Biology 5C ~ Lecture 9 ~ Population Growth
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
1
New cards
Change in population size...
births + immigrants - deaths - emigrants leaving population
-if immigration and emigration are ignored, a population's growth rate (per capita increase) equals birth rate minus death rate
-if immigration and emigration are ignored, a population's growth rate (per capita increase) equals birth rate minus death rate
2
New cards
Exponential growth
-the parameter r is the instantaneous per capita rate of increase
-the balance of births and deaths determine r
-in an open population, you would include immigrants with births (=gains per capita) and emigrants with deaths (=losses per capita)
-the balance of births and deaths determine r
-in an open population, you would include immigrants with births (=gains per capita) and emigrants with deaths (=losses per capita)
3
New cards
Exponential growth where...
b=the instantaneous number of births *per capita --- [the per capita birth rate]
m=the instantaneous number of deaths *per capita --- [the per capita death rate]
m=the instantaneous number of deaths *per capita --- [the per capita death rate]
4
New cards
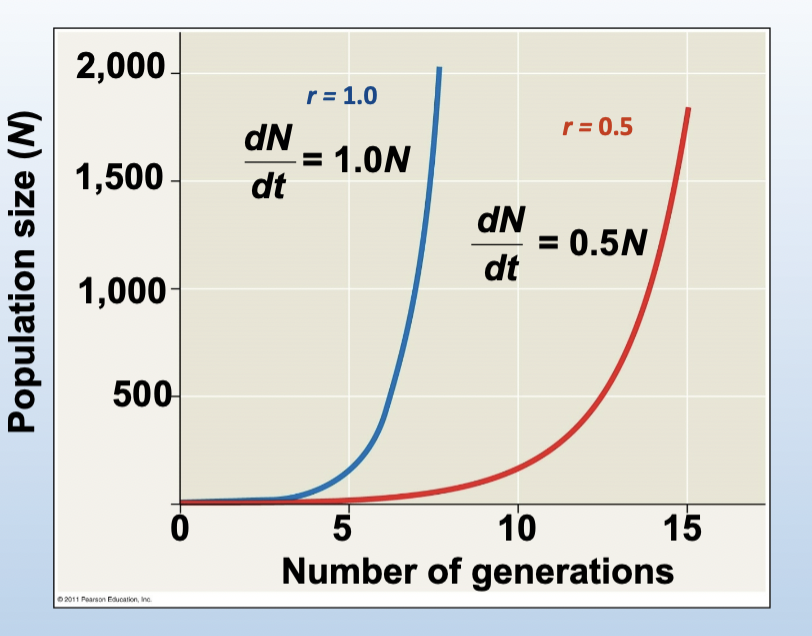
if r, the instantaneous per capita rate of increase, is constant...
the population grows exponentially
5
New cards
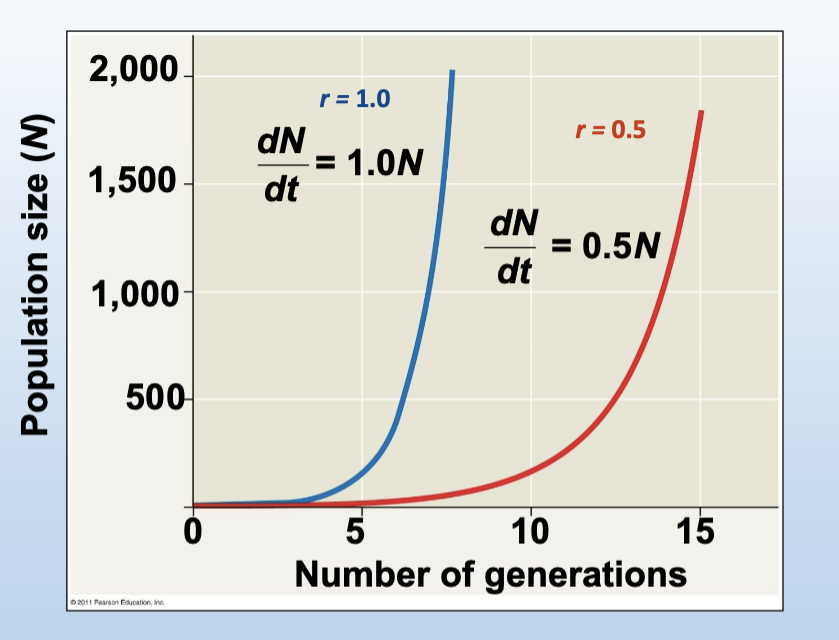
In unrestrained growth, with constant r,...
dN/dt increases as population size increases (i.e., growth accelerates)
6
New cards
Populations cannot continue to increase indefinitely b/c...
-exponential growth cannot be sustained for long in any population
7
New cards
A more realistic population model limits growth by...
incorporating carrying capacity (K), which is the maximum population size the environment can support
8
New cards
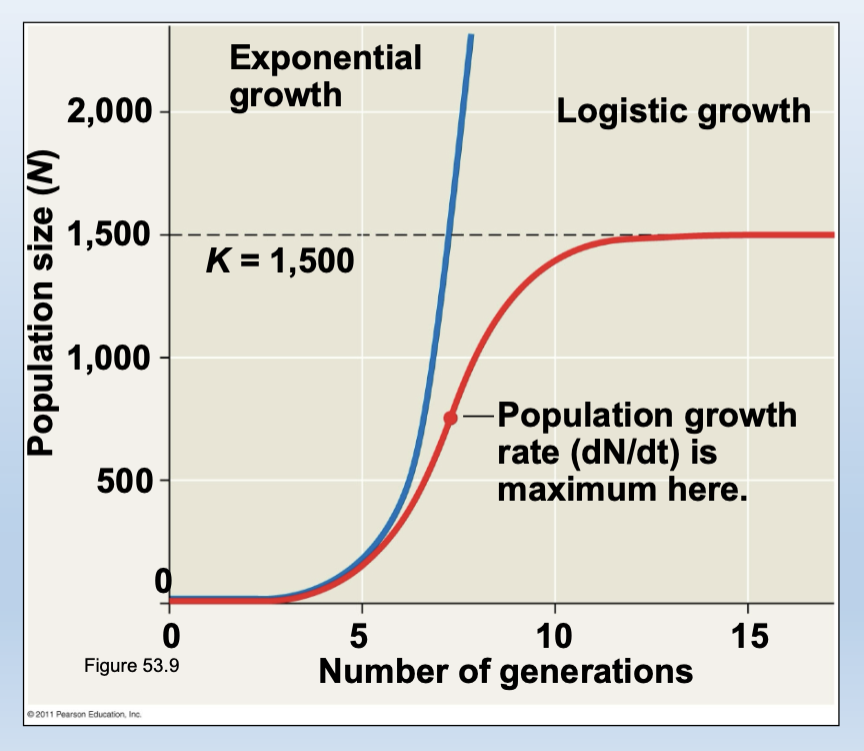
The logistic growth model
-Starts with the exponential model and adds an expression that reduces the instantaneous per capita rate of increase as N approaches K
9
New cards
the instantaneous per capita rate of increase under logistic growth is always less than or equal to r:
the logistic model of population growth produces a sigmoid (S-shaped) curve
-insert image slide 11
-insert image slide 11
10
New cards
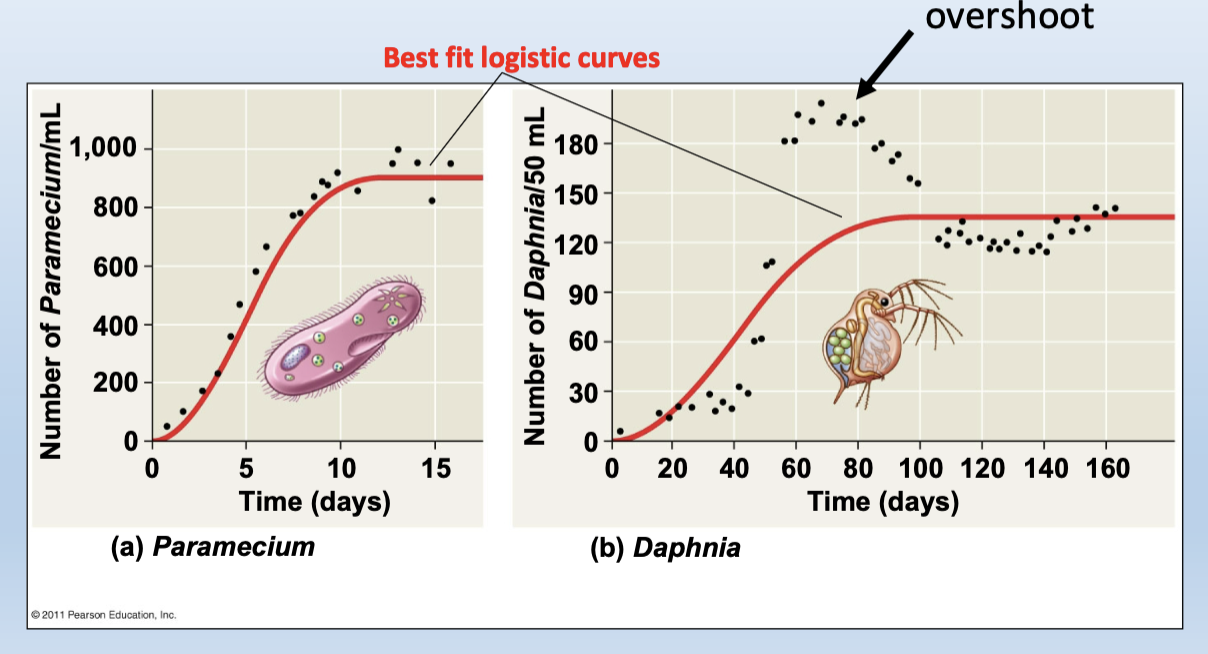
Examples of limited growth:
the growth of laboratory populations in a constant environment lacking predators but with limited food
-insert image slide 12
-insert image slide 12
11
New cards
Under the logistic growth model,...
the per capita instantaneous population growth rate is negatively density-dependent
12
New cards
As N increases,...
the instantaneous growth rate decreases
13
New cards
Logistic growth of a hypothetical population (K = 1,500):
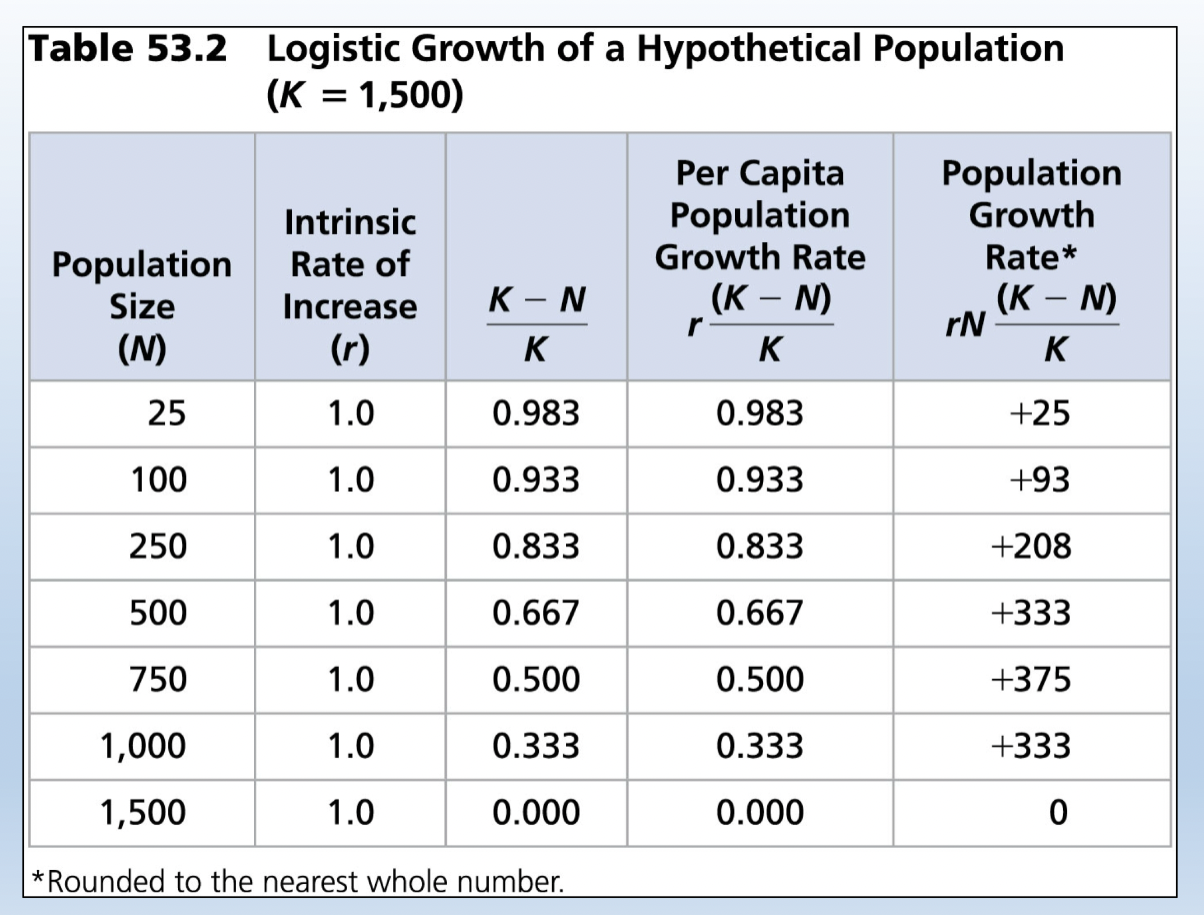
14
New cards
Population density vs. birth or death rate per capita graph: slide 17
-when the density is low, b > m
-when the density is high, m > b
-when the density is high, m > b
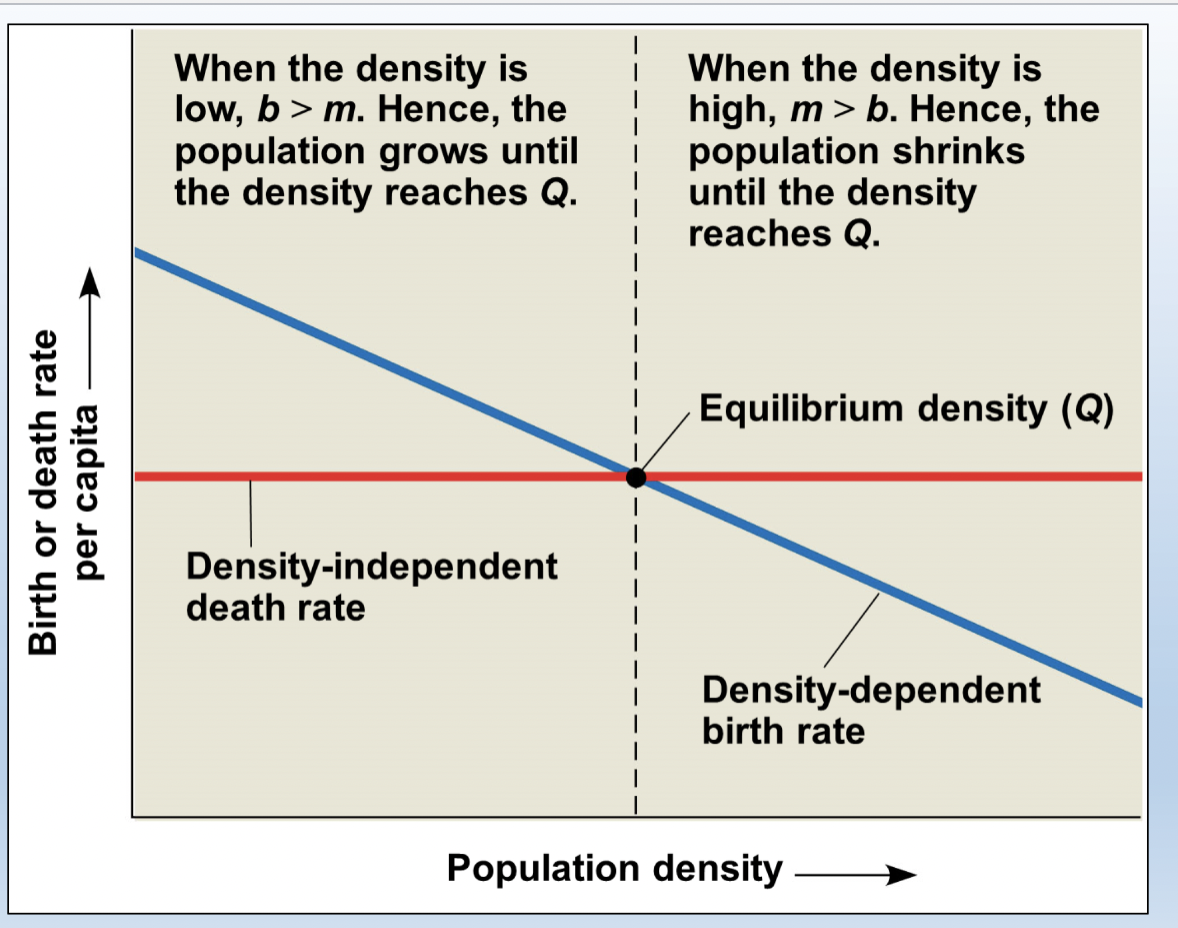
15
New cards
Negative density dependence:
-when a population growth is reduced by crowding, predators and competition
16
New cards
SLIDES TO KNOW FOR THE EXAM
-exponential growth
-logistic growth
-negative density dependence
-watch the video for more understanding
-logistic growth
-negative density dependence
-watch the video for more understanding