Treatment for Diabetes
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcard set is only half of lecture slides
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
What are the goals of therapy?
reduce risk of micro and macro-vascular disease complications
ameliorate symptoms
reduce mortality
improve quality of life
What are microvascular complications of diabetes vs macrovascular complications
Microvascular complications
retinopathy, nephropathy, neuropathy
Macrovascular complications
CV disease (MI, stroke)
Which target tissues have an increase in peripheral glucose uptake?
adipose tissue
skeletal tissue
Which target tissue has an increase in insulin secretion?
pancreas
Which target tissue has a decreased glucose reabsorption?
Kidney
Which target tissue has a decreased glucose introduction?
liver
which target tissue has a decreased glucose absorption?
Intestines
What are the rapid acting insulins?
(GAL)
Glulisine (Apidra)
Aspart (Novolog)
Lispro (Humolog)
What are the short acting insulins? (8 hours)
Humalin R
Novolin R
R = regular
What are the intermediate acting insulins? (12 hours)
Humalin NPH
Novolin NPH
N = neutral
What are the long acting insulins?
Glargine (Lantus, Basaglar, Tojueo)
Detemir (Levemir)
L = long
Which insulin is ultra long acting up to 48 hours?
Tresiba (degludec)
____ provides the basal rate
____ covers glucose from a meal
Long acting insulin
rapid acting (GAL)
What are the pros and cons of using the basal/bolus regimen?
Pros
Mimics what body does naturally
provides ideal coverage
easily adjusted
Con
multiple shots
$$$
What are the 2 modified insulin regimens?
Intermediate acting and rapid acting (70/30)
Sliding scale
Which insulin option regimen has:
Pros: less injections, cheaper
Cons: difficult to individualize, lunch is not covered
Intermediate acting and rapid acting (70/30)
Which insulin option regimen has:
Pros: individualized doses
Cons: requires significant pt education (best for T1D)
sliding scale
What is the sliding scale regimen for insulin?
The sliding scale regimen for insulin involves adjusting insulin doses based on blood glucose levels at specific times of day.
Have to be able to count carbs and administer insulin
When would you expect to see a intermediate acting regimen?
inability to afford traditional basal/bolus
What is Afrezza?
Rapid acting inhaled insulin
fixed dose cartridges and multiple are needed to provide sufficient insulin coverage
Which insulin has a BBW for acute bronchospasm in chronic lung disease pts (asthma, COPD) and hypoglycemia?
Afrezza`
What are the ADE of Insulin?
hypoglycemia MC)
weight gain
injection site rnx
lipodystrophy (at site of injection)
What are the sx of hypoglycemia?
shaky
fast HR
sweaty
dizzy
anxious
hungry
blurred vision
weak or tired
HA
nervous or upset
Check your BG, eat to increase sugar, check again
oral glucose normally results in a higher release of insulin than when an IV glucose load is delivered is known as the _____
incretin effect
Incretin effect occurs in response to a glucose load the _____ releases
a. liver
b. adipose tissue
c. gut
d. skeletal muscle
c. gut
_____ is responsible for 60-70% of post-prandial insulin secretion
incretin response
T/F: the incretin response is significantly lower in type 2 diabetics
true
What are examples of drugs that produce the incretin effect?
GLP-1
GIP
which drug has the MOA of:
improving glucose dependent insulin secretion
slow gastric emptying
enhance satiety (reducing food intake)
decrease postprandial glucose secretion
promote beta cell proliferation = increase in insulin secretion from pancreas
GLP-1 analogs
How are GLP-1 Analogs administered?
SubQ
What are the GLP-1 Analog drugs and which are used FDA approved for diabetes?
Exenatide (Byetta)
Exendatide (Bydureon)
Liraglutide (Victoza, Saxenda)
Dulaglutide (Trulicity)
Semaglutide (Ozempic, Ryblesus, Wegovy
FDA approved for diabetes: Victoza, Trulicity, Ozempic, Wegovy
Which GLP-1 Analog is FDA approved for weight loss?
Saxenda
Wha are the ADE of GLP-1 Analogs?
N/V/D
Risk of pancreatitis - discontinue immediately or when abd pain is experienced
which diabetic drug has a BBW for thyroid C-cell tumors
not confirmed in rats
GLP-1 Analogs
Why should GLP-1 analogs be avoided in patients with diabetic gastroparesis?
They can delay gastric emptying, worsening symptoms.
Can lead to impaction
If a patient is placed on Insulin glargine + lixisenatide (Soliqua) or Insulin degludec + liraglutide (Xultophy),
What combination of diabetic drugs is this?
what would be their future regimen?
Why isn’t this regimen recommended for all patients?
GLP-1 and long acting insulin
discontinue therapy with basal and GLP-1 prior to initiation; dose once daily
regimen may increase risk of hypoglycemia or weight gain; not suitable for all patients.
Tirzepatide (Mounjaro and Zepbound) are examples of which combination of drugs?
GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonists (glucose dependent polypeptide)
Which drug group has an MOA of:
increase insulin sensitivity
increase insulin secretion
decrease glucagon secretion
slows gastric emptying
GLP-1 + GIP (Tirzepatide)
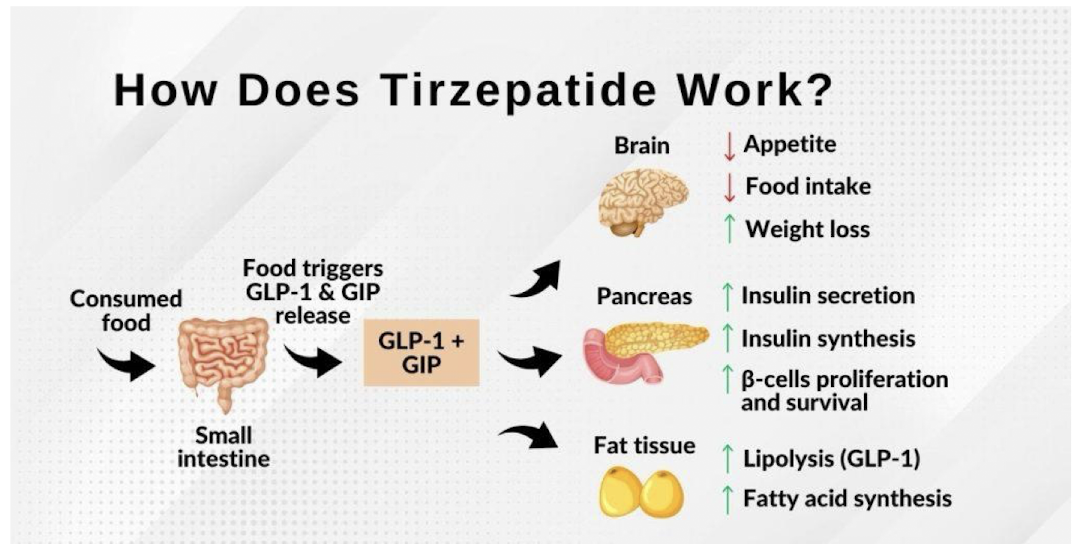
What is the mechanism of Tirzepatide?
When food is consumed, it will enter the small intestine and trigger GLP-1 and GIP release leading to effects on the brain, pancreas, and fat tissue
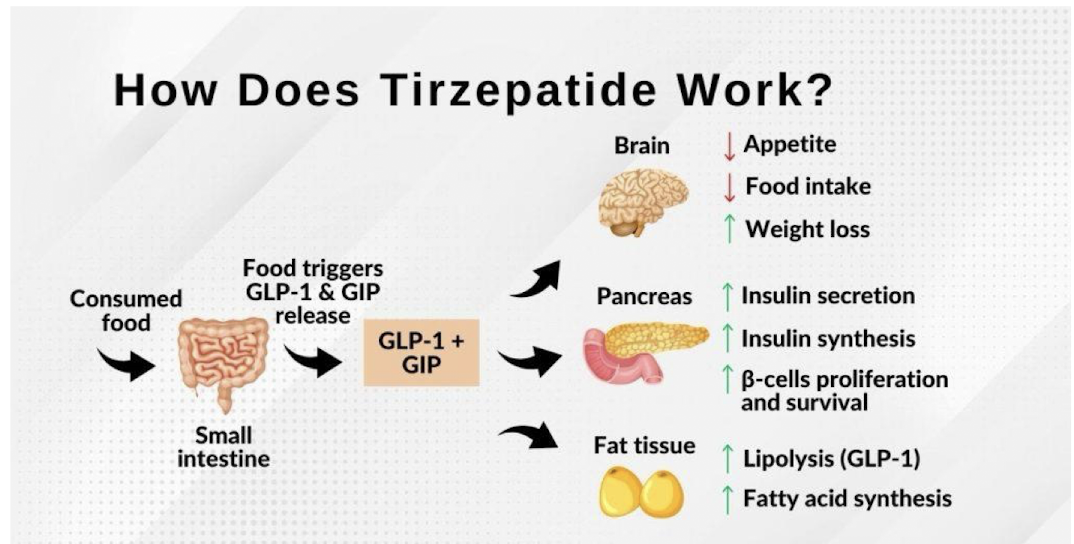
How does Tirzepatide impact fat tissue?
increase in lipolysis (GLP-1)
fatty acid synthesis
Why shouldn’t GLP-1s be used on T1D?
These patients are already underweight and don’t need to effects of the drug
What is Amylin?
hormone co-secreted with insulin
delays gastric emptying
decreases post-prandial glucogon secretion
improves satiety
What is the synthetic amylin analog?
Pramlintide (Symlin)
When is Pramlintide (symlin) used?
Adjunct to mealtime insulin in patients with T1D and T2D
Administer subQ immediately before meals
Meal-time insulin should be reduced by 50% if Pramlintide is added
Which drug has the BBW when combined with meal-time insulin and/or when used in T1D leading to hypoglycemia?
Pramlintide
What are ADE of Pramlintide?
hypoglycemia
N/V
Anorexia - not wanting to eat
injection site rxn
avoided in pts with diabetic gastroparesis
Which of the following is a basal insulin?
a. Pramlintide
b. Aspart
c. Lispro
d. Glargine
d. Glargine
Which classes can cause weight gain?
a. GLP-1/GIP
b. long-acting insulin
c. amilyn analog
d. short-acting insulin
e. NPH
b. long-acting insulin
d. short-acting insulin
e. NPH (intermediate acting - Humalin and Novolin N)