12- Health Literacy
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Personal health literacy
the degree to which individuals have the ability to find, understand, and use information and services to inform health-related decisions and actions for themselves and others
Organizational health literacy
the degree to which organizations equitably enable individuals to find, understand, and use information and services to inform health-related decisions and actions for themselves and others
health literacy
____________ occurs when health information and services created for patients and the public match with their capacity to find, understand, and use them
Social-Ecological Model
Examines health literacy
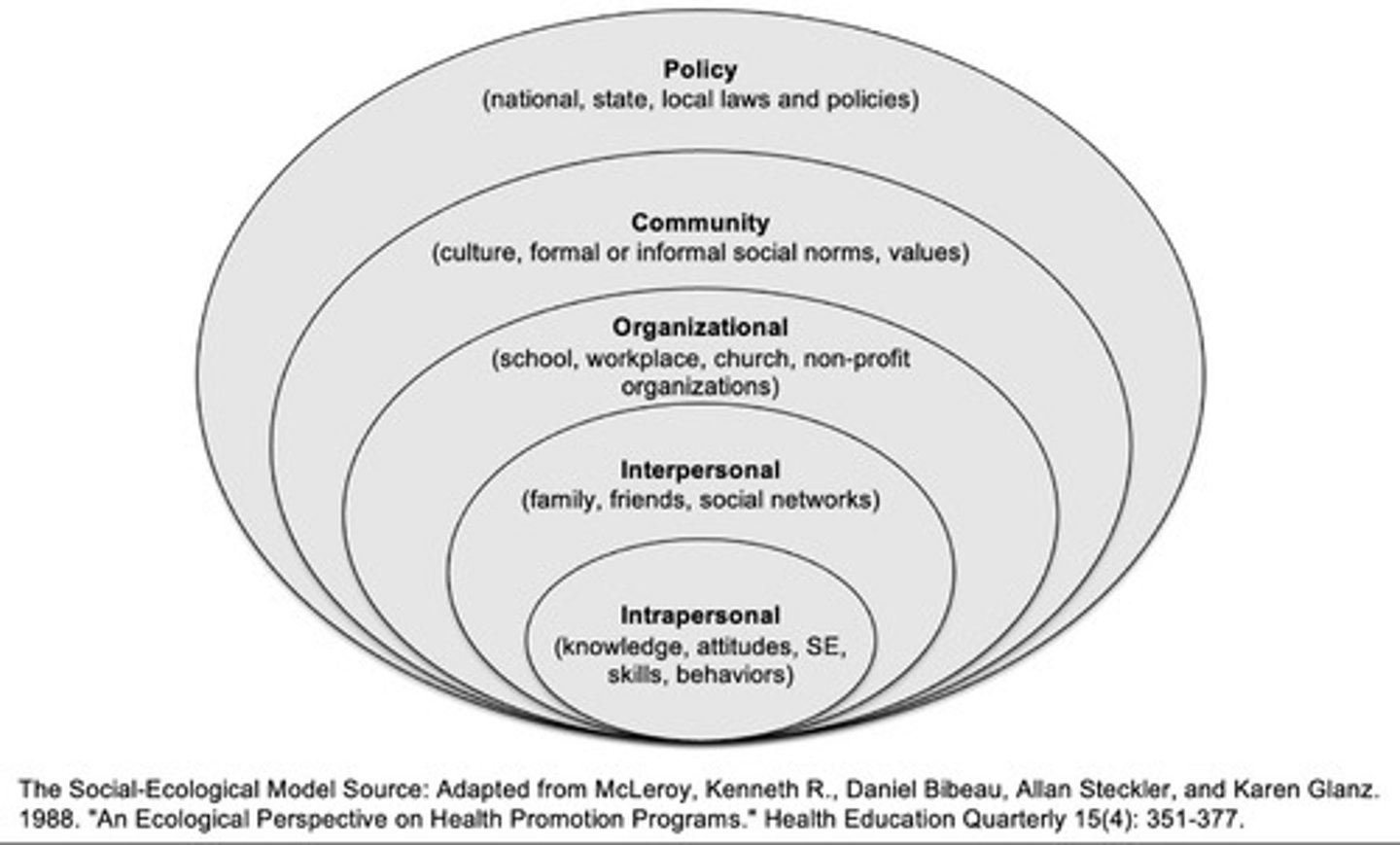
Intrapersonal, Interpersonal, Organizational, Community level, Policy
What kind of factors impact health literacy?
Intrapersonal
A person’s knowledge, attitudes, behavior, and self-efficacy
Interpersonal
Who an individual surrounds themselves with (social identity, support networks, social roles can determine what you think about health issues, impacting our actions)
Organizational health literacy
The study and evaluation of what organizations do to make it easier (or more difficult) for people to understand heatlth information, navigate the health care system, engage in the healthcare process, and manage health
Community level
Where people look for information (how easy/difficult, values/beliefs of a community)
Policy
out of the factors that impact health literacy, ______ is the most effective broadly
Health literacy in the healthcare context
-accessing health information
-navigating the healthcare system
-engaging in self-care and disease management
Health literacy universal precautions
A universal precautions approach means treating all people as if they are at risk of not understanding health information
health literacy universal precautions
reasons to use _______________
-Limited health literacy is common and hard to recognize
-Concerns about asking questions
-Shame around not understanding
-It's hard to think clearly when sick, anxious, or afraid
Plain language
Communication your audience can understand the first time they read it
Plain language strategies
1) organize content (put the most important message first)
2) choose words and numbers carefully
3) keeping things short
4) using pronouns (instead of "anyone, their", use "your, you")
5) make information easy to find and understand (white space, bullets)
false
Limited health literacy is uncommon but heard to recognize, T/F?
true
Plain language reduces miscommunication, T/F?
Jargon
Latin and other specialized vocab that insiders use among themselves; language specifics to profession or group
Types of jargon
-Unnecessarily complex, technical, or lesser-known language
-Latin, Greek, or other foreign words or abbreviations
-Words that have different meanings depending on context
jargon
When _________ is common, patients, clients, caregivers, and the public won't be able to:
-Follow verbal instructions
-listen to and understand recommendations
-explain what they heard in their own words
-read print education materials
-share accurate info
translation, interpretation
Jargon interferes with ________ & ____________
-Certified translators and interpreters must adhere to the
original language
-When professionals use jargon, translators and interpreters must use jargon too
-Jargon creates the same comprehension problems across
languages
Plain language numbers
• Whole numbers are best
• Avoid decimals, fractions, and percentages
• Make probabilities concrete
words, numbers, images
-Recommendation: use _____, ______, ______ to communicating & explaining risks and to help grasp concepts
-images can also contain jargon
false
Short words (one and two syllables) are always the best choice for clarity, T/F?
any type of communication
Jargon applies to:
a) Spoken words and phrases
b) Spoken and written words and phrases
c) Spoken and written words, phrases and numbers
d) Any type of communication
Speech speed, How long a person talks before stopping, How often people take turns when talking
factors of communication
Teach-back method defined
Evidence-a seed way to confirm you have explained things in a way the listener understands
Undetected communication barriers and misunderstanding
Allowing people explain information in their own words reduces:
pros of using teach-back
1) Improves communication and engagement
2) Improves disease-specific knowledge, understanding, self-efficacy, and adherence
3) Reduces medication errors and mistakes with care instructions
4) Decreases call backs and cancelled appts
5) *Improves patient satisfaction and health outcomes
Using open-ended questions, Keep it conversational and shame-free
Using teach-back effectively includes:
What to do when misunderstanding persists
-Rephrase and explain again
-Include a family member
-Ask another team member to explain
-Take a break
Implementing teach-back in organizations
Start with one person a day
Plan your approach
Use handouts
Share stories
Practice
teach-back method
method for providers to ensure they explained info in a way the patient/client understands
A) Give instructions using plain language
C) Give information that focuses on what the patient or client needs to do
Which of the following are elements of effective teaching-back?
a) Give instructions using plain language.
b) Use non-shaming, closed-ended questions.
c) Give information that focuses on what the patient or client needs to do.
d) Ask patients or clients to repeat your instructions verbatim to ensure they understand.