Alcohols
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What is the general formula of an alcohol
CnH2N+1OH
Nomencalture for alcohols (How do you name alcohols)
Alcohols are named using the IUPAC system by identifying the longest carbon chain containing the hydroxyl (-OH) group. The suffix '-ol' is added to the name of the corresponding alkane. Number the carbon chain to assign the lowest possible number to the hydroxyl group. If there are multiple -OH groups, use prefixes like 'di-' or 'tri-' to indicate their quantity.
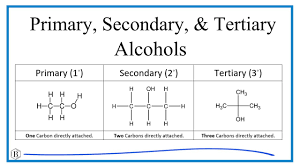
Alcohols (primary, secondary and tertiary) Image
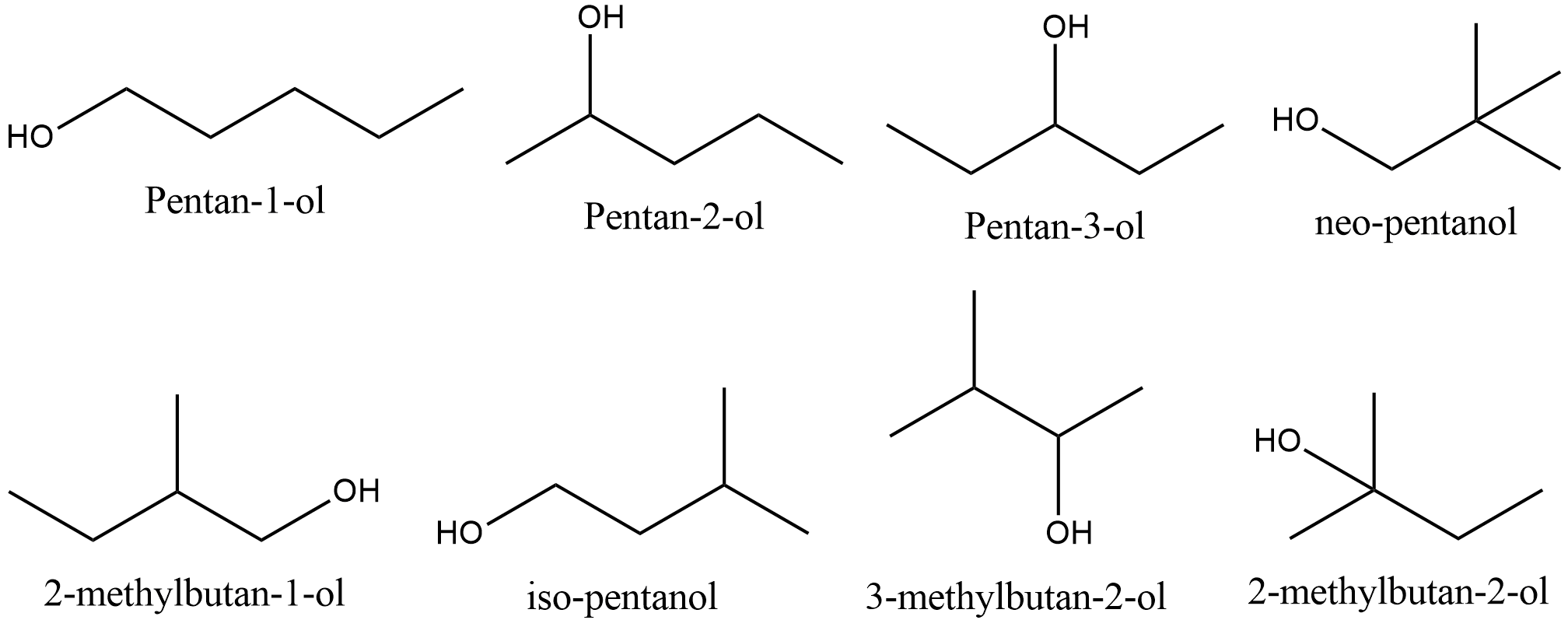
Positional isomer for alcohols (image)
What are 2 methods for producing ethanol
Fermentation and the hydration of ethene
Fermentation balanced symbol equation
C6H12O6 (aq) → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Glucose solution → ethanol + carbon dioxide
What are the conditions of fermentation
35oc - 40oc (to not denature enyzme) Anaerobic (absence of O2 to prevent oxidation Aqueous) pressure of 100KPa
Economic and enviromental advantages of of fermentation
Economic: Low equipment and running costs, limited fossil fuels burned
Environmental: Renewable resources, effectively carbon neutral
Economic disadvantages of fermentation ( The environmental disadvantage is the same as the economic)
Slow batch process low purity/yield (15%) takes up a large are of land to grow crops which could be used to grow crops for food → increase in food prices.
How do you industrially produce ethanol
Hydration of ethene (addition of water)
C2H4(g) +H2O → CH3CH2OH(g)
What are the conditions for the hydration of ethene to produce ethanol
300oc 6500KPa pressure, concentrated H3PO4 (Phosphoric Acid) or concentrated H2SO4 (Sulfuric acid)
Economic and environmental advantages of the Hydration of ethene
Economic: High purity/ yield (99%). Fast and continuous
Land not required to grow large amounts of crops so it can be used for food.
Economic and environmental disadvantages of the hydration of ethene
Environmental: Non-renewable resources large quantities of fossil fuels burned → Global warming
Economic: High equipment and running costs.
When ethanol is produced by fermentation what is it called?
A bio fuel (Similar to vegetable oils which are grown and converted into bio-diesel.)
What is a bio fuel
A biofuel is a renewable energy source derived from organic materials, such as plants and waste.
Advantages of biofuel use
They are considered “Carbon neutral” as the amount of CO2 taken in during photosynthesis equals the amount of CO2 released during fermentation and combustion.
They are renewable resources so are sustainable, only release CO2 and H2O when combusted and no sulfur impurities.
Disadvantages of biofuel use
Land used to grow crops for fuel and not for food which could lead to food shortage and prices increases.
Need to convert car engines to run on a high concentration of ethanol.
Deforestation to make room to grow crops for fuel. Fertilisers used on crops can polute waterways and release nitrous oxide.
Is ethanol a carbon neutral biofuel?
During photosynthesis: 6H2O + 6CO2 → C6H12O6 + 6O2 (6 moles of CO2 taken in)
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
2C2H5OH + 6O2 → 4CO2 + 6H2O (6 moles CO2 released)
However fossil fuels are burned to power machinery to harvest crops, refine and transport these biofuel. These will release extra CO2 so it is not completely carbon neutral
How do you differ between different classes of alcohols (Primary etc)
Using acidified potassium dichromate, alcohols undergo oxidation reactions on heating.
What does a primary alcohol oxidise to?
It oxidises to an aldehyde then to a carboxylic acid
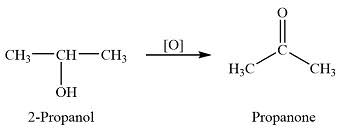
What does a secondary alcohol oxidise to
A ketone
What does a tertiary alcohol oxidise to
Do not oxidise → no hydrogen bodned directly to carbon so no oxidation
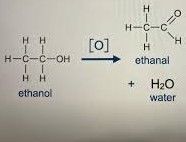
What does [O] represent?
Oxygen from oxidising agent
Example of making an aldehyde from an alcohol
Function group = COH
Example of how a carboxylic acid is made from an aldehyde and what condition is needed for this to occur
(It needs to be in reflux condition)
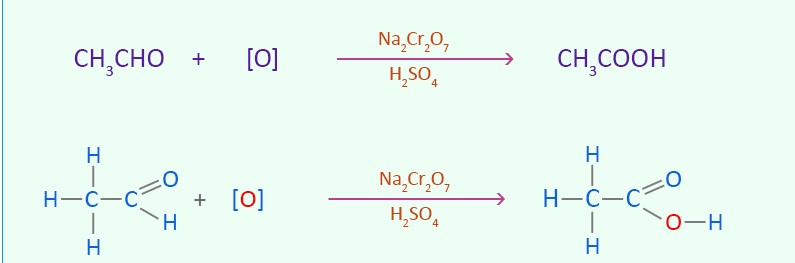
What happens when an alcohol reacts with an aldehyde in reflux conditions?
It is converted straight to a carboxylic acid
What colour change happens when an alcohol goes to an aldehyde or when an aldehyde goes to a carboxylic acid?
Orange → green colour chnage
Example of making a ketone from a secondary alcohol
No second oxidation occurs.
Why does the orange to green colour change occur
When a primary or secondary alcohol oxidses Cr2O72- (orange) → Cr3+ (green)
Balanced symbol equation for potassium dichromate → Chromium
Cr2O72- + 6e- + 14H+ → 2Cr3+ +7H2O

What are the 2 mild oxidising reagent thatr eact with aldehydes?
They are known as fehling solution and tollens reagent.
How is tollens reagent made?
It is made by combinding AgNO3 with excess aqueous NH3 . On warming, an aldehyde reduces the Ag+ ions to Ag. This Ag precipitates in the form of a silver mirror on the side of tes tube. Ketones, however do not show such a reaction.
What is the observation with tollens reagent
SILVER MIRROR
Reduction reaction for Ag
Ag+ (aq) + e- → Ag(s)
Balanced symbol equation form ethanal for ethanoic acid
CH3COH + [o] -. CH3COOH
How is fehling solution made?
Fehlings solution is made up by adding a solution of Cu2+ ions to sodium posttassium tartrate dissolved in excess NaOH. This produces a blue solution. An aldehyde reduces the Cu2+ ions to a red/brown Cu2O ppt on warming.
What is made in both tollens reagent reaction and fehlings solution reagent
They both make ethanoic acid from ethanal.
Reduction reaction for fehlings solution
2Cu2+ +2H2O +2e- → Cu2O(s) + 2H+
Observation from fehlings solution
Red/brown ppt( precipitate) formed
Test for carboxylic acid
Add sodium carbonate/sodium hydrogen carbonate to unknown solution. Bubbles of gas are positive result. To test gas bubble it through limewater and CO2 it will turn cloudy
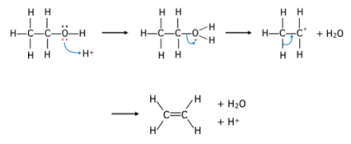
Elimination reaction for alcohols