ICT All Lesson Prelims G12
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
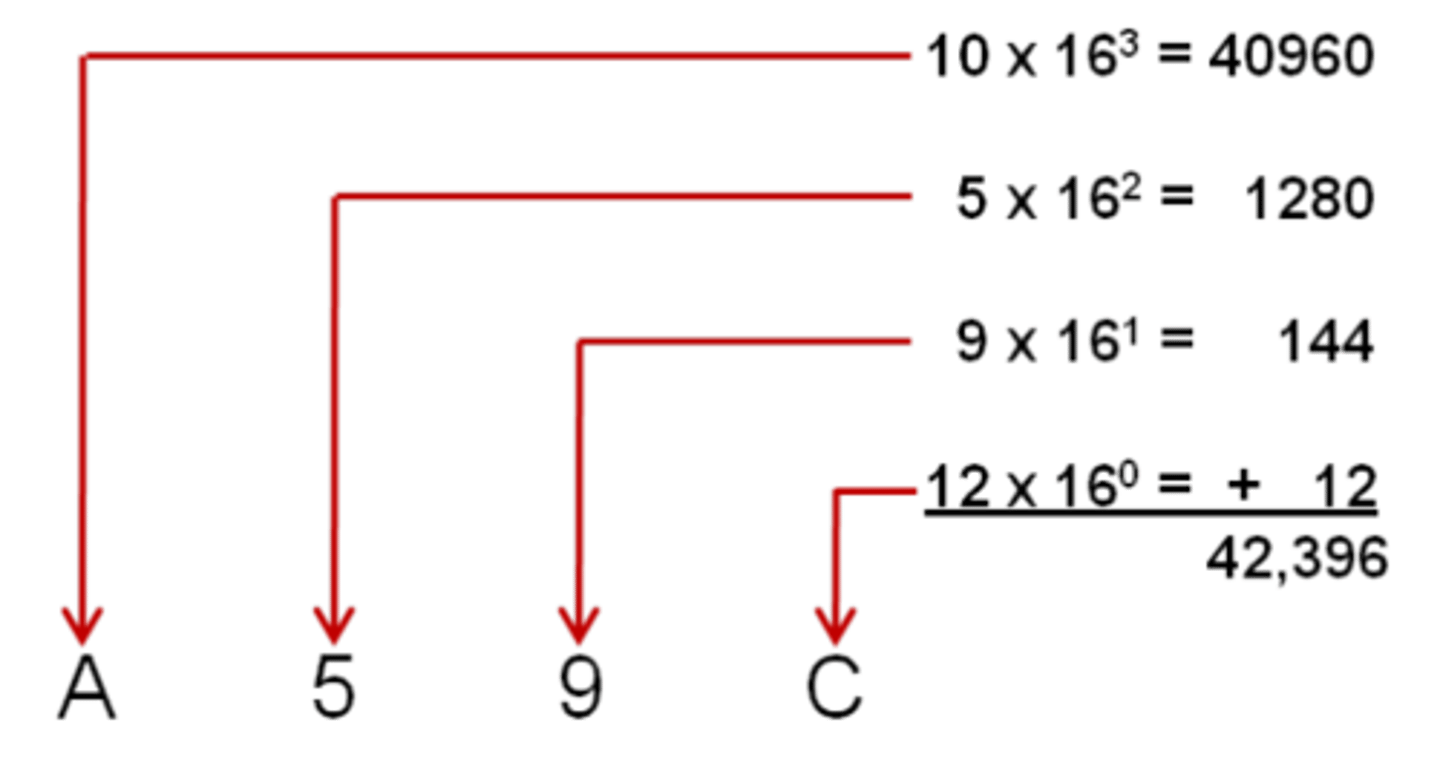
hexadecimal to decimal
Multiply hex digits by powers of 16.
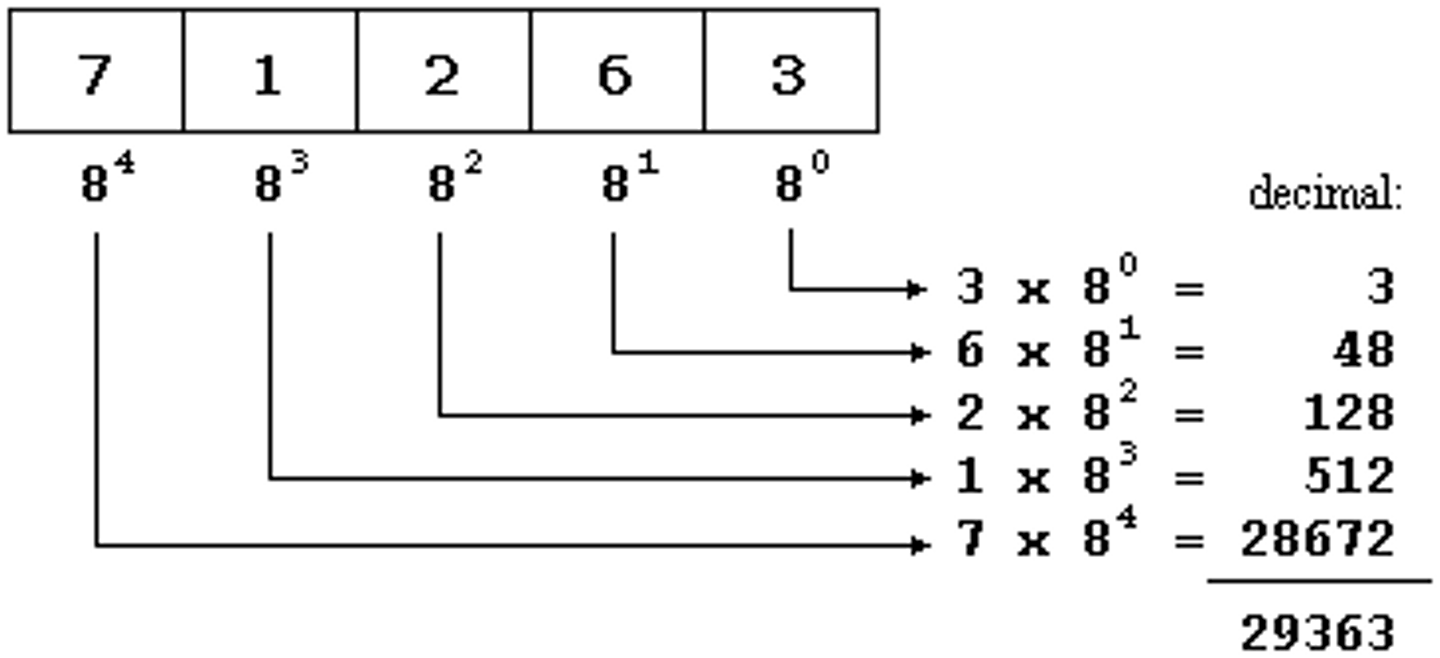
octal to decimal
Make a vertical column of the number in order from right to left, top to bottom. Multiply each number by 8 raising the top number to a power of 0 and giving each consecutive power the next number in sequence (1,2,3)
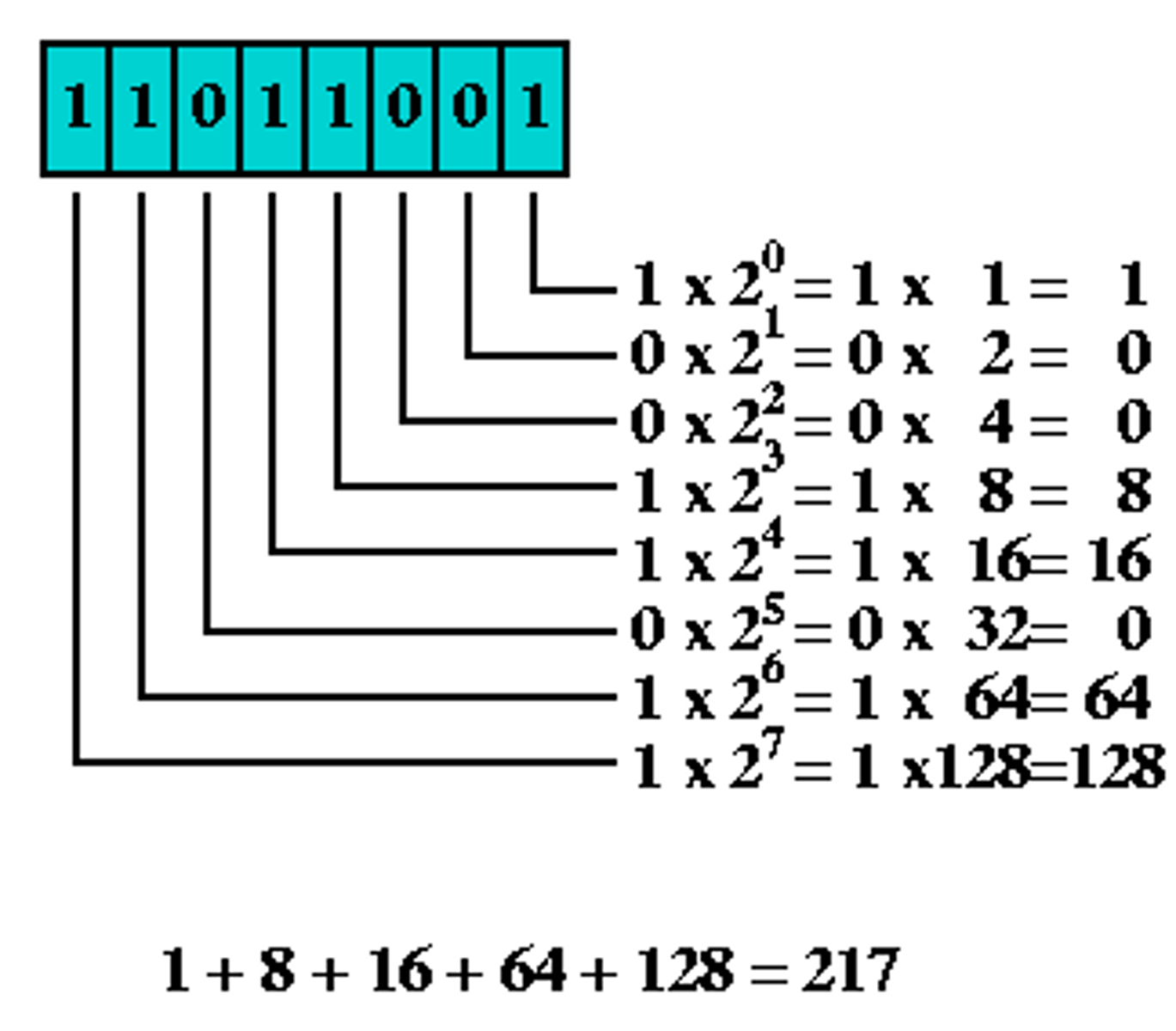
Binary to Decimal
Multiply by powers of 2 beginning with the rightmost digit
Binary to Octal
Break up the binary code into sections of three from right to left. if the last section has less than 3, add enough 0's to make a group of 3. Convert the groups of 3 into their corresponding numbers 0-7.

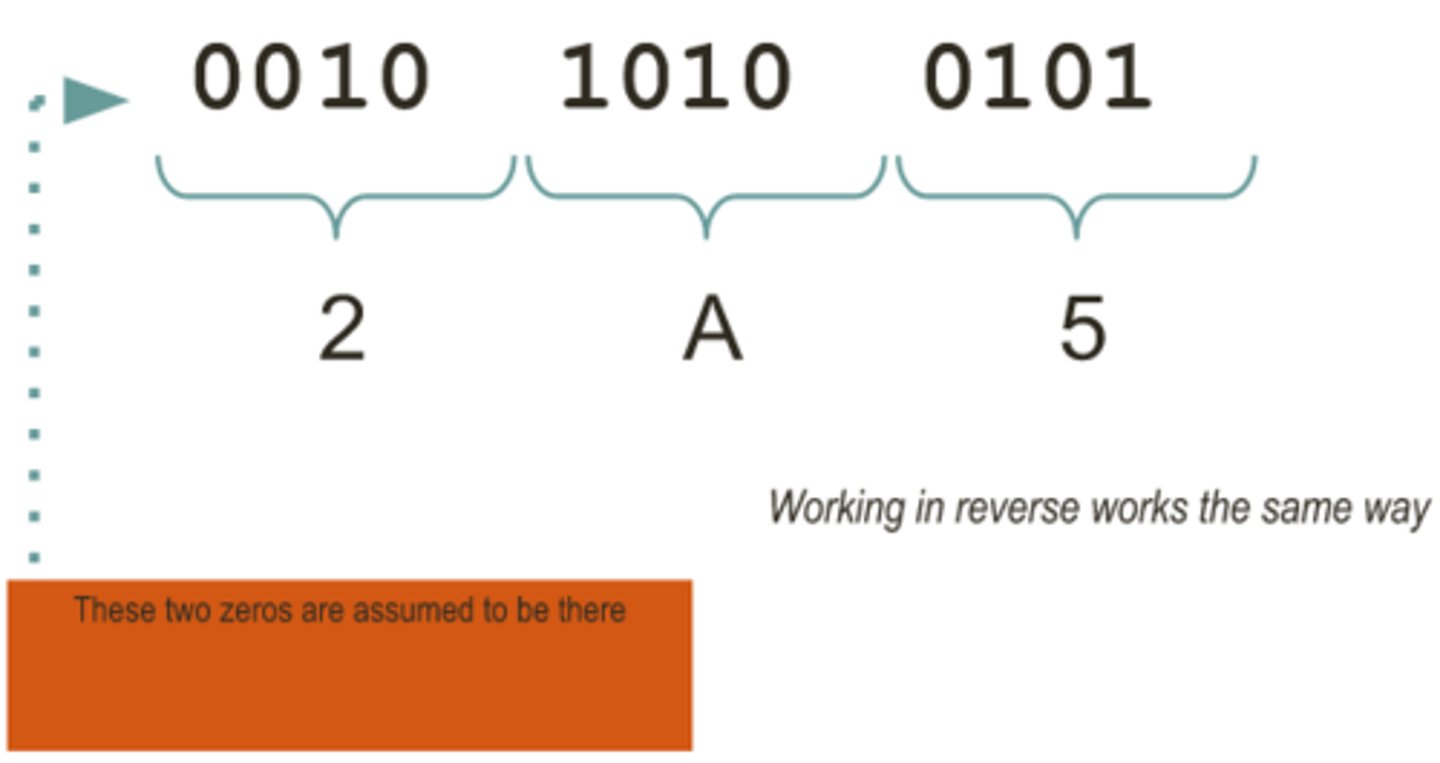
Binary to Hexadecimal
Combine each group of four binary bits into a single hexadecimal digit and convert it into corresponding numbers 0-9 and a-f
Octal to Binary
Divide the number by 8 until there is nothing left, accumulating 1's and 0's
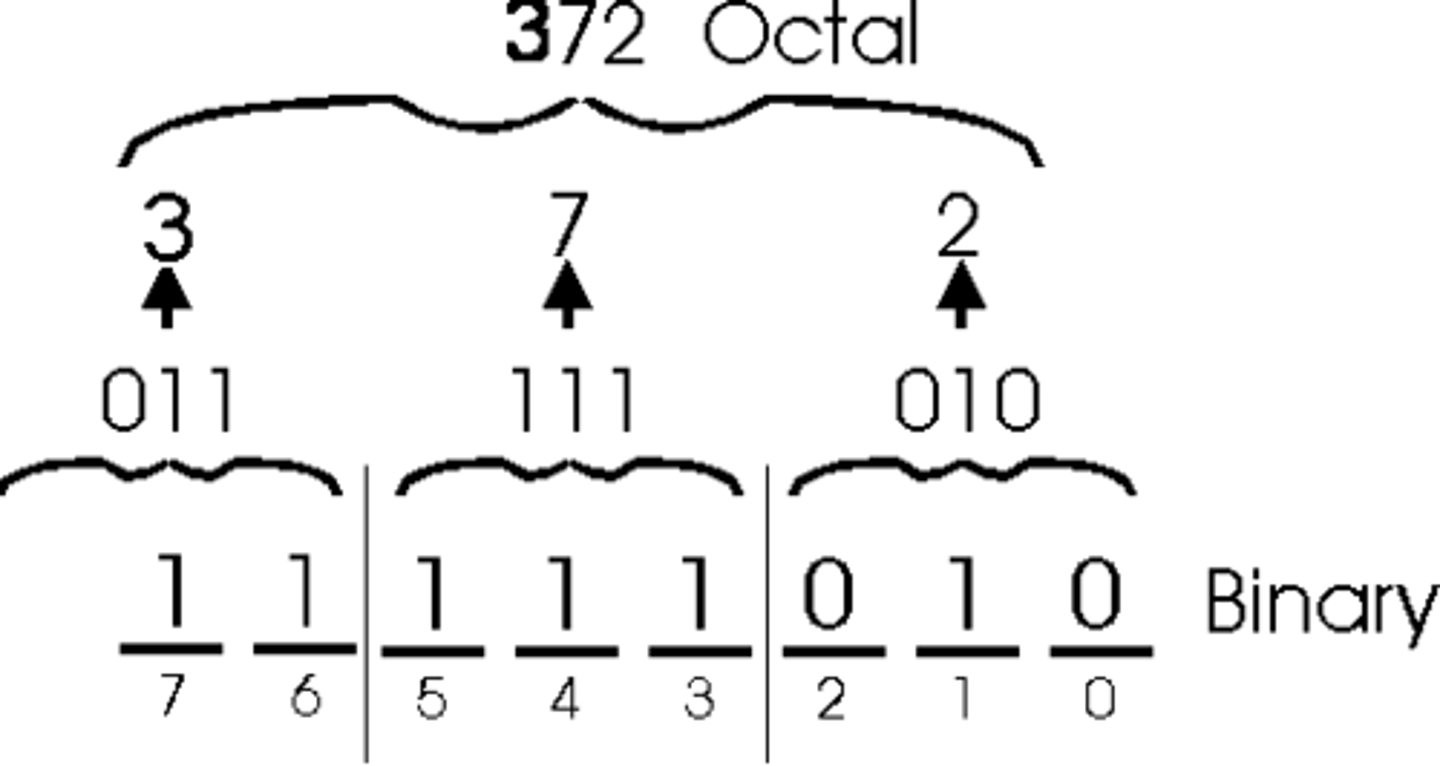
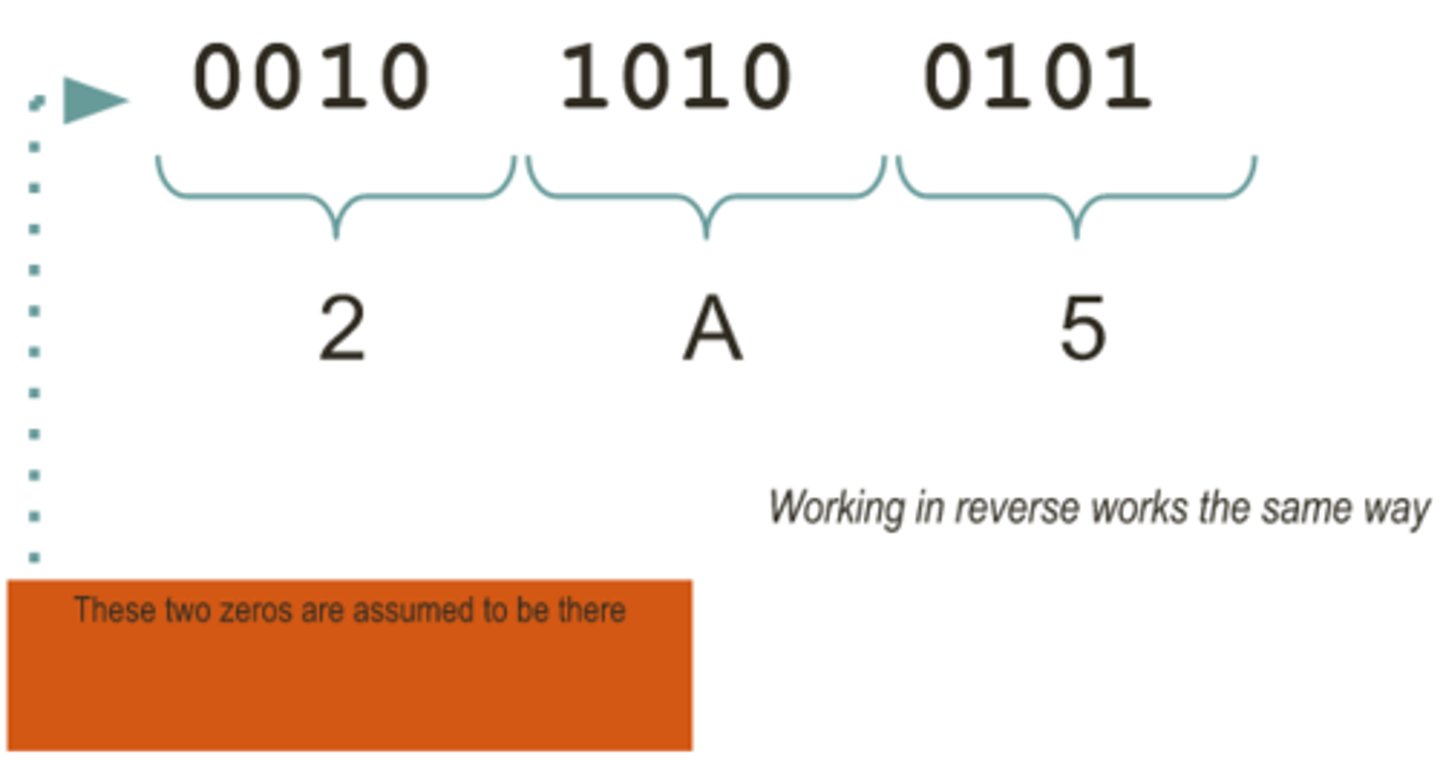
Hexadecimal to Binary
Split up the hexadecimal digits into single digits, convert each digit to binary nibbles using the headings 8421. Put the nibbles into order for the final binary value
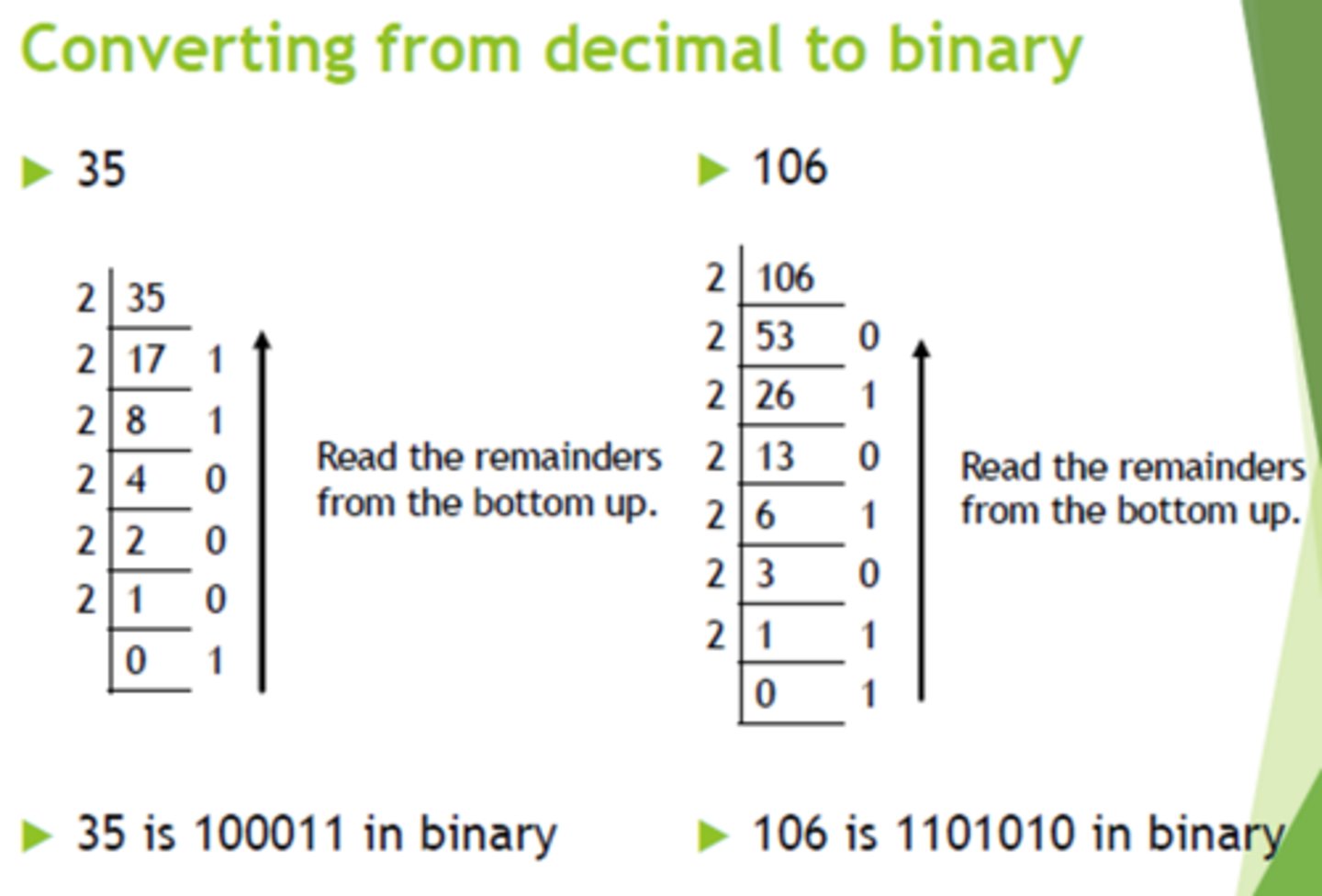
Decimal to Octal
*divide by 8
*keep track of remainder
Decimal to Hexadecimal
divide by 16
Decimal to Binary
divide by 2 and keep remainder
octal to hexadecimal
Octal -> Binary -> Hexadecimal
hexa to octal
hexa->binary->octal
The Computer System
consists of three components: Hardware, Software, and Peopleware.
Hardware
Includes Input Devices, Output Devices, and Storage Devices.
Software
Includes System Software / Operating System, Application Software, and Programming Languages.
Peopleware
Refers to people involved in the computing process such as users, programmers, and IT staff.
Human Language
Commonly used to express feelings and understand other person's expression. It can be oral or gestural kind of communication.
Computer Language
The language by which a user commands a computer to work on the algorithm which a user has written to get an output.
Programming Language
Set of words, symbols, and codes that enables humans to communicate with computers.
Basic Elements of Programming Language
Includes: Programming Environment, Data Types, Variables, Keywords, Arithmetical and Logical Operators, If-Else Conditions, Loops, Numbers, Characters and Arrays, Functions, Input and Output Operations.
Computer Program
A series of organized instructions that directs a computer to perform tasks. A sequence of instructions that dictate the flow of impulses within a computer system.
Editor
allows the user to enter the program source code and save it to files.
Syntax
A language refers to the way pieces of the language are arranged to make well-formed sentence (grammar).
Compiler
A computer program which reads source code and outputs assembly code or executable code. This software converts the code written in high-level language into object file. Translate entire programs into machine code, which can be run later on the target computer. Examples: C, C++
Compiler Process
Includes three stages: Preprocessor, Compiler, Linker.
Preprocessor
Adds to or modifies the contents of the source file before the compiler begins processing the code.
Compiler Stage
Translates C++ source code to machine code.
Linker
Combines the compiler-generated machine code with precompiled library code or compiled code from other sources to make a complete executable program.
Source Code
In the form of text, is human-readable, generated by human, and is input to the compiler.
Object Code
In the form of binary numbers, is machine-readable, generated by compiler, and is output of the compiler.
Debugger
Allows a programmer to more easily trace a program's execution in order to locate and correct errors in the program's implementation.
Debugger (Function)
A developer can simultaneously run a program and see which line in the source code is responsible for the program's current actions.
Profiler
Collects statistics about a program's execution allowing developers to tune appropriate parts of the program to improve its overall performance. Indicates how many times a portion of a program is executed during a particular run, and how long it takes to execute. The main purpose of profiling is to find the parts of a program that can be improved to make the program run faster.
Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
Includes editors, debuggers, and other programming aids in one comprehensive program. Microsoft Visual Studio 2015, Eclipse Foundation's Eclipse CDT, and Apple's Xcode.
C++ History (Creator)
Bjarne Stroustrup
C++ History (Creation)
Created in 1979 at Bell Labs, Murray Hill and originally called C with Classes.
C++ History (Renaming)
Renamed as C++ in 1983; pronounced as see-plus-plus.
C++ History (Standardization)
A standardized language (ISO standard) in 1998.
C++ Features
List: Simple, Portable, Powerful, Platform Dependent, Object-Oriented, Case Sensitive, Compiler-Based, Syntax-Based Language, Use of Pointers.
C++ Feature - SIMPLE
Can be written in simple English language.
C++ Feature - PORTABILITY
The concept of carrying the instruction from one system to another system.
C++ Feature - POWERFUL
It has a wide variety of data types, functions, control statements, decision-making statements, etc.
C++ Feature - PLATFORM DEPENDENT
Applications that run under only one operating system in one series of computers.
C++ Feature - CASE SENSITIVE
It treats the lower-case letter separately from upper-case letter.
C++ Feature - OBJECT ORIENTED
It follows the concept of OOP like polymorphism, inheritance, encapsulation, abstraction.
C++ Feature - COMPILER-BASED
Without compilation, no C++ program will be executed.
C++ Feature - SYNTAX-BASED LANGUAGE
A strongly tight syntax-based programming language.
C++ Feature - USE OF POINTERS
A variable which holds the address of another variable; directly directs access to a memory address of any variable.
Software Written in C++
Examples: Windows XP, iPad, Google Chrome, Safari, MS Office, YouTube, VLC media player, MySQL, Warcraft, Adobe applications.
Computer Language
The language by which a user commands a computer to work on the algorithm which a user has written to get an output.
Programming Languages
Used to write application programs which are used by end users.
C++ Overview
A statically typed, compiled, general purpose, case sensitive, free-form programming language that supports procedural, object-oriented, and generic programming.
C++ programming language is case-sensitive.
true
Input and Output
This property of an algorithm specifies the set of elements to be encoded and the expected outcomes.
Flow lines
Connects the steps of the flowchart and indicates the sequence of procedures.
Human Language
Commonly used to express feelings and understand another person's expression.
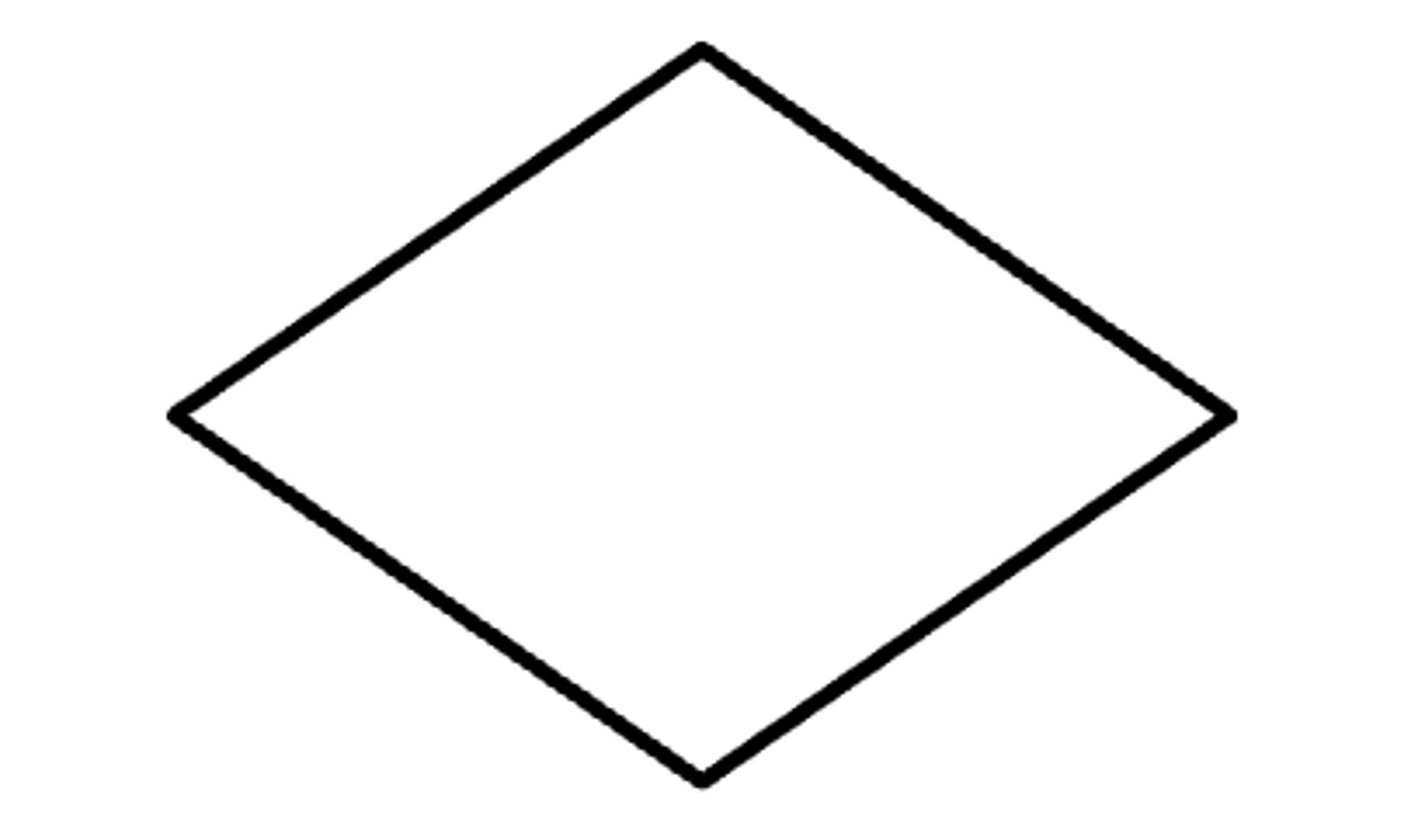
Decision
Used to evaluate condition and decide for a course of action.
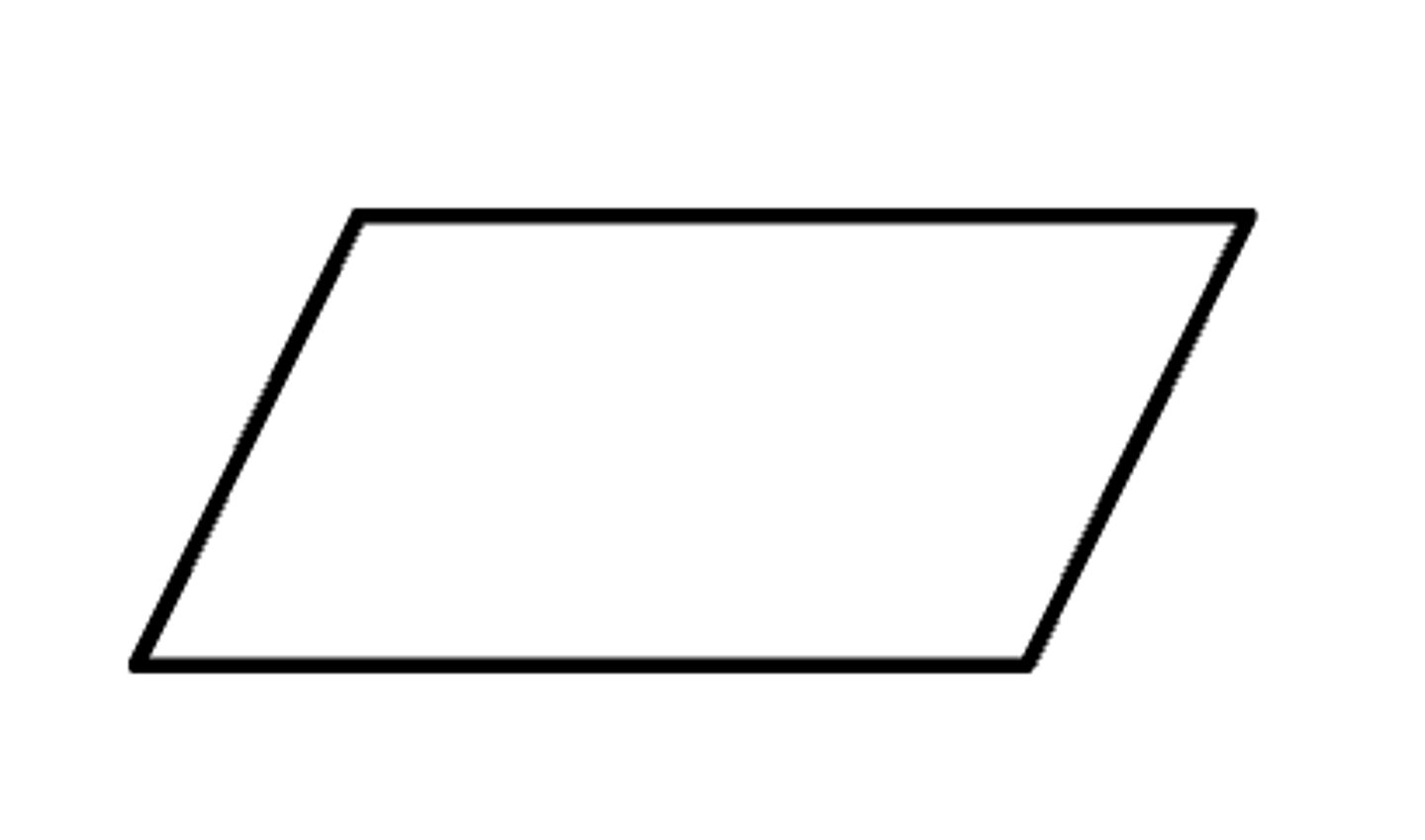
It is an input given to the compiler.
Does not describe the object code?
Input/Output
Used to represent any of the devices used to accept or give our data.
top to bottom
A flowchart should flow from?
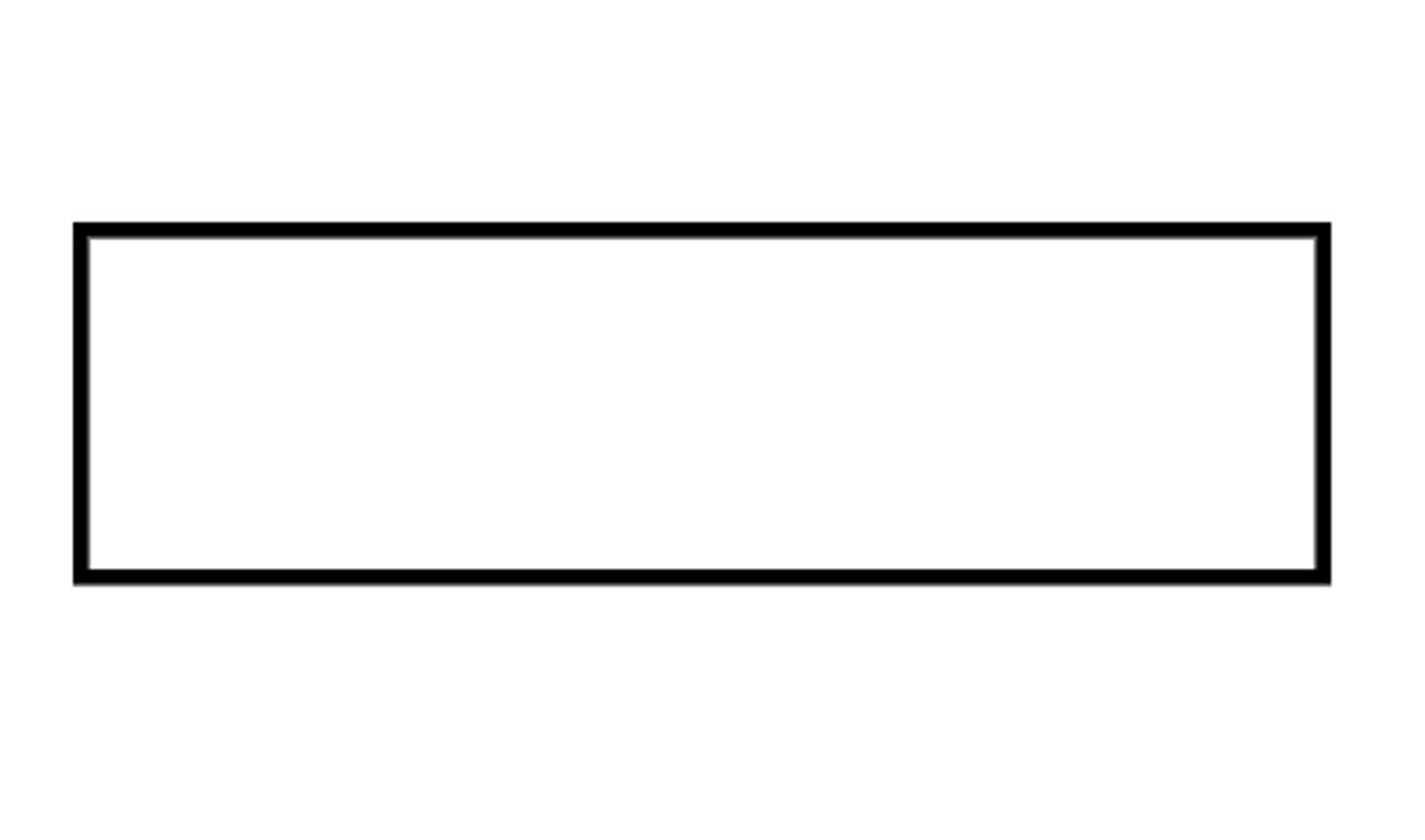
Process
Used to represent an operation or a procedure.
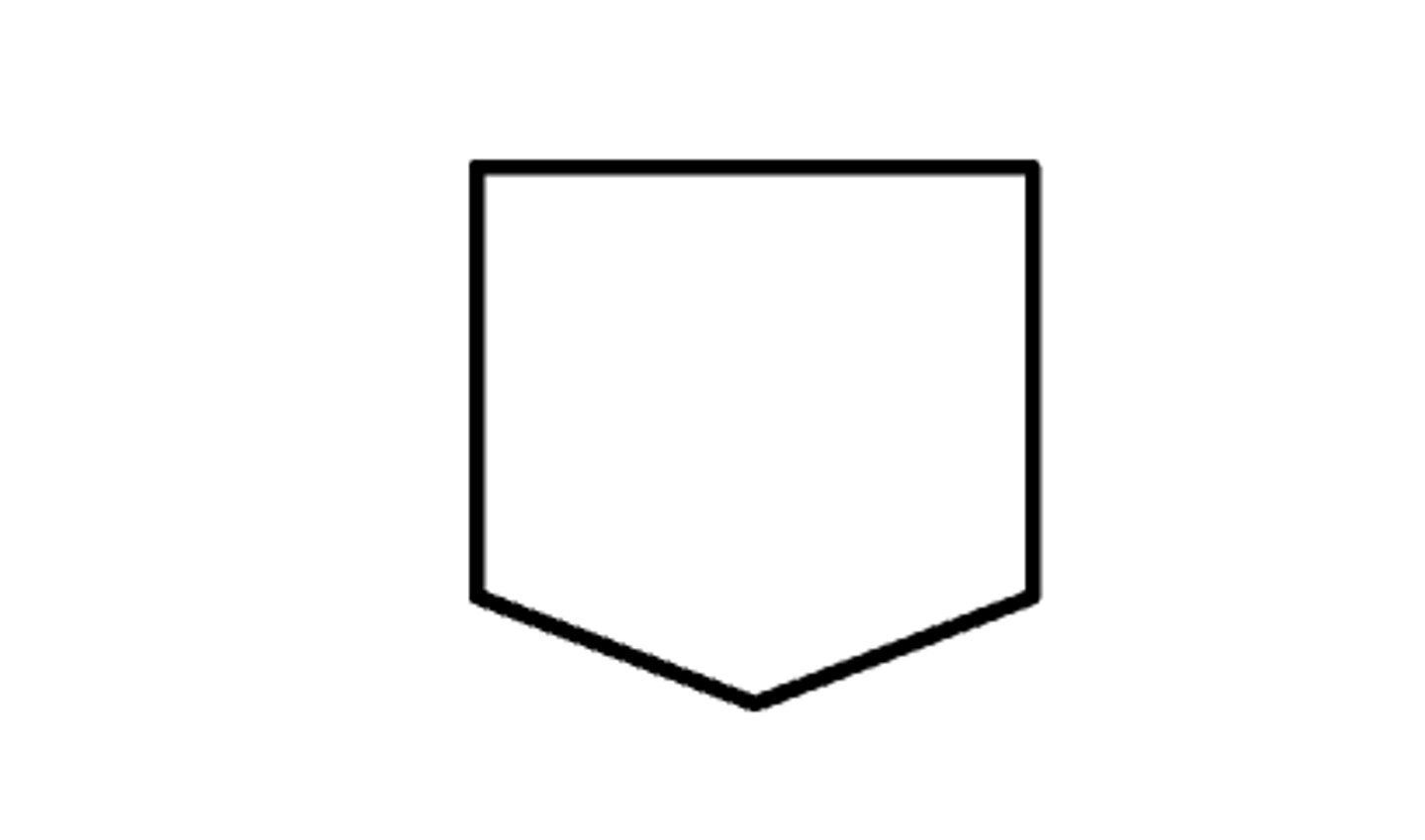
Terminal
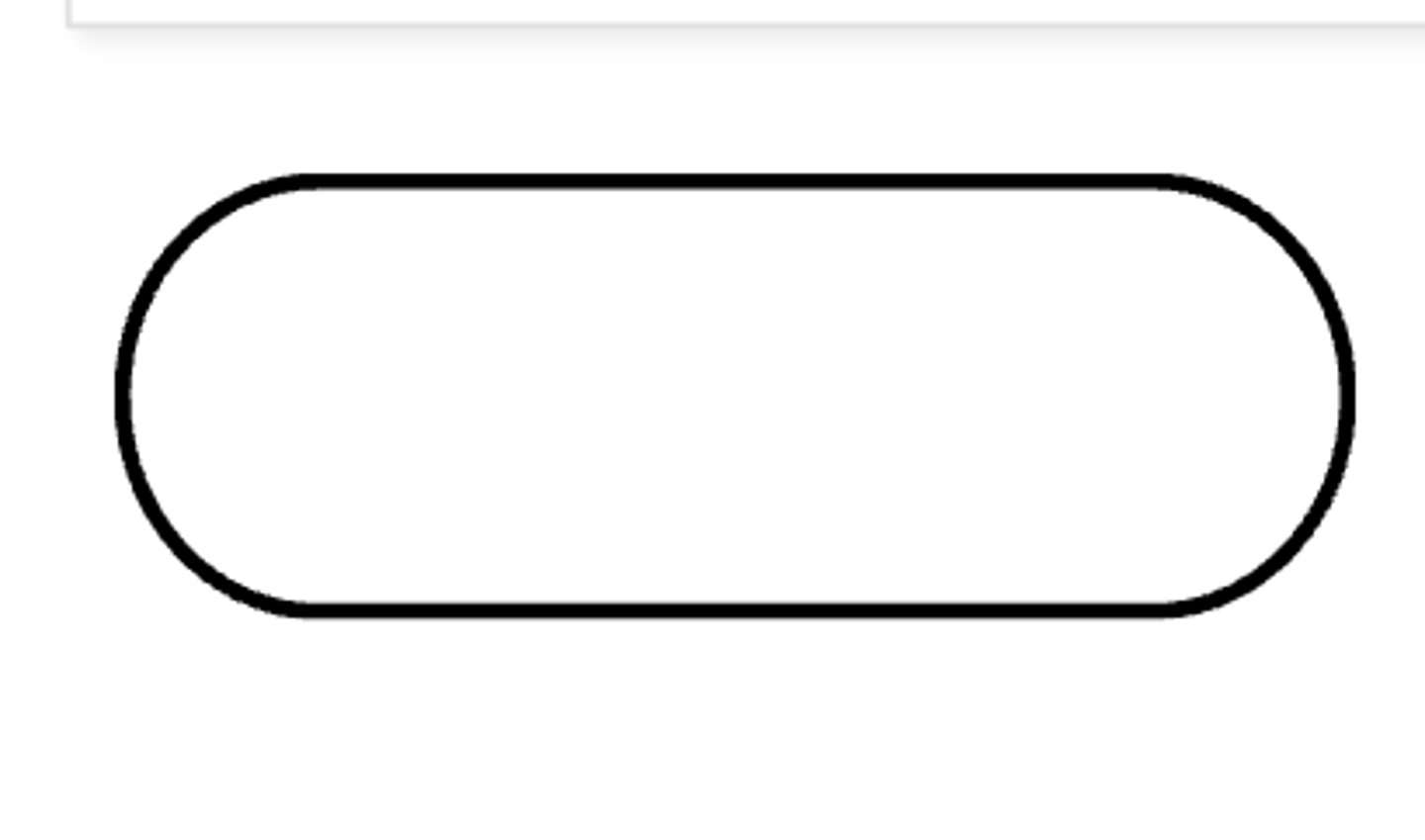
Indicates the start and end of the algorithm.

Compiler
Converts the written high-level programming language into an object code.
Off-page connector
Connects one step of the flowchart to another step on the other page.
On-page connector
Connects one step of the flowchart to another step on the same page.
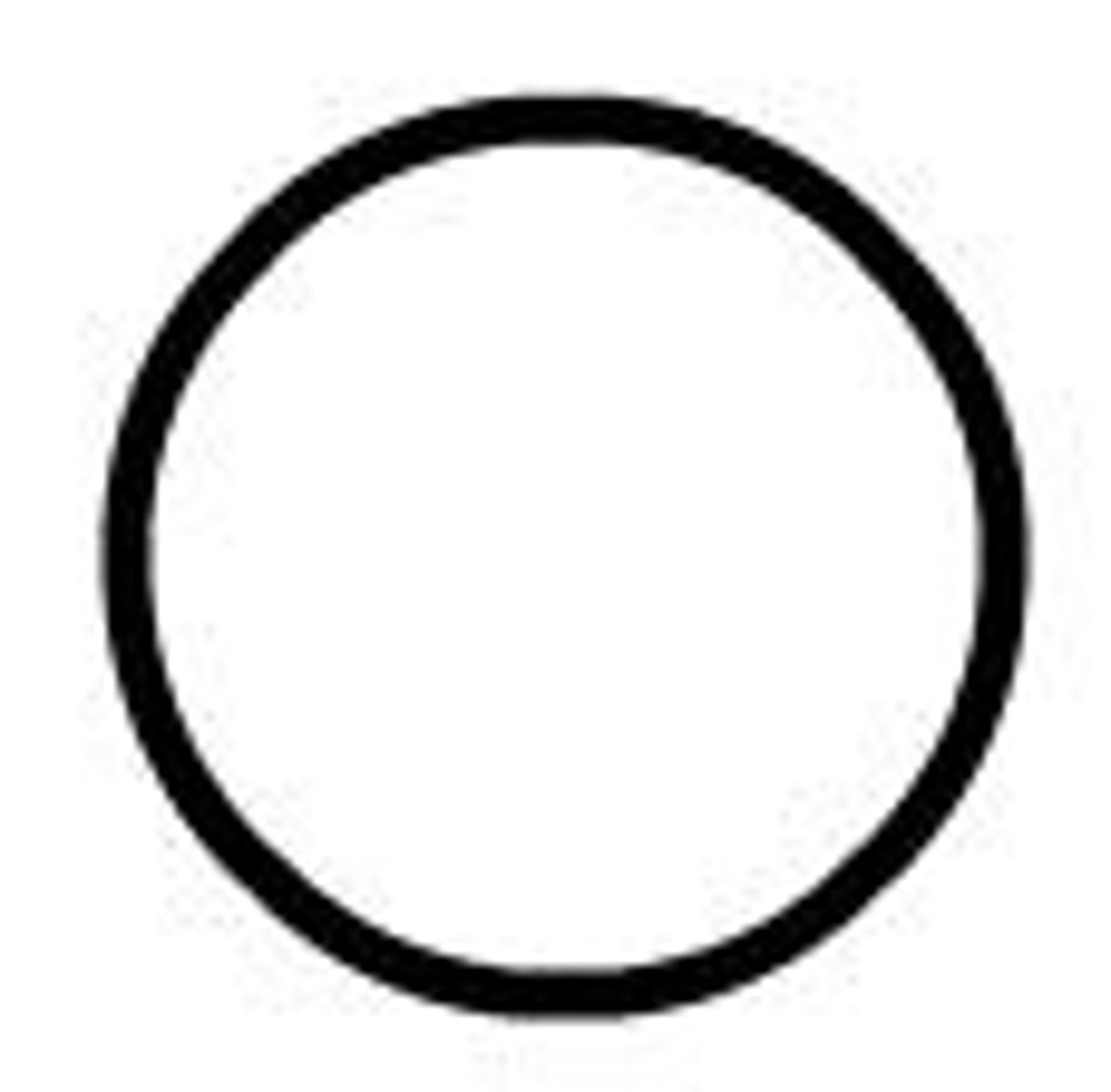
Initialization
Used to represent starting values of variables.
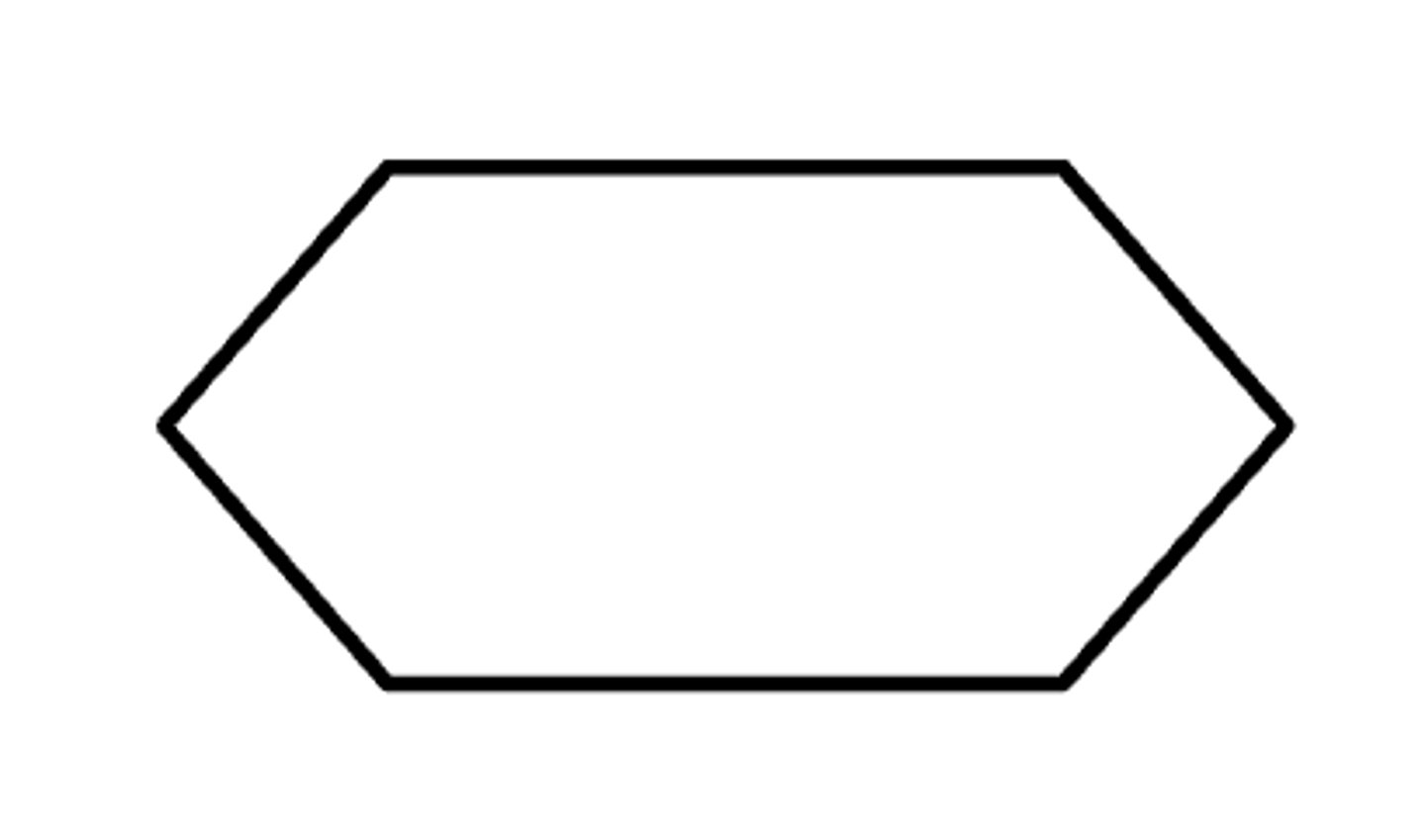
CODING
The stage where the actual computer program is written using languages like C, Visual Basic, or Java. Syntax errors such as spelling and missing commas are eliminated here.
TESTING AND DEBUGGING
Testing ensures that all functions in the system work correctly. Debugging is the process of identifying and fixing errors found during testing.
DOCUMENTATION
The phase where development records of the current software version are kept for reference in redesigning and maintaining the program.
MAINTENANCE
The process of updating and correcting the program when errors are found during actual use or execution.
ALGORITHM
A formula or set of steps for solving a particular problem. A logical sequence of steps that solve a problem. It is used as a guide to solve problems. Can be expressed in English-like language called pseudocode. Can also be expressed in graphical form called flowchart
Finiteness
There is an exact number of steps to be taken.
Absence of ambiguity
Every instruction is precisely described and clearly specified.
Sequence of execution
Instructions are performed from start to bottom.
Input and output
The unknown of the problem is specified and with the expected outcome.
Effectiveness
The solution prescribed is guaranteed to give a correct answer and specified process is carried out.
Scope definition
Applies to a specific problem or class of problem.
IPO model
The input-process-output model presents the flow how data entered by the user should be processed by the machine to produce result.
Pseudocode
An artificial and informal language that helps programmers develop algorithms. A shorthand notation for programming which uses a combination of informal programming structures and verbal description of code. Emphasis is placed on expressing the behavior or outcome of each portion of code rather than on strict correct syntax.
Writing a pseudocode
Several keywords are often used to indicate common input, output and processing operations:
- input: read, obtain, get
- output: print, display, show
-compute: compute, calculate, determine
- initialize: set init
- add one: increment, bump
Flowcharting
One of the processes used in designing or planning the solution to a problem. A graphical representation to the solution of the problem. Uses shapes to show instructions and arrow lines and heads to display the flow.
Flowcharting guidelines
The flowchart should flow from top to bottom. If the chart becomes complex, utilize connecting blocks. Avoid intersecting flowlines. Use meaningful description in the symbol.