Ch 23 Pt 2: Protists
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Stramenopiles
Diatoms
Brown Algae
Oomycetes
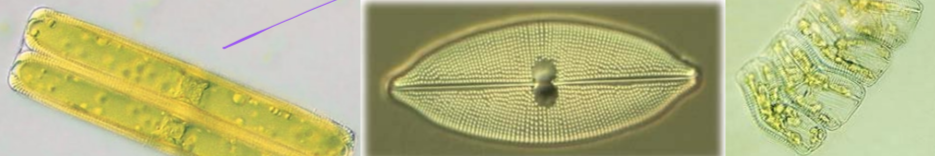
Diatoms
stramenopiles
unicellular phytoplankton (algae)
key primary producers
w/ yellow and brown accessory pigments
silica walls, like a petri dish
“diatomaceous earth” deposits
no flagellum except in gamete
what color pigments do diatoms have?
yellow, brown, and green
are diatoms unicellular or multicellular?
unicellular phytoplankton
what are the walls of diatoms made of?
siliica
diatoms don’t have flagellum except where?
in the gamete
what are the fossilized remains of diatoms used in?
water filters
diatoms: storing energy as oils help them _____
float
true or false. diatoms are heteroautotrophs.
false. diatoms are photoautotrophs.
diatoms: overview of phototrophs (autotrophs)
all with chloroplasts containing chlorophyll a
accessory pigments vary
some chloroplasts: secondary endosymbiosis (of red algae)
brown algae
stramenopiles
multicellular, mostly marine “seaweeds” (some edible - kelp)
major primary producers
w/ brownish accessory pigments w/ chlorophyll
large thallose form
cell wall w/ cellulose and algin

brown algae: thallus
blade
stipe
holdfast
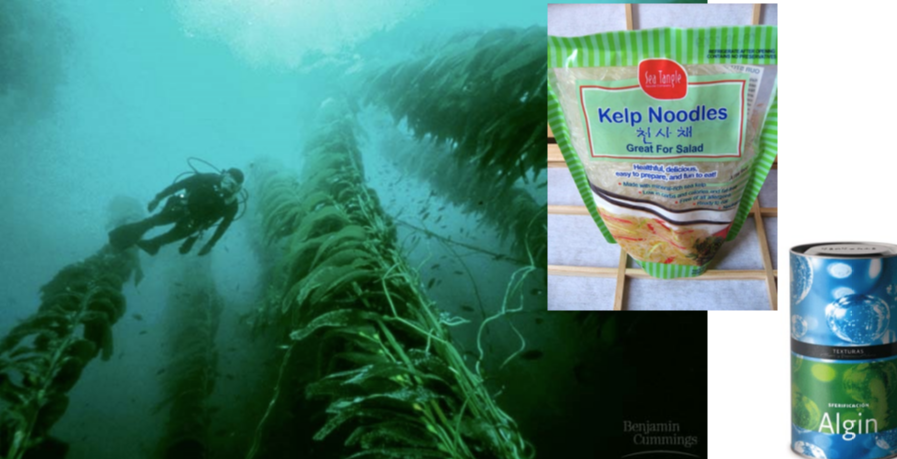

brown algae ex: kelp
Laminaria and other species
humans eat it
algin used as commercial food thickener
oomycetes
stramenopiles
filamentous, multinucleate, absorptive heterotrophs; some infest plants
superficially resemble fungi
but cell walls w/ cellulose, not chitin
filamentous growth (mycelia) is diploid
spores have flagella

oomycetes ex: Phytophthora infestans
“potato late blight” - a plant parasite: caused Irish famine
alveolates
dinoflagellates
apicomplexans
ciliates
true or false. all alveolates have membrane-enclosed sac beneath the cell membrane called alveolus.
true
what is alveolus speculated to aid protists with?
osmoregulation
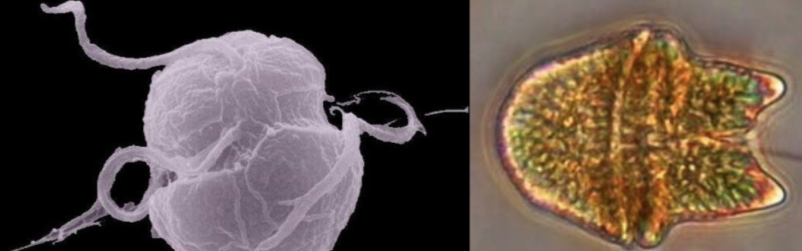
dinoflagellates
alveolates
unicellular aquatic heterotrophs or phytoplankton w/ reddish accessory pigments
pair of flagella in perpendicular grooves
some are bioluminescent
many are photosynthetic mutualists within corals
dinoflagellates ex. Pfiesteria
chemoheterotroph, causes lesions on fish
dinoflagellates ex. Akashiwo
photoautotroph: likely that chloroplasts are from secondary endosymbiosis of a red algae
true or false. blooms of species of Dinoflagellates kill fish or create toxic “red tides”
true
dinoflagellates ex. Karena brevis
brevetoxins, neurotoxic, causes a “red tide”
how are some dinoflagellates photoysnthetic?
provide products of photosynthesis (glucose + O2) to corals
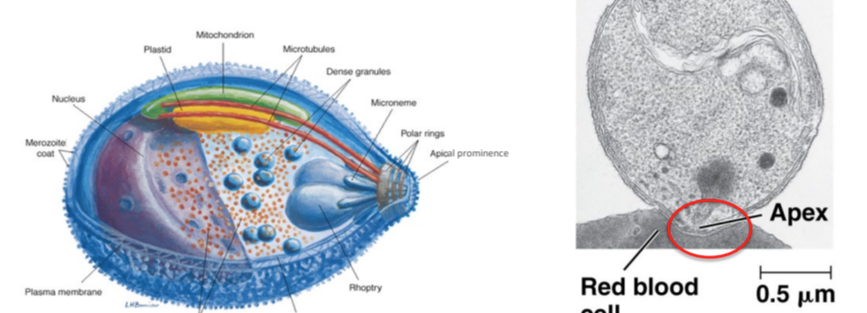
ampicomplexans
alveolates
unicellular parasites of animals; no cell wall
apical complex helps them enter host cells
complex life cycles:
requires more than one host
multiple forms
apicomplexans ex. Plasmodium
causes malaria, carried by mosquitos (Anopheles)
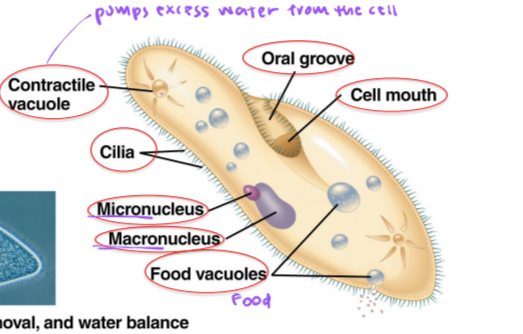
ciliates
alveolates
unicellular ingestive heterotrophs w/ no cell wall; aquatic
cilia for feeding and locomotion
animal-like in function
ciliates ex.
Paramecium
macronucleus
asexual binary fission
micronucleus
sexual reproduction
contractile vacuole
pumps excess water from the cell