Carbohydrates
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
D-Glucose [most important]
D-Galactose [must be converted to glucose to be used as energy]
D-Fructose [must be converted to glucose to be used as energy]
GGF
Enumerate the monosaccharides
Maltose [ 2 Glucose]
Lactose [Glucose + Galactose]
Sucrose [Glucose + Fructose]
MLS
Enumerate the Disaccharides and what monosaccharide unit are they made of
Starch
Glycogen
Cellulose
Inulin [composed of Fructose unit only]
Enumerate the Polysaccharides
Galactokinase
1-phosphate uridyl transferase
What are the enzyme deficiency will cause Galactosemia
Guthrie test
Beutler method
Galactokinase and 1-phosphate uridyl transferase deficiency can cause Galactosemia. What are the screening test done for this
Whole Blood
Plasma
Serum
Carbohydrate Concentration
Urine
CSF
Other body fluids
Specimen used for Carbohydrate Measurement
Urine
CSF
Other Body Fluids
Carbohydrate Measurement
Whole blood
Plasma
Serum
Specimen used for Carbohydrate Concentration

Glycolysis
GLUCOSE METABOLISM:
It is the metabolism of glucose to pyruvate or lactate for production of energy
GLYCOLYSIS
Pyruvate
Lactate
To produce energy, glucose is metabolized into ______ and ______

Gluconeogenesis
GLUCOSE METABOLISM:
Formation of glucose-6-phosphate from noncarbohydrate sources

Glycogenolysis
GLUCOSE METABOLISM:
Breakdown of Glycogen to Glucose for use of energy

Glycogenesis
GLUCOSE METABOLISM:
Glucose to Glycogen for storage

Lipogenesis
GLUCOSE METABOLISM:
Conversion of carbohydrates to fatty acids

Lipolysis
GLUCOSE METABOLISM:
Decomposition of fat
INSULIN —the only hormone lower glucose level
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
Hormone that lowers blood glucose level
Inhibit Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
Increase Glucose uptake by peripheral Tissue
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
What are the actions of Insulin (lower glucose level)
Starvation (low dietary feul)
Stress / Trauma (Epinephrine increases)
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
In what instances does Insulin (lower glucose) Decreases
C-Peptide
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
Used as marker to differentiate Endogenous (body) and Exogenous (injected) insulin
5:1
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
C-Peptide to Insulin ration
NV: <1.2 ng/mL
Hyperinsulinism: >1.9 ng/mL
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
C-peptide normal value
What level can cause hyperinsulinism
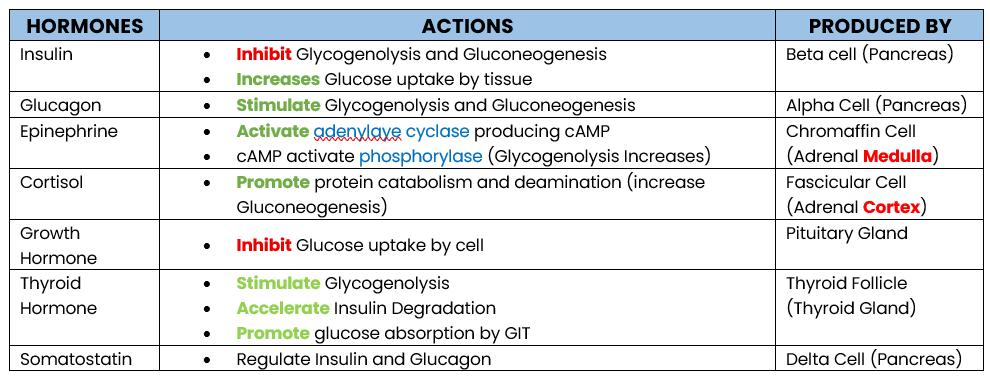
Glucagon
Epinephrine
Cortisol
Growth Hormone
Thyroid Hormone
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
Enumerate hormone that increases Glucose Level
Insulin ONLY
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
Enumerate hormone that decreases Glucose level
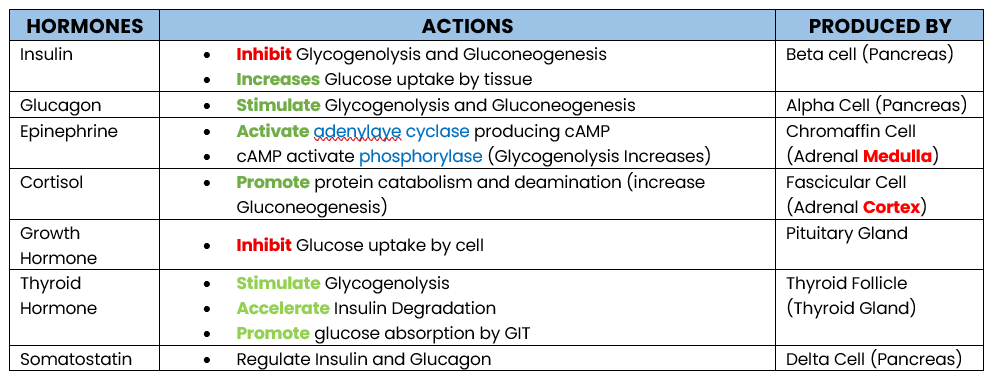
Stimulate Glycogenolysis and Gluconeogenesis
PRODUCED: Alpha Cell (Pancrease)
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
Action of Glucagon
Produced by?
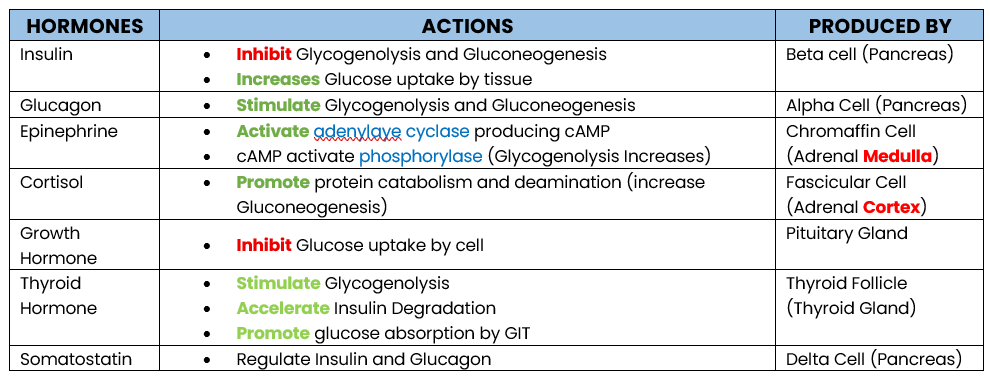
Activate adrenylate cyclase producing cAMP
cAMP activates phosphorylase which stimulates Glycogenolysis
PRODUCED: Chromaffin Cell (Adrenal Medula)
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
Action of Epinephrine
Produced by?
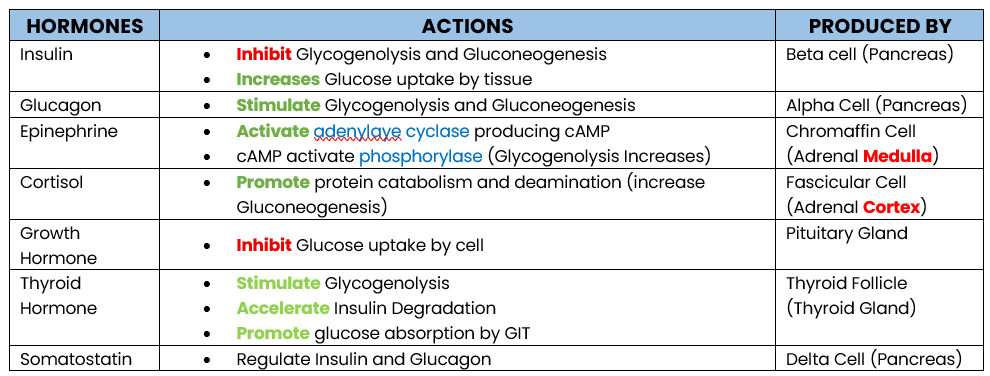
Promote protein catabolism and deamination, increasing Gluconeogenesis (protein → glucose)
Inhibit Glucose uptake by tissue (storage)
PRODUCED BY: Fascicular Cell (Adrenal Cortex)
STIMULATED BY: Adrenocorticutrophic Hormone (ACTH)
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
Action of Cortisol
Produced by?
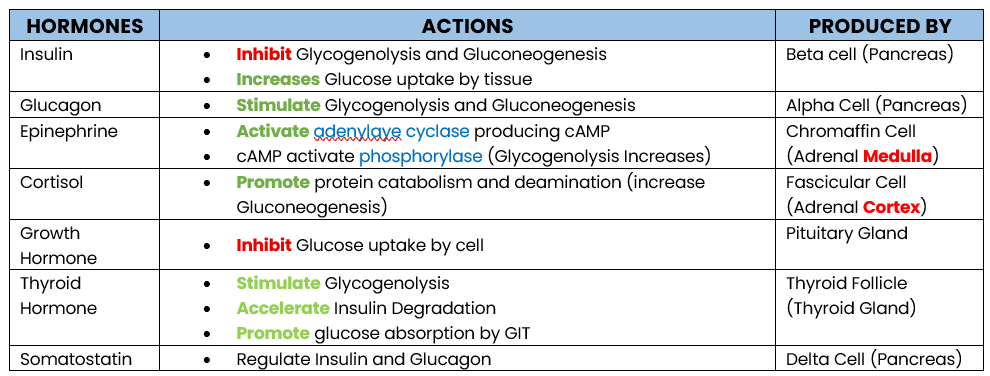
Inhibit Glucose uptake by cell (storage)
Antagonize Insulin
PRODUCED: Pituitary Gland
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
Action of Growth Hormone
Produced by?
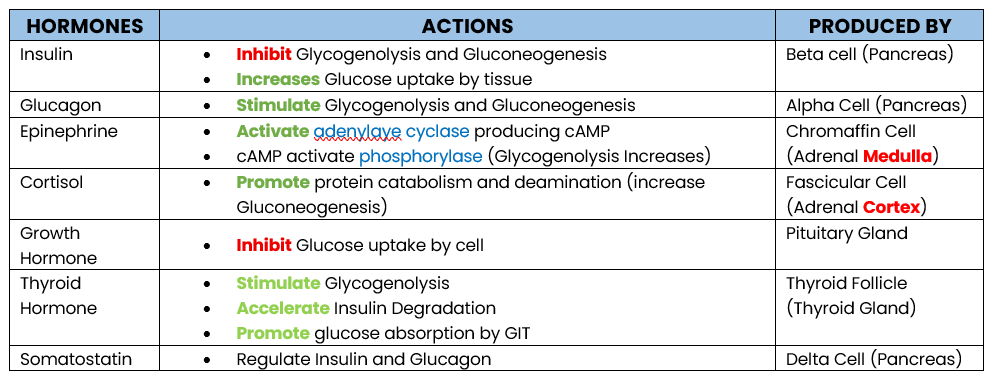
Stimulate Glycogenolysis
Accelerate Insulin Degradation
Promotes Glucose Absorption by GIT
PRODUCED: Thyroid Follicle (Thyroid Gland)
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
Action of Thyroid Hormone
Produced by?
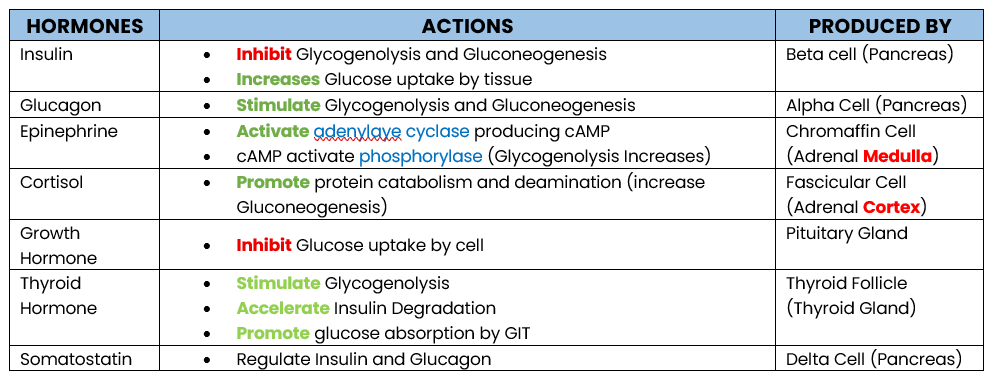
Inhibit Insulin and Glucagon (Regulator)
PRODUCED: Delta Cell (Pancrase)
GLUCOSE REGULATING HORMONE:
Action of Somatostatin
Produced by?

50-100 mg/dL
2.8-6.2 mmol/L (mg% to mM = 0.055)
Normal value of glucose is serum or plasma

45-100 mg/dL
10% lower than serum/plasma due to RBC glucose utilization
Normal value of glucose in Whole Blood

40-70 mg/dL
60-75% of serum/plasma
Normal values of glucose in CSF
Folin-Wu
Somogyi-Nelson
Neocuproine
Benedict
Schaeffer-Hartmann Somogyi
[F,S, National Book Store]
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
Enumerate the Reduction Methods (Copper Reduction)
Hagedorn-Jensen
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
Enumerate the Ferric Reduction Method
Dubowski (Ortho-toluidine method)
Anthrone Condensation
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
Enumerate the Condensation Methods
Glucose Oxidase (GOD) Coupled Reduction
Polarographic GOD Method
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
Enumerate the Enzymatic Methods
Hexokinase Method
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
The most specific methods and considered as reference method for glucose determination
WHOLE BLOOD (Folin-Wu)
10% sodium tungstate
2/3N sulfuric acid
SERUM (Somogyi-Nelson)
5% zinc sulfate
0.3N barium hydroxide
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
State the sample used for Folin-Wu and Somogyi Nelson
Include the chemical used for deproteinization
Phosphomolybdate Reagent
PRODUCED: Phosphomolybdenum blue
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
In Folin-Wu what reagent does the cuprous oxide (Cu1+) reacts with and what is the formed product
Arsenomolybdate
PRODUCED: Arsenomolybdenum blue
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
In Somogyi-Nelson what reagent does the cuprous oxide (Cu1+) reacts with and what is the formed product
Ferricyanide Ions
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
In Hagedorn-Jensen what ions is used
Yellow Ferricyanide is reduced by glucose present to colorless ferrocyanide solution
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
What is the principle of Hagedorn-Jensen
Ferrocyanide is less likely to be reoxidized by air
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
Why is ferrocyanide more advantagous than cuprous ions
Condensation Method
Dubowski (Ortho-Touidine Method)
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
Most specific nonenzymatic glucose determination
Glucose is converted to gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide. The presence of enzyme peroxidase , a chromogen is oxidized gives a colored complex
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
In Glucose Oxidase (GOD) Coupled Reaction, glucose is converted into __________ and ______ in the presence of ________. The presence of enzyme ________, a chromogen is oxidized to give a colored complex
p-aminophenzone (PAP) oxidized to quinone imine dye (pink/red)
o-dianisidine oxidized to orange product
o-toluidine oxidize to green product
indophenol blue oxidize to blue product, iodide is oxidized to purple product
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
Enumerate the chromogen used in GOD Coupled Reaction

Glucose is phosphorylated by hexokinase and magnesium ions to form glucose-6-phosphate
G-6-P turns to 6-phosphogluconolactione by G-6-PD, w/ the reduction of NAD or NADP
GLUCOSE DETERMINATION TESTS:
Principle of Hexokinase Method
![<ul><li><p><span style="color: red;"><strong>Type1 DM </strong></span>[beta cell is damaged]</p><ul><li><p><span style="color: blue;"><em>Type 2 [insulin is enough but cells don’t respond]</em></span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/7af71e3e-dd43-48d7-bd8b-774e59f8b21f.png)
Type1 DM [beta cell is damaged]
Type 2 [insulin is enough but cells don’t respond]
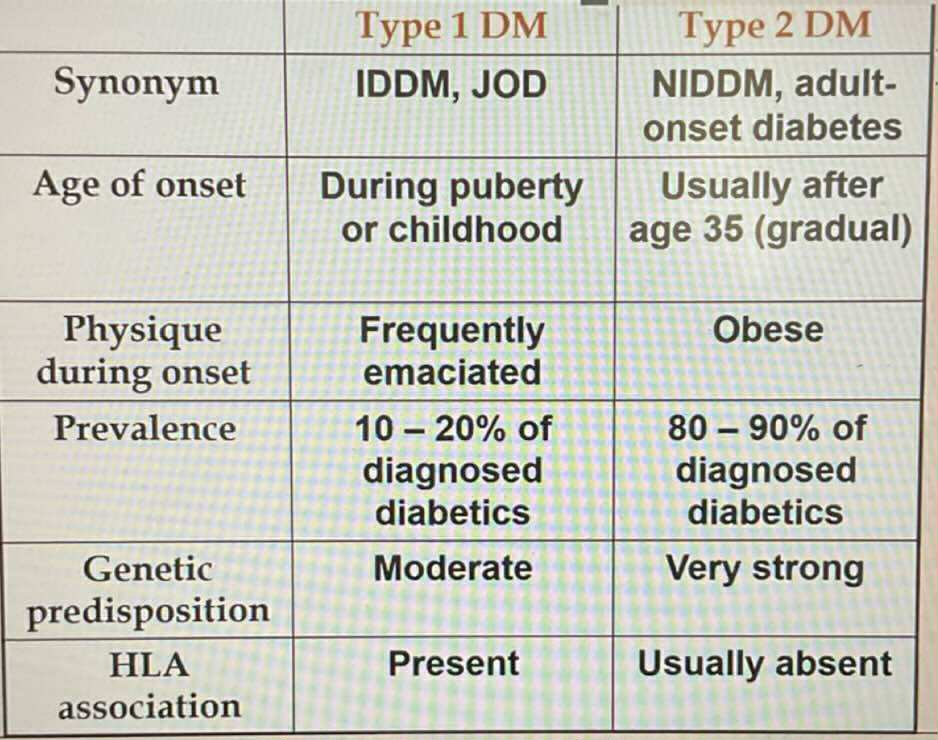
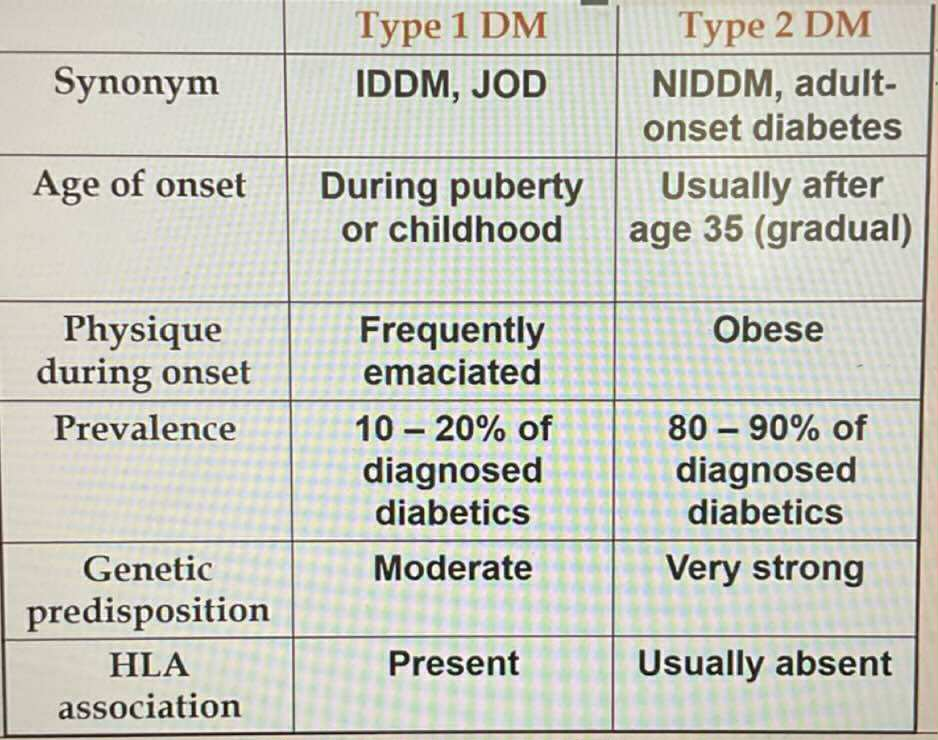
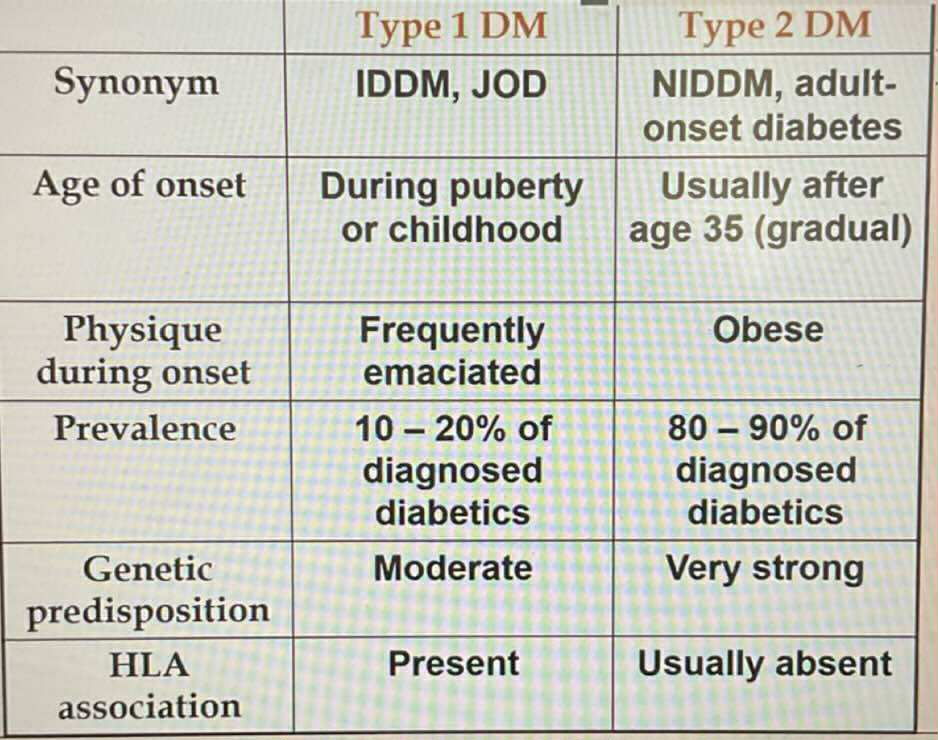
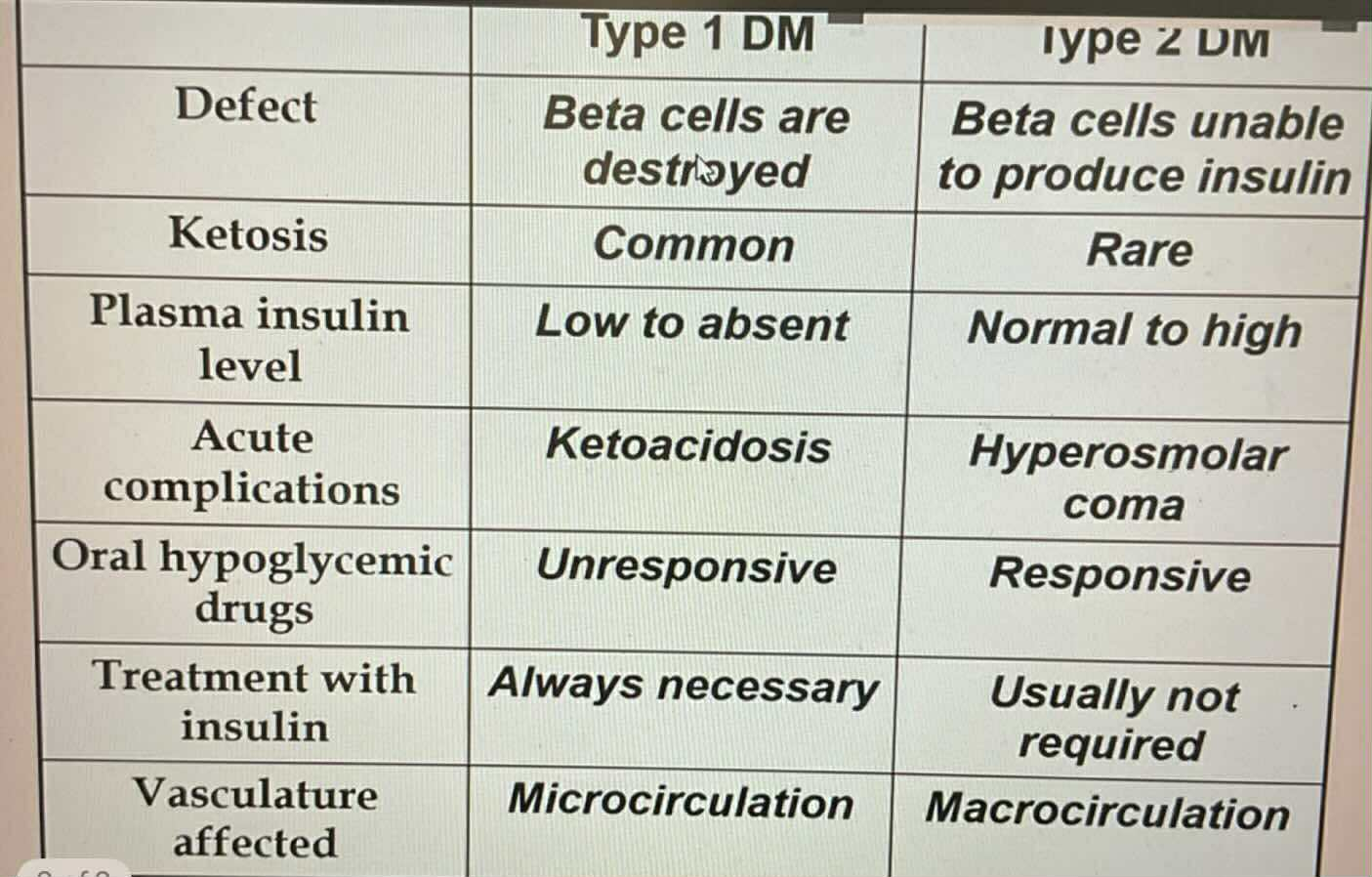
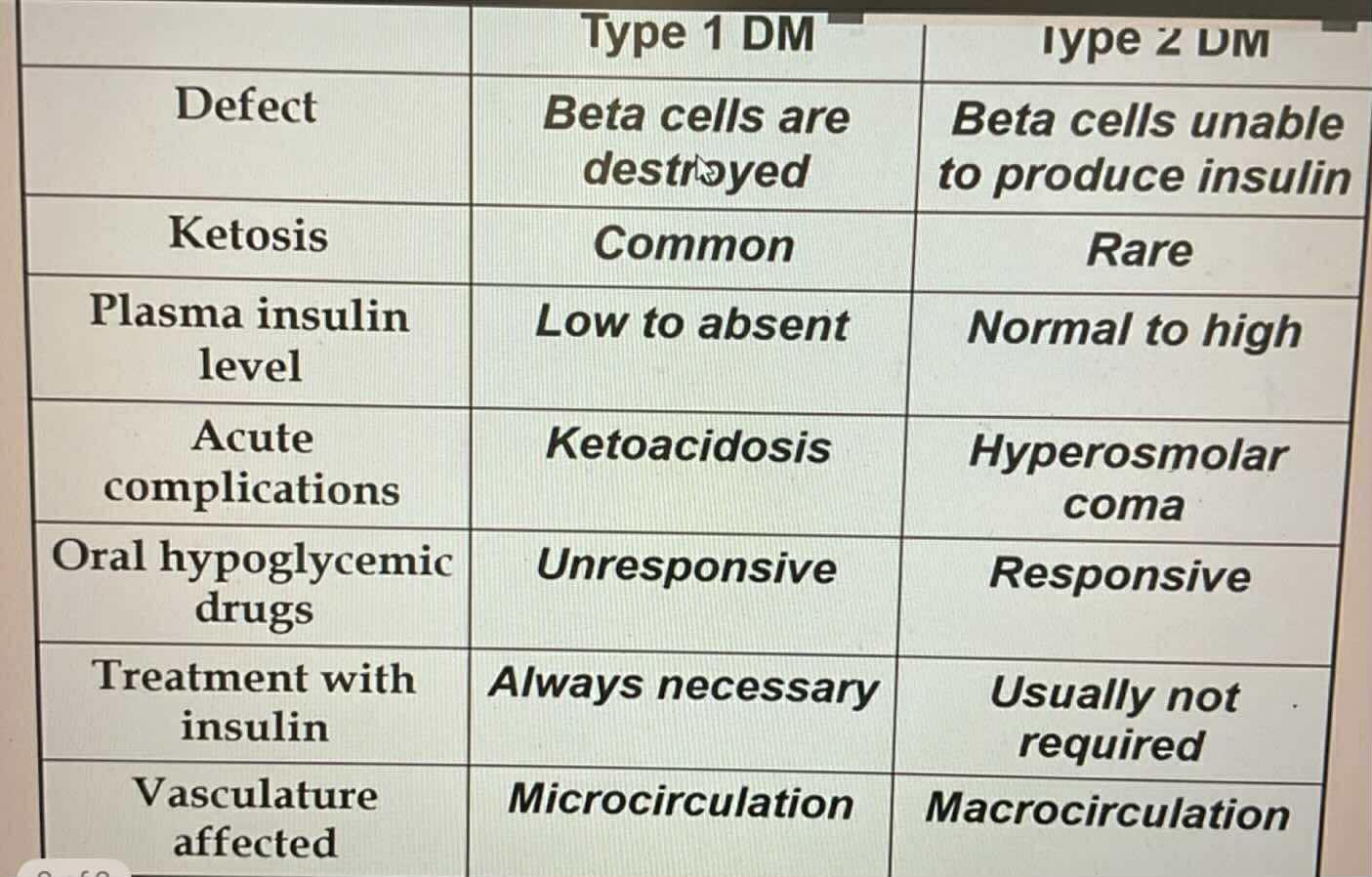
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Insulin Dependent
Type 2 DM
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Seen in obese patients
Type 2 DM
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Most common 80-90% prevalence
Type 2 DM
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Usually inhereted (very strong)
![<ul><li><p><span style="color: red;"><strong>Type 1 DM </strong></span>[autoimmune]</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1f25015c-6531-4710-a683-c04babdb69b2.png)
Type 1 DM [autoimmune]
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Human Leukocytes Antigen (HLA) associated
Type 2 DM
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Beta cells are unable to produce insulin
Type 2 DM
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Responsive to Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs
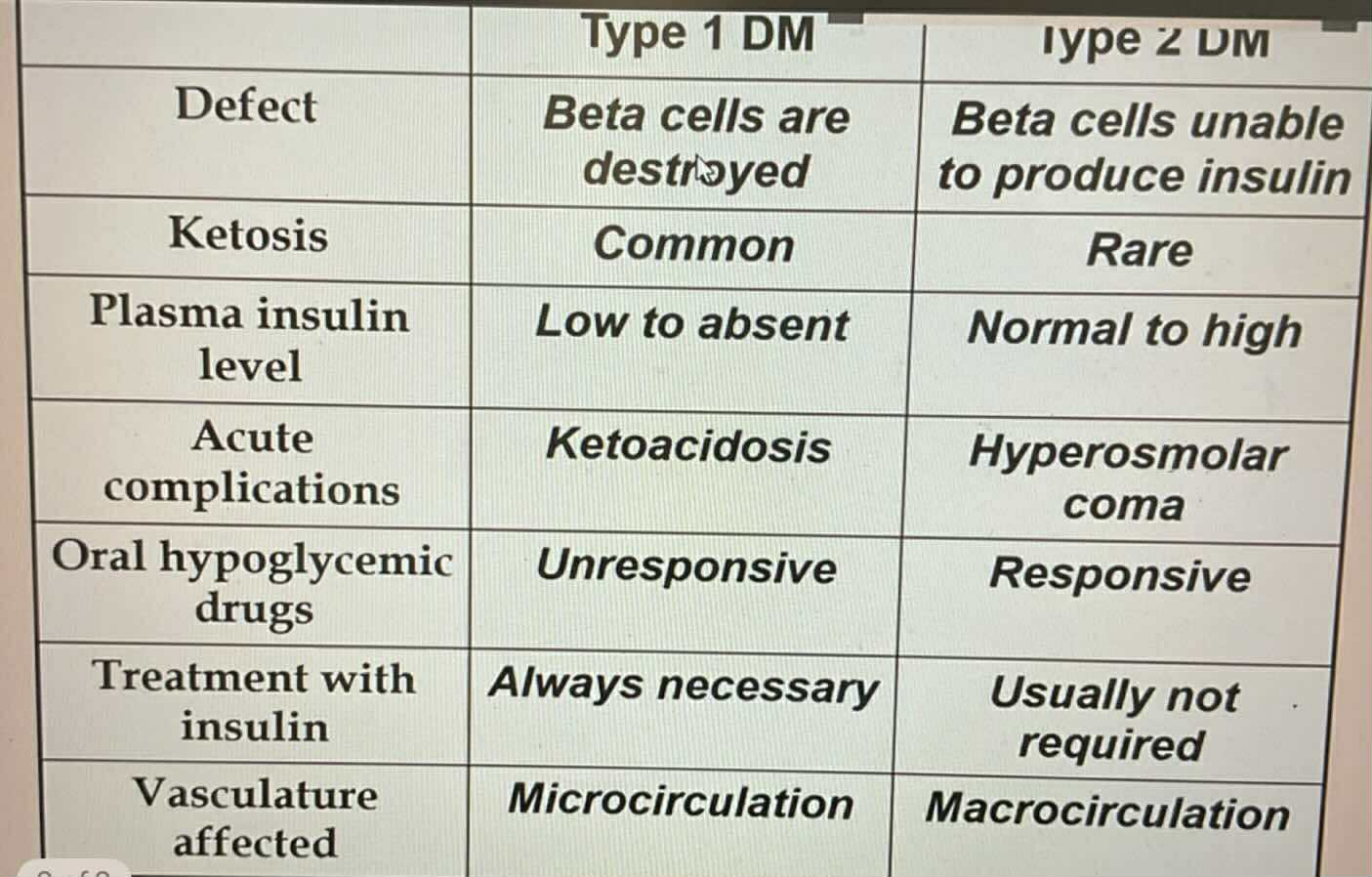
Type 1 DM
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Unresponsive to Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs
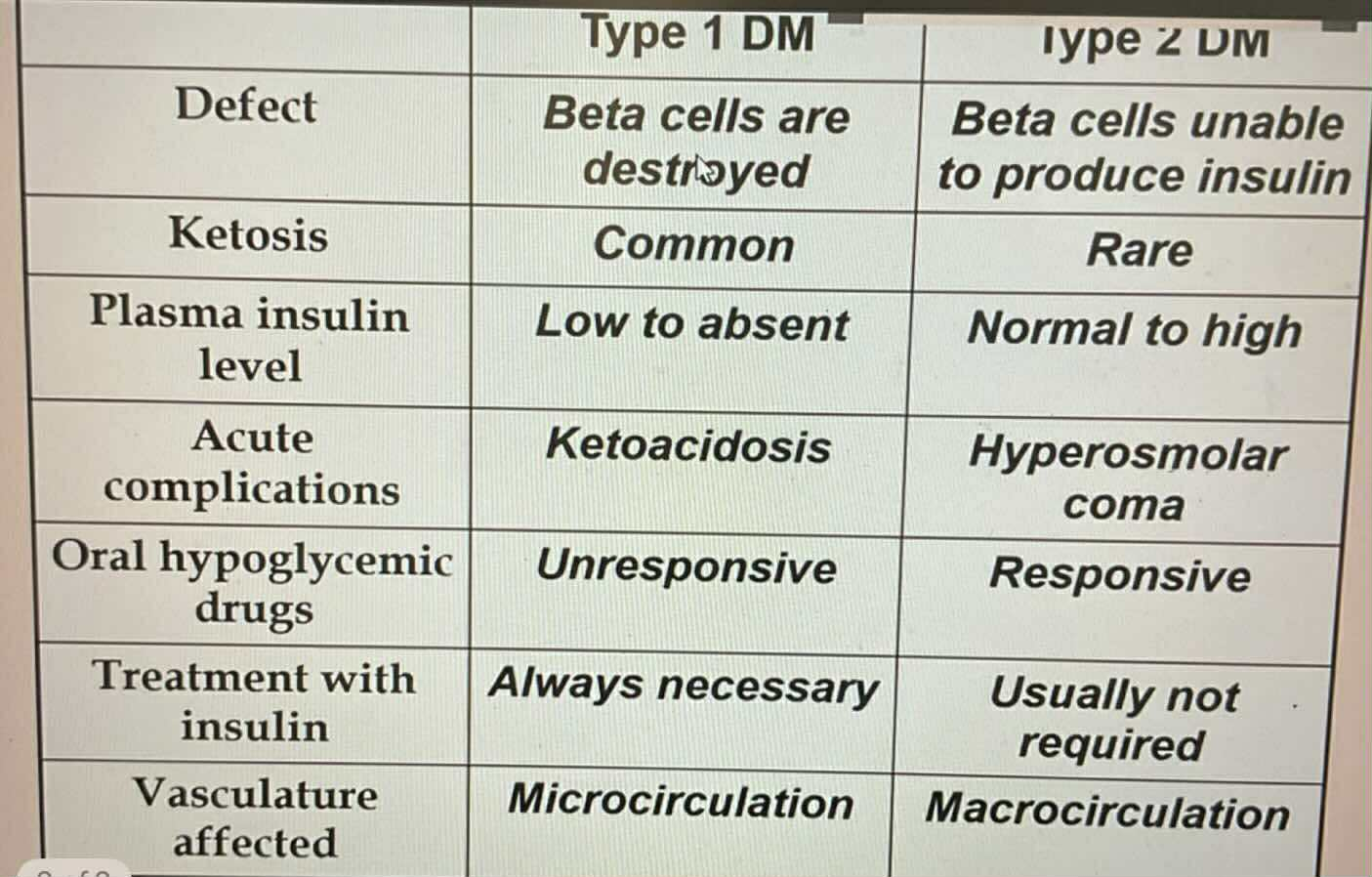
Type 1 DM
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Always require insulin treatment
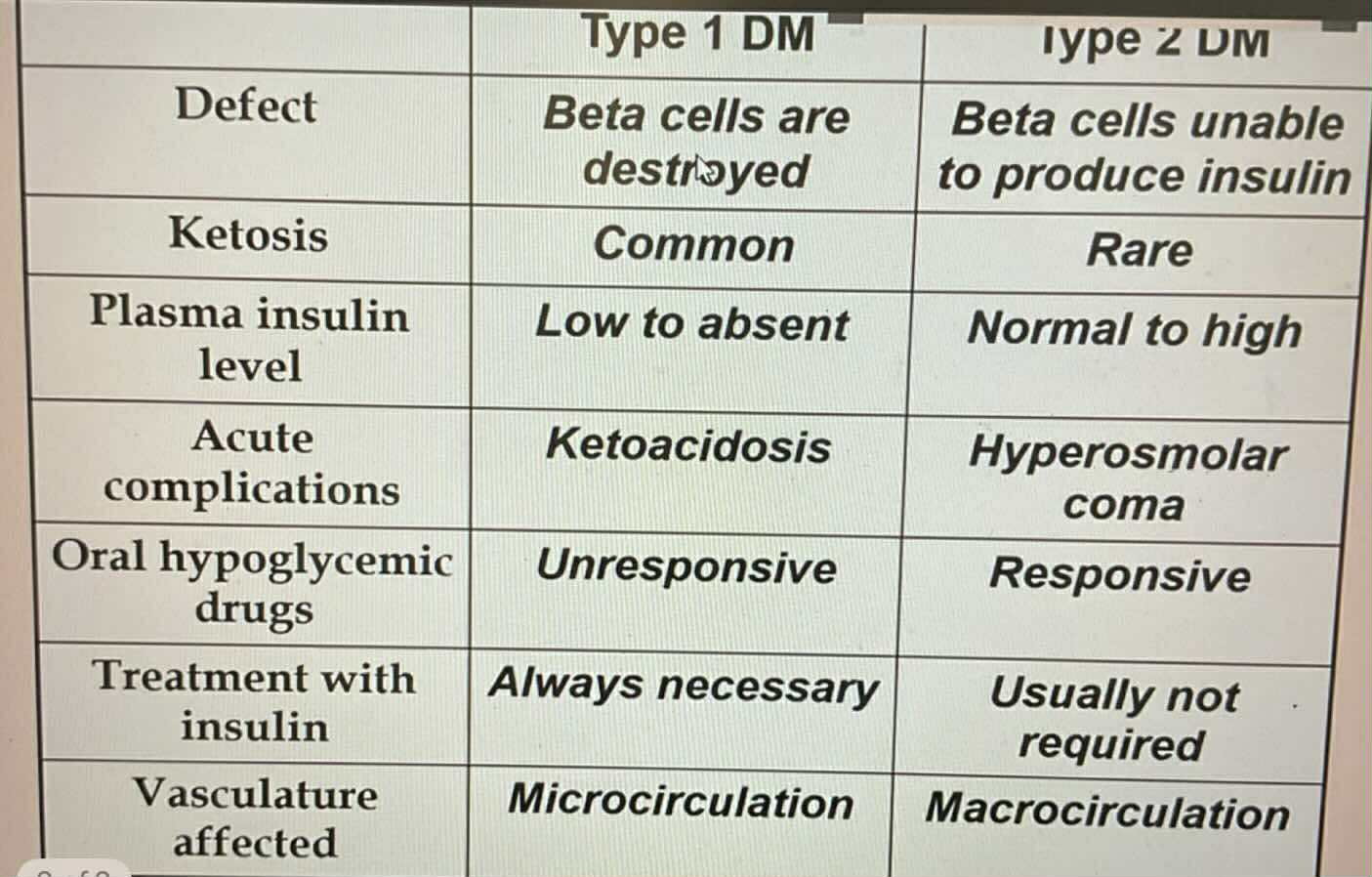
Type 1 DM
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Microcirculation vasculate affected
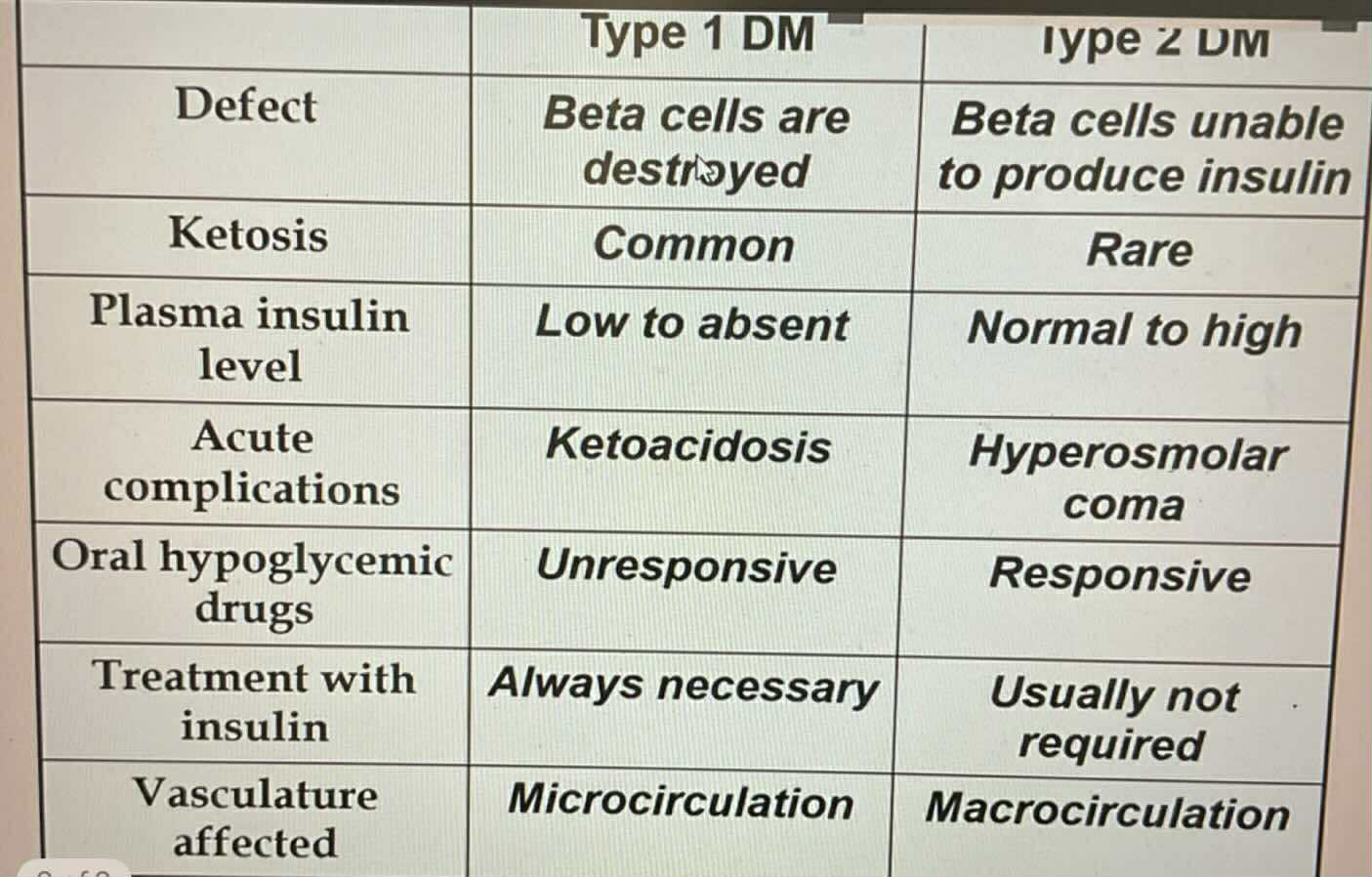
Type 2 DM
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Macrocirculation vasculate affected
Polyuria
Polydipsia
Polyphagia
What are the 3Ps of Diabetes Mellitus symptoms
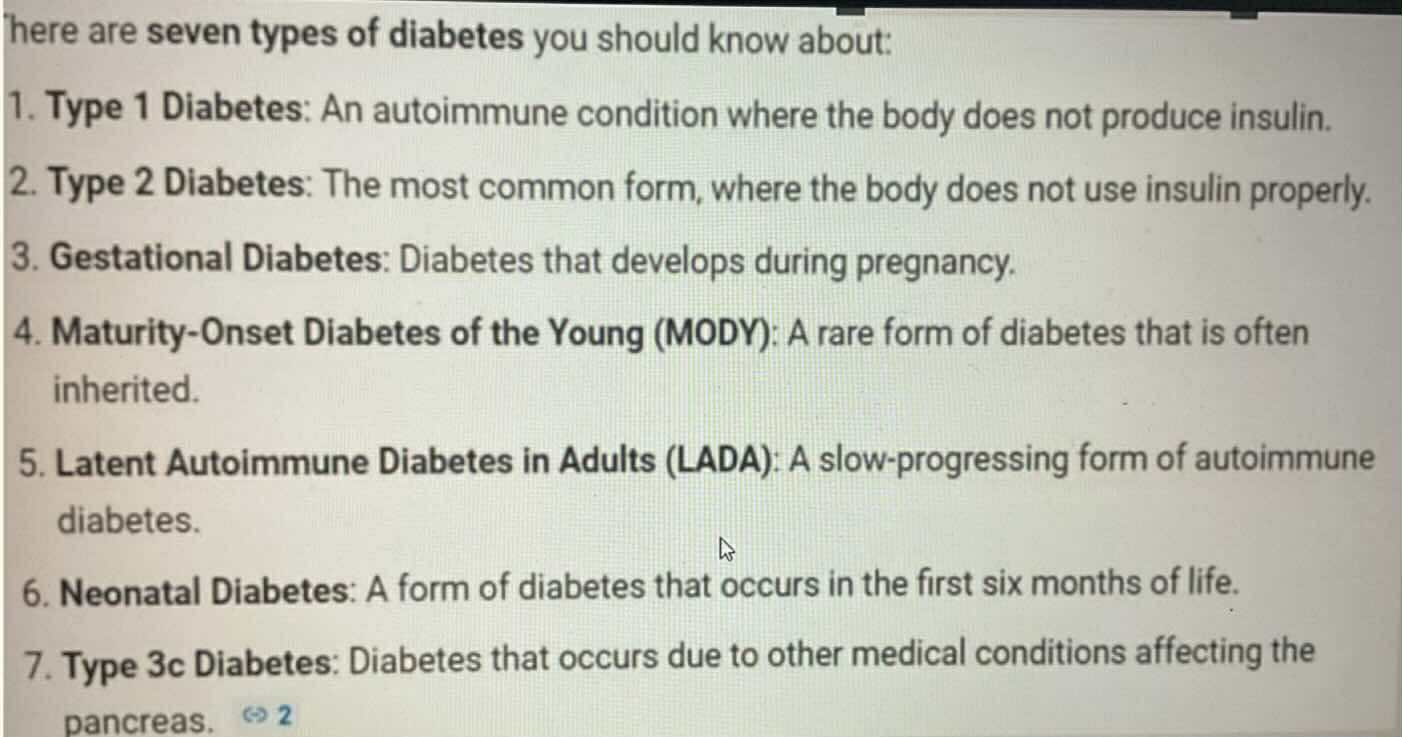
Gestational Diabates
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Diabetes during pregnancy
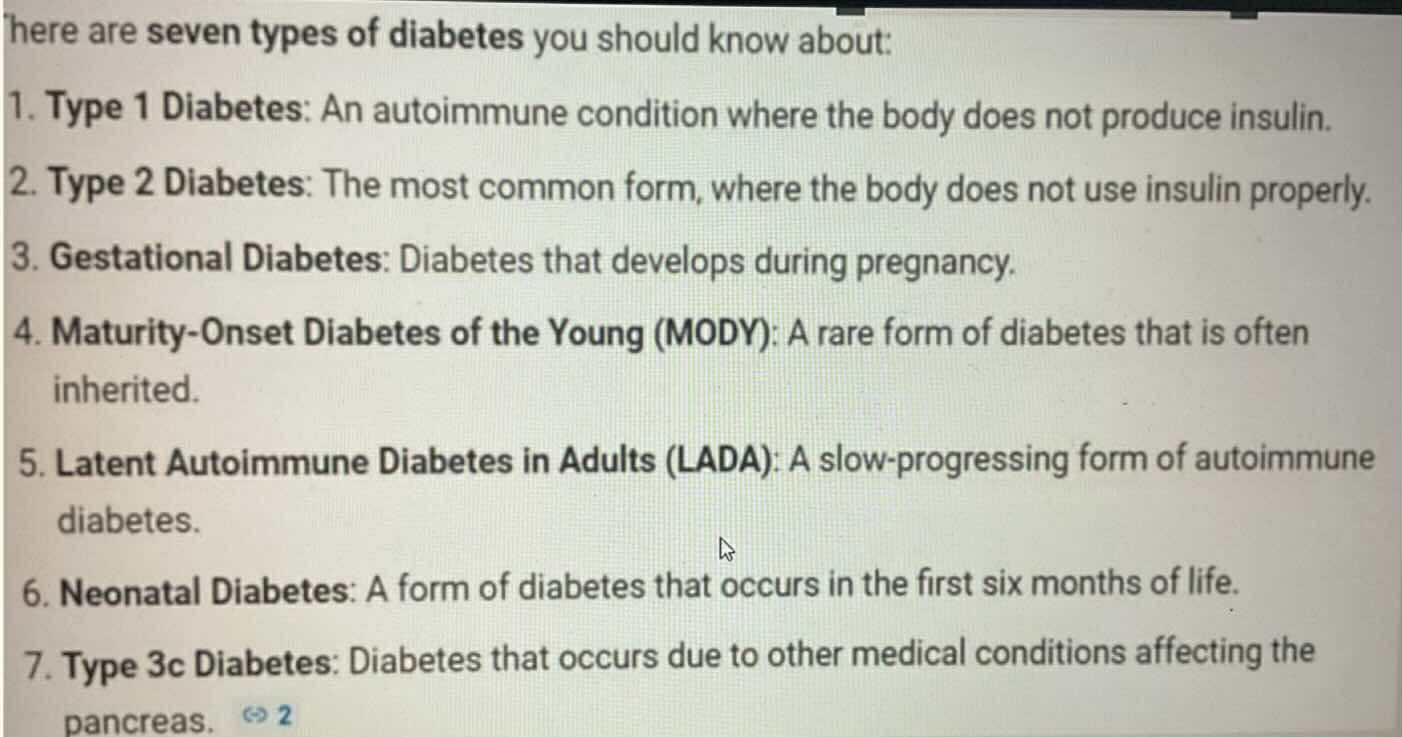
Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Rare form of diabetes that is inheried
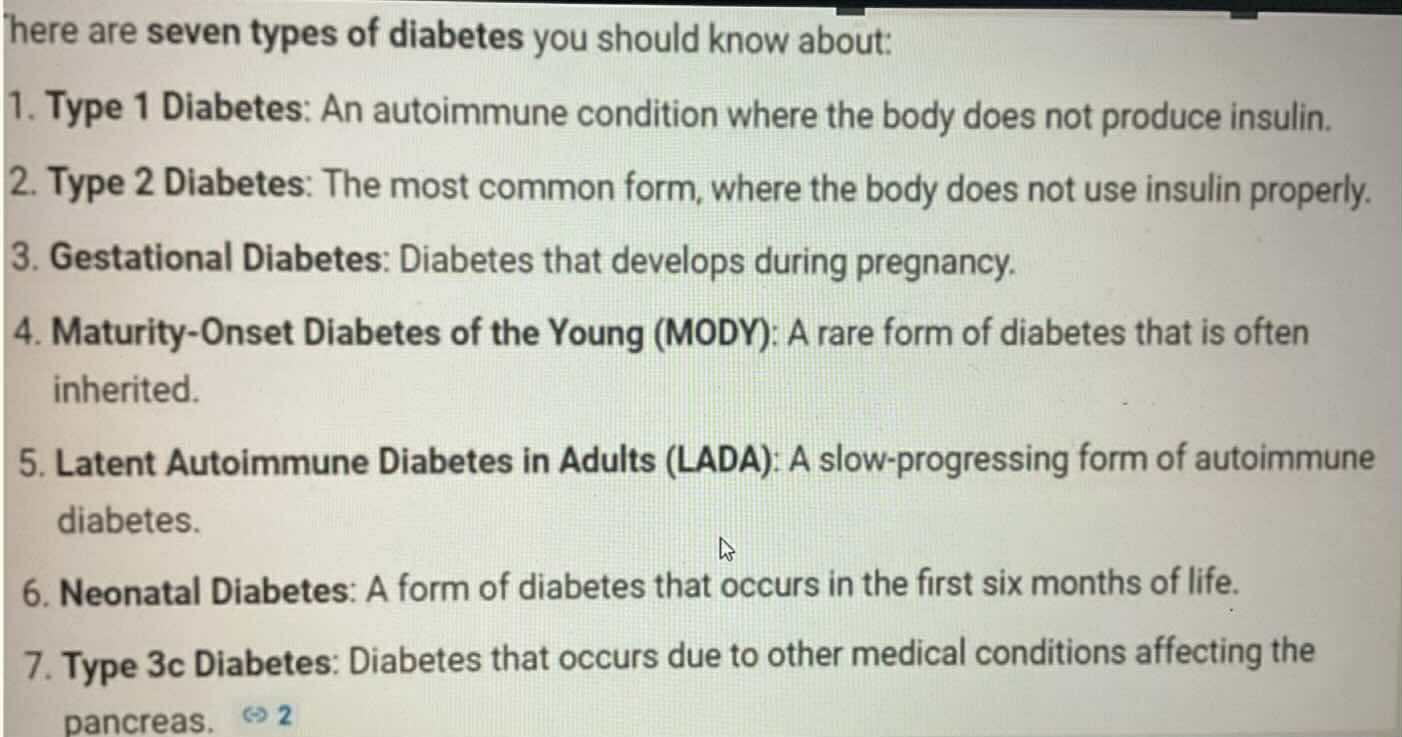
Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adult (LADA)
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Slow-Progressing autoimmune diabetes
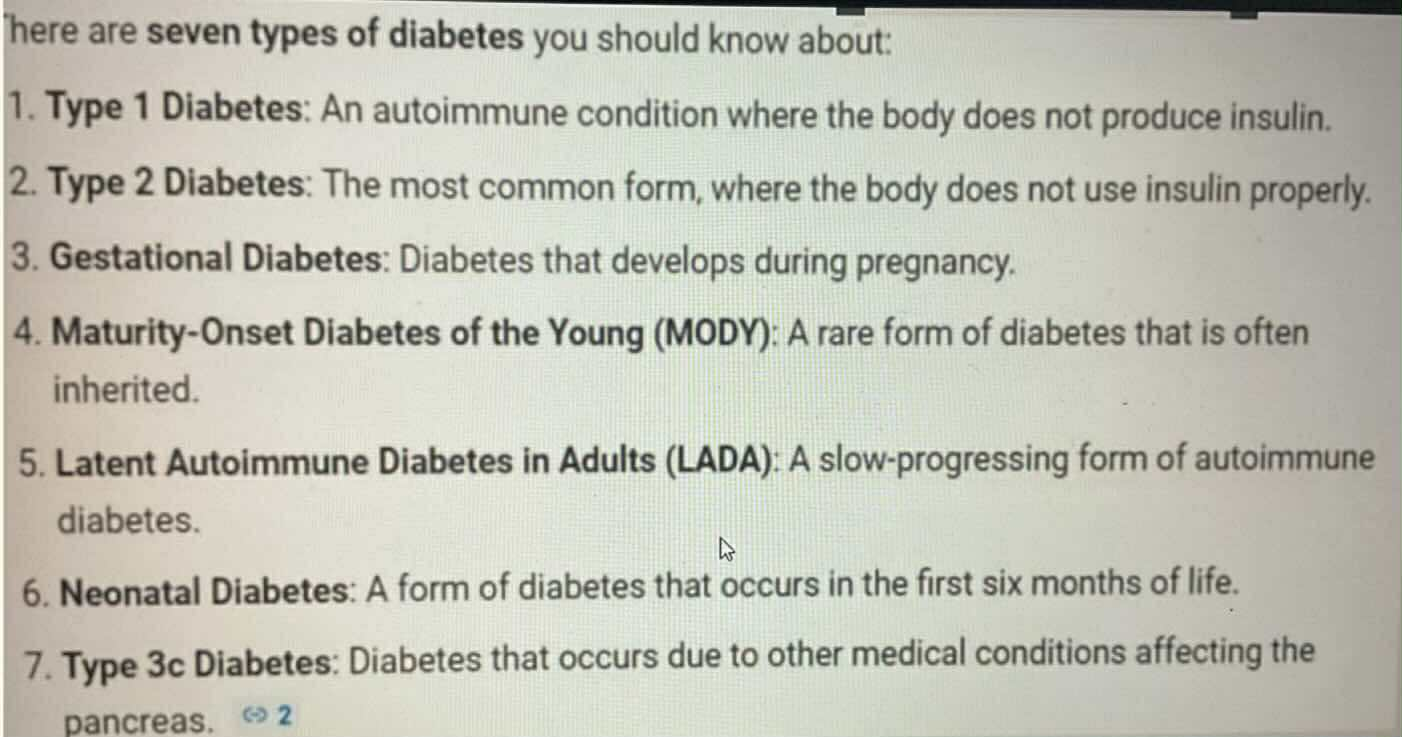
Type 3c Diabetes
TYPES OF DIABETES:
Diabetes that occur dur to other medical condition affecting the pancrease
Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS)
Random Blood Sugar (RBS)
2Hr Postprandial Test
Oral Glucose Tolerance test (IGTT)
Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Test (IVGTT)
Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1c)
Fructosamine
Enemurate the Tests used to Diagnose Diabetes Mellitus
FBS = 30-110 mg/dL
RBS = 45-130 mg/dL
TEST IN DIAGNOSING DM:
Normal values of FBS and RBS
After 60-90 mins = highest glucose concentration
After 2hr = equal to FBS (30-110 mg/dL)
TEST IN DIAGNOSING DM:
Normal Glucose Level for 2Hr Postprandial Test
Glycosylated Hemoglobin (HbA1c)
TEST IN DIAGNOSING DM:
Monitor long-term glucose control
Fructosamine
TEST IN DIAGNOSING DM:
Monitor short-term glucose control
1-hr OGTT w/ 50g glucose load (no fasting)
<140 mg/dL [GDM ruled out]
>140 mg/dL [Dianostic Test should be done (3hr OGTT)]
DIAGNOSING GESTATIONAL DIABETES:
What is the screening method used
What is the anticipated result (w/ interpretation)
3hr OGTT w/ 100g Glucose Load (overnight fasting)
>140 mg/dL confirmed GDM
DIAGNOSING GESTATIONAL DIABETES:
What is the diagnostic method
45 mg/dL
less = hypoglycemia
Normal value of Plasma Glucose
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA: Enzyme Deficient
Liver and Kidney Glucose-6-Phosphate
Type II (Pompe)
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA: Enzyme Deficient
All tissue alpha 1,4-glucosidase
Type III (Cori-Forbes)
Type IV (Adersen) = brancher enzyme
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA: Enzyme Deficient
All tissue debrancher enzyme
Type IV (Adersen)
Type III (Cori-Forbes) = debrancher enzyme
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA: Enzyme Deficient
All tissue brancher enzyme
Type V (McArdle)
Type VI (Hers) = Liver phosphorylase
Type IX = Liver phosphorylase kinase
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA: Enzyme Deficient
Muscle phosphorylase
Type IV (Hers)
Type V (McArdle) = Muscle Phosphorylse
Type IX = Liver Phosphorylase kinase
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA: Enzyme Deficient
Liver phosphorylase
Type IX
Type V (McArdle) = Muscle phosphorylase
Type IV (Hers) = Liver phosphorylase
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA: Enzyme Deficient
Liver phosphorylase kinase
Type VII (Tarui)
Type VII = adenylate
Type X = cAMP-dependent
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA: Enzyme Deficient
Muscle and Liver phosphofructokinase
Type VIII
Type VII (Tarui) = fructokinase
Type X = cAMP-dependent
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA: Enzyme Deficient
Brain and Liver adenylate kinase
Type X
Type VII (Tarui) = fructokinase
Type VIII = adenylate
TYPES OF HYPOGLYCEMIA: Enzyme Deficient
Liver and Muscle cAMP-dependent kinase
Whipple’s Triad
Hypoglycemia is diagnosed by