Neural basis of Speech Perception
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Motor Theory of Speech Perception
Proposed by Alvin Lieberman, this theory suggests that speech perception involves a specialized module in the brain specifically for processing speech, separate from nonspeech sounds.
Categorical Perception
The phenomenon where speech sounds are perceived distinctly and categorically, as opposed to non-speech sounds which are perceived along a continuum.
Unique Points
In the cohort model, the moment when only one word becomes consistent with the speech input, allowing for recognition.
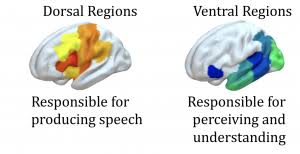
Ventral Stream
The pathway in the brain involved in word recognition and semantic processing, spanning from the auditory cortex to the frontal cortex.
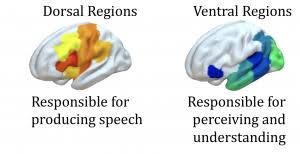
Dorsal Stream
The pathway that links speech perception with speech production, involved in sound discrimination and phonological processing.
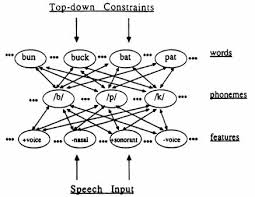
Trace Model
A computational model of speech perception that emphasizes both bottom-up and top-down processing, using neural-like units to represent different levels of speech processing.
Lexical Competition
The process in which multiple word representations become activated and compete for recognition during speech perception.
Evidence against Motor Theory
Categorical perception has been demonstrated in non-speech sounds and in animals, suggesting that a specialized speech module may not exist.
Cohort Model
A model of spoken word recognition proposing that words are activated immediately upon hearing speech, with representations competing until a uniqueness point is reached.
TMS Study
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation study that disrupts neural activity, providing evidence of brain area involvement in specific cognitive tasks, like phoneme discrimination.
fMRI
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is a neuroimaging technique that measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow, providing insights into the functioning of different brain areas during various cognitive tasks.
Alvin Lieberman
A psychologist who proposed the Motor Theory of Speech Perception in the 50s and 60s.
Broca's Area
An area in the inferior frontal gyrus that is traditionally associated with speech production.
Wernicke’s Area
Located in the superior temporal gyrus, it is involved in language comprehension, named after the neurologist Carl Wernicke.
Semantic Processing Task
A task assessing the ability to understand the meaning of words and associate them with relevant concepts.
Categorical Perception in Animals
The phenomenon where animals, such as chinchillas, have demonstrated categorical perception, suggesting it's not uniquely human.
Auditory Cortex
The part of the brain responsible for processing sound information, where both the ventral and dorsal streams originate.
Context Effects
Phenomena in speech perception whereby the understanding of speech is influenced by contextual information, such as previous words or anticipated meanings.
Phoneme Boundary
The point in speech perception where a change in the acoustics leads to a change in the identification of a phoneme.
Activations in Motor Areas during Listening
Findings from studies where brain scans show activations in motor regions when participants listen to speech, supporting links between perception and production.