Study Guide Test 1
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Thyroid hormone secretion is stimulated by?
primarily controlled by the thyroid-
stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the pituitary gland
Common sonographic findings with adenoma
commonly have peripheral ‘halo’
‘eggshell’ calcification (posterior shadowing)
complex cyst
PTH target hormones
1. Bone
2. Kidney
3. Intestine to enhance calcium absorption
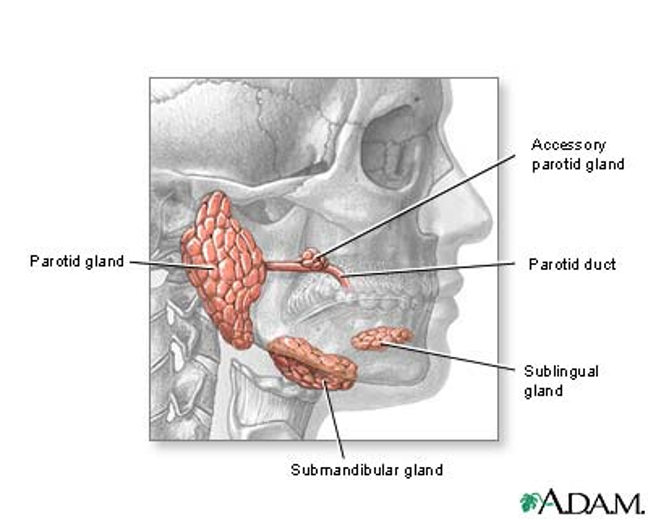
Salivary gland anatomy
Hormones secreted by thyroid
1. thyroxine (T4)
2. triiodothyronine (T3)
3. calcitonin (thyrocalcitonin
malignant sonographic characteristics
solid, hyperechoic
Calcifications
Most common thyroid abnormalities / inflammations
Nodular Thyroid Disease
Graves disease
autoimmune caused by antibodies that continuously activate TSH receptors.
underlying cause of hyperthyroidism in 50-80% of cases
Hyperparathyroidism lab tests
-↑ PTH -↑ Calcium -↑ Alk Phos
Parathyroid Adenoma lab test
-↑ Calcium -↓ Phosphate
Hypothyroidism
Decreased activity of the thyroid gland
associated with infertility
Benign sonographic characteristics
hypoechoic
Thyroid Sonography
hyperechoic
homogenous
Hypothyroidism causes T3, T4, and TSH to do what?
T3 and T4 = LOW
TSH = HIGH
Hyperthyroidism causes T3, T4, and TSH to do what?
T3 and T4 = HIGH
TSH = LOW
Hypothyroidism
most common
Decreased activity of the thyroid gland
associated with infertility
Primary Hypothyroidism
Most common
Caused by
Defective hormone synthesis
iodine deficiency
Secondary Hypothyroidism
Less common
Caused by
Pituitary adenoma
Signs of Hypothyroidism
Myxedema (thickening and swelling of skin)
Weight gain
Hair loss
Increased subcutaneous tissue around eyes
Hyperthyroidism
Hyperactivity of thyroid gland
Dramatically increases metabolic rate
Primary Hyperthyroidism
Excess thyroid hormone that is synthesized and secreted by thyroid gland itself
Secondary Hyperthyroidism
Rare
pituitary adenoma
Signs of Hyperthyroidism
Nervousness
Weight loss
Increased appetite/constant hunger
Exophthalmos (protruding eyes)
Hypothyroidism Causes
Low intake of iodine (food)
Inability to produce thyroid hormone
Masses on pituitary gland
TSH lab values
3-30 ng/mL
T4 lab values
free 0.8-2.4 ng/dL
total 4-11 ng/mL
T3 Lab values
75-220 ng/mL
Calcitonin Lab values
<100 pg/mL
subacute thyroiditis
viral infection that causes diffuse inflammation
brachial cleft cyst
remnant of embryonic development that appears as a cyst in the lateral neck
parathyroid adenoma
small, solid, oval
homogenous
hypoechoic
produces TSH
pituitary gland
parathyroid gland function
maintain homeostasis of blood calcium concentration
brachial cleft cyst
superficial cystic structure lying directly below the angle of the mandible
adenoma
benign solid tumor
normally solitary
adenopathy
enlargement of glands
cold nodule
area seen on nuclear medicine study as a region of thyroid where the radioisotope has not been taken up
euthyroid
thyroid producing the right amount of hormone
goiter
focal or diffuse thyroid gland enlargement due to iodine deficiency
hashimoto’s thyroiditis
most common inflammatory disease of the thyroid
heterotopic
occuring in abnormal place or wrong part of body
hyperparathyroidism
disorder associated with elevated serum calcium levels, usually caused by benign parathyroid adenoma
indolent
little pain
slow growing
microcalcifications
hyperechoic foci that may or may not shadow
papillary carcinoma
most common form of thyroid cancer
ages 20-30
hypoechoic, microcalcification
parathyroid hormone
regulates serum calcium and phosphorus
primary hyperparathyroidism
over secretion of parathyroid hormone
thyroglossal duct
congenital anomaly located anterior to trachea, extending from base of tongue to isthmus of thyroid
follicular carcinoma
irregular margins
thick irregular ‘halo’
nodular enlargement
(must use histology NOT FNA)
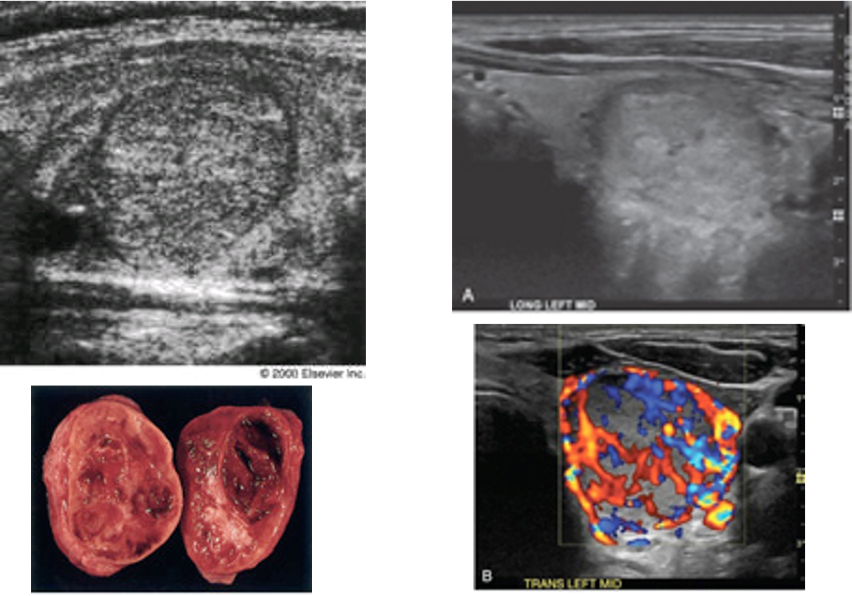
medullary carcinoma
hypoechoic solid mass
multiple
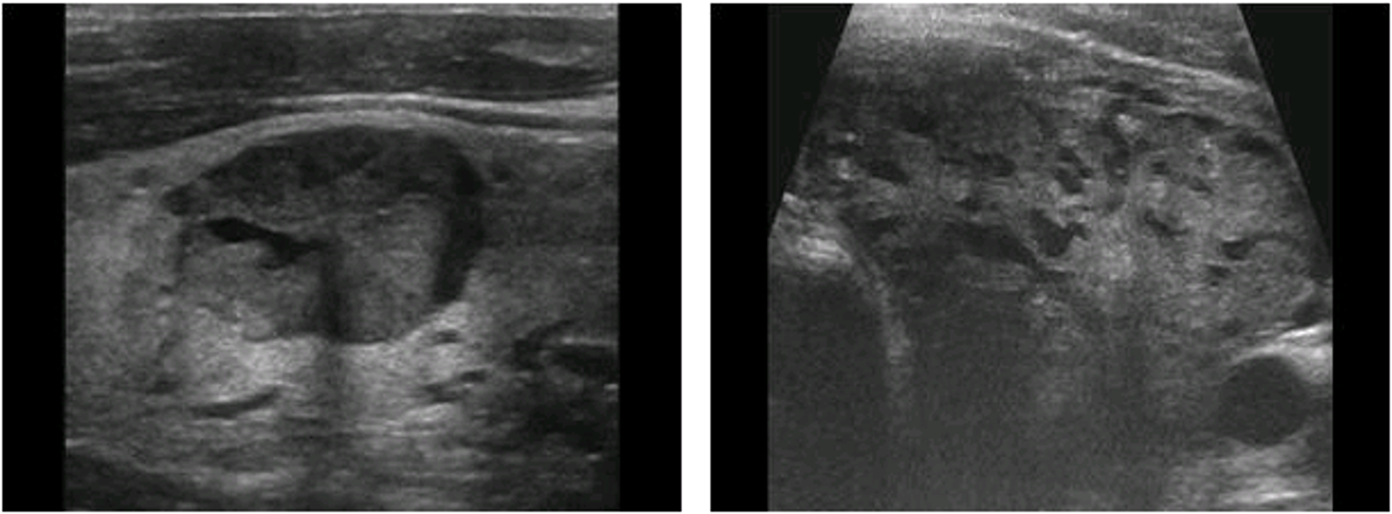
anaplastic carcinoma
large, solid, hypoechoic
aggressive, can compress local structures of the neck
rare, <10 % survive after 5 years, no effective therapy
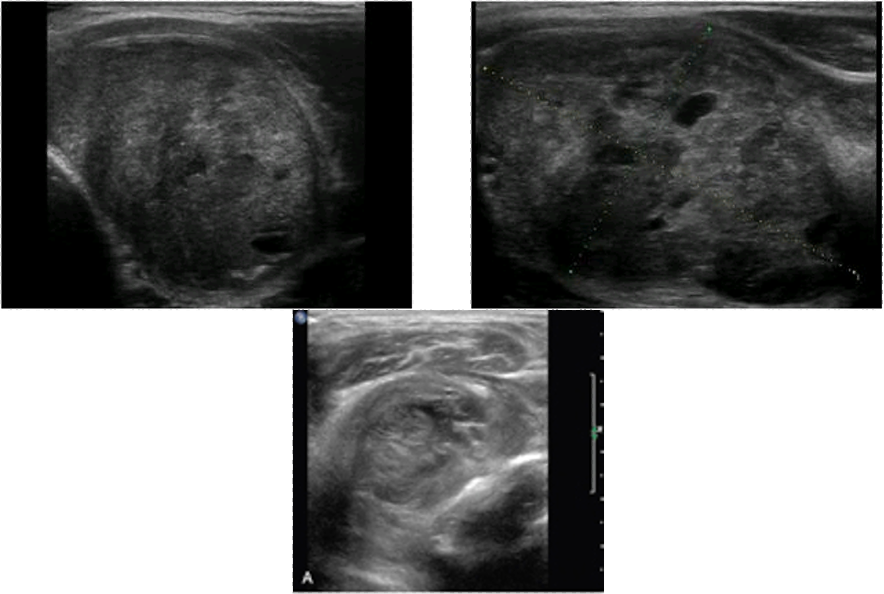
secondary hyperparathyroidism
vit D deficiency or
chronic renal failure
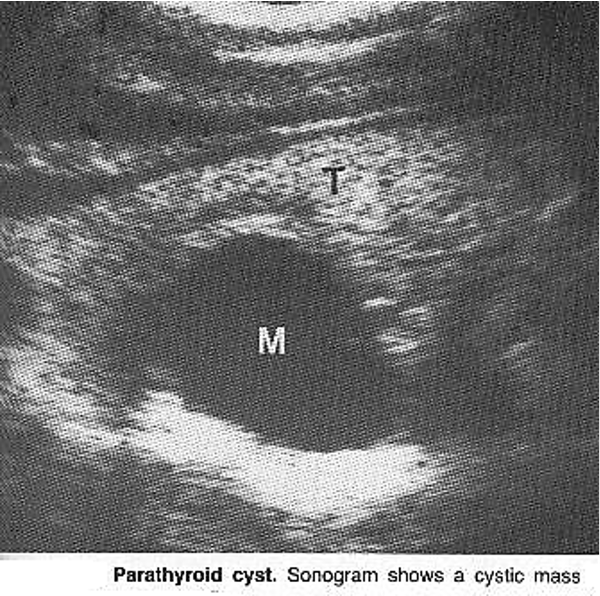
parathyroid cyst
Sonographically CANNOT be differentiated from other cystic neck masses
parathyroid carcinoma
malignant
associated with primary hyperparathyroidism
↑ PTH ↑ Calcium
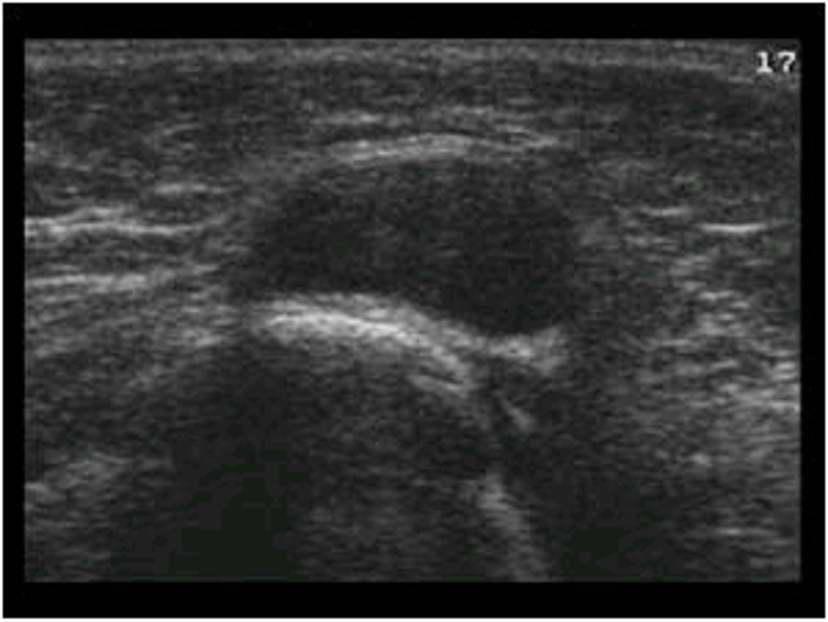
thyroglossal duct cyst
most common
oval
midline of neck anterior to trachea, superior to isthmus
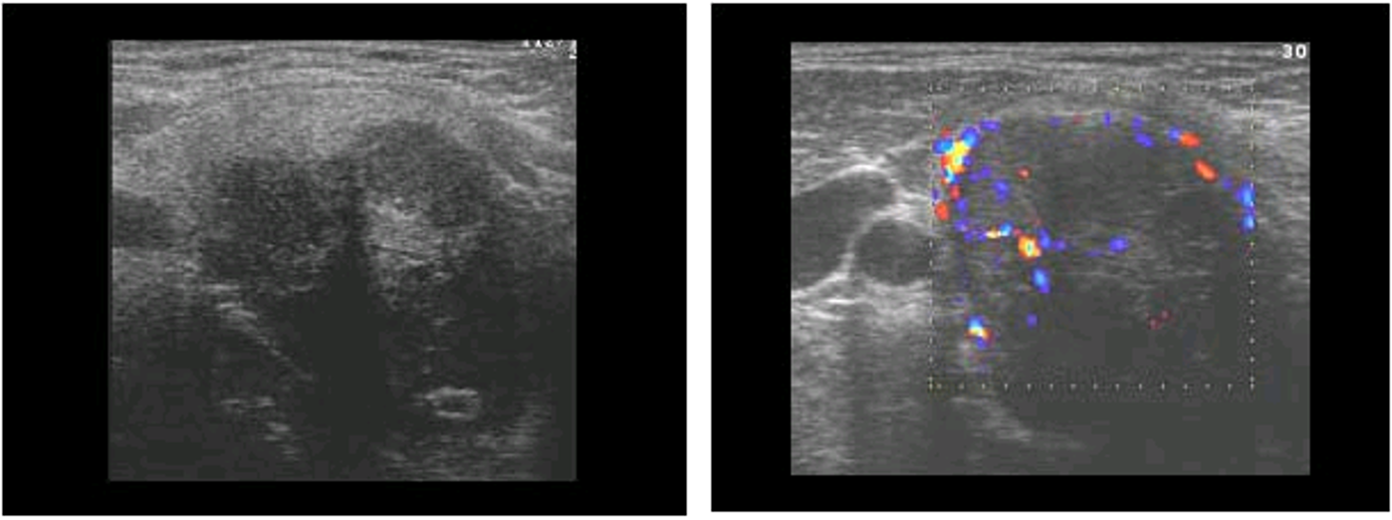
thyroid adenoma
nodules contained in fibrous capsule
nontoxic goiter
without evidence of discrete nodulant and without functional disturbance
most common cause of primary hypothyroidism
hashimotos
definitive diagnosis of papillary carcinoma
FNA
parathyroid gland location
2 superior, posterior to mid portion of thyroid
2 inferior,, posterior to lower thyroid
most common cause of hyperparathyroidism
parathyroid adenoma
most common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism
parathyroid adenoma
most common sonographic appearance of thyroid carcinoma
hypoechoic
subacute thyroiditis
causes diffuse inflammation
pleomorphic adenoma
most common benign salivary tumor
parotidectomy recommended
Warthin’s tumor
2nd most common benign salivary tumor
parathyroid adenoma
↑ serum Calcium ↓ Alk Phos ↓Vit D
multiple small echogenic foci with posterior shadowing bilaterally
Signs of Papillary Carcinoma
firm right lateral neck swelling
unexplained weight loss
no diet