Exam 2 Cell Structure and Function
1/233
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
234 Terms
Virchow added to the cell theory
All cells arise only from preexisting cells
What year did Virchow add to the cell theory
1855
Where did the first cells come from?
Abiotic (nonliving) synthesis of simple organic compounds
Abiotic polymerization of these into macromolecules
Emergence of a macromolecule capable of replication and storing genetic information
encapsulation of the first living molecule in one membrane.
Step 1 of cell appearance
Abiotic (nonliving) synthesis of simple organic compounds
Step 2 of the appearance of cells
Abiotic polymerization of simple organic compounds into macromolecules
Step 3 of the appearance of cells
Emergence of a macromolecule capable of replication and storing genetic information
Step four of the appearance of cells
encapsulation of the first living molecule in one membrane.
What was Stanley Miller’s experiment on?
Abiotic synthesis of organic molecules
Stanley miller experiment results
amino acids and nucleotides were observed in end product
What did Stanley Miller’s 1953 experiment test, and what did it produce?
Tested if lightning energy + early Earth gases (CH₄, NH₃, H₂, H₂O vapor) could form organic molecules; produced glycine, alanine, and other simple organics (later found: sugars, HCN, adenine).
How do Miller’s results compare with amino acids in modern proteins?
Miller’s experiment generated both D- and L- amino acids; proteins today only use L- amino acids.
_ May have been the first informational molecule
RNA
How are deoxyribonucleic acids derived
enzymatically from the corresponding ribonucleotides
deoxyribonucleic acids are used to
form DNA
Ribozymes are
RNAS
Ribozymes are capable of performing
certain enzymatic reactions
Example of Ribozyme enzymatic reaction
formation of the peptide bonds during translation
Did an RNA or DNA world exist first (before the appearance of DNA and proteins)
RNA
Where did primordial lipids come together
in an early ocean
Primordial lipids
the earliest simple fat-like molecules that could spontaneously form under prebiotic (non-living, early Earth) conditions.
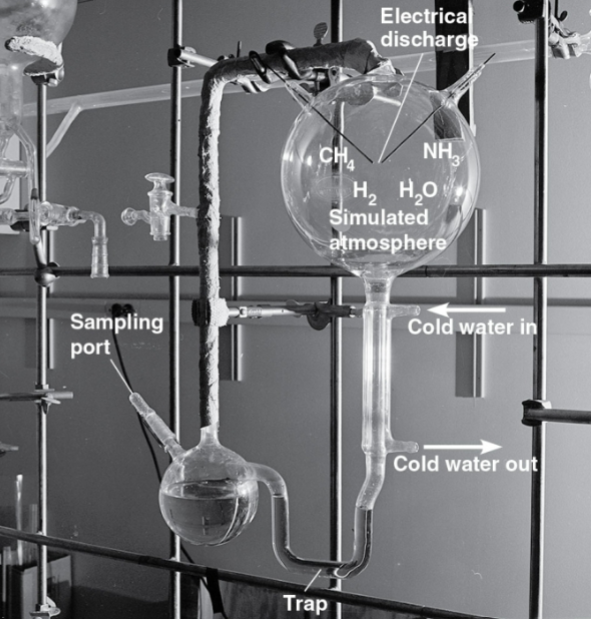
Stanley Miller Experiment
Liposome
A spherical vesicle formed by lipid bilayers, capable of enclosing molecules like RNA
Role of primordial lipids in origin of life
May have trapped RNAs in vesicles, forming the first protocells
Protocells
Primitive cell-like structures with lipid membranes and enclosed RNA, considered a step toward living cells
Liposomes form when
membrane lipids are added to water
Liposome
Cell characteristics
Organizational Complexity
molecular components
sizes and shapes
specialization
What is the likely order of appearance of macromolecules in early life?
RNA → amino acids (proteins) → lipids (membranes) → DNA
Three domains of life
Archaea, Bacteria, Eukarya
Eukarya are
eukaryotes
Relationship between Bacteria and Archaea
They are as divergent from one another as humans are from bacteria
Ancestral cell
The common ancestor that gave rise to all three domains of life
What are the requirements for an efficient reaction involving molecules? (think macromolecule synthesis, addition of monomers)
Two or more molecules come close enough
High concentration of the molecules
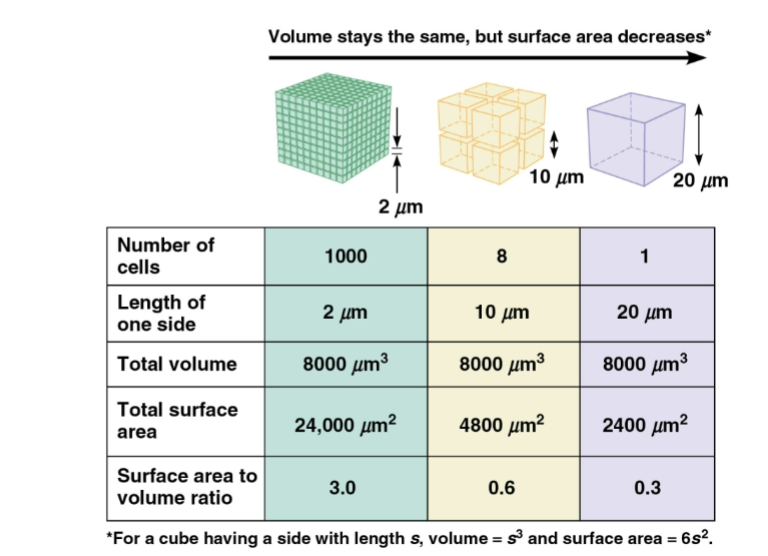
Limitation on cell size is determined by
surface area-to-volume ratio
What happens as a cell gets larger?
Volume increases faster than surface area → lower surface area/volume ratio
Why do cells need a high surface area/volume ratio?
To efficiently exchange nutrients, gases, and wastes with the environment
How do cells adapt if they are large?
Stay small, or use shapes with folds/projections to increase surface area
Surface Area to volume ratio chart
Cells specialized for absorption have
adaptations to maximize surface area
Example of absorption-specialized cells
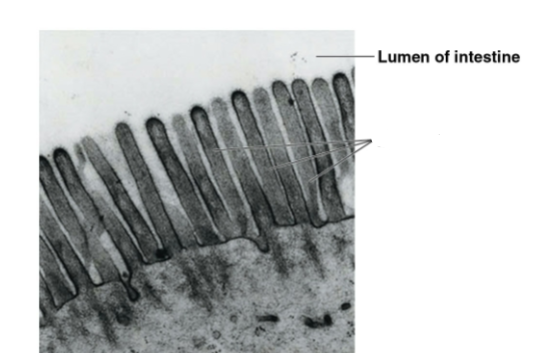
Intestinal epithelial cells
What structures increase surface area in intestinal cells?
Microvilli on the cell surface
Function of microvilli
Increase surface area to enhance nutrient absorption from the intestine
Intestinal Epithelial Cell
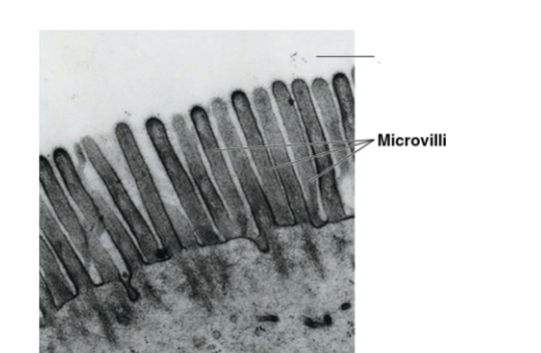
Microvilli
How do many cells move through the cytoplasm
diffusion
What is diffusion
The unassisted movement of a substance from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
As cell size increases what happens to molecular concentration
it falls
As cell size increases what happens to reaction rates
they slow down
What happens when the same amount of juice (macromolecules) is present, but the cell size increases
molecular concentration falls/ decreases
reaction slows
Prokaryotic DNA
Organized as a nucleoid, some bacteria also contain plasmids
Plasma membrane (prokaryotes)
Controls transport in and out of the cell
Prokaryotic cell walls
Differ among bacteria (Gram-positive vs. Gram-negative)
Other common prokaryotic structures
Ribosomes, pilus, flagellum
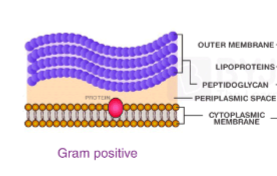
Gram-positive cell wall
Thick peptidoglycan layer, no outer membrane
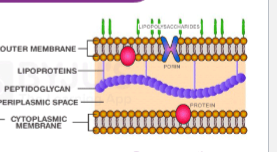
Gram-negative cell wall
Thin peptidoglycan layer, has an outer membrane with lipoproteins and porins
Gram positive cell wall image
Gram Negative cell wall
What does cytoplasmic streaming help deal with
cell size
cytoplasmic streaming (cyclosis in plants)
moves cytoplasmic contents actively
Vesicle transport
Molecules are moved through cell in vesicles along protein fibers via motor proteins
Role of organelles in large cells
Allow localized concentration of molecules for specialized cellular functions
eukaryotic cells are
plants and animal cells
Eukaryotic cells are structurally
complex
All eukaryotic cells typically have
a plasma membrane
a nucleus
membrane-bound organelles
cytosol
cytoskeleton
Cytosol is interlaced by a
cytoskeleton
The extracellular matrix and cell walls are - the plasma membrane
outside
Extracellular matrix provides
support
Main components of ECM (animal cells)
Collagen fibrils and proteoglycans
Cell walls (plants & fungi)
Extracellular structures composed mainly of cellulose microfibrils
Cell walls in bacteria
Mainly composed of peptidoglycans
General role of extracellular structures
Provide physical support to cells
Plasma membrane
Defines cell boundaries and retains cell contents
Structure of plasma membrane
Lipid bilayer with membrane proteins suspended in it
Orientation of membrane proteins
Hydrophobic regions face bilayer interior, hydrophilic regions protrude inside or outside the cell
Glycoproteins in plasma membrane
Membrane proteins with carbohydrate side chains attached on the external side
Function of plasma membrane
Regulates interactions between inside and outside of the cell
Cytoskeleton
An interconnected 3D network of protein structures in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells
Main functions of the cytoskeleton
Provides structure to cells, performs mechanical functions, mediates transport
Importance of cytoskeleton
Organizes cytoplasm and supports intracellular movement
Which type of cell does NOT have a cell wall?
Animal cell
Endomembrane system
Network of organelles that synthesize, modify, and transport proteins
Main role of endomembrane system
Synthesizes proteins for organelles, membranes, or secretion
How proteins are transported
Packaged into small membrane-bound vesicles for delivery
Organelles of endomembrane system
Endoplasmic Reticulum (smooth and rough), Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Largest organelle in the cell, major site of synthesis and transport
Functions of ER
Protein synthesis & transport, protein folding, lipid & steroid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, calcium storage
Rough ER
Studded with ribosomes, specializes in protein synthesis
Smooth ER
Lacks ribosomes, specializes in lipid/steroid synthesis and calcium storage
Role of ribosomes in ER
Involved in protein synthesis on rough ER
Smooth ER
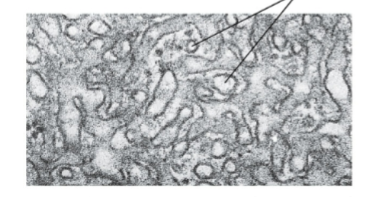
Rough ER
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis, more numerous than most other intracellular structures
Where ribosomes are found
In all cells (bacteria, archaea, eukaryotes) with differences in size and composition
Ribosomal RNA
Each cell type has its own unique type of rRNA
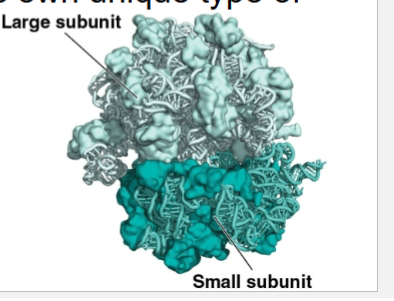
Ribosome structure
Composed of a large subunit and a small subunit
Ribosomal RNA image
Golgi apparatus
Organelle involved in modifying, packaging, and transporting proteins and lipids
Main functions of Golgi
Trafficking, processing, and sorting of newly synthesized membrane and secretory proteins and lipids
Structure of Golgi
Consists of stacks of flattened membranes (Golgi stack) with vesicles forming and budding off
Role of vesicles in Golgi
Carry processed proteins and lipids to their destinations in the cell or outside