1.3.1 Networks and topologies
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is a Stand alone device?
any computer or device that is not connected to any other computer or device via a network
What is a computer network?
two or more computers that are connected together to allow the sharing of resources and information
What are the two types of networks? Explain each one?
LAN(Local Area Network) - computers connected over a small geographical area or a single site eg. home, school, small business, it has its own infrastructure of cabling and network hardware in each site
WAN(Wide Area Network) - computers are connected over a large geopgraphical area, collection of LANs joined together eg. large multi-site businesses, The Internet, uses external infrastructure that is leased to people like satellites and phone lines
What does infrastructure mean?
The basic systems and services, such as transport and power supplies, that a country or organization uses in order to work effectively.
What are the advantages of networks?
sharing resources eg. files, peripherals like printers/scanners
centralised management eg. managed user profiles and security, software distribution, backup of files
communication eg. email, instant messaging, file transfer
what are the disadvantages of networks?
increased security risk
servers and switches could fail
factors can impact peformance of network
What factors affect the performance of a network?
Number of users
Bandwidth
Latency
Error rate
Transmission
Interference
distance to travel/ signal strength
How does number of users affect performance of a network?
too many users on a network at the same time can cause the network to slow down if there is not enough bandwidth for all data being sent and received
What is bandwidth? How does it affect network performance?
The number of bits of data that can be transmitted at the same time measured in megabits per second (Mbps)
higher the bandwidth, the faster the data is transferred
What is latency? How does it affect network performance?
the delay between data being sent and received
if there is a big delay between te two, more data will be on the network causing collisions
What is error rate? How does it affect network performance?
measure of how many packets of data do not reach their destination
an increased error rate occurs in less reliable connections
What is transmission media? How does it affect network performance?
the type of media used to transmit data eg. wired/wireless
different media have different bandwidths such as wired connections offer higher bandwidth
What hardware is required to make a Local Area Network?
router
Wireless Access Point (WAP)
Switch
Network Interface Card(NIC)
transmission media
What is a Network Interface Card(NIC)?
internal piece of hardware with a MAC address that allows a device to connect to a network either wired or wireless
What is a switch?
device that connects multiple wired devices together on a computer network with packet switching and uses MAC address to route data to correct destination avoiding data collisions
What is a router?
device that forwards data packets between computer networks using IP addresses to route traffic and connects LAN to WAN
What is a Wireless Access Point(WAP)?
device that allows wireless devices to connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi
What is an IP address?
unique address assigned to a device on a network
identifies location on a network
What is a MAC address?
unique identifier assigned to a device an cannot be changed
identifies device
What are the types of transmission media?
Ethernet/ twisted pair
affordable
networking standard
low bandwidth
twisted to reduce interference
coaxial
older networking standard
large and chunky
used in large scale networks and industry eg. satlelite TV, telephone networks
Fire optic
high bandwidth
very expensive
durable
unaffected by interference
uses light to transmit data
fast transmission speeds
How can computers be connected over a network?
In a client-server network
In a peer-to-peer network
What is a client-server network?
a powerful computer with a specialised role known as the server which provides services and resouces that is requested by the clients
What are the typical servers?
file servers - hold and maintain user files
applications servers - allow programs to be run over a network
web servers - hold and share web pages
print servers - manage printing across a network
mail servers - handle emails between users
Advantages and Disadvantages of a client-server network?
Advantages
central backing up for all computers
central installing and updating of software
Security controlled by central server
scalable as it is easy to add clients
Disadvantages
servers are a single point of failure
expensive to set up and maintain
requires specialists
users lose access if server fails
What is a peer-to-peer server?
computers connected together where all computers are equal and act as both client and servers
What are the advantages of peer-to-peer networks?
Advantages
simple setup and maintainance
clients are not dependent on single server
cheap setup
Disadvantages
no central device to manage security or backups
each device must be individually backed up/updated
performance decreases with more devices connected, especially if other devices are slow
network can be less secure
What is the internet?
a world wide connection of computer networks
refers to network infrastructure not content stored on it
example of a WAN
largely works on client server model
purpose is to enable communication on an international level
What is the World Wide Web(WWW)?
all the web pages that are accessible via the internet
What is a node?
each connection point/device on a network
What is a topology?
layout/pattern/physical tructure in which nodes are connected in a network
Examples of topologies?
star
mesh
bus
ring
What is a star topology?
a topology with a central switch which all the other devices connect to
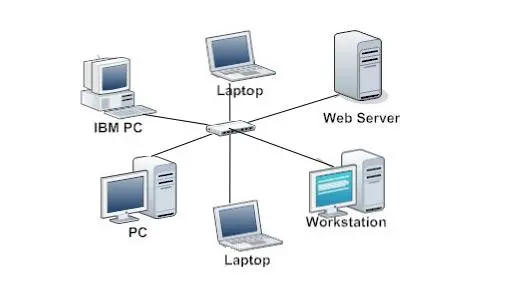
Advantages of a star topology? Disadvantages?
Advantages
if one cable fails, other nodes are unaffected
good performance as few data collisions
Disadvantages
expensive to install
if central switch/ server fails, whole network fails
What is a mesh topology?
a topology where all nodes are connected together
Advantages of a mesh topology? Disadvantages?
Advantages
if one cable fails, nodes are unaffected as data can find another route
more nodes makes faster wireless network
best suited to wireless networks
new nodes automatically added to wireless network
Disadvantages
expensive to install
What is a partial mesh topology?
a mesh topology but where some nodes are notconnected