vascular plants lab - 7
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
selective advantage of flowers
less energy required to make a bit of pollen
attract an animal to carry the pollen to another plant, rather than making gobs of pollen and hoping that the wind will pollenate a neighbour
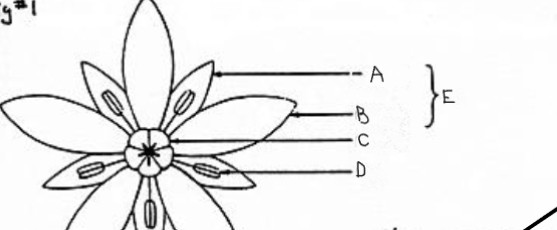
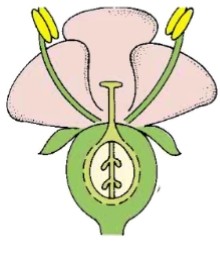
identify a-e
a. sepal
b. petal
c. pistil
d. stamen
e. perianth
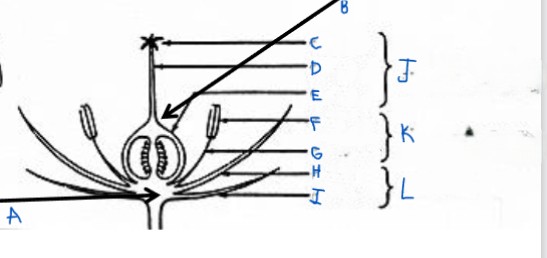
identify A-L
a. receptacle
b. ovary (fused carpels)
c. stigma
d. style
e. ovary
f. anther
g. filament
h. petal
i. sepal
j. pistil
k. stamen
l. perianth
carpel/pistil
modified megasporophyll
encloses and protects the ovules
ovules develop into…
seeds
Inflorescence
Ways flowers are clustered together into aggregations
Peduncle
The stalk of an inflorescence (cluster of flowers)
Pedicel
The stalk of a single flower in an inflorescence
Receptacle
The part of the flower stalk to which the floral appendages are attached
What parts of the flowers are the stable appendages
Sepals and petals
What parts of the flower are fertile
Stamens and carpels
Calyx
All the sepals together
Corolla
All the petals together
Perianth
The calyx and corolla together
What are stamens and their two parts
Stamens are microsporophylls
They consist of the filament and anther
The anther contains
Four pollen sacs (microsporangia)
Parts of the carpel
lower part: the ovary
Middle part: the style
Upper part: the stigma
Ovary function
Enclose and protect the ovules
Stigma function
receives the pollen from the pollinating agent (insect, animal, wind)
Assists in germination
Style function
connects stigma to ovary
Elevates stigma so it’s receptive to pollen
Provides entry route and nutrition to to pollen tube of a germinated pollen grain
Perfect flower
has both carpels and stamens on same flower
Imperfect flower
Lacking either stamens or carpels on flowers
Staminate flowers
Only have stamens on flowers
Carpellate flowers
Only have carpels on flower
Monoecious
Same plant has both staminate flowers and carpellate flowers
Dioecious
Staminate and carpellate flowers are found on different plants of the same species
Complete flowers
Have all floral parts (sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels)
Incomplete flowers
Lacking one or more floral parts (carpel, stamen, sepal, petals)
All imperfect flowers are incomplete
regular/actinomorphic flowers
radially symmetrical
floral parts are similar in shape and radiate from center of the flower and are equidistant from each other
irregular/zygomorphic flowers
bilaterally symmetrical
one or more of the floral parts (often petals) have different form than other members of the same whorl
hypogynous flowers
the sepals, petals, and stamens are attached to the receptacle below the ovary
the ovary is said to be superior and the flower is said to be hypogynous
epigynous flowers
the sepals, petals, and stamens apparently grow from the top of the ovary, which is therefore inferior
perigynous flowers
the petals and the stamens are attached to the margin of a
cup-shaped extension of the receptacle (the hypanthium)ovaries still considered superior

what type of symmetry does this flower have
radial = regular/actinomorphic

what kind of symmetry does this flower have
bilateral = irregular/zygomorphic
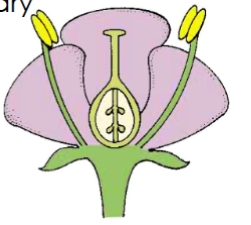
what type of flower is this based on ovary position
hypogynous
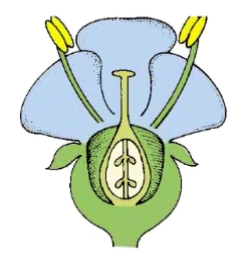
what type of flower is this based on the position of the ovary
perigynous
what type of flower is this based on the position of the ovary
epigynous
placenta
The portion of the ovary where ovules originate and remain attached
until maturity
parietal placentation
the ovules are borne on the ovary wall or on extensions of it
axile placentation
the ovules are borne on a central column of tissue in a partitioned ovary
with as many locules as there are carpels.Also called central
free central
the ovules are borne on a central column of tissue not connected
by partitions with the ovary wall
basal placentation
a single ovule at the very base of a unilocular ovary.
pendulous placentation
a single ovule at the top of the ovary
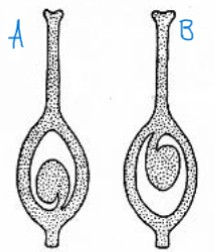
identify the placentation types a and b
a. basal
b. pendulous
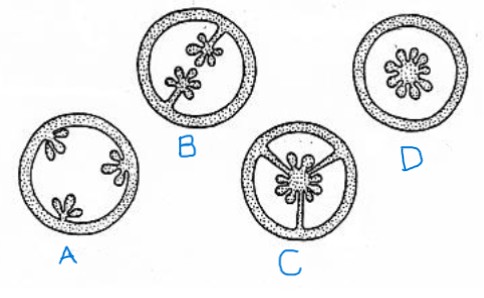
identify the placentation types for a-d (two are the same type)
a. parietal
b. parietal
c. axile/central
d. free central
trimerous flowers
3 sepals, 3 petals, 6 stamens and 3 carpels
monocots
tetramerous and pentamerous flowers
multiples of 4 or 5
eudicots
how are the floral parts arranged in a floral diagram (outermost to innermost)
sepals
petals
stamens
carpe
how should a hypogynous floral diagram be drawn
no lines attaching the floral parts
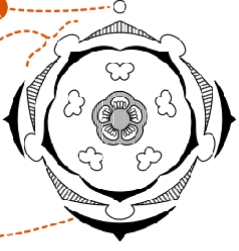
how should a epigynous floral diagram be drawn
the stamens, petals, and sepals, should be attached directly to the carpels by lines
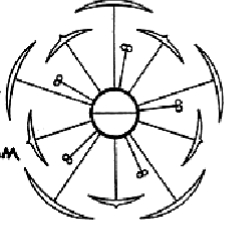
how should a perigynous floral diagram be drawn
the hypanthium should be drawn as a circle with the stamens, petals, and sepals attached to it by lines
the carpel should be inside the hypanthium

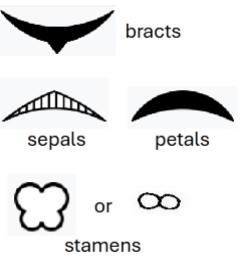
bracts
modified leaves or scales arising from the peduncle or pedicels.
involucre
Clusters or whorls of bracts
spathe
a single, highly colored, conspicuous bract
subtends a fleshy inflorescences called a spadix
solitary inflorescences
a single flower at the top of a peduncle
spike inflorescences
Flowers attached to the peduncle, which is the main stalk of the inflorescence
raceme inflorescence
There’s a peduncle, but the flowers are attached to pedicels, which are side stalks that come out of the peduncle
catkin inflorescences
A catkin is a specialized type of raceme or spike that is drooping, cylindrical, and composed of small, unisexual flowers that often lack petals
panicle inflorescences
A panicle is a branching cluster of flowers, where the main stem branches out and then those branches branch again
corymb inflorescences
a flower cluster whose lower pedicel stalks are proportionally longer so that the flowers form a flat or slightly convex head
The oldest flowers are on the outside of the cluster
cyme inflorescences
a flower cluster whose lower pedicel stalks are proportionally longer so that the flowers form a flat or slightly convex head
The oldest flowers are in the middle of the cluster
umbel inflorescences
has all the pedicels attached at a central point on the peduncle
head inflorescences
consist of two flower types: ray flowers on the perhiphery that are
showy and usually sterile, and disk flowers in the middle that are fertileThe receptacle is large and fleshy to support the entire structure
compound umbel
umbels attached to more umbels
determinate inflorescences
the main axis ends with a terminal flower, and subsequent flowers develop from lateral buds below it, meaning the main axis growth is halted
ex: solitary and cyme
indeterminate inflorescences
the peduncle keeps growing and producing flowers. Thus, the youngest
flowers are at the top of an elongated axis, or the centre of a head or umbel

identify the inflorescence
solitary

identify the inflorescence
spike

identify the inflorescence
raceme

identify the inflorescence
catkin

identify the inflorescence
panicle

identify the inflorescence
corymb
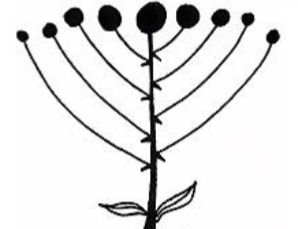
identify the inflorescence
cyme
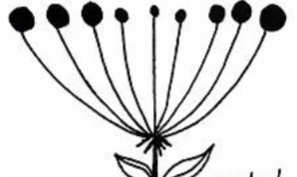
identify the inflorescence
umbel
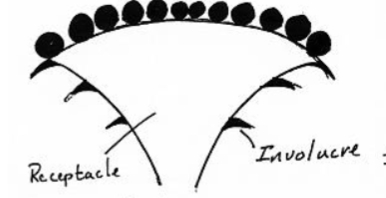
identify the inflorescence
head
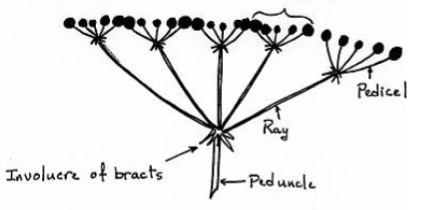
identify the inflorescence
compound umbel
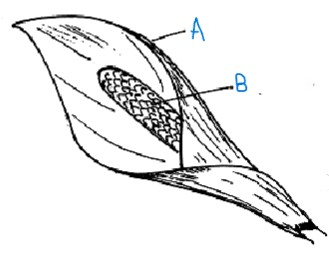
identify the inflorescence
spathe and spadix