Anthropology Chapter 3
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Slides: Primate Habitats and sociality
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
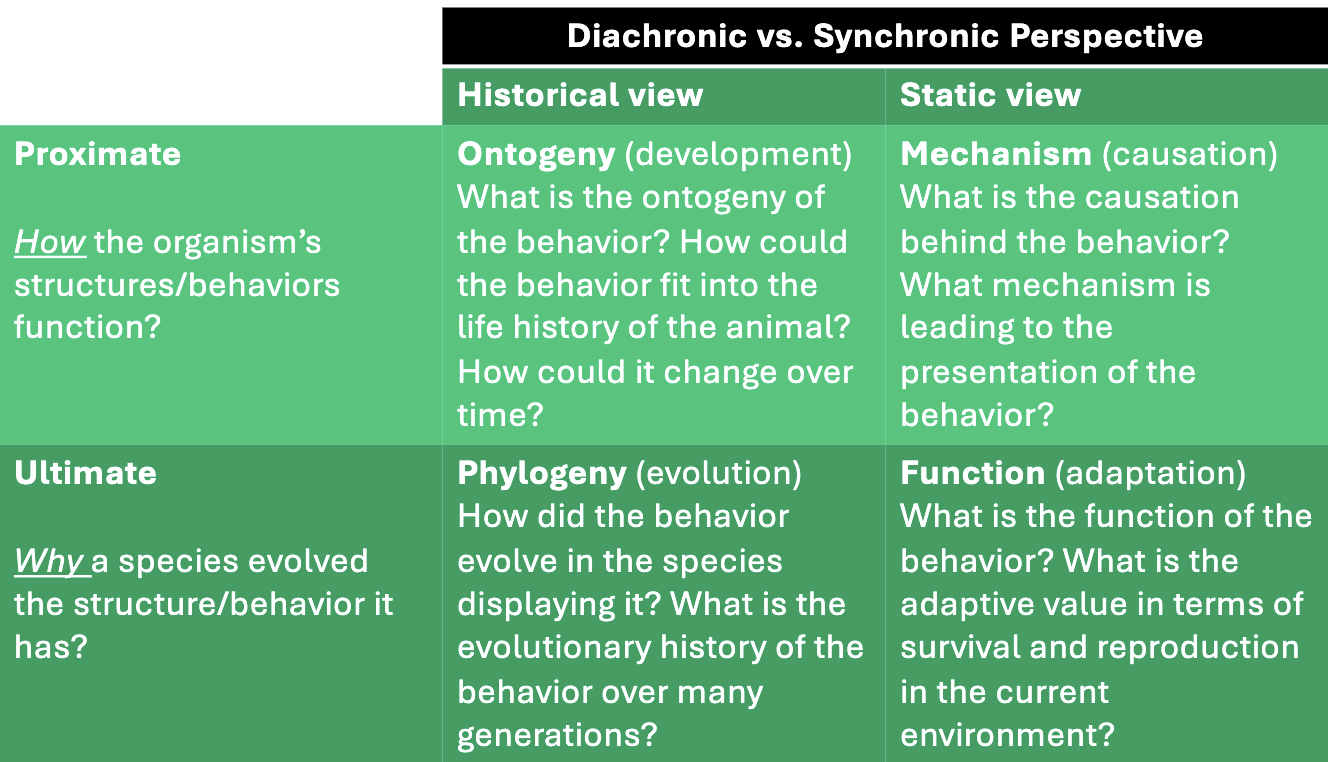
Studying behavior
-Proximate — How did it develop
-Ultimate — Why did it evolve
Mating Systems
Monogamy - Breeding (1 male:1 female)
Polygyny - Breeding (1 male: multifemale)
Polyandry - Breeding (multimale: 1 female)
Polygyandry - Breeding (multimale: multifemale)
Social Systems
Solitary/semi-solitary
One male units
Multimale/multifemale group
One female, multimale units
Fission-fussion groups - Groups always changing in size and composition
Fission-fussion determinants
-Resources
-Leadership ability
-Species density
-Predation risks
Who takes care of babies
-Mostly mothers
-Sometimes males significantly help
-Sometimes other females
Who’s in charge
-Alpha males
-Alpha/mother female
*Baboon Social Rank
*Marmosets and tamarins
-Both/unknown
Foraging Theories
-Optimal foraging theory and Marginal Value Theorem
-Geometric Framework of Nutrition
Optimal Foraging Theory
• Maximizing intake of energy or nutrient/time
• Energy or nutrient = currency
• Other needs = constraint
• Useful and testable
Optimal Foraging Theory Criticisms
Too simplistic
Dynamic nature of food and nutrient interactions unaccounted for
Constraints are not viewed as critical parts of model
Optimal Foraging Theory: Marginal Value Theorem
Leaving the space when the food supply is lower than average. The linger you spend in a place, the less consumption
MVT is not supported in…
Meta-analysis
Orangutans
Gibbons
Geometric Framework of Nutrition
Seeking nutrients that you need.
Capital Breeders
-Organisms that build up
energy reserves prior to
breeding, then reproduce
Income Breeders
-Organisms that rely on
energy intake during
breeding season for
reproduction
Energy and Ovulation in Humans
Human female bodies automatically
regulate ovulation so that as the
energy levels decrease, the likelihood
of pregnancy decreases all the way to
anovulation and cessation of cycling
Theoretical Backgrounds
-Socioecological model
-Evolutionary Model
-Sexual Selection
Male Reproductive Competition
Sperm competition male chimpanzees
Female Reproductive Competition
When the females become more aggressive towards each other.
Ex: Gorillas – Females mate during pregnancy, mate more on days when
other females are mating
Primate Sexuality
Sexuality is situationally dependent
Ex: Female langurs solicit invading males even
though already pregnant (to confuse
paternity),
Bonobo sexuality
Not procreative sexual activity always
Estrus Swelling
• Attraction of many males
• Inciting competition -> best mate
• Confuses Paternity
• Infanticide avoidance strategy
• Allowing female transfer between groups