Science grade 8
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
physical properties
A characteristic of a pure substance that can be observed without changing it into another substance.
chemical properties
Characteristic that cannot be observed without altering the substance

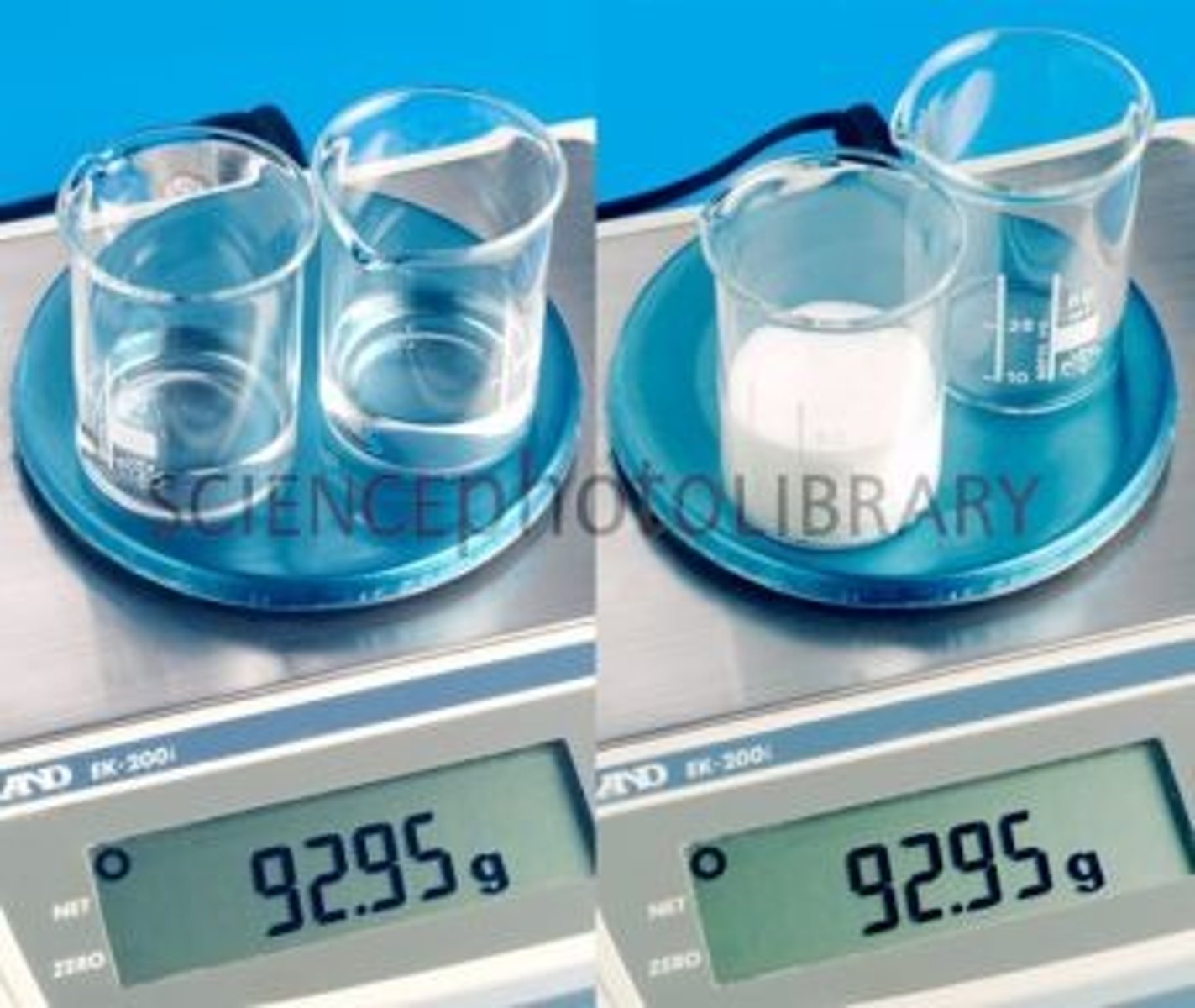
mass
Amount of matter in an object

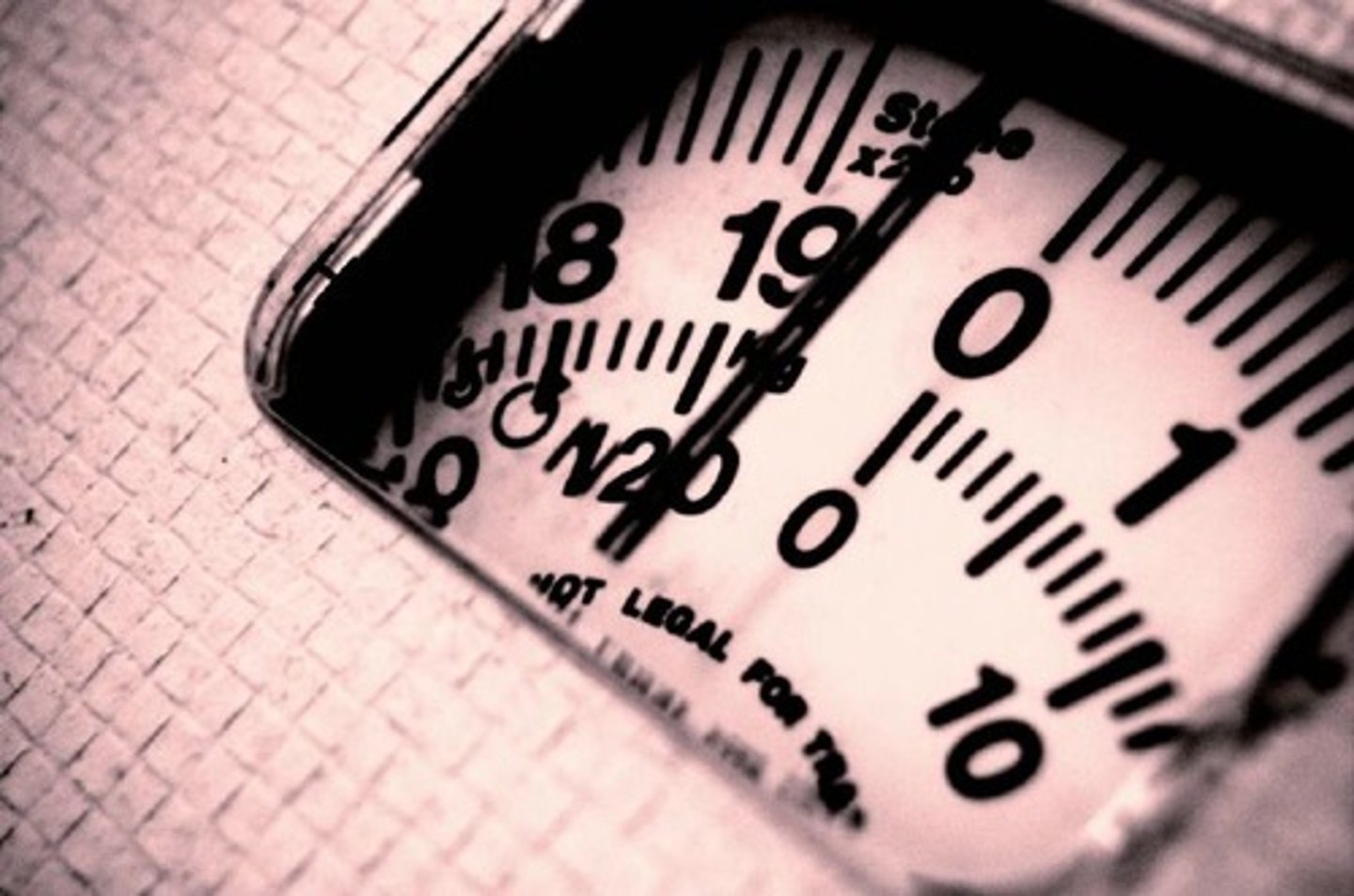
weight
A measure of the force of gravity on an object

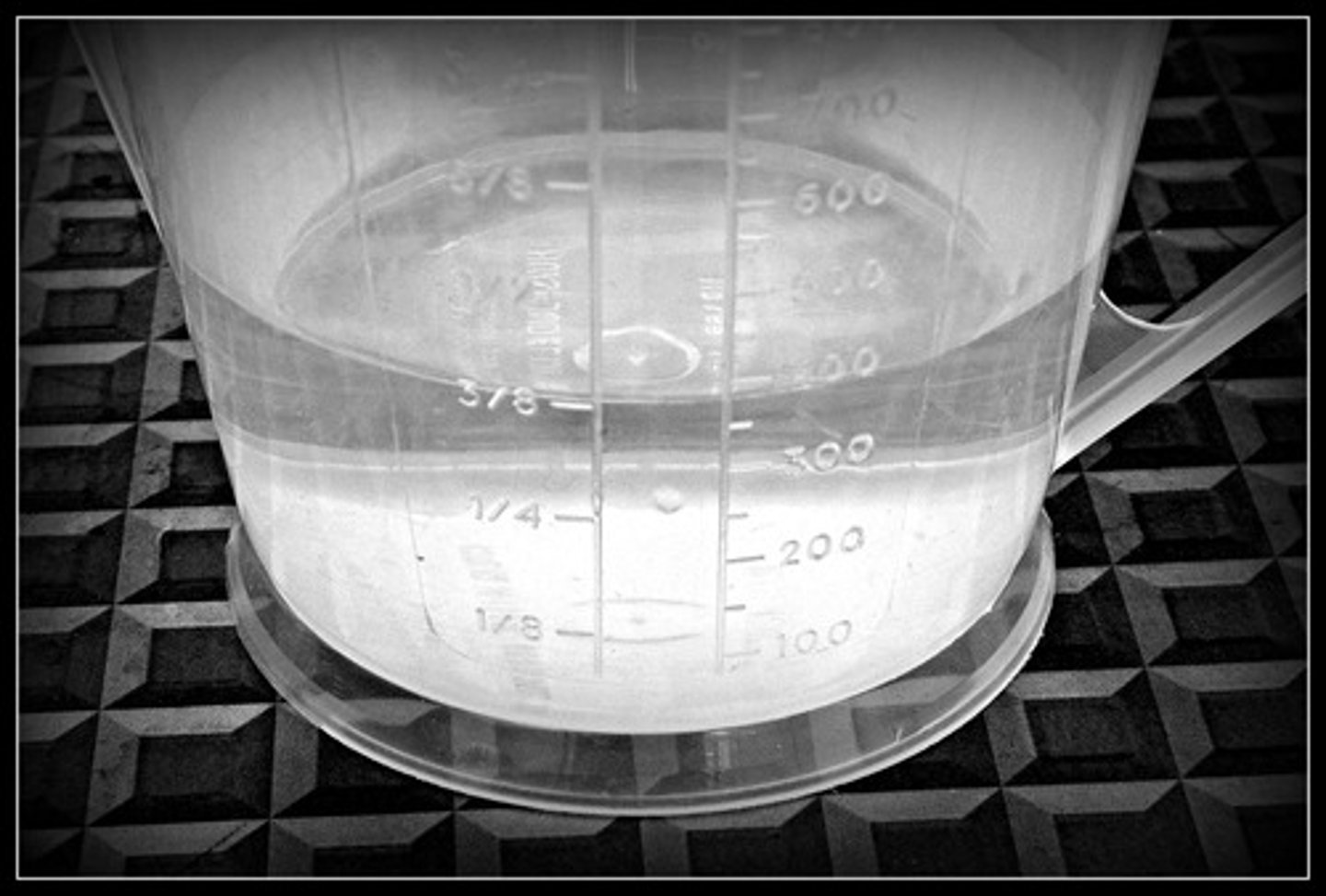
volume
A measure of the size of a body or region in three-dimensional space

density
Mass / Volume
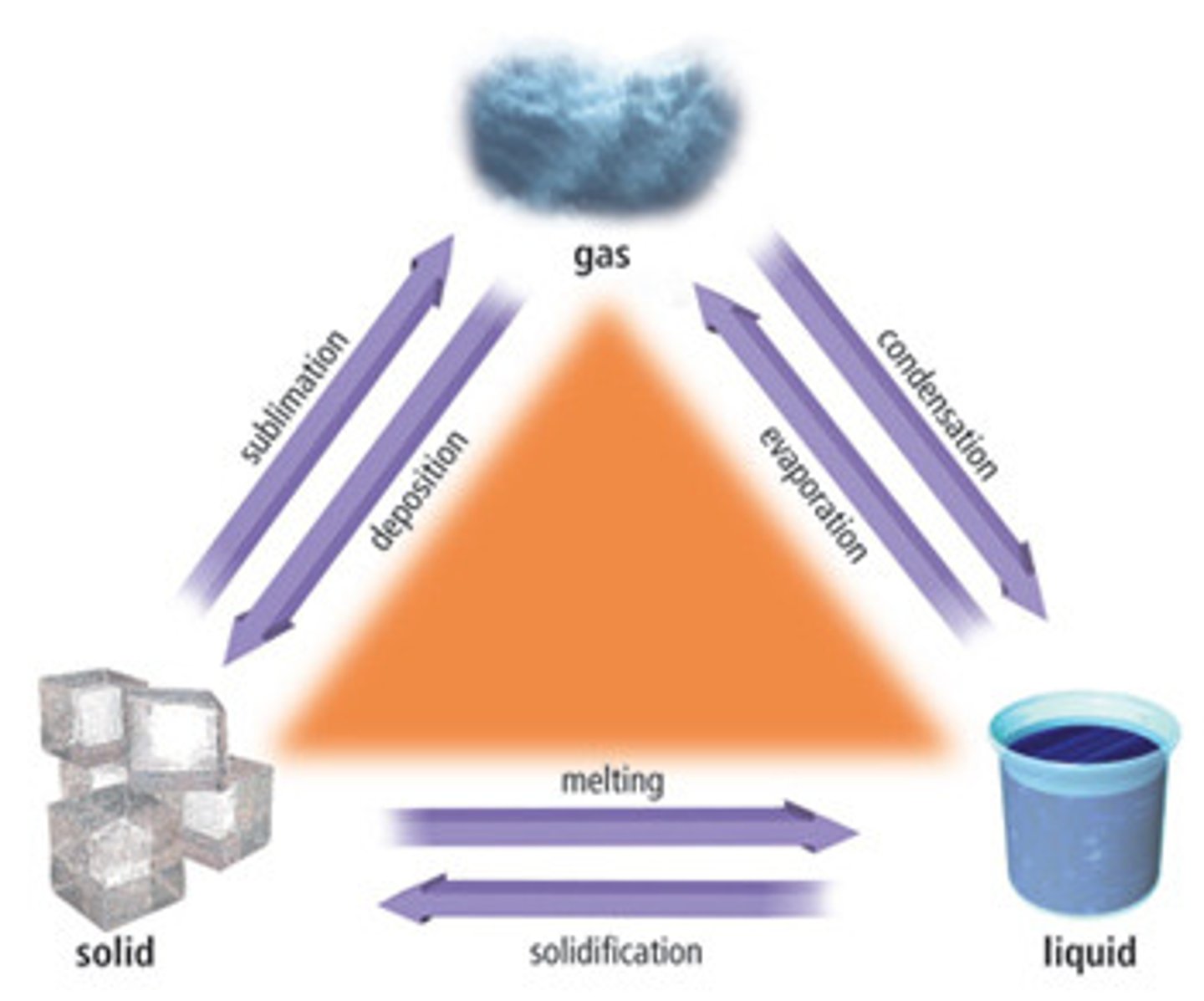
state of matter
(chemistry) the three traditional states of matter are solids (fixed shape and volume) and liquids (fixed volume and shaped by the container) and gases (filling the container)
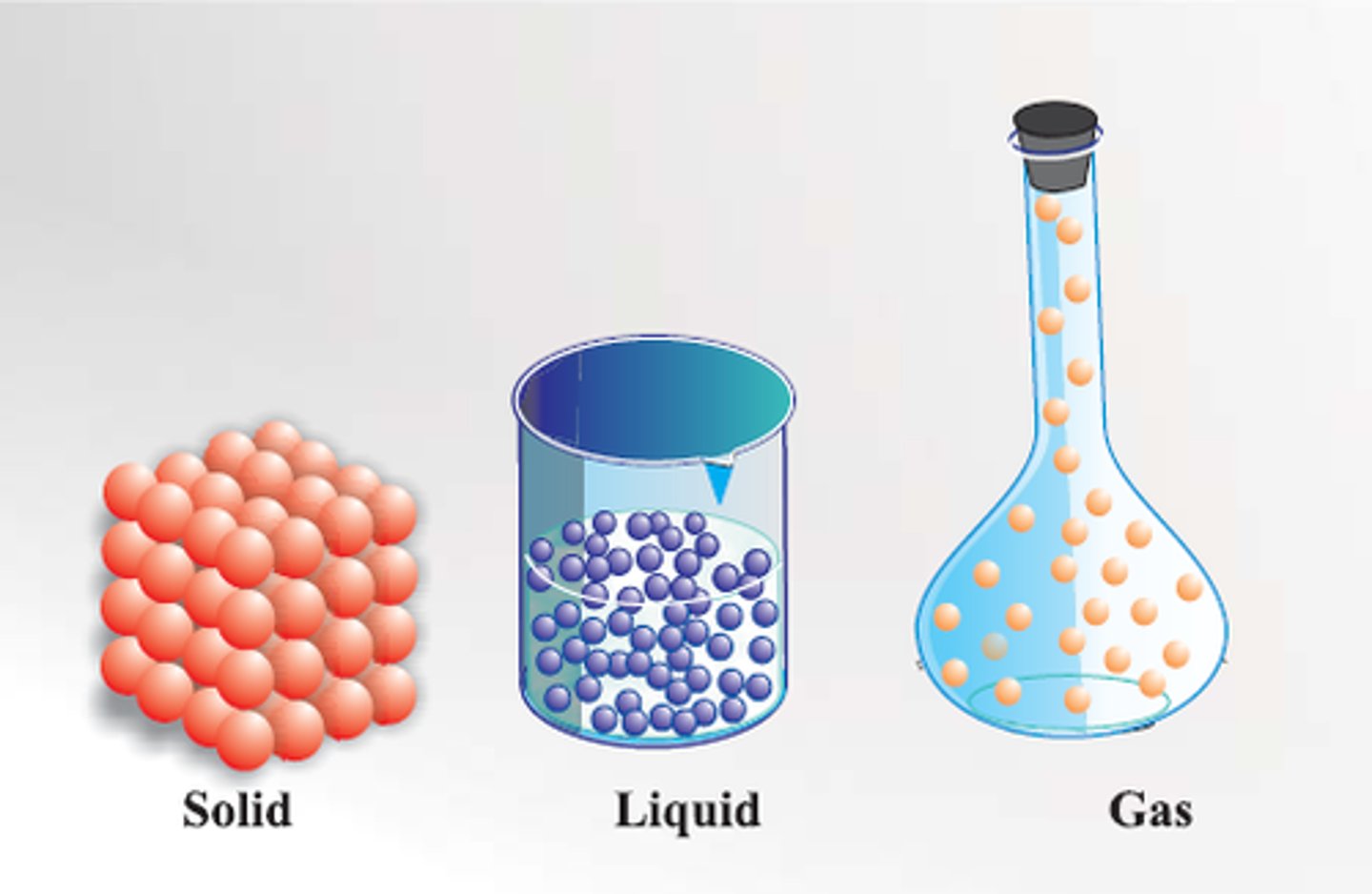
solid
Definite shape and volume

gas
A state of matter with no definite shape or volume
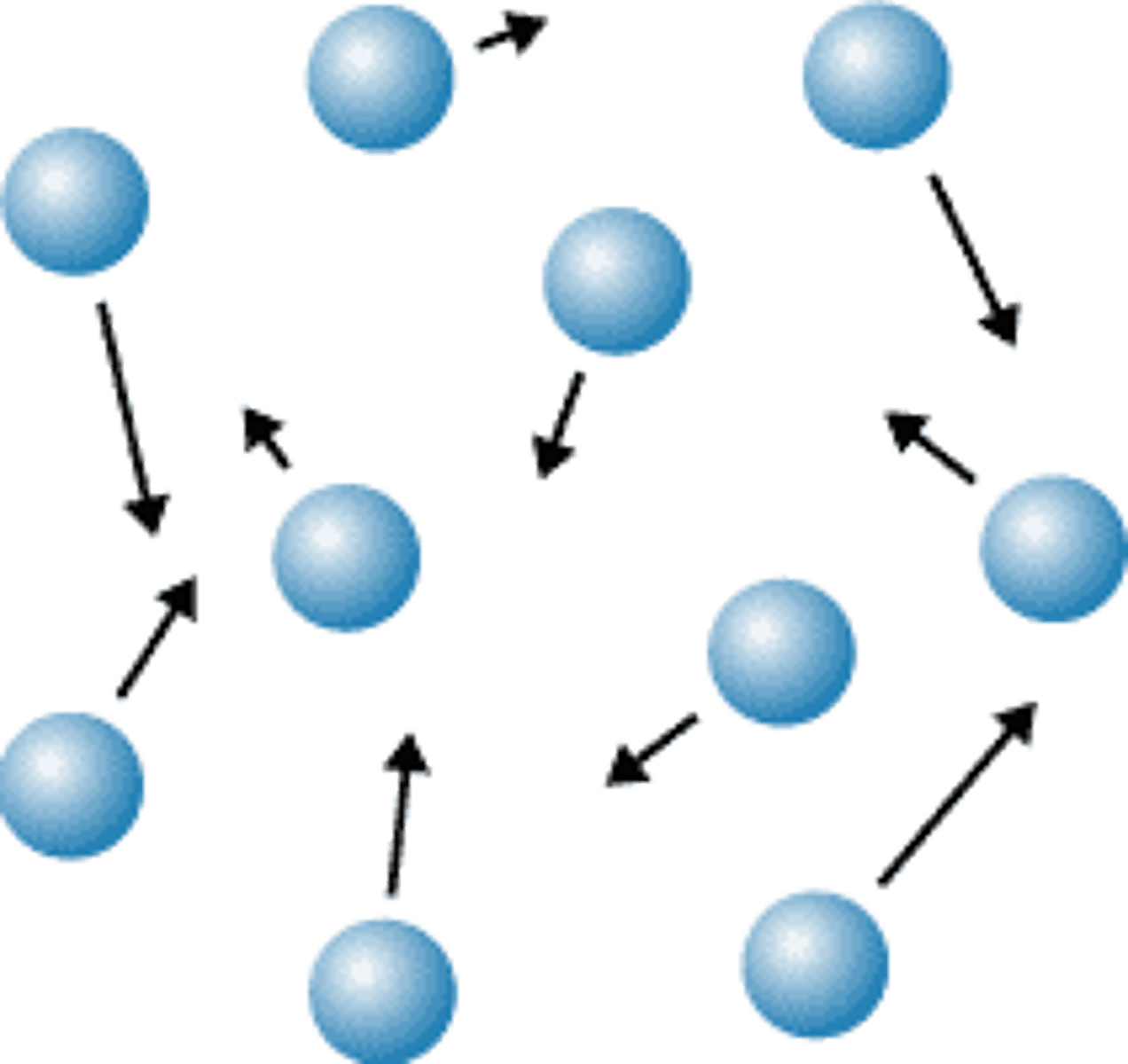
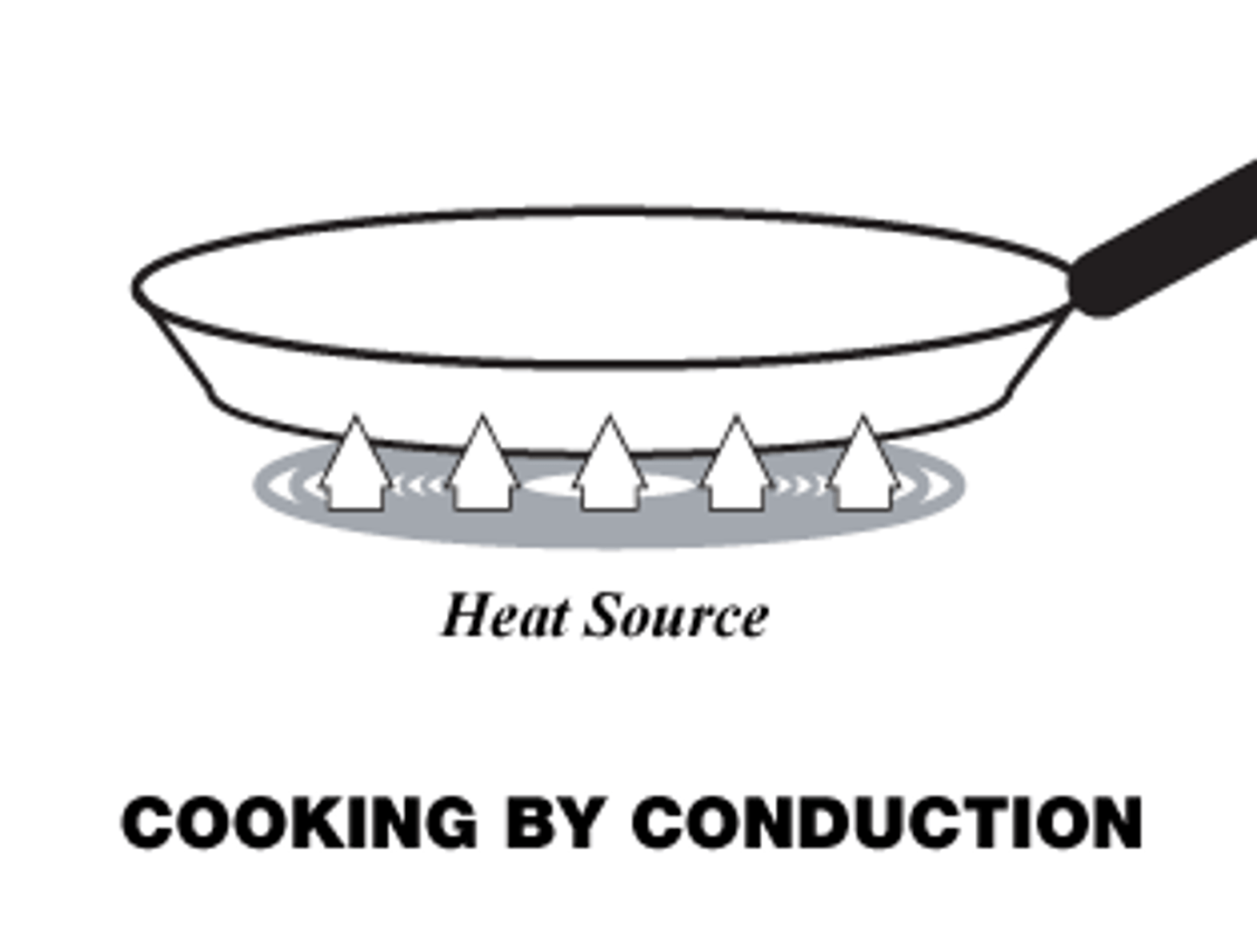
conductivity
The ability of an object to transfer heat or electricity to another object.
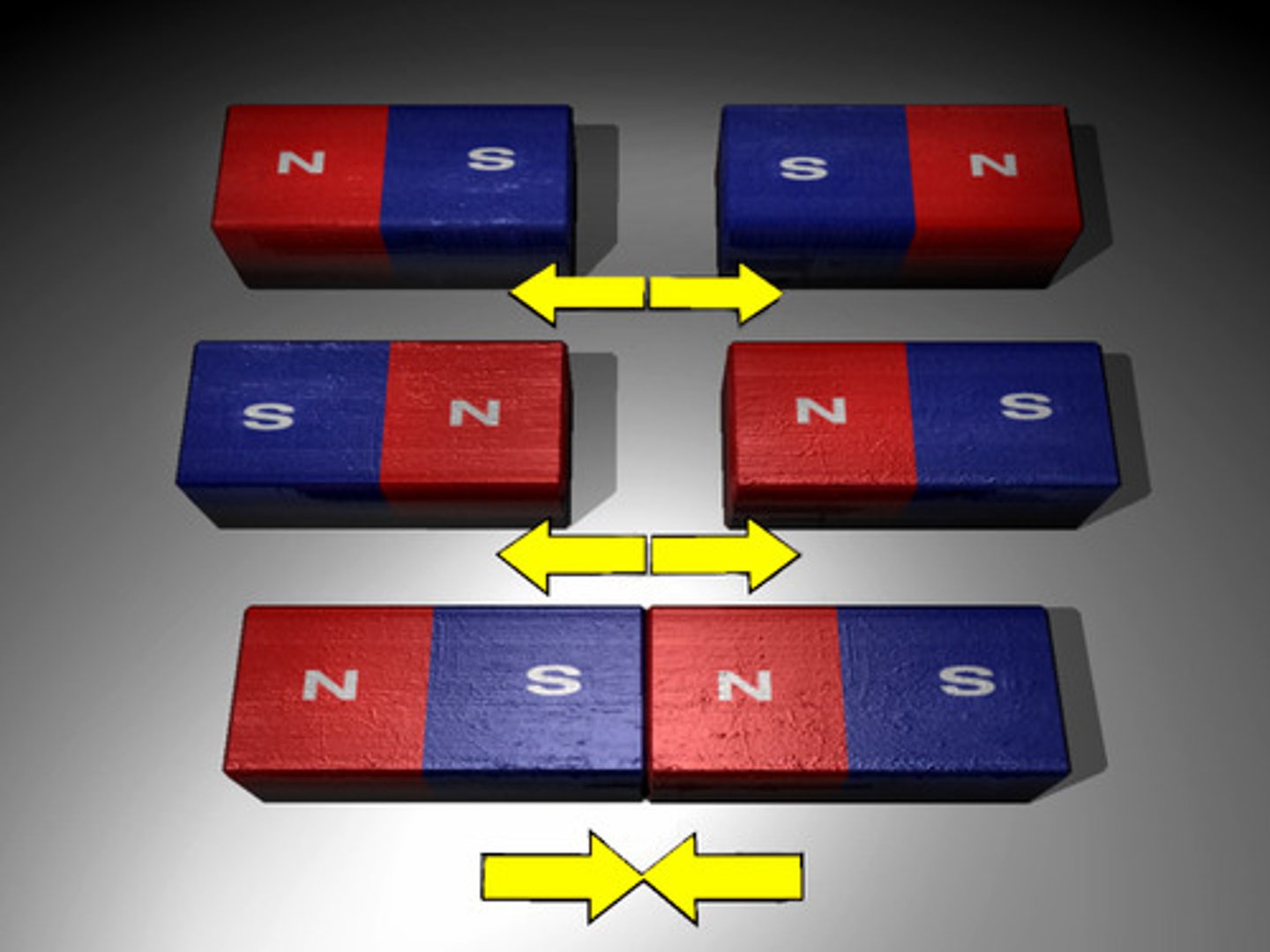
magnetism
A property of some materials in which there is a force of repulsion or attraction between certain like and unlike poles
texture
The feel, appearance, or consistency of a surface, substance, or fabric.

solubility
A measure of how much solute can dissolve in a given solvent at a given temperature.

combustibility
A measure of how easily a substance will set on fire, through fire or combustion

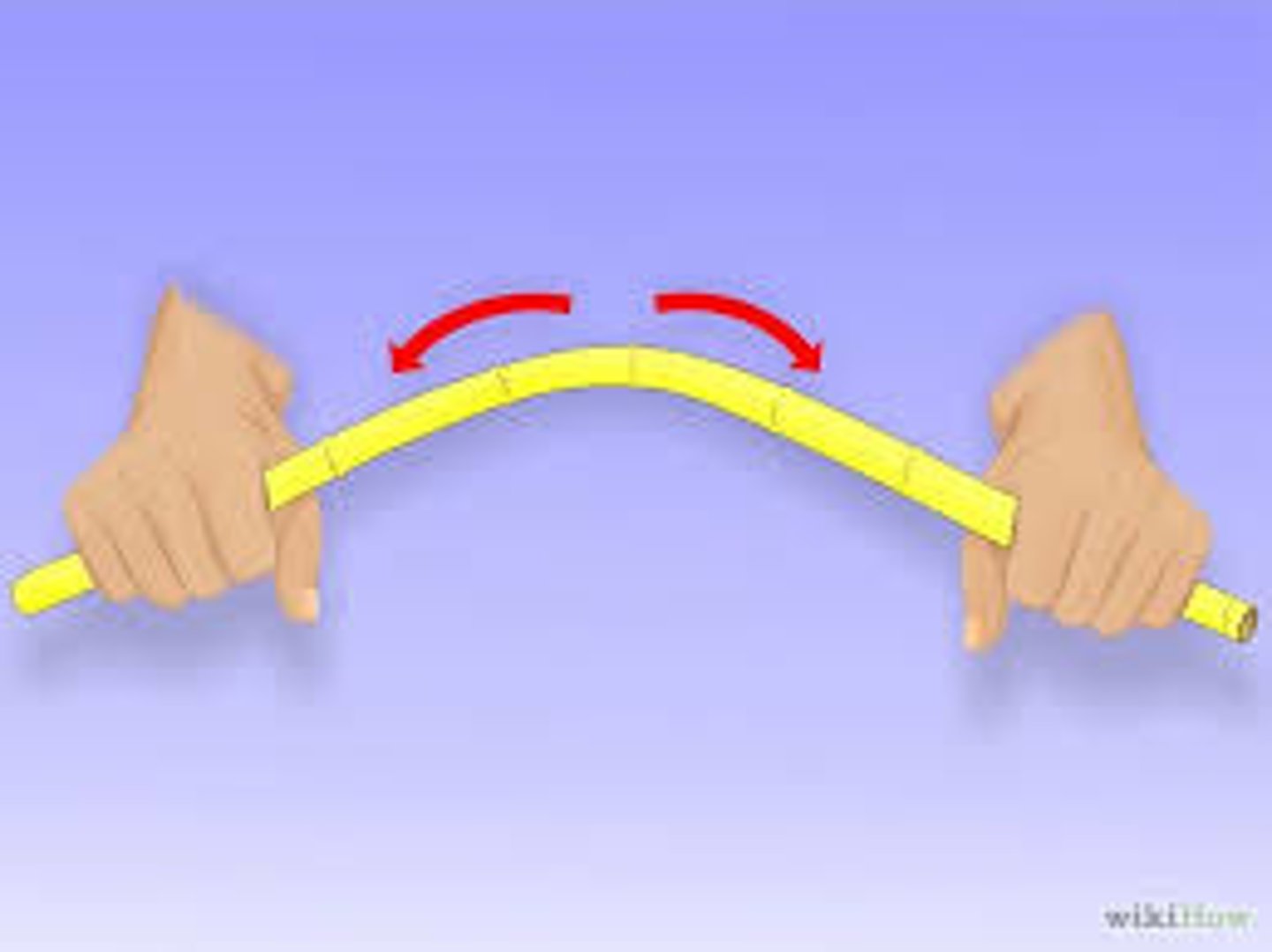
mallability
how easy you can bend something
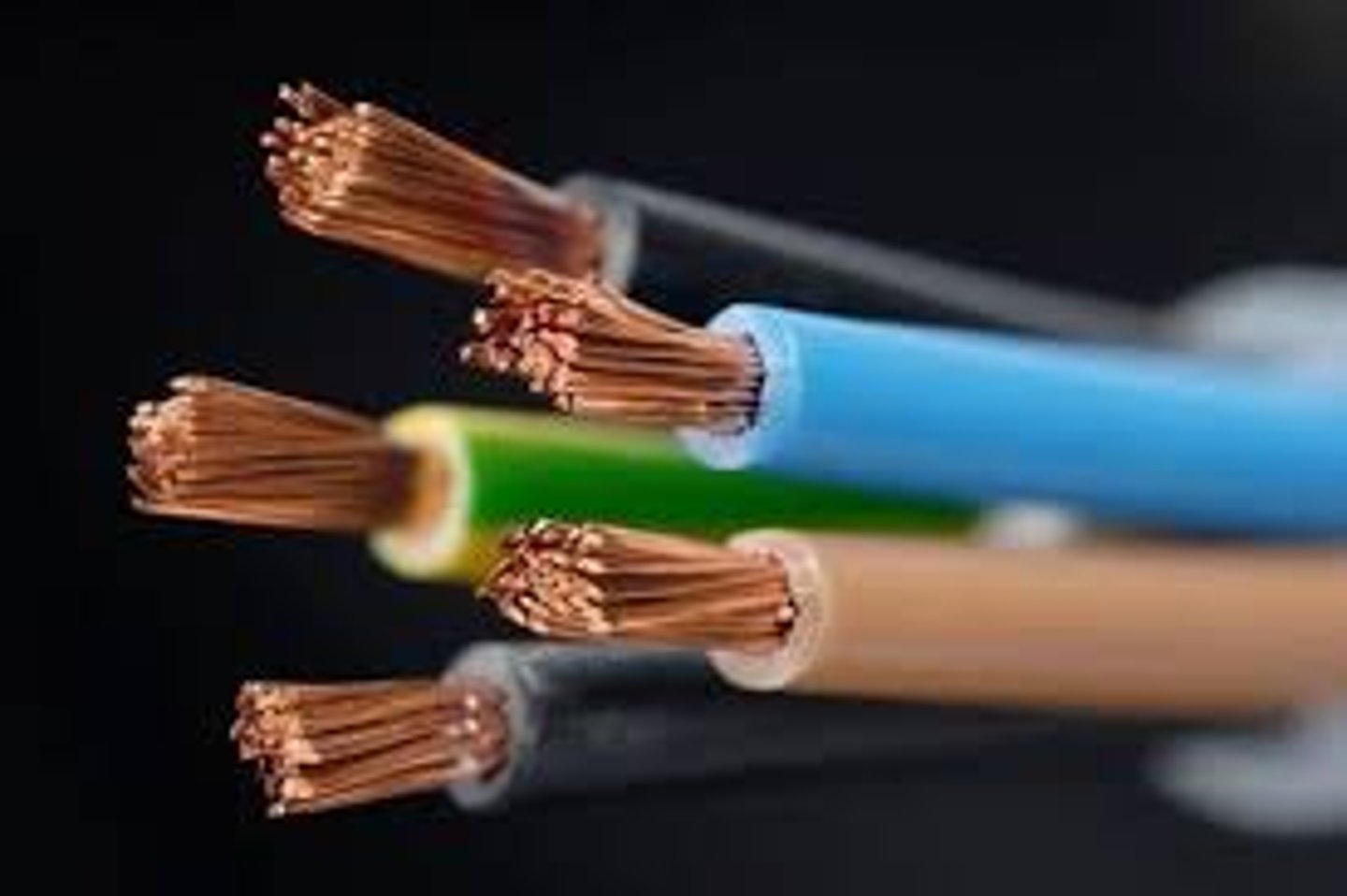
ductility
the ability of a substance to be drawn, pulled, or extruded through a small opening to produce a wire
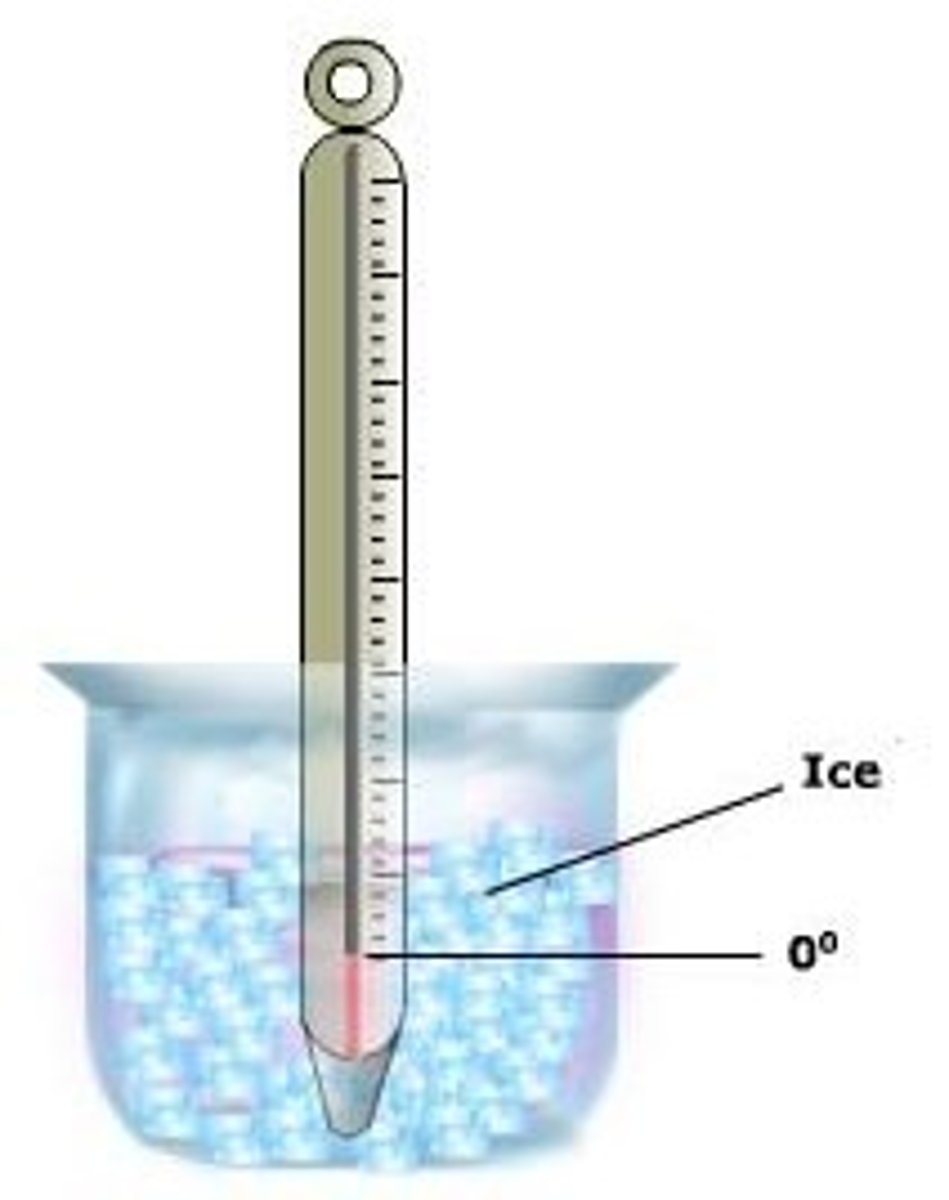
melting point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid
odor
smell

flammability
Ability to burn

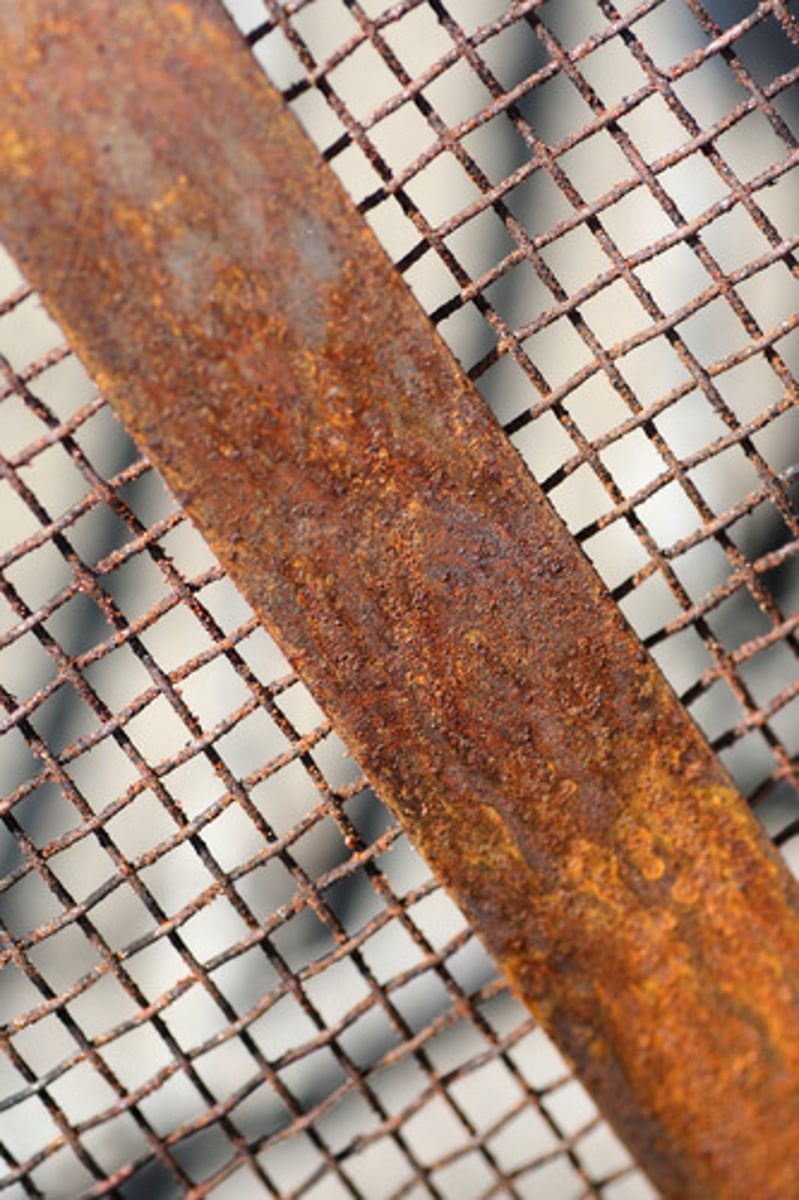
oxidation
A chemical change in which a substance combines with oxygen, as when iron oxidizes, forming rust

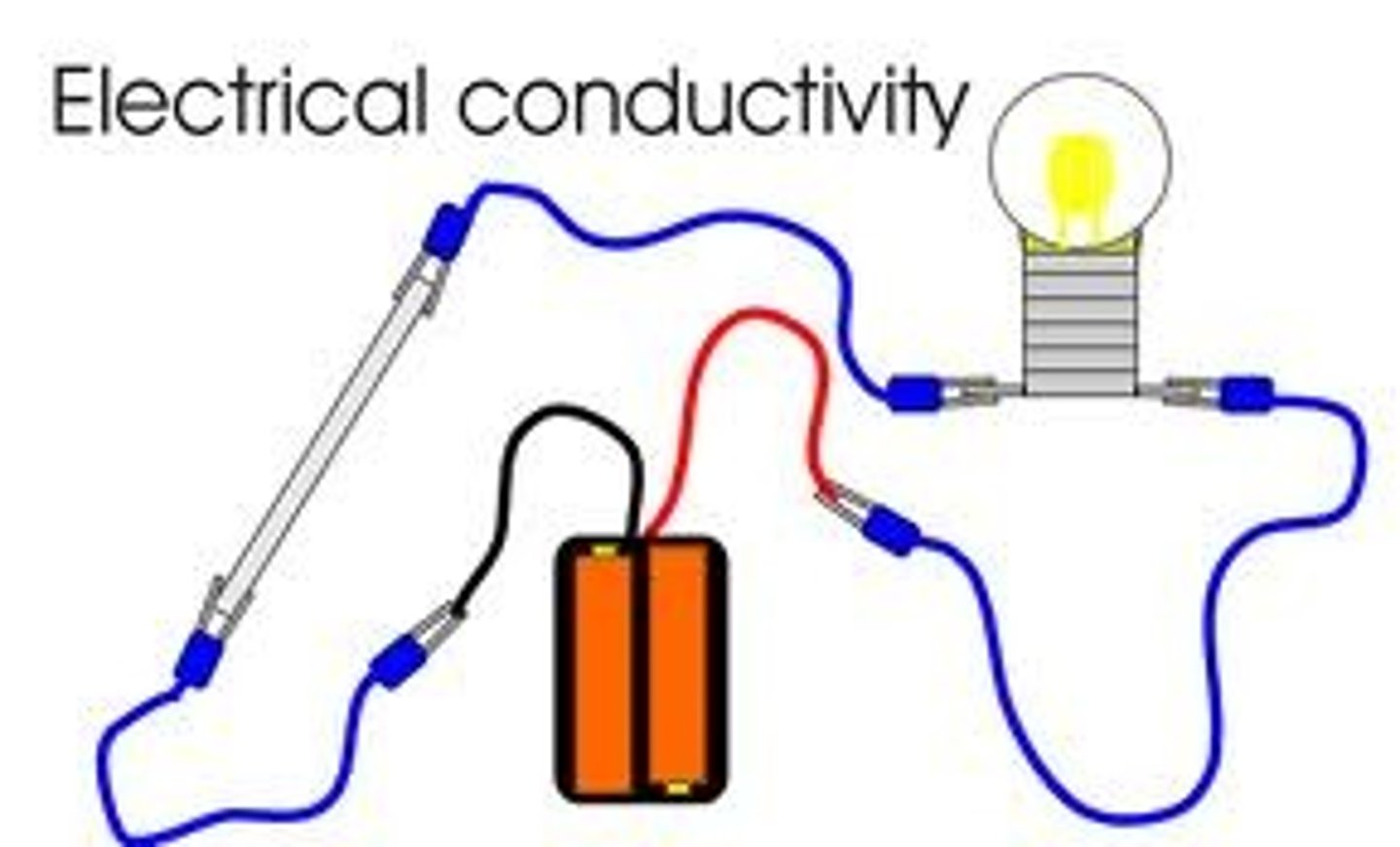
electrical conductivity
How well a substance allows electricity to flow through it.
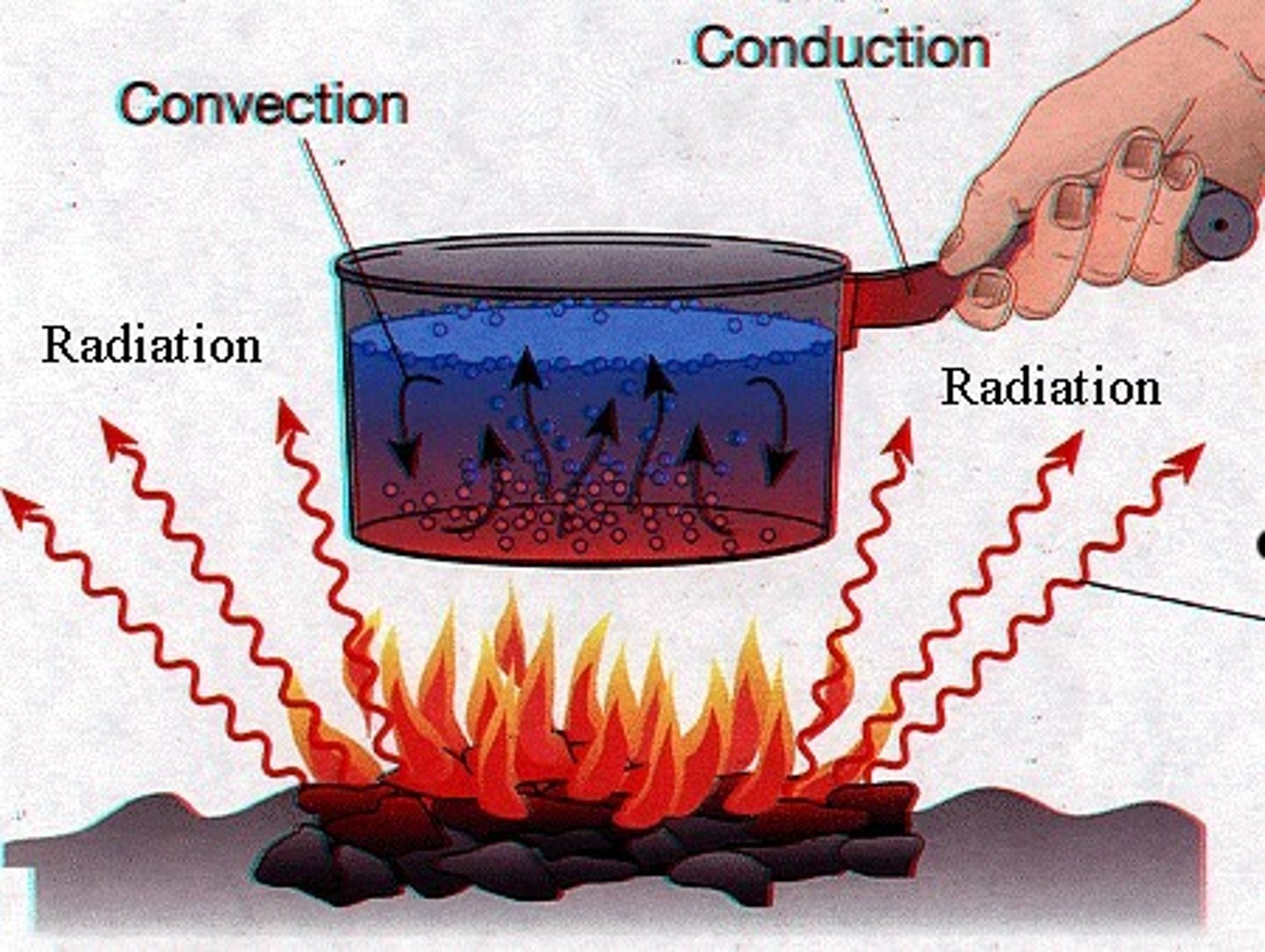
thermal conductivity
the rate at which a substance transfers heat
pH
acidic or base

temperature
A measure of how hot or cold something is.
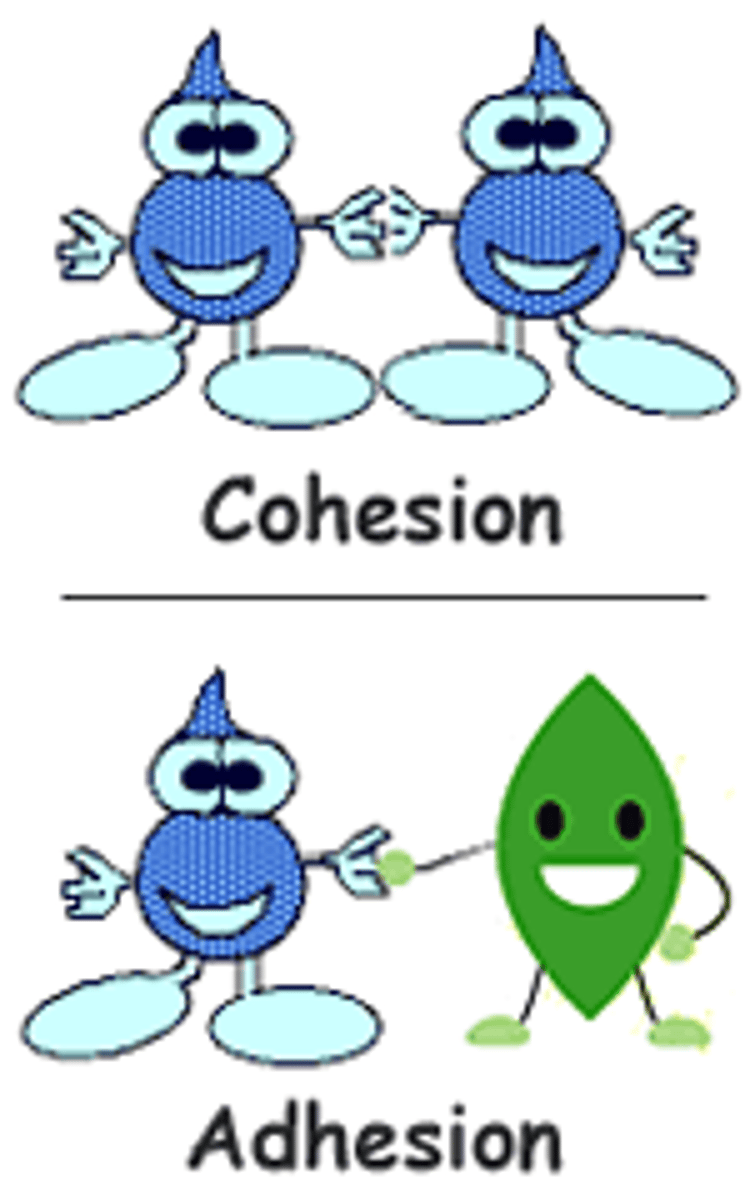
cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
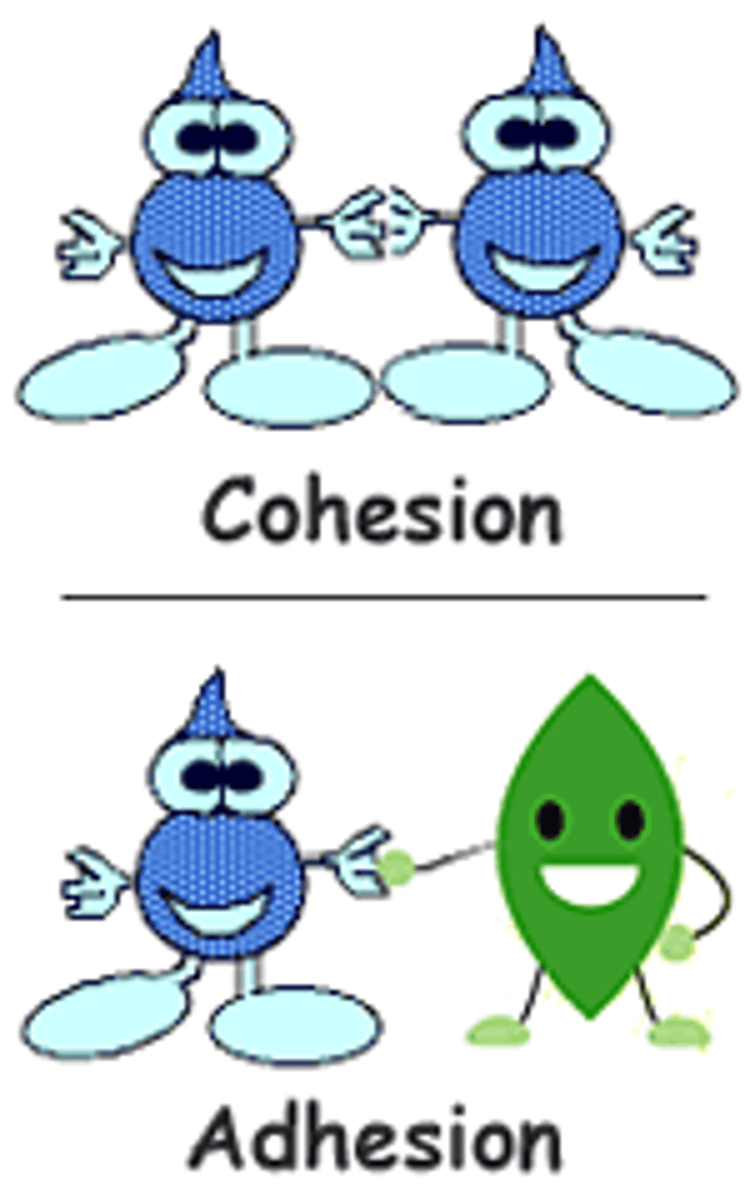
adhesion
Force of attraction between different kinds of molecules
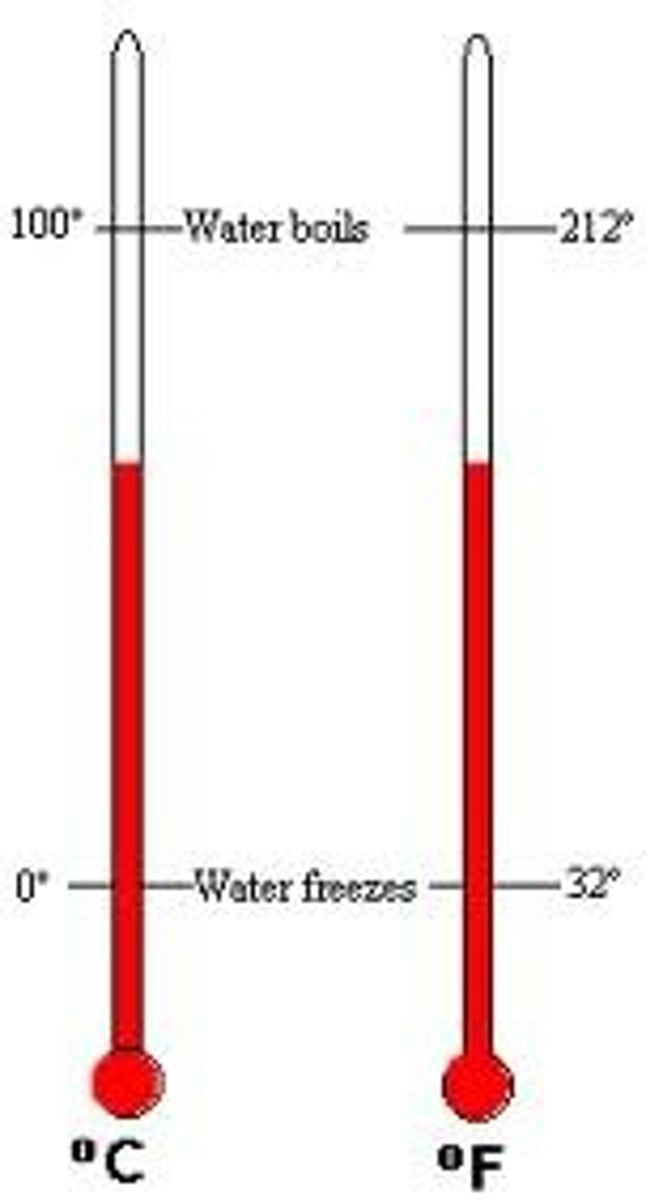
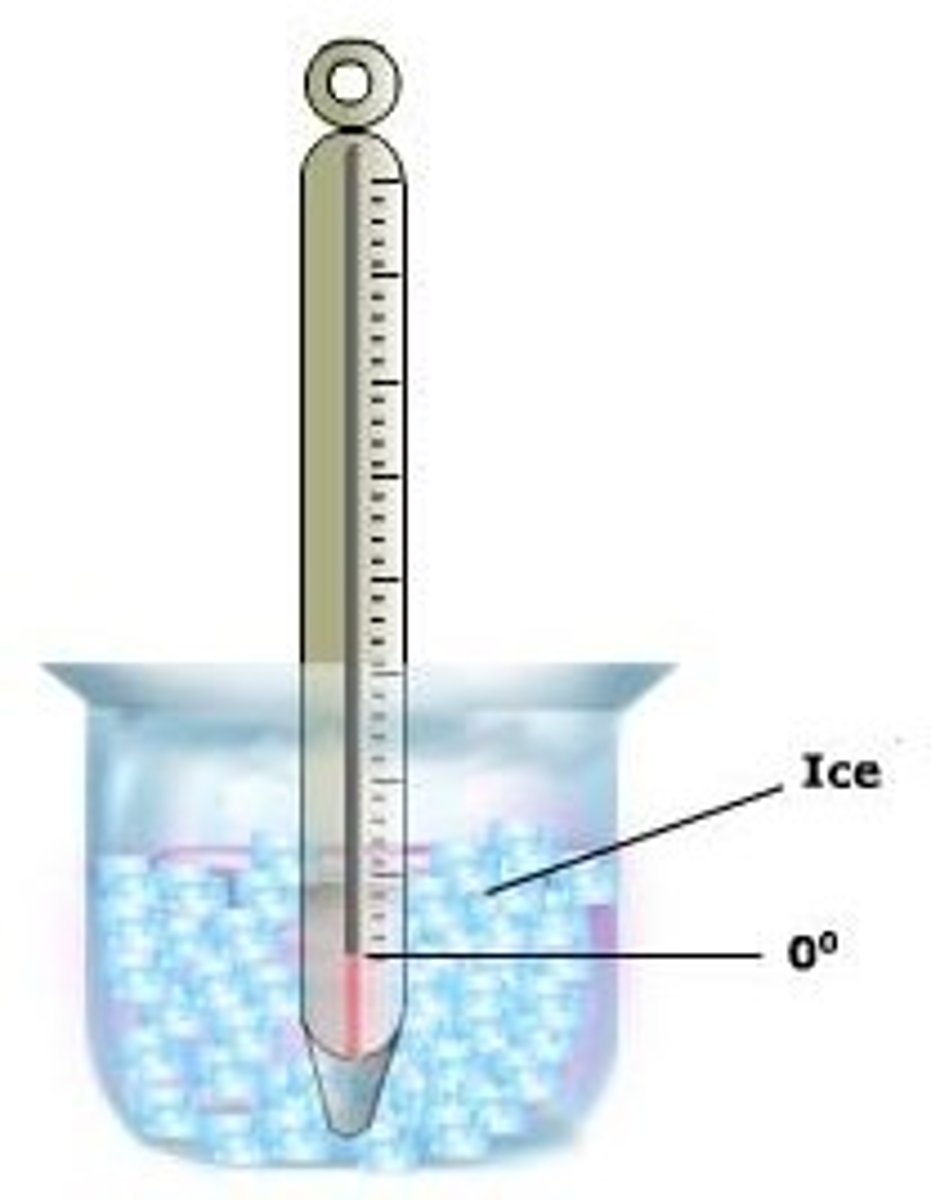
freezing point
The temperature at which a liquid changes into a solid
boiling point
The temperature at which a liquid changes to a gas
condensation point
is the change of the physical state of matter from gas phase into liquid phase.

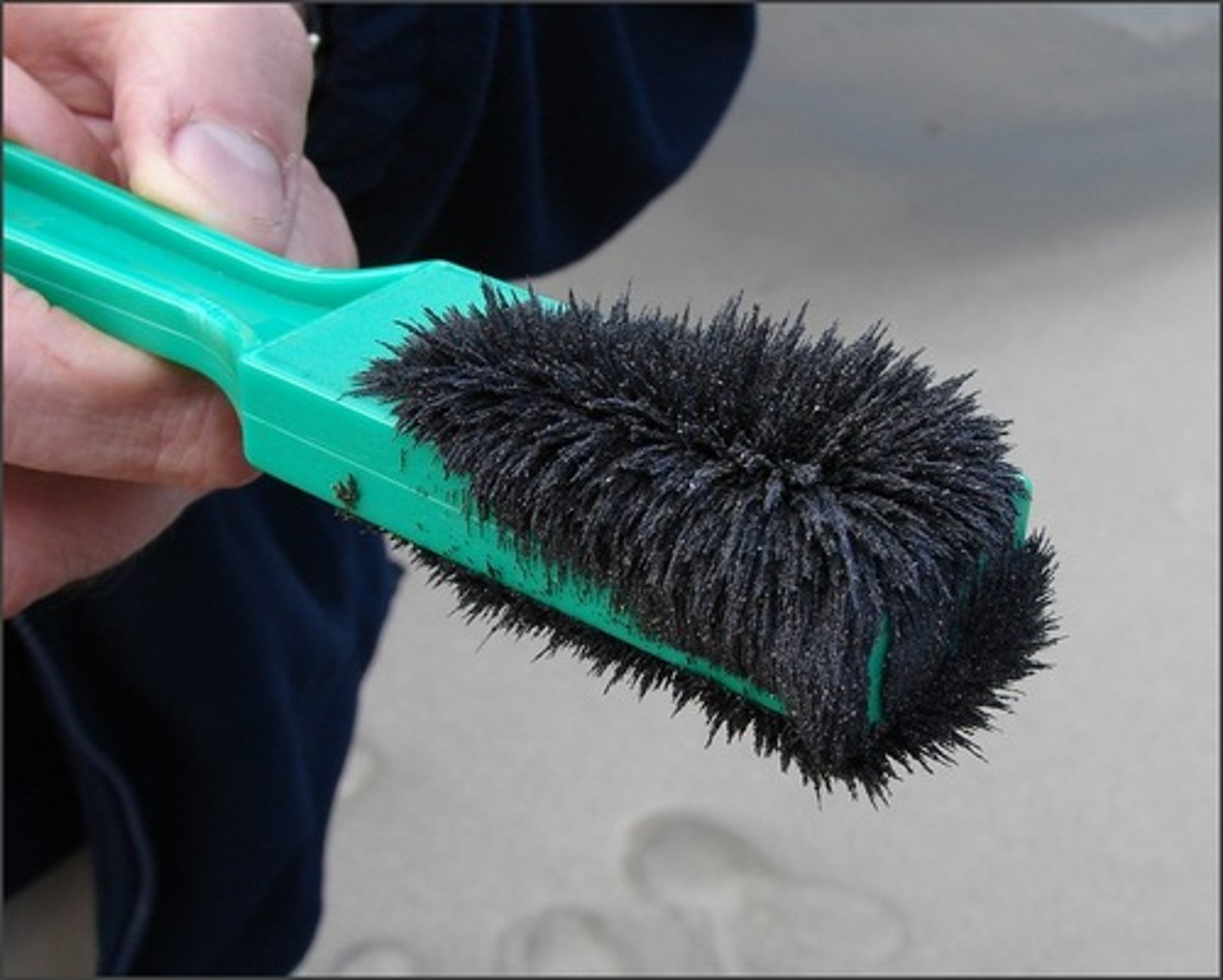
magnetization
magnetization If a mixture contains magnetic particles ex. iron, steal the particles can be separated from the mixture with a magnet.

surface tension
A measure of how difficult it is to stretch or break the surface of a liquid

luster
The way a mineral reflects light

viscosity
A liquid's resistance to flowing

elasticity
The ability of a material to bounce back after being disturbed

tensile strength
A measure of how much stress from pulling, or tension, a material can withstand before breaking.

texture
The feel, appearance, or consistency of a surface, substance, or fabric.