master table vs the subset table (related by foreign keys).
Do ERDs have keys?
No, they only have unique identifiers that are usually underlined.
No attribute is repeated, it is all joint with cardinality legends.
Business Intelligence
Information collected from multiple sources such as suppliers, customers, competitors, partners, and industries that analyzes patterns, trends, and relationships for strategic decision making
operational decisions
short-run decisions to help implement strategies
day-day activities
TPS (Transaction Processing System)
supports the monitoring, collection, storage, and processing of data from the organization's basic business transactions, each of which generates data
Managerial Decisions
decisions about the allocation and utilization of resources
Supported by MIS
Management Information Systems (MIS)
A business function, like accounting and human resources, which moves information about people, products, and processes across the company to facilitate decision-making and problem-solving
Strategic Decisions
those that support broad-scope, organizational issues
EIS
Executive information system (EIS)
A specialized DSS (Decision Support System) that supports senior level executives within the organization
structured decisions
Situations where established and accepted methods for making a decision
More so TPS (operational)
unstructured decisions
Occurs in situations in which no procedures or rules exist to guide decision makers toward the correct choice
More so EIS systems (Strategic)
i.e: Who should I marry?
OLTP (online transaction processing)
Capturing and storing data from ERP, CRM, POS
Day-to-day business transactions
The main focus is on efficiency of routine tasks
OLAP (online analytical processing)
Manipulation of information to create business intelligence in support of strategic decision making
Ability to sum, count, average,
data warehouse
a large repository database that supports management decision making
Prepares data for BI Processing
Extract and clean data from opeational systems and other sources
data mart
a data collection, smaller than the data warehouse, that addresses the needs of a particular department or functional area of the business
data mining
the process of analyzing data to extract information not offered by the raw data alone
How do you identify a continuous field in Tableau
Green Pill in a visualization
What data type contains a Tableau workbook along with local data
.twbx
T/F - Can Tableau automatically create the correct data types, once uploaeded?
False - Have to double check to make sure.
What colour in Data Panes are discrete values?
Blue
IT projects
- Have a large information technology component (in terms of budget or personnel)
- Such projects affect data, people, and processes
Risks with IT projects
Hard to get good estimates
Lack of experience in the project team
Lack of Support from Top Management
IT operations
Service, maintenance, protection, and management of IT infrastructure
Project Triple Constraints
time, cost, scope
Can only have 2 out of 3
Project Life Cycle
The series of phases that a project passes through from its initiation to its closure.
What are the 4 phases of the project life cycle
Initiation, planning, execution, evaluation (close)
Traditional Project Management
Like a waterfall, slow, structured, standardized