ba 350 exam 1 (cobb sdsu)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
1
New cards
WHAT IS ORGANIZATIONAL BEHAVIOR?
...
2
New cards
organizational behavior (OB)
a field of study that investigates the impact that individuals, groups, and structure have on behavior within organizations for the purpose of applying such knowledge toward improving an organization's effectiveness
\
(no absolutes bc contingencies exist)
\
(no absolutes bc contingencies exist)
3
New cards
four disciplines that contribute to OB
1. PSYCHOLOGY\= measure, explain, and sometimes change the behavior of humans and animals
2. SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY\= the influence of people on one another
3. SOCIOLOGY\= people in relation to social environment or culture
4. ANTHROPOLOGY\= studies societies to learn about human beings and their activities
2. SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGY\= the influence of people on one another
3. SOCIOLOGY\= people in relation to social environment or culture
4. ANTHROPOLOGY\= studies societies to learn about human beings and their activities
4
New cards
contingency variables
= situational factors or variables that moderate the relationship between two to more variables
\-appropriate management depends on the demand of the situation or conditions... aka how individuals attitude change when something happens
(ex. when a senior leader quits, it can negatively affect the morale and dynamics of other employees)
\
OR a specific factor that could impact the outcome of a particular situation positively or negatively
\-appropriate management depends on the demand of the situation or conditions... aka how individuals attitude change when something happens
(ex. when a senior leader quits, it can negatively affect the morale and dynamics of other employees)
\
OR a specific factor that could impact the outcome of a particular situation positively or negatively
5
New cards
VUCA acronym
volatility, uncertainty, complexity, ambiguity
*vuca environment is influencing ob*
*vuca environment is influencing ob*
6
New cards
VUCA...
-managing workforce diversity and inclusion
-responding to globalization
-technology and social media
-always on work cultures
-focus on CSR
-artificial intelligence and machine learning
-shift to gig economy (non traditional 9-5 jobs such as door dash, uber eats, etc.)
-responding to globalization
-technology and social media
-always on work cultures
-focus on CSR
-artificial intelligence and machine learning
-shift to gig economy (non traditional 9-5 jobs such as door dash, uber eats, etc.)
7
New cards
counterproductive work behavior (CWB)
refers to employee voluntary behaviors that harm organizations or people working in the organizations
ex. destroying company property, calling in sick when not ill, insulting an employee, stealing, etc.
ex. destroying company property, calling in sick when not ill, insulting an employee, stealing, etc.
8
New cards
systematic study of behavior
\=looking at relationships, attempting to attribute causes and effects, and drawing conclusions based on evidence
-cause and effect focused
-behavior generally is predictable (perception, importance)
-cause and effect focused
-behavior generally is predictable (perception, importance)
9
New cards
EBM
\= evidence based management ; basing managerial decisions on the best available scientific evidence
-complements systematic study
-argues for individuals to make decisions based on evidence
-complements systematic study
-argues for individuals to make decisions based on evidence
10
New cards
intuition
\=an instinctive feeling not necessarily supported by research
-systematic study and EBM add to intuition (aka those "gut feelings" about "why i do what i do" and "what makes others tick")
-if we make all decisions with intuition or gut instinct, we're likely working with incomplete information
-systematic study and EBM add to intuition (aka those "gut feelings" about "why i do what i do" and "what makes others tick")
-if we make all decisions with intuition or gut instinct, we're likely working with incomplete information
11
New cards
organization
a consciously coordinated social unit composed of two or more people that functions on a relatively continuous basis to achieve a common goal or set of goals
(coordinated effort to bring people together to contribute to the goal of a company, like a mission statement)
(coordinated effort to bring people together to contribute to the goal of a company, like a mission statement)
12
New cards
manager
someone who gets things done through other people in organizations ; an individual who achieves goals through other people
(they need to build on the skillsets of the people they hired and then let them go apply that to the workforce)
(they need to build on the skillsets of the people they hired and then let them go apply that to the workforce)
13
New cards
worker
someone who contributes to the accomplishment of goals
14
New cards
basic OB model
inputs -\> processes -\> outcomes
\** occurs on an individual, group, and organizational level
\** occurs on an individual, group, and organizational level
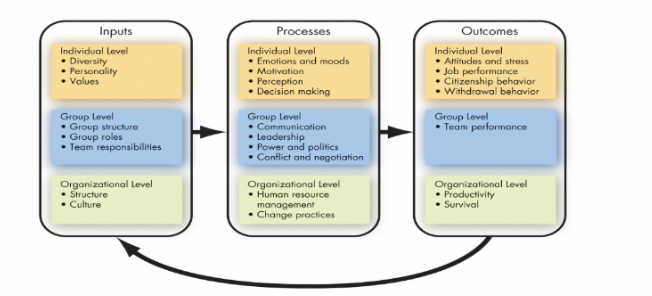
15
New cards
input variables
\=people team, etc. (think of it as a noun)
INDIVIDUAL:
-diversity
-personality
-values
GROUP:
-group structure
-group roles
-team responsibilities
ORGANIZATIONAL:
-structure
-culture
INDIVIDUAL:
-diversity
-personality
-values
GROUP:
-group structure
-group roles
-team responsibilities
ORGANIZATIONAL:
-structure
-culture
16
New cards
process variables
\=defined as actions that individuals, groups, and organizations engage in as a result of inputs, and that lead to certain outcomes (if input is a noun, process is a verb)
INDIVIDUAL:
-emotions and moods
-motivation
-perception
-decision making
PROCESSES:
-communication
-leadership
-power and politics
-conflict and negotiation
ORGANIZATIONAL:
-human resource management
-change practices
INDIVIDUAL:
-emotions and moods
-motivation
-perception
-decision making
PROCESSES:
-communication
-leadership
-power and politics
-conflict and negotiation
ORGANIZATIONAL:
-human resource management
-change practices
17
New cards
outcome variables
\=key variables that you want to explain or predict, and that are affected by some other variables
INDIVIDUAL:
-attitudes and stress
-job performance
-citizenship behavior
-withdrawal behavior (doing the bare minimum or "silent quitting"... gossip, not doing work, etc.)
GROUP:
-team performance
ORGANIZATION:
-productivity (transforming inputs to outputs aka efficiency)
-survival (evidence you will continue to exist as a company)
INDIVIDUAL:
-attitudes and stress
-job performance
-citizenship behavior
-withdrawal behavior (doing the bare minimum or "silent quitting"... gossip, not doing work, etc.)
GROUP:
-team performance
ORGANIZATION:
-productivity (transforming inputs to outputs aka efficiency)
-survival (evidence you will continue to exist as a company)
18
New cards
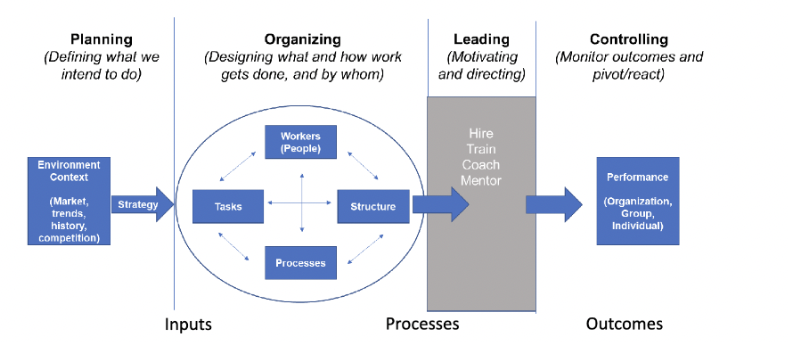
four functions of managers
1. planning
2. organizing
3. leading
4. controlling
2. organizing
3. leading
4. controlling
19
New cards
planning
\= a process that includes DEFINING GOALS, establishing strategy, and developing plans to coordinate activities
-environment context: market, trends, history, competition
-environment context: market, trends, history, competition
20
New cards
organizing
\= determining WHAT tasks are to be done, WHO is to do them, HOW the tasks are to be grouped, who reports to whom, and where decisions are to be made
-workers/people, tasks, structure, processes
*role clarity
-workers/people, tasks, structure, processes
*role clarity
21
New cards
leading
\= a function that includes MOTIVATING employees, DIRECTING others, selecting the most effective communication channels, and resolving conflicts
-hire, train, coach, mentor
-hire, train, coach, mentor
22
New cards
controlling
\= MONITORING activities to ensure that they are being accomplished as planned, and correcting any significant deviations (aka pivot/react!)
-performance: organization group, individuals
-did we perform and achieve what we set out to achieve?
-performance: organization group, individuals
-did we perform and achieve what we set out to achieve?
23
New cards
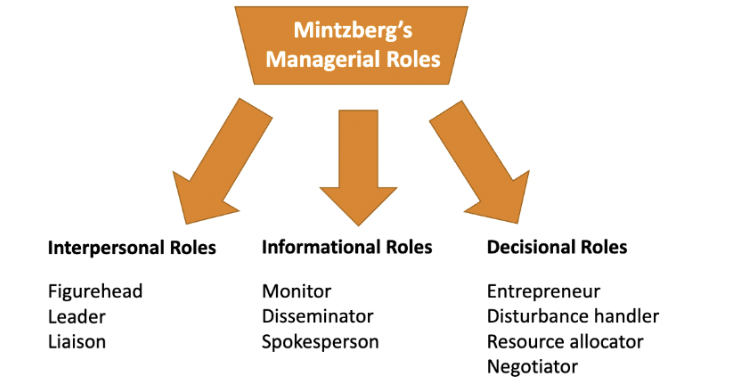
mintxberg's managerial roles
1. interpersonal roles
2. informational roles
3. decisional roles
2. informational roles
3. decisional roles
24
New cards
interpersonal roles
\= face of the organization (internal and external)
-figurehead
-leader
-liaison
-figurehead
-leader
-liaison
25
New cards
figurehead
symbolic head; required to perform a number of routine duties of a legal or social nature (represents the organization)
ex. president of a college hands out diplomas or giving high school students a tour
ex. president of a college hands out diplomas or giving high school students a tour
26
New cards
leader
responsible for the motivation and direction of the employees (communicating with people about what you need them to do)
27
New cards
liaison
maintains a network of outside contacts who provide favors and information (going outside of organization to create partnerships)
ex. when a sales managers obtains info from quality control manager of their own company, it's internal liaison relationship.... if sales manager has contact with other sales executives, external
ex. when a sales managers obtains info from quality control manager of their own company, it's internal liaison relationship.... if sales manager has contact with other sales executives, external
28
New cards
informational roles
\= eyes and ears of the company
-monitor
-disseminator
-spokesperson
-monitor
-disseminator
-spokesperson
29
New cards
monitor
receives a wide variety of information; serves as nerve center of internal and external information of the organization (keeping our eyes on the external environment to see if something is affecting our business)
30
New cards
disseminator
transmits information received from outsiders or from other employees to members inside of the organization (bring outside info inside)
31
New cards
spokesperson
transmits information to outsiders on organization's plans, policies, actions, and results; serves as expert on organization's industry (telling the outside world what we are doing to hold onto shareholder values)
ex. we are changing out name and here is why
ex. we are changing out name and here is why
32
New cards
decisional roles
\= brain or head decisions of the company
-entrepreneur
-disturbance handler
-resource allocator
-negotiator
-entrepreneur
-disturbance handler
-resource allocator
-negotiator
33
New cards
entrepreneur
searches organization and its environment for opportunities and initiates projects to bring about change (brings new business)
34
New cards
disturbance handler
responsible for corrective action when organization faces important, unexpected disturbances
35
New cards
resource allocator
makes or approves significant organizational decisions
(deciding where to put money or human resources in order to help us accomplish our goals)
(deciding where to put money or human resources in order to help us accomplish our goals)
36
New cards
negotiator
responsible for representing the organization at major negotiations (when working with an outside partner, how do we best get outcomes for our organizations)
37
New cards
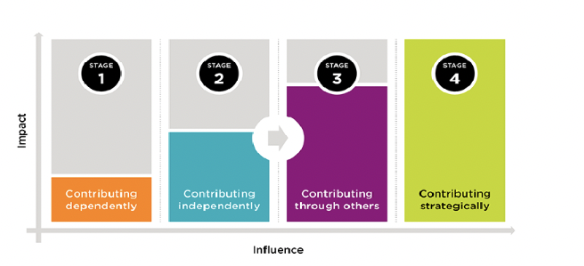
stages of management skills
four stages:
1. contributing dependently
2. contributing independently
3. contributing through others
4. contributing strategically
1. contributing dependently
2. contributing independently
3. contributing through others
4. contributing strategically
38
New cards
stage 1: contributing dependently
need managers to guide you, tell you what to do, and how to navigate the organizations culture (usually when first our of college and get first major job)
39
New cards
stage 2: contributing independently
not as much guidance from manager, getting goals done with very little coaching, delegating tasks only
40
New cards
stage 3: contributing through others
where management starts to happen; contributing through other people rather than contributing to work yourself
41
New cards
stage 4: contributing strategically
looking at the outside world (risks and threats) and bringing that information back inside the company to figure out game plans
42
New cards
between what stages does it become hardest for people to move up? why?
stages 2 to 3
-\> when you contribute independently, you can control the outcome and get credit... when you move to stage 3, you have to let go of owning that outcome and learn to trust your people (hard for people to not do the work themselves so they are stuck in stage 2)... or some people are so good at what they do that people don't see them as a leader/manager and will never reach stage 3 level
-\> when you contribute independently, you can control the outcome and get credit... when you move to stage 3, you have to let go of owning that outcome and learn to trust your people (hard for people to not do the work themselves so they are stuck in stage 2)... or some people are so good at what they do that people don't see them as a leader/manager and will never reach stage 3 level
43
New cards
technical skills
the ability to apply specialized knowledge or expertise
-critical at stages 1 and 2
-ex. civil engineers or oral surgeons
-critical at stages 1 and 2
-ex. civil engineers or oral surgeons
44
New cards
people skills
the ability to work with, understand, and motivate other people, both individually and in groups (need to be a good listener, understand what others needs, and good at managing conflicts)
-stage 3
-stage 3
45
New cards
conceptual skills
the mental ability to analyze and diagnose complex situations (integrate new ideas with existing processes and innovate on the job)
-stage 4 (knowing whats happening in your own business/area, but also looking at the bigger picture to see how you can get your organization to the next level)
-stage 4 (knowing whats happening in your own business/area, but also looking at the bigger picture to see how you can get your organization to the next level)
46
New cards
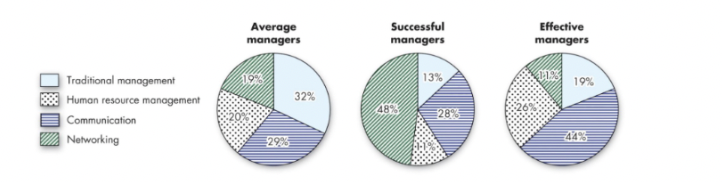
effective vs successful managers
based on...
* traditional management (decision making, planning, controlling)
* communication (exchanging routine info and processing paperwork)
* human resources management (motivating, disciplining, managing conflict, staffing, and training)
* networking (socializing, politicking, and interacting w outsiders)
* traditional management (decision making, planning, controlling)
* communication (exchanging routine info and processing paperwork)
* human resources management (motivating, disciplining, managing conflict, staffing, and training)
* networking (socializing, politicking, and interacting w outsiders)
47
New cards
compare/contrast successful vs effective managers...
successful managers:
\-based on getting promoting quickly
\-more NETWORKING aka spending time outside of organization
\
effective managers:
\-employees are satisfied; seek input from employees and explains reason for their decisions
\-more COMMUNICATION aka more time inside of the organization
\-based on getting promoting quickly
\-more NETWORKING aka spending time outside of organization
\
effective managers:
\-employees are satisfied; seek input from employees and explains reason for their decisions
\-more COMMUNICATION aka more time inside of the organization
48
New cards
PERSONALITY, INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES, AND VALUES
...
49
New cards
personality
the sum of ways in which an individual reacts to and interacts with the world around them
measurable traits a person exhibits
measurable traits a person exhibits
50
New cards
personality traits
enduring characteristics that describe an individual's behavior
-the things that stick with us over time... the traits people would use to describe us
-the things that stick with us over time... the traits people would use to describe us
51
New cards
person-job fit theory
\= a theory by John Holland that identifies six personality types and proposes that the fit between type and occupational environment determines satisfaction and turnover
1. realistic
2. investigative
3. artistic
4. social
5. enterprising
6. conventional
-\> how to use personality traits to figure out what type of job would be the best fit for you (what are you good at and when are you at your best?)
1. realistic
2. investigative
3. artistic
4. social
5. enterprising
6. conventional
-\> how to use personality traits to figure out what type of job would be the best fit for you (what are you good at and when are you at your best?)

52
New cards
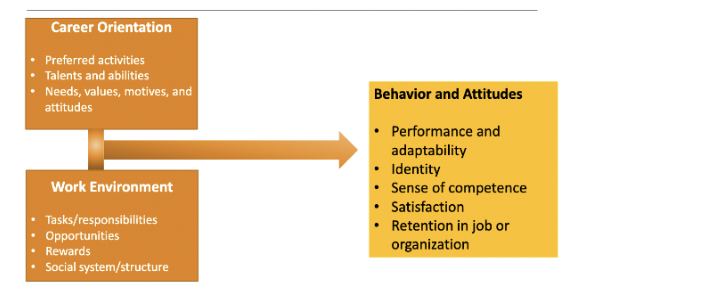
person-organization fit theory
\= suggests that people are attracted to and selected by organizations that match their values and leave when there is no compatibility
career orientation + work environment \= behavior and attitudes
ex. we could expect that extroverts fit well with organizations that value relationships and socialization
career orientation + work environment \= behavior and attitudes
ex. we could expect that extroverts fit well with organizations that value relationships and socialization
53
New cards
why do we measure personality?
-to predict behavior (and emotion)
-to predict how X situation will produce Y behavior
-to determine proclivity/tendency
(no personality test will give you a better understanding of someone than repeated interaction and conversation)
-to predict how X situation will produce Y behavior
-to determine proclivity/tendency
(no personality test will give you a better understanding of someone than repeated interaction and conversation)
54
New cards
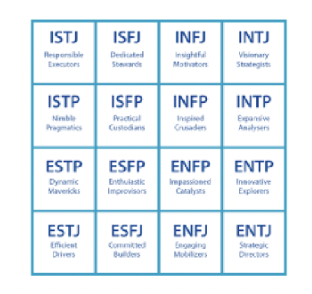
Myers-Brigg Type Indicator (MBTI)
\= a personality test that taps four characteristics and classifies people into one of sixteen personality types (the most widely used personality assessment instrument in the world)
individuals are classified as:
-extroverted or introverted (E or I)
-sensing or intuitive (S or N)
-thinking or feeling (T or F)
-perceiving or judging (P or J)
**not super reliable or research based
individuals are classified as:
-extroverted or introverted (E or I)
-sensing or intuitive (S or N)
-thinking or feeling (T or F)
-perceiving or judging (P or J)
**not super reliable or research based
55
New cards
the big five
\= a personality model that proposes five basic dimensions encompass most of the differences in human personality
OCEAN
Openness to experience
Conscientiousness
Extroversion
Agreeableness
Emotional stability (Negative emotionality)
**way to measure personality that is backed by a lot more research than myers-brigg
OCEAN
Openness to experience
Conscientiousness
Extroversion
Agreeableness
Emotional stability (Negative emotionality)
**way to measure personality that is backed by a lot more research than myers-brigg
56
New cards
the dark triad
\= a constellation of negative personality traits consisting of...
1. machiavellianism
2. narcissism
3. psychopathy
1. machiavellianism
2. narcissism
3. psychopathy
57
New cards
machiavellianism
the degree to which an individual is pragmatic, maintains emotional distance, and believes that ends can justify means
ex. "i do whatever i have to do to get ahead"
ex. "i do whatever i have to do to get ahead"
58
New cards
narcissism
the tendency to be arrogant, have a grandoise sense of self importance, require excessive admiration, and possess a sense of entitlement
-like to be the center of attention, have fantasies of grand success, a tendency to exploit situations/people, and can be hypersensitive or fragile
ex. ceo bc they tend to be more close minded
-like to be the center of attention, have fantasies of grand success, a tendency to exploit situations/people, and can be hypersensitive or fragile
ex. ceo bc they tend to be more close minded
59
New cards
psychopathy
the tendency for a lack of concern for others and a lack of guilt or remorse when actions cause harm
-lack of empathy, willingness to use deceit to obtain desired ends (ex. i want what i want)
-lack of empathy, willingness to use deceit to obtain desired ends (ex. i want what i want)
60
New cards
core self evaluation
bottom line conclusions individuals have about their capabilities, competence, and worth as a person (how we think about ourselves)
-if evaluation is positive, it allows us to build resilience and work better; if negative, we might give up quicker and look for external evaluation which is not good
-if evaluation is positive, it allows us to build resilience and work better; if negative, we might give up quicker and look for external evaluation which is not good
61
New cards
self monitoring
measures an individual's ability to adjust his or her behavior to external, situational factors
(how we perceive ourselves and how we may need to regulate ourselves)
-high self monitors show considerable adaptability and are sensitive to external cues and can behave differently (big difference bw their public and private selves) ; low self monitors tend to display their true dispositions and attitudes in every situation
(how we perceive ourselves and how we may need to regulate ourselves)
-high self monitors show considerable adaptability and are sensitive to external cues and can behave differently (big difference bw their public and private selves) ; low self monitors tend to display their true dispositions and attitudes in every situation
62
New cards
proactive personality
people who identify opportunities, show initiative, take action, and persevere until meaningful change occurs
-high levels of job performance, do not need much oversights (given more autonomy), achieve career success; but are often envied by coworkers and teams
-high levels of job performance, do not need much oversights (given more autonomy), achieve career success; but are often envied by coworkers and teams
63
New cards
INDIVIDUAL DIFFERENCES - SITUATIONS AND VALUES
...
64
New cards
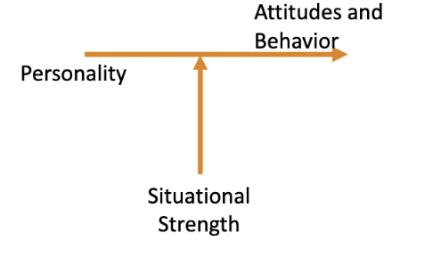
situation strength theory
\= the way personality translates into behavior depends on the strength of the situation (the degree to which norms, cues, or standards dictate appropriate behavior)
-\> strong situations show us what right behavior is, pressure us to exhibit it, and discourage the wrong behavior; weak situations "anything goes," and freer to express our personality
-clarity
-consistence
-constraints
-consequences
-\>we need situations at work with less constraints!! the minute people think they can't communicate, is when ideas shut down and the organization suffers
-\> strong situations show us what right behavior is, pressure us to exhibit it, and discourage the wrong behavior; weak situations "anything goes," and freer to express our personality
-clarity
-consistence
-constraints
-consequences
-\>we need situations at work with less constraints!! the minute people think they can't communicate, is when ideas shut down and the organization suffers
65
New cards
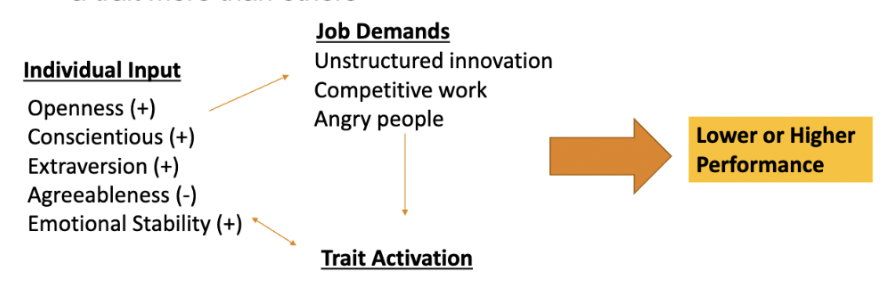
trait activation theory (TAT)
predicts that some situations, events, or interventions "activate" a trait more than others
(if these traits that need to be activated are not activated, then you may have a lower performance at work)
ex. a commission based compensation plan would activate extroversion bc extroverted people are more reward sensitive
ex. in jobs that encourage creativity, activating openness may better predict desired behavior
(if these traits that need to be activated are not activated, then you may have a lower performance at work)
ex. a commission based compensation plan would activate extroversion bc extroverted people are more reward sensitive
ex. in jobs that encourage creativity, activating openness may better predict desired behavior
66
New cards
values
basic convictions that some actions and outcomes are more morally, socially, or personally preferable than others
-evaluative
-enduring
-influential
-evaluative
-enduring
-influential
67
New cards
evaluative
-judgmental (what is right, good, or desirable)
-content (mode of conduct)
-intensity (how important)
-content (mode of conduct)
-intensity (how important)
68
New cards
enduring
-tend to be stable (values tend to be really hard to change)
-often established early in life
-often established early in life
69
New cards
influential
-attitudes and behavior (positive or negative)
-can cloud objectivity
-can cloud objectivity
70
New cards
terminal values
\= lifetime goals, desirable end states of existence (what do i care about for my life, why am i here, whats the purpose of my life)
ex. money, internal peace, contentment/fulfillment, family, self respect, health
ex. money, internal peace, contentment/fulfillment, family, self respect, health
71
New cards
intrinsic values
personal feelings that stem from the direct relationship between you and the work (joy, helping, innovating)... thing that come INSIDE from ourselves
72
New cards
extrinsic values
rewards or benefits that that stem from the work environment or evaluation (money, promotion, recognition)... thing that come OUTSIDE from ourselves
73
New cards
generational values
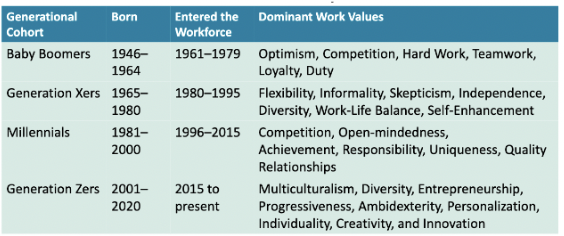
74
New cards
instrumental values
\= preferred modes or behavior or means of achieving terminal values
(things that get us to our end game)
ex. going to college/ getting an education, perseverance, if end goal is your health then you go to the gym and eat good
(things that get us to our end game)
ex. going to college/ getting an education, perseverance, if end goal is your health then you go to the gym and eat good
75
New cards
JOB ATTITUDES
...
76
New cards
attitudes
judgements or evaluative statements (either favorable or unfavorable) about objects, people, or events
-they reflect how we feel about something or someone
-they reflect how we feel about something or someone
77
New cards
components of an attitude
1. cognitive \= evaluation (opinion or belief)
2. affective \= feeling (emotional)
3. behavioral \= action (an intention to behave in a certain way)
2. affective \= feeling (emotional)
3. behavioral \= action (an intention to behave in a certain way)
78
New cards
cognitive dissonance
a psychological discomfort that results from holding two conflicting attitudes or between behavior and attitudes
-creates a disequilibrium within us... brain hold two contradicting ideas until WE change them to become consistent with each other
- people tend to seek consistency in their attitudes so the conflict causes discomfort which motivates us to take action
-creates a disequilibrium within us... brain hold two contradicting ideas until WE change them to become consistent with each other
- people tend to seek consistency in their attitudes so the conflict causes discomfort which motivates us to take action
79
New cards
ways we avoid the discomfort of cognitive dissonance:
-reject information
-explain or rationalize away
-reduce the significance
-avoid new information
-explain or rationalize away
-reduce the significance
-avoid new information
80
New cards
organizational identification
extent to which employees define self by the same characteristics that define the organization
-how i define the organization is how i define my situation (company becomes an extension of you)
-how i define the organization is how i define my situation (company becomes an extension of you)
81
New cards
job satisfaction
positive feelings about a job based on its characteristics
*attitudes are the most important driving factor for job satisfaction
*attitudes are the most important driving factor for job satisfaction
82
New cards
job involvement
extent to which we identify with a job and consider it important to self worth
83
New cards
organizational commitment
extent to which we identify with and desire to maintain membership in the organization
-how long will i stay here and how committed am i to making this organization succeed
-how long will i stay here and how committed am i to making this organization succeed
84
New cards
employee engagement \=
satisfaction + involvement + enthusiasm
(am i satisfied with day to day work, does my job make me feel involved and personable, and am i excited or passionate about coming in)
(am i satisfied with day to day work, does my job make me feel involved and personable, and am i excited or passionate about coming in)
85
New cards
measurement (job satisfaction)
-the single global rating
-summation of job facets
-summation of job facets
86
New cards
influences of job satisfaction
-economic conditions
-job facets
(if economy is bad, people may say they are satisfied just bc they actually have a job... when economy is good, it is okay to not be satisfied bc u can find another job)
-job facets
(if economy is bad, people may say they are satisfied just bc they actually have a job... when economy is good, it is okay to not be satisfied bc u can find another job)
87
New cards
what contributes to job satisfaction?
job conditions
-nature of the work itself
-social interactions
-supervisions
personality and individual differences
-self core evaluations
-culture
pay
**people do not prioritize high pay, but rather the people and the work itself
-nature of the work itself
-social interactions
-supervisions
personality and individual differences
-self core evaluations
-culture
pay
**people do not prioritize high pay, but rather the people and the work itself
88
New cards
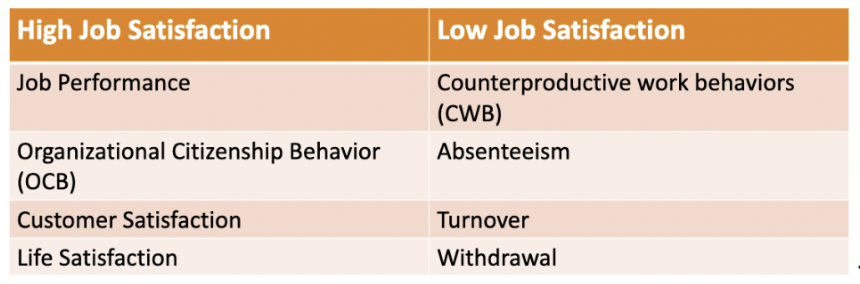
contrasting satisfaction levels
high job satisfaction:
-job performance
-organizational citizenship behavior (OCB)
-customer satisfaction
-life satisfaction
low job satisfaction:
-counterproductive work behaviors (CWB)
-absenteeism
-turnover
-withdrawal
-job performance
-organizational citizenship behavior (OCB)
-customer satisfaction
-life satisfaction
low job satisfaction:
-counterproductive work behaviors (CWB)
-absenteeism
-turnover
-withdrawal
89
New cards
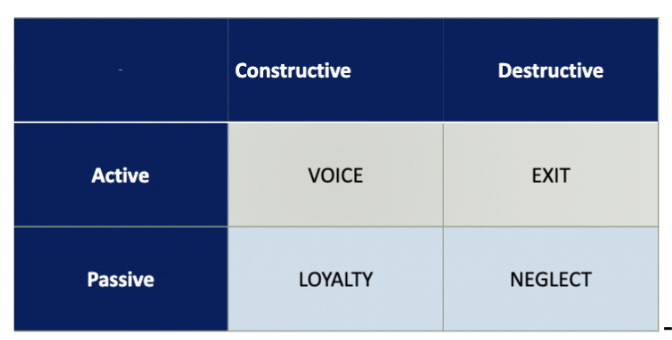
responses to dissatisfaction
active (take initiative)
passive (sit back)
constructive (do something that makes it better)
destructive (do something that makes it worse)
passive (sit back)
constructive (do something that makes it better)
destructive (do something that makes it worse)
90
New cards
EMOTIONS AND MOOD
...
91
New cards
how many emotions do we all express? what are they?
6 different emotion:
1\. anger
2\. fear
3\. disgust
4\. surprised
5\. happiness
6\. sadness
\
\*\*employee emotions CANNOT be separated from work
1\. anger
2\. fear
3\. disgust
4\. surprised
5\. happiness
6\. sadness
\
\*\*employee emotions CANNOT be separated from work
92
New cards
affect
a term used to describe a broad range of feelings that people experience, including emotions and moods
93
New cards
emotions
intense, discrete, and short-lived feelings directed at someone or something and often caused by a specific event (indicated by distinct facial expressions)
94
New cards
moods
feelings that tend to be longer-lived and less intense than emotions, and lack a contextual stimulus (aka we do not know what brought them on)
95
New cards
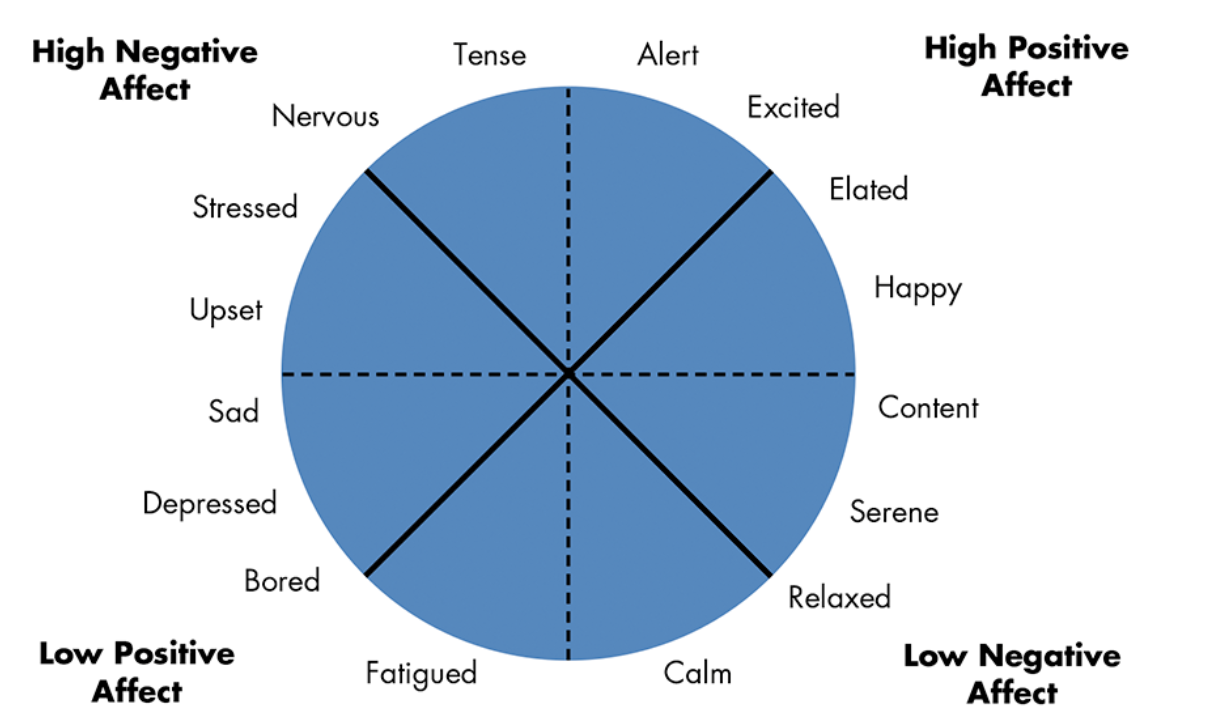
the affective circumplex
categorizes and arranges emotions by their degree of positivity and negativity
\
4 quadrants:
\-high positive affect
\-high negative affect
\-low positive affect
\-low negative effect
\
4 quadrants:
\-high positive affect
\-high negative affect
\-low positive affect
\-low negative effect
96
New cards
high positive affect
alert, excited, elated, happy, content
97
New cards
low negative affect
happy, content, serene, relaxed, calm
98
New cards
low positive affect
calm, fatigued, bored, depressed, sad, upset
99
New cards
high negative effect
upset, stressed, nervous, tense, alert
100
New cards
moral emotions
emotions that have moral implications because of our instant judgement of the situation that evokes them
\
if something is programed with more positive language, it will be more appealing even if all options are the same (ex. save half or kill half… tempted to save half even though they are the same outcome)
\
if something is programed with more positive language, it will be more appealing even if all options are the same (ex. save half or kill half… tempted to save half even though they are the same outcome)