PSY 1003: Lecture 4: Nature, Nurture, & Human Diversity
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Genes
the biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosome; small segments of DNA capable of synthesizing proteins
humans have around 20,000
can be active (provide code for our body’s building blocks: proteins) or inactive
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
humans have 46 (23 matching pairs), each from one biological parent and the other half from the other biological parent
Cells
where chromosomes are housed within the nuclei
many different types (i.e. skin, blood, nerve, etc.)
Genetic Expression
process by which proteins are made based off of the “instructions” provided by genes
When encoded information in a gene is turned into a kind of function (i.e., environmental factors can influence which genes are expressed)
Identical (Monozygotic) Twins
individuals who developed from a single fertilized egg that split in two, genetically identical organisms
Fraternal (Dizygotic) Twins
individuals who developed from separate fertilized eggs; they are genetically no closer than siblings, but they shared a prenatal environment
Studying Genetics Identical vs. Fraternal Twins
Identical Twins
share more similarities in physical attributes, personality, interests, fears, etc. compared to fraternal twins
environment still plays a role, e.g. having access to better nutrition or speech therapy led to different outcomes for the sets twins
Studying Genetics Outside of Identical Twins
Individuals who are raised together in the same environment do not resemble each other in personality (even biological siblings)
Adopted— personality traits like extroversion or agreeableness have been found to be more closely aligned with their biological parents
Study with macaque monkeys showed that babies raised by foster mothers still showed social behavior that was more similar to their biological mothers
Epigenetics
“in addition to” or “above” the genetics; tell us about how the environment influences our genome and our genetic expression
not fixed traits—can change
trauma, exposure to toxins, etc. can all influence us
Evolutionary Psychology
the study of evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
Natural Selection
the principle that inherited traits that better enable an organism to survive and reproduce in a particular environment (in competition with other trait variation) most likely be passed on to succeeding generations
varied offspring compete for survival
various biological and behavioral variation increase survival changes for organisms
the offspring that survive are more likely to pass their genetics to following generations
over time, characteristics of a population change
Mutation
a random error in gene replication that leads to a change
Humanity’s Genetic Legacy
humanity shares a common genetic profile
across cultures we tend to share certain predispositions—research tends to show that when faced with certain moral dilemmas people will opt for responses that ensure the survival of more people
there are ways that our previous evolutionary makeup has prepared us for aspects of life that are not necessarily part of our current experiences
Evolutionary Explanations for Sexuality (Theory)
women tend to be choosier than men when it comes to picking a sexual partner-related to ensuring survival of offspring; whereas men would tend to be more likely to have more sexual partners to create more offspring
women prefer partners who are more likely to be loyal and have social or other resources, whereas men prefer partners who show signs of potential future fertility
Critiques of the Evolutionary Perspective
natural selection plays a role in helping with survival and reproduction
may be social consequence for conclusions drawn by evolutionary psychology research (i.e., consequences for social movements to reduce aggression)
some behaviors are not easily explained by evolutionary perspective
still has limitations
Social scripts
a culturally modeled guide for how to act
Experience Influences Development
biological and environmental interact with one another to influence brain development
Example: a research study showed that rats raised in an environment with more enrichment showed more cerebral cortex than rats in an environment without enrichment
nature and nurture influence our synaptic connections
various experiences strengthen these synaptic connections—sensations, movement, activity, etc.; if other pathways are not used, they become weaker (i.e., a trail that is not used)
by puberty, synaptic pruning causes a significant loss of connections that are not used
important to remember that brain development does not end in childhood
neuroplasticity allows our brains to change and reorganize in response to our experiences
Influences of Parents and Peers
parenting can influence development, but we tend to see more intense influences when children are exposed to extremes (i.e., abuse)
parents and family environment can have an impact on academics, vocation, political affiliation, and religiosity
there is a significant amount of peer influence during our childhood and adolescent years as we attempt to connect socially with others
Norms
certain rules or behaviors that are expected and followed in a given environment (i.e., gender norms)
Culture
the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, values, and traditions shared by a group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next
Tight Culture
places with clearly defined and reliably imposed norms
Loose Culture
places with flexible and informal
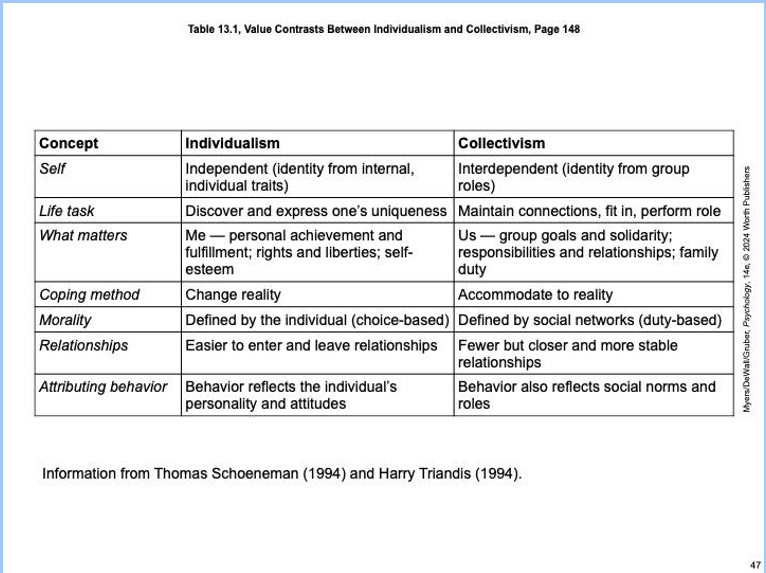
Cultural & Self (Individualism vs. Collectivism)
various cultures (in different places) are going to view this differently
informs our human functioning
Gender Identity
how you think about yourself
Gender Expression
how you demonstrate your gender
Biological Sex
organs, hormones and chromosomes
Sexual Orientation
physical, spiritual and emotional attraction
X Chromosome
sex chromosomes found in both males and females; two X chromosomes are present in females and one X chromosome is present in males
Y Chromosome
sex chromosome that is typically found in only males; an X chromosome paired with a Y chromosome leads to the production of a male child
Testosterone
the most predominant male sex hormone (found in both males and females); contributes to development of male sex organs during fetal development, and during adolescent development, it contributes to male sex characteristics
Estrogen
sex hormones that are secreted in larger amounts in females compared to males; contributes to female sex characteristics
Intersex
a term that is used to describe someone with a combination of male and female sex characteristics
individuals with sexual development differences have faced significant oppression over the years
in recent years, California has dictated that surgeries or procedures to assign a particular sex to such individuals are not to be done until that person is able to give consent
Role
expectations that are put in place regarding how people in certain social positions should interact and behave
Gender Role
expectations regarding the attitudes and behaviors that are exhibited by different genders
Sexual Aggression
any physical or verbal behavior of a sexual nature that is unwanted or intended to harm someone physically or emotionally; can be expressed as either sexual harassment or sexual assault
Cisgender
when a person’s gender identity parallels to their assigned sex
Transgender
when a person’s gender identity differs from their assigned sex
Non-binary
a person who does not identify with a specific binary gender
evidence that dates back to ancient times and civilization that shows the existence of gender-expansive individuals
Social Learning Theory
a theory that describes the process of learning certain behaviors through observation of the environment
Gender Typing
when a person acquires a role that is specifically mirroring traditional masculine or feminine gender roles
Androgyny
a mixture of traditionally feminine and masculine characteristics
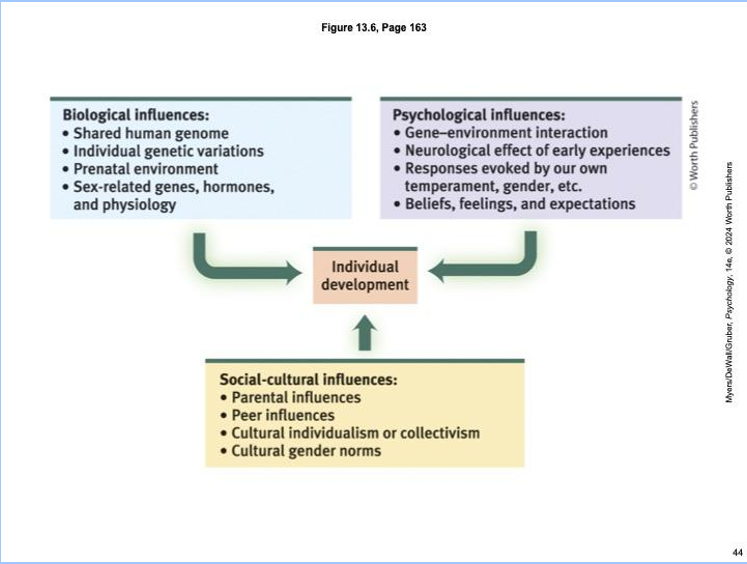
The Biopsychosocial Approach
Biological Influences
Psychological Influences
Social-cultural influences
all contribute to individual development