Exam 4 Medchem 2 v.10 FINAL
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
N2O
Nitrous Oxide
Class: Gaseous anesthetic
MOA: disrupts protein/lipid membranes
Clinical Use: Analgesia in combination
Onset/Duration: Very rapid onset/recovery
MAC: 104% (very weak)
BGPC: 0.47 (fast recovery)
Not muscle Relaxing
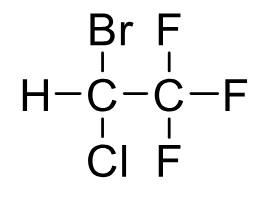
Halothane
Class: Volatile anesthetic
Clinical Use: General anesthesia
MAC: 0.74% (high potency)
BGPC: 2.5 (rapid induction, slower recovery)
Metabolism: ~20% → TFA (toxic metabolite), Cl⁻, Br⁻; hepatotoxicity
Side Effects: Cardiac sensitization (arrhythmia), liver/kidney damage
BP 50.2 C
Muscle Relaxing
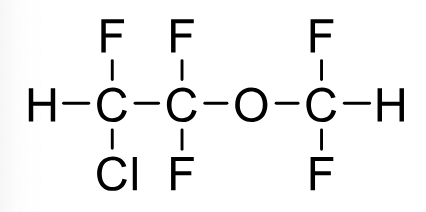
Enflurane
Class: Volatile anesthetic
Clinical Use: General anesthesia
MAC: 1.7%
BGPC: 1.9
Metabolism: ~5%; toxic metabolites
2nd highest F toxicty
BP 56,5 C
Muscle relaxing
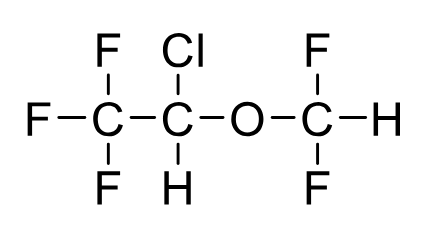
Isoflurane
Class: Volatile anesthetic
Clinical Use: General anesthesia
MAC: 1.17%
BGPC: 1.4
Metabolism: 0.2%
SM relaxation: Yes
BP 48.5C
Commonly used
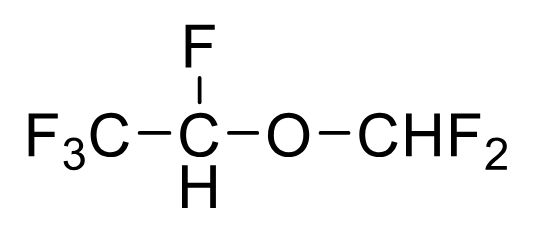
Desflurane
Class: Volatile anesthetic
Clinical Use: maintenance of anesthesia in combo
outpatient surgery due to rapid recovery
MAC: 6% (least potent)
BGPC: 0.42 (fastest recovery)
Metabolism: <0.02%
Least F toxicity
Notes: Airway irritant, requires special packaging due to BP
BP 23.5 C
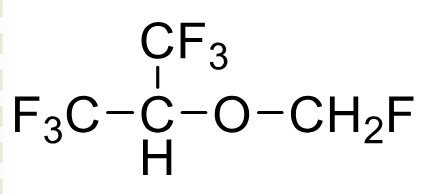
Sevoflurane
Class: Volatile anesthetic
Clinical Use: Induction/Maintenance of Anesthesia
MAC: 2.05%
BGPC: 0.68
Rapid recovery from anesthesia
Metabolism: ~5%; fluoride release (renal risk)
Highest F toxicty
Notes: Pleasant taste, low airway irritation
BP 58.6 C

Cyclopropane
Clinical Use: Historical general anesthesic
MAC: 17.5%
SM relaxation: Yes
Safety: Explosive with O₂
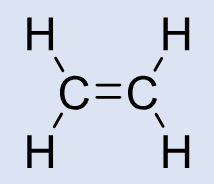
Ethylene
Clinical Use: Historical general anesthesia
MAC: Higher than cyclopropane (less potent)
Safety: Explosive with O₂
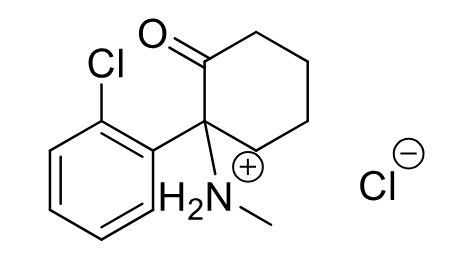
Ketamine C-III
Class: NMDA receptor antagonist
MOA: Non-competitive NMDA antagonist
Clinical Use: dissociative anesthetic, causes amnesia
Onset/Duration: Rapid onset, short duration
SM relaxation: No
Side Effects: Hallucinations, emergence reactions
Formulations: IV
Metabolism: dealkylation to ACTIVE metabolite
S > R enantiomer activity (racemic mix)
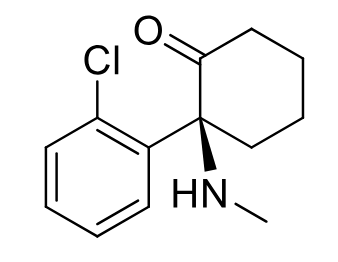
Esketamine C-III
Class: NMDA receptor antagonist
MOA: Non-competitive NMDA antagonist
Clinical Use: Treatment-resistant depression
Onset: Fast (intranasal)
Admin: Under healthcare supervision only (2x per week)
Formulations: Intranasal only
S enantiomer only
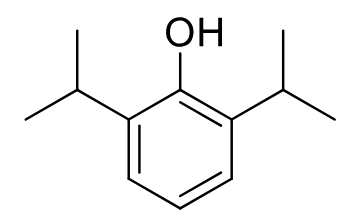
Propofol
Class: IV anesthetic
MOA: Enhance GABA transmission
Clinical Use: Induction, maintenance, of anesthesia + ICU
Fast onset: ~40 sec, 2-24hr duration
Rapid recovery from anesthesia
Muscle Relaxing
Metabolism: Hepatic glucuronidation/sulfation
Properties: Anti-emetic, lipid emulsion, non-controlled
Formulations: IV
Pain in inj site
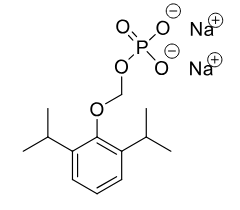
Fospropofol C-IV
Class: IV anesthetic prodrug
MOA: Prodrug of propofol
Onset: 4–8 min
Properties: Water-soluble, requires alkaline phosphatase
Discontinued
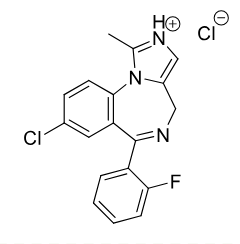
Midazolam C-IV
Class: Benzodiazepine
Clinical Use: pre op Sedation (Muscle Relaxing)
induction of anesthesia,
anxiety,
seizures
Onset: IV ~5 min, 10-20 min IM
Long recovery time for PTs
amnesia affect
Formulations: IV, PO, IM
Metabolism: hydroxylation ACTIVE metabolite
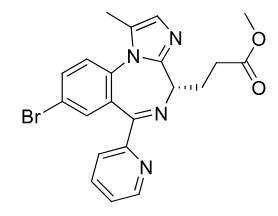
Remimazolam C-IV
Class: Softdrug benzodiazepine
gives predictable PK
MOA: GABA-A potentiation
Clinical Use: Short procedures, procedural sedation
Rapid Onset , Short duration
Muscle Relaxing
Metabolism: Tissue esterases create charged carbolic acids which prevents CNS penetration
Formulations: IV
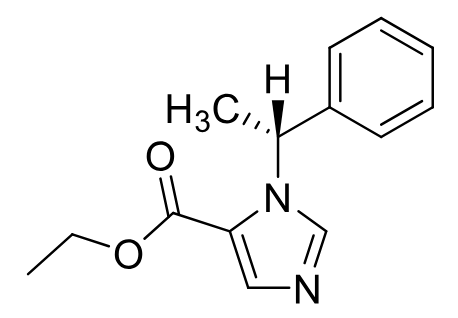
Etomidate
Class: IV anesthetic (imidazole)
MOA: GABA-A receptor enhancement
Clinical Use: induction of general anesthesia for short procedures
Rapid onset, short duration: 3–5 min
Notes: No analgesia, nausea/vomiting common, No Muscle relaxing
Formulations: IV
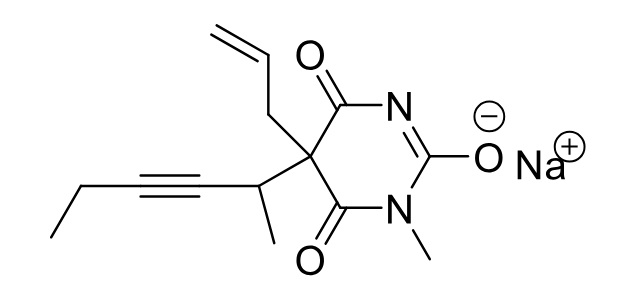
Methohexital C-IV
Class: Ultra-short Barbiturate
Clinical Use: Induction of anesthesia
Rapid onset, short duration: 20 min
No Muscle Relaxing
Formulations: IV
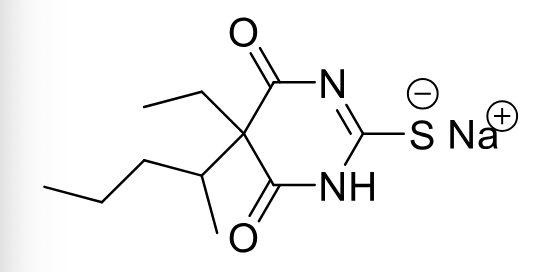
Thiopental C-III
Class: Ultra-short Barbiturate
MOA: GABA-A agonist
Clinical Use: Induction of anestheisa, (now propofol is favored)
Duration: Ultra-short (lipophilic)
can have long term sedating effect
Formulations: IV
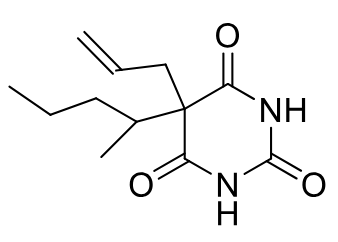
Secobarbital (C-II)
Class: Short-acting barbiturate
MOA: GABA-A receptor agonist
Clinical Use: Hypnotic, preanesthetic
Onset/Duration: Onset 10–15 minutes; Duration 3–4 hours
Metabolism: Epoxide formation → hydrolysis deactivates it
Formulation: PO
Notes: Branching and unsaturation promote metabolism; epoxide may covalently bind CYP450; two hydroxyl groups increase water solubility
Pentobarbital (CII)
Class: Short-acting barbiturate
MOA: Enhances GABA-A receptor activity (↑ Cl⁻ influx)
Clinical Use: Hypnotic and preanesthetic
Onset/Duration: 10–15 min onset, 3–4 hr duration
Metabolism: Hepatic; includes oxidation and glucuronidation
Formulation: PO/IV
Notes: One chiral center (racemic)
Amobarbital (CII)
Class: Intermediate-acting barbiturate
MOA: GABA-A receptor enhancer
Clinical Use: Sedative-hypnotic
Onset/Duration: 45–60 min onset, 6–8 hr duration
Metabolism: Hepatic oxidation/conjugation
Formulation: PO/IV
Notes: no chiral center due to symmetry
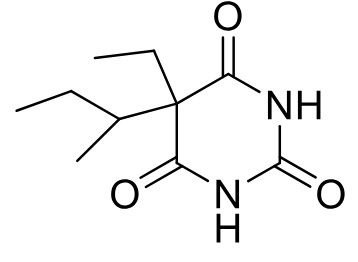
Butabarbital C-III
Class: Intermediate-acting barbiturate
MOA: GABA-A receptor enhancer
Clinical Use: Sedative-hypnotic
Onset/Duration: 45–60 min onset, 6–8 hr duration
Formulation: PO
Phenobarbital (CIV)
Class: Long-acting barbiturate
MOA: GABA-A agonist (↑ Cl⁻ channel open duration)
Clinical Use: sedative hypnotic + Grand mal seizure
Onset/Duration: 30–60+ min onset, 10–16 hr duration; half-life 53–118 hrs
Metabolism: oxidation, glucuronidation at 3-N (preferrs S enantiomer at 6.8 S/R ratio) sulfation
Formulation: PO/IV
Notes: Benzene ring allows conjugation;
Chloral Hydrate (CIV)
Class: Old (1832) sedative-hypnotic
MOA:(GABA-A enhancer)
Use: Sedation, helping sleep, especially in children
Favored formation from trichloracetaldehyde
Gemdiol is reduced to active Metabolite
Synergism CNS depression with alcohol
also prevents alcohol withdrawl
misued as roofie drug
Issues: Bitter taste (given with fruit juice), GI irritation
Formulations: PO
Diphenhydramine
Class: 1st-gen antihistamine
MOA: H1 antagonist, anticholinergic
Clinical Use: Allergy, insomnia (structurally non specific)
Controlled in Zambia
Not used in children less than 6 y/9
Formulations: PO, IV
Zolpidem Tartrate (Ambien) (CIV)
Class: Z-drug
MOA: BZT1 (GABA-A α1) receptor agonist
Selective for type 1 receptor
Clinical Use: Short-term insomnia, no go pill for military
Half-life: 2 hrs
extensively metabolized (hydroxilation, oxidation)
Non chiral
Formulations: 2:1 Salt with Tartrate PO (IR, ER)
Zaleplon (CIV)
Class: Z-drug
MOA: BZT1 receptor agonist
Clinical Use: Sleep-onset insomnia
Half-life: ~1 hr
Metabolism: Extensively metabolized, hydroxylation, dealkylation
PO
Eszopiclone (CIV)
Class: Z-drug
MOA: selective BZT1 receptor agonist
Clinical Use: Sleep onset + maintenance
Metabolism: demethylation of N gives ACTIVE metabolite (weaker)
Formulations: PO (once-daily oral)
S enantiomer
Dexmedetomidine
Class: sedative hypnotic
MOA: alpha a2 adrenergic agonist
Clinical Use: ICU sedation, adjunct to anesthesia
Metabolism: Extensive metabolism, oxidation, glucuronidation
Formulations: IV
Onset/Duration: Onset 5–10 min, duration 1–2 hrsNotes: More sedative, less hypotensive than clonidine
S enantiomer
Ramelteon
Class: Melatonin receptor agonist
MOA: MT1 (sleep onset) and MT2 (circadian rhythm) agonist
Use: Chronic insomnia (sleep onset)
Half-life: 1–2.6 hrs
Metabolism: hydroxylation → ACTIVE metabolite (10× conc, 1/10 activity)
high first pass OBA, much lower 2nd pass
Formulations: PO (once-daily)
Tasimelteon
Class: Melatonin receptor agonist
MOA: MT1 and MT2 agonist (MT2 Selective)
Use: Non-24-hour sleep-wake disorder (blind patients), Smith-Magenis syndrome, night time sleep disturbances
Half-life: ~1.3 hrs
R, R enantiomer
Formulations: PO (once-daily) Taken WITHOUT food
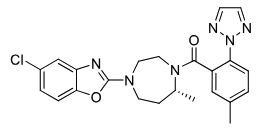
Suvorexant (CIV)
Class: Orexin receptor antagonist (DORA)
MOA: OX1R & OX2R antagonist
Use: Insomnia (onset + maintenance)
Half-life: ~12 hrs
Notes: Take 30 min before bed, not with food
30 min before sleep
Negative food effect, take WITHOUT food
Formulations: PO (once-daily), no generic available
R enantiomer
Daridorexant (CIV)
Class: DORA
MOA: Dual orexin antagonist
Use: non-first line tx Insomnia (for ≥7 hr sleep)
Half-life: ~8 hrs
Formulations: PO (once-daily) high cost, no generic
Lemborexant (CIV)
Class: DORA
MOA: Dual OX1R/OX2R blocker; stronger OX2R affinity
Use: Insomnia (sleep onset + maintenance)
30 min before bedtime
Half-life: 17–19 hrs (due to F)
Extensively Metabolized,
Negative food effect, take WITHOUT food
Formulations: PO (once-daily) high cost, no generic
Chlordiazepoxide (Librium) (C-IV)
Benzodiazepine
MOA: Type 1+2 BZ binding and enhancing of GABA binding
Use: Anxiety, alcohol withdrawal
Metabolism: dealkylation, hydrolysis, oxidation and reduction are all ACTIVE.
hydroxylation on phenol is INACTIVE
Formulations: PO, IM, IV
Diazepam (Valium) C-IV
Benzodiazepine
MOA: Type 1+2 BZ binding and enhancing of GABA binding
Use: Anxiety, seizures, muscle spasms, alcohol withdrawal
Metabolism: demethylation to ACTIVE → nordiazepam with longer (t½ ~200 hrs)
Hydroxylated to temazepan which is also active
Half-life: 60–72 hrs
Formulations: PO, IV, IM
Temazepam C-IV
Benzodiazepine
Use: Insomnia (preferred hypnotic)
Hydroxylated metabolite of diazepam
Half-life: 4–18 hrs
PO
Oxazepam C-IV
Benzodiazepine
Use: Anxiety, alcohol withdrawal
hydroxylated and demethylated metabolite of diazepam
Half-life: 6–8 hrs
PO
Clorazepate C-IV
Benzodiazepine
MOA: Type 1+2 BZ binding and enhancing of GABA binding
Use: Anxiety, alcohol withdrawal, seizures
Notes: Prodrug; decarboxylated in stomach → nordiazepam
Half-life: Long (~200 hrs)
PO
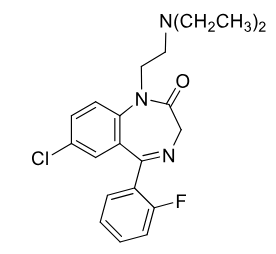
Flurazepam C-IV
Benzodiazepine
MOA: Type 1+2 BZ binding and enhancing of GABA binding
Notes: Prodrug; active N-desalkyl metabolite
Use: sedative hypnotic, Insomnia (maintains REM)
Half-life: 47–100 hrs
PO
Quazepam C-IV
Benzodiazepine
MOA: Type 1+2 BZ binding and enhancing of GABA binding
Use: Insomnia (frequent waking)
Metabolized by hydrolysis (removal) of sulfur to ACTIVE metabolite.
sulfur gives higher CNS pen (lipophilicity)
Half-life: 47–100 hrs
Lorazepam C-IV
Benzodiazepine
MOA: Type 1+2 BZ binding and enhancing of GABA binding
Use: Anxiety, seizures, delirium
Half-life: 10–20 hrs
Notes: Glucuronidated
Chlorines give higher lipophilicity
Formulations: PO, IV, IM
Alprazolam C-IV
Triazolobenzodiazepine
Use: Anxiety, panic disorder, agoraphobia
Dose: 0.25–2.5 mg TID
Metabolism: aHydroxylation gives ACTIVE metabolite, hydroxylation of phenol gives inactive
Formulations: PO
Estazolam C-IV
Triazolobenzodiazepine
Use: Insomnia
Dose: 1–2 mg at bedtime
weaker than alprazolam
Formulations: PO
Triazolam C-IV
Triazolobenzodiazepine
Use: Insomnia
Dose: 0.25 mg at bedtime
Notes: Highly potent (more than alprazolam), narrow therapeutic index (more sides)
Formulations: PO
Flumazenil
Class: GABA-A receptor antagonist
Use: Benzo OD reversal, anesthetic awakening
Metabolism: Ester hydrolysis
Half-life: 7–15 min (peripheral), 20–30 min (CNS), terminal 40–80 min
Notes: May precipitate seizures
Formulations: IV
Buspirone Hydrochloride
Class: Anxiolytic (non-BZD)
MOA: 5-HT1A partial agonist; D2 antagonist
Use: short term anxiety tx (non-sedating)
Metabolism: CYP3A4, becomes α2 antagonist
Formulations: PO
Gepirone Hydrochloride (Exxua)
MOA: 5-HT1A partial agonist; no D2 binding
Use: Major depressive disorder MDD (FDA approved 2023)
Formulations: PO
more potent than buspirone
Hydroxyzine
Class: H1 antihistamine (mild tranq)
MOA: H1 antagonist
Use: Anxiety, sedation, pruritus
Notes: Teratogenicity concern
Meprobamate (Miltown) (CIV)
MOA: GABA-A enhancer (exact binding unclear)
Use: Anxiety, sedative
Metabolism: hydroxylation→ inactive
Formulations: PO
NON chiral
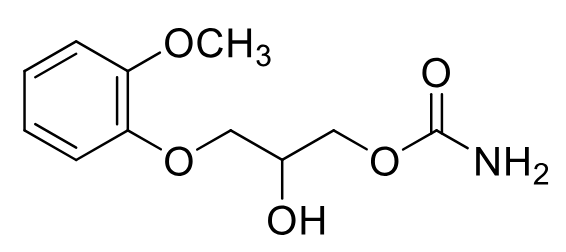
Methocarbomal (Robaxin)
Class: Centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant
Clinical Use: Relief painful musculoskeletal conditions; tetanus-induced spasm
Metabolism: not converted to guaifenesin although similar looking
has metabolically stable carbamate
with acetaminophen (Robaxacet),
ibuprofen (Robax Platinum),
aspirin (Robaxisal)
PO
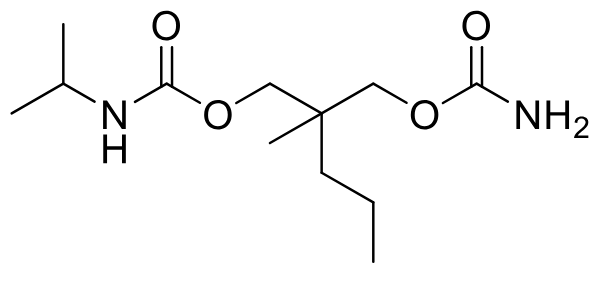
Carisoprodol (C-IV)
Class: Centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant
Clinical Use: Adjunct treatment for acute musculoskeletal conditions
Onset/Duration: Not specified
Metabolism: N-dealkylation of isopropyl gives active meprobamate (PRODRUG)
PO
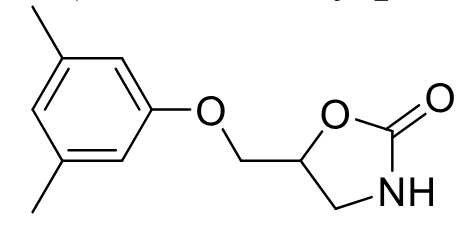
Metaxalone
Class: Centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant
MOA: Unknown
Clinical Use: Adjunct for acute musculoskeletal pain
Notes: Contains internal carbamate group
PO
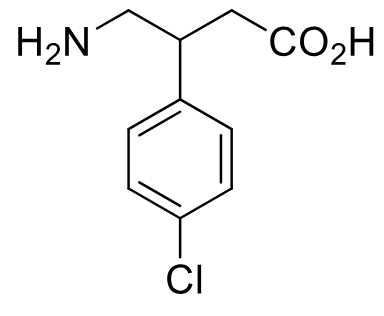
Baclofen
Class: Centrally acting antispasmodic
MOA: GABA-B receptor agonist (GABA analog)
Clinical Use: Spasticity due to MS and spinal cord trauma
Notes: Cl at para position confers resistance to metabolic hydroxylation
Eliminated unchanged
racemic mixture (chiral)
does not reduce muscle strength like other agents
less sedation than diazepam
PO
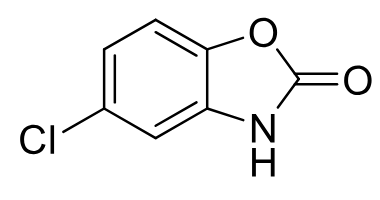
Chlorzoxazone
Class: Centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant
Clinical Use: Muscle spasms, strains, back pain
Notes: Contains carbamate
PO
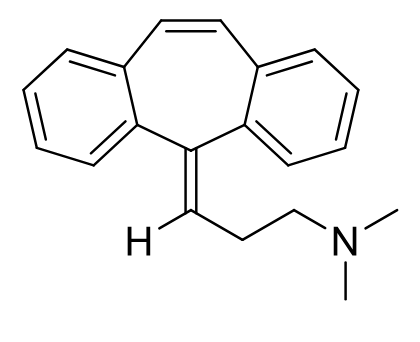
Cyclobenzaprine
Class: Centrally acting muscle relaxant (TCA analog)
Clinical Use: Skeletal muscle spasms
Onset/Duration: Long duration; available in once-daily formulations
Metabolism: (extensive) sulfated, glucuronidated, hydroxylated or demethylated (also epoxide formation)
without double bond = nortriptyline
PO
Dantrolene
Class: Peripherally acting muscle relaxant
MOA: Ryanodine receptor (RYR) antagonist → inhibits Ca²⁺ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Clinical Use: Spasticity from spinal cord injury, MS, cerebral palsy, malignant hyperthermia
Metabolism: oxidation of nitro group to hydroxy amine is carcinogen and hepatically toxic
muscle weakness
IV/PO
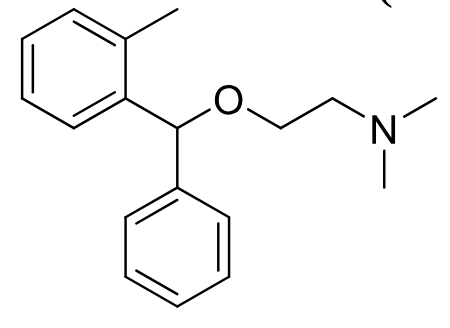
Orphenadrine
Class: Centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant
Clinical Use: Adjunct for acute musculoskeletal pain, leg cramps
Notes: Structural analog of diphenhydramine;
Sedative and anticholinergic effects
PO
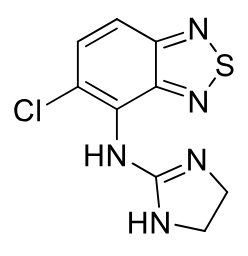
Tizanidine
Class: Centrally acting muscle relaxant
MOA: α2-adrenergic agonist, similar to clonidine
Clinical Use: Spasticity due to MS, spinal cord injury;
Extensively metabolized to inactive in liver
Notes: Structural analog of clonidine;
less BP effect, 1/10 to 1/50 th
more CNS sedation;
acts on spinal cord
PO
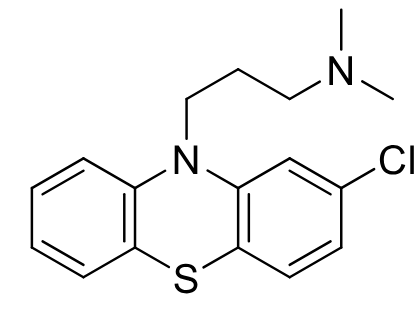
Chlorpromazine
Class:typical antipsychotic
Aliphatic Phenothiazine
MOA: D2 receptor antagonist
Use: antiemetic/antipsycotic
Metabolism: Oxidation of sulfur in air to→ sulfoxide/sulfone
can also be demethylated and hydroxylated
Cl blocks hydroxylation
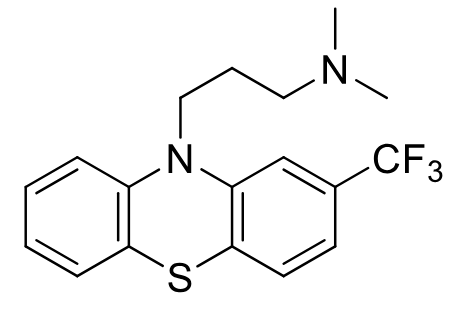
Triflupromazine
Class: Typical antipsychotic
Aliphatic Phenothiazine
MOA: D2 antagonist
Use: antiemetic/antipsycotic
Structure: Trifluoromethyl enhances potency (lipophilicity)
Oxidation of sulfur in air + hydroxylation and demethylation
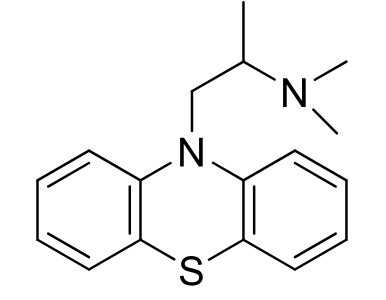
Promethazine
Aliphatic Phenothiazine
Use: antiemetic in motion sickness and post operative patients
low antipsychotic activity (~1/10 chlorpromazine)
Also anti histamine activity
Racemic mixture
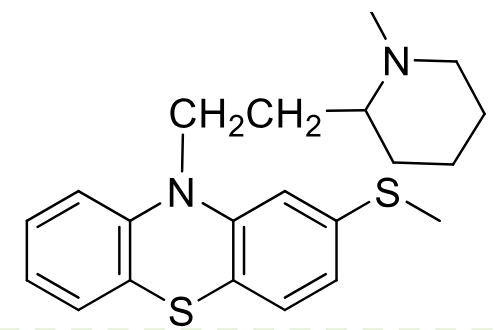
Thioridazine
Class: typical antipsychotic
Piperidine Phenothiazine
MOA: D2 antagonist
Use: 2nd line schizophrenia
weak antipsycotic
Metabolism: sulfide is oxidized sulfoxide (activex2), and then sulfone (more active x8)
Side Effect: QT prolongation
Oxidation of sulfur in air + hydroxylation and demethylation
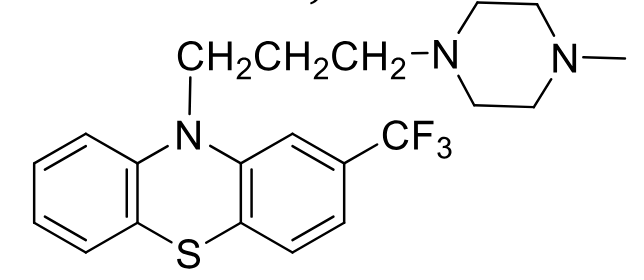
Trifluoperazine
Class: typical antipsychotic
piperazine phenothiazine
MOA: D2 antagonist
Use: Schizophrenia 2nd line, short-term anxiety
Side Effects: More EPS, less sedation
Oxidation of sulfur in air + hydroxylation and demethylation
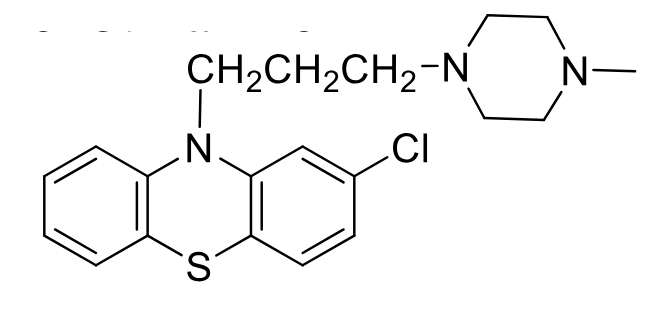
Prochlorperazine
Class: Typical antipsychotic
piperazine phenothiazine
MOA: D2 antagonist
Use: short term treatment of non psycotic anxiety, N/V
Oxidation of sulfur in air + hydroxylation and demethylation
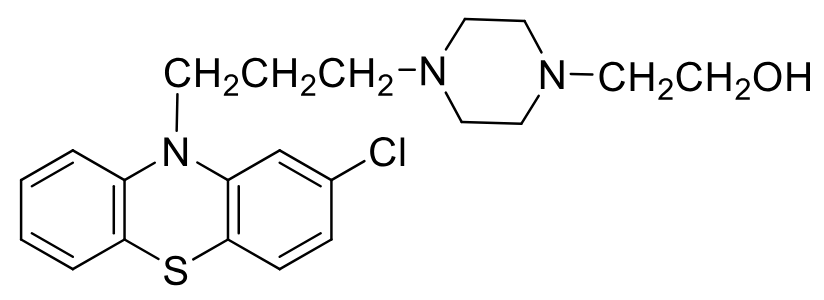
Perphenazine
Class: typical antipsycotic
Piperazine Ethanol Phenothiazine
MOA: D2 antagonist
Use: antipsycotic, N/V
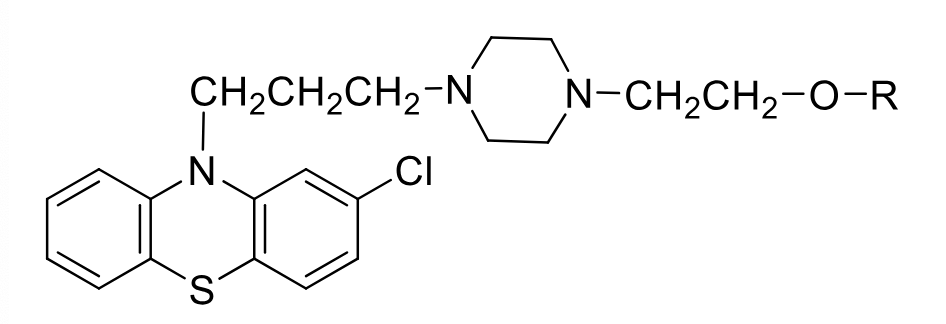
Fluphenazine
Class: typical antipsycotic
Piperazine Ethanol Phenothiazine
MOA: D2 antagonist
Use: antipsycotic + n/v
Formulations: 2 prodrugs available
enanthate IM every 2 weeks
decanoate IM/SubQ every 3-4 weeks
3-4x per day of oral
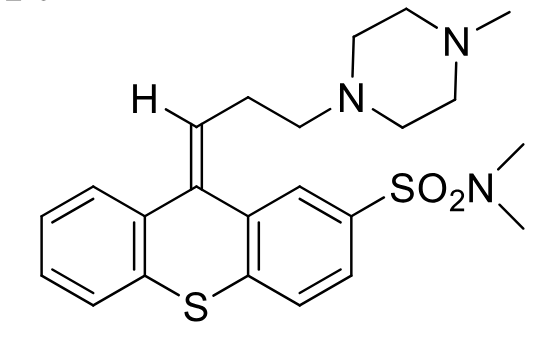
Thiothixene
Class: typical antipsycotic
(bioisosteric phenothiazine)
MOA: D2 antagonist
Use: antipsycotic
Double bond is sp2 hybridized in Z config
solfonamid is non oxidizable
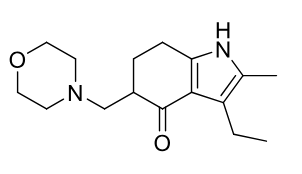
Molindone (Moban)
Class: typical antipsychotic
Indole
MOA: unknown MOA, suspected D2
Use: antipsycotic
Notes: Extensive hepatic metabolism; only 2–3% unchanged
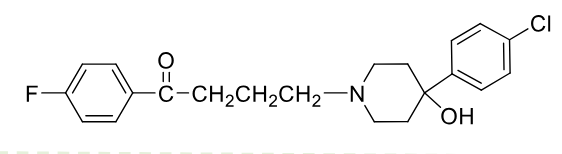
Haloperidol
Class: Typical antipsycotic
Butyrophenone
MOA: inverse agonist (↑cAMP)
Use: Schizophrenia, Tourette's
Metabolism: 50–60% conjugation, 20–30% N-dealkylation, 23% reduction
Half-life: 12–38 hrs;
Formulations: PO 2-3x per day,
IM deconate formulation dosed monthly
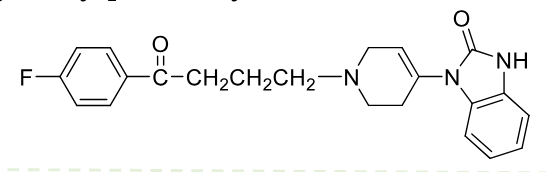
Droperidol
Class: Typical antipsycotic
Butyrophenone
MOA: D2 antagonist
Use: Post-op nausea or chemo nausea,
Half-life: 2 hr
Formulations: IV, IM
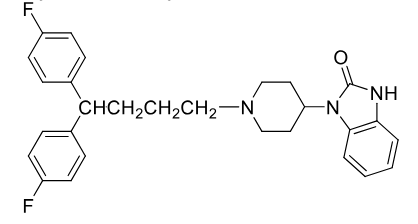
Piomozide
Class: Typical antipsycotic
Butyrophenone
MOA: D2 antagonist
Use: Tourette’s
Metabolism: C–N bond cleavage
split down middle
Half-life: 29 ± 10 hrs
Notes: No ketone; limited metabolism
Li2CO3
Lithium Carbonate
Class: Mood stabilizer
MOA: Increases norepinephrine reuptake and increases serotonin receptor sensitivity
Clinical Use: manic episodes of Bipolar disorder
effects sodium levels
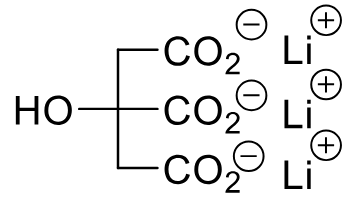
Lithium Citrate
Class: Mood stabilizer
MOA: Increases norepinephrine reuptake and increases serotonin receptor sensitivity
Clinical Use: Bipolar disorder
effects sodium levels
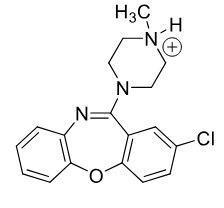
Loxapine
typical antipsycotic
MOA: unknown
Use: schizophrenia
rremoval of methyl group gives ACTIVE amoxipine (depression drug)
Extra Pyrmidal
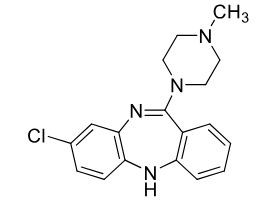
Clozapine
Atypical antipsycotic (2nd gen)
MOA: D2 antagonist
Use: antipsycotic
both + and - sypmtoms
Agranulocytosis
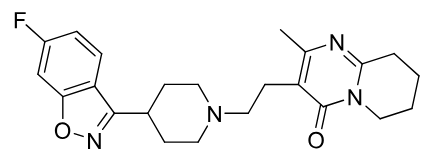
Risperidone
2nd Gen antipsycotic
MOA: D2 and 5-HT2A antagonist
Use: Schizophrenia, bipolar
Metabolites:
9-hydroxy active metabolite (Paliperidone - marketed as drug) once a day dosing
PRODRUG paliperidone Palmitate ,nanocrystal IM monthly
also er tablet available
EPS side effect
Notes: PO ODT IM
contains benzoisoxazole
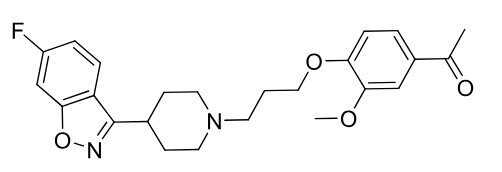
Iloperidone
2nd gen antipsycotic
MOA: D2, 5-HT2A antagonist
Use: Schizophrenia
Extensive Metabolism, Ketone reduction, hydroxylation, demethylation. ACTIVE metabolites
contains benzoisoxazole
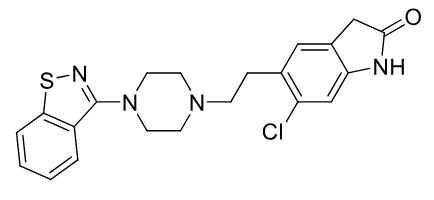
Ziprasidone
2nd gen antipsycotic
MOA: D2, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B antagonist; 5-HT1A agonist
Use: Schizophrenia, bipolar
extensively metabolized
positive food effect
benzisothiazol
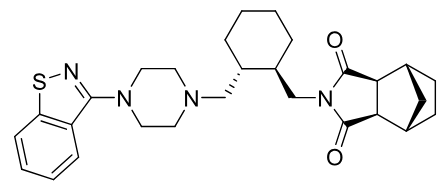
Lurasidone
2nd gen antipsycotic
MOA: D2, 5-HT2A, 5-HT7 antagonist
Use: Schizophrenia, bipolar depression
positive food effect
benzisothiazol
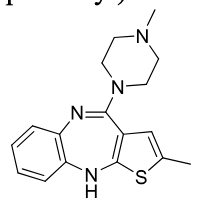
Olanzapine
2nd gen antipsycotic
MOA: D2, 5-HT2A antagonist
Use: Schizophrenia, bipolar
Structure: bioisostere Thiophene ring (less oxidizable)
Half-life: 21–54 hrs
uncommon agranulocytosis
similar to clozapine
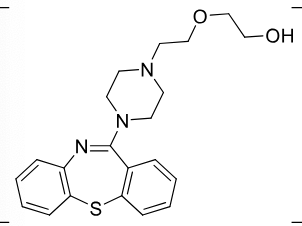
Quentiapine
2nd gen antipsycotic (atypical)
MOA: D2, 5-HT2A antagonist
Use: Schizophrenia, bipolar, depression
Notes: Sulfur in ring oxidation possible
2:1 quentiapine to fumarate salt
Aripiprazole
2nd gen antipsycotic
MOA: D2 partial agonist, 5-HT1A agonist, 5-HT2A antagonist
Use: Schizophrenia, bipolar, Tourette’s
Metabolism: Dealkylation, hydroxylation, hydrogenation to ACTIVE metabolite (40%)
Half-life: ~75 hrs
Forms: PO (High OBA), IM (Maintena, Lauroxil)
Brexpiprazole
2nd gen antipsycotic
MOA: D2 partial agonist, 5-HT1A agonist, 5-HT2A antagonist
Use: Depression, schizophrenia
High oral bioavailability
Half-life: ~91 hrs
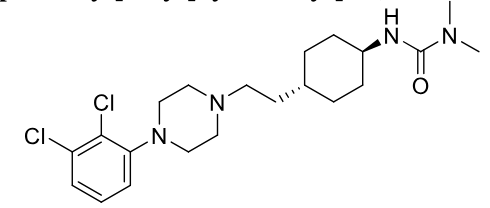
Cariprazine (vraylar)
2nd gen antipsycotic
MOA: D2, 5HT1a partial agonist, 5HT2b and 5HT2a antagonist
Use: Schizophrenia, bipolar, MDD
demethylated to ACTIVE metabolite
Half-life: 2–4 days; active metabolite: ~8 days
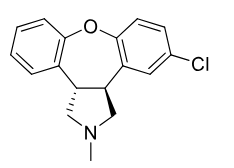
Asenapine
2nd gen antipsycotic
MOA: D2, 5-HT2A antagonist
Use: Schizophrenia, bipolar
2 chiral centers gives 4 enantiomers
Mirtazepine is an antidepressant drug that looks similar
Formulations: Sublingual tablet
Avoids 1st-pass metabolism
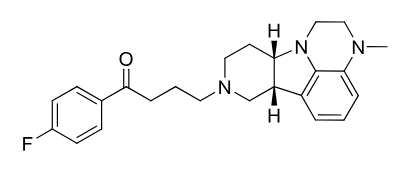
Lumateperone
2nd gen antipsycotic (atypical)
MOA: D2 and 5-HT2A antagonist
Use: Bipolar, schizophrenia
Metabolism: reduction at ketone and demethylation by CYP3A4 (extensively metabolized), avoid grapefruit juice
Half-life: ~18 hrs
Ethosuximide
Class: Succinimide
anti seizure
MOA: Inhibits T-type Ca²⁺ channels in thalamic neurons
Use: Absence seizures (petit mal)
Metabolism: no dealkylation
Notes: Less adverse effects than valproate
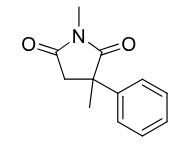
Methsuximide
Class: Succinimide
MOA: T-type Ca²⁺ channel blocker
Use: Absence seizures (petit mal)
Metabolism: demethylation → active metabolite (N-desmethylmethsuximide)
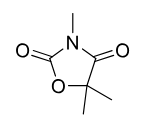
Trimethadione
Class: Oxazolidinedione
MOA: T-type Ca²⁺ channel inhibitor
Use: Absence seizures (petit mal)
Metabolism: Hepatic demethylation to active metabolite
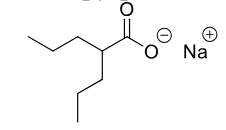
Valproic Acid
MOA: unknown
Use: First Line for Absence (petit mal) seizure, also partial, complex seuziures.also bipolar disorder
Metabolism: omega and β-oxidation, glucuronidation
BBW for
hepatotoxicity
teratogenic
fatal pancreatitis
banned in france and europe
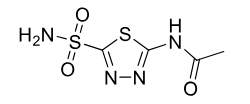
Acetazolamide
Class: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
Use: absence seizure (petit mal) glaucoma, mountain sickness
diuretic effect, raises urine pH
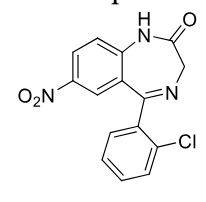
Clonazepam C-IV
Class: Benzodiazepine
MOA: GABA-A enhancement (binding to BZ site)
Use: absence seizures (petit mal) and status epilepticus
Chorazepate is prodrug for seizures too
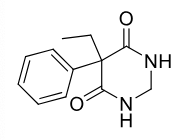
Primidone
Class: isoteric barbituarate
Use: petit and grand mal seizure, weak anticonvulsant
metabolized by hydroxylation and hydrolysis to active metabolites
Parent and all metabolites are active
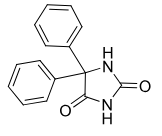
Phenytoin
Class: Hydantoin
Use: grand mal seizure
Metabolism: S-enantiomer preferred formation after hydroxylation
Formulations: PO (poor OBA), IV (alkaline, painful 50mg/ml and pH12)
resembles barbituates
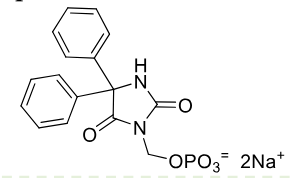
Fosphenytoin
Class: Prodrug of phenytoin
MOA: Converts to phenytoin in vivo by alkaline phosphatase
Use: Status epilepticus, neuro surgery seizures
Formulations: IV
very water soluble
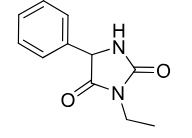
Ethotoin
Class: Hydantoin
Use: grand mal, petit mal, psychomotor seizures
Metabolism: N-demethylation, ring hydroxylation
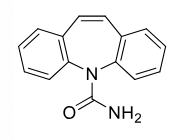
Carbamazepine
Class: Dibenzazepine
Use: grand mal seizure, bipolar
Metabolism: CYP3A4 → epoxide (active), induces own metabolism
Side Effects:
Aplastic anemia,
agranulocytosis
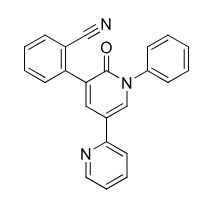
Perampanel
Non competetive AMPA receptor antagonist (allosteric)
use for grand mal seizure in people 12 and older
partial onset in people 4 and older
once daily dosing
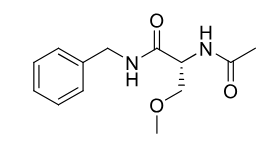
Lacosamide
Partial + grandmal seizure
amino acid derivative of d-serine
high oral bioavailability
40% elim unchanged
t1/2 12-16 hours
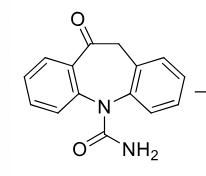
Oxcarbazepine
Class: Dibenzazepine
Use: Partial seizures
reduced to active metabolite
can be acetylated to make a Prodrug Eslicarbazepine (aption) which has once a day dosing