MCB 150 Exam 1 Review
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Carbohydrates (polysaccharides)
Complex sugars made of long chains of monosaccharides, serving as energy storage and structural components in organisms. They include starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
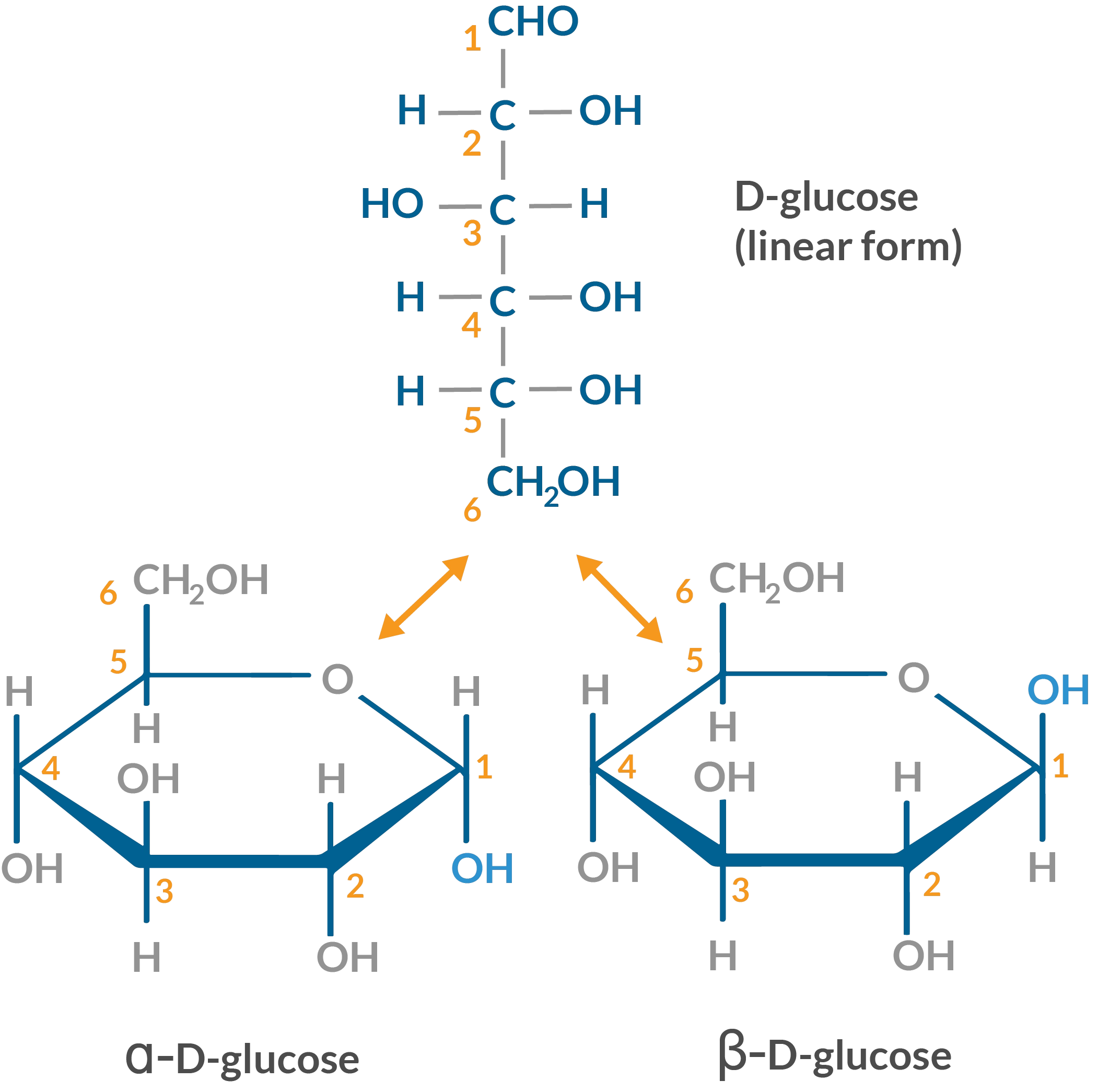
glucose
hexose sugar; monomer of lactose, maltose, sucrose and polysaccharides like starch and glycogen. aldehyde
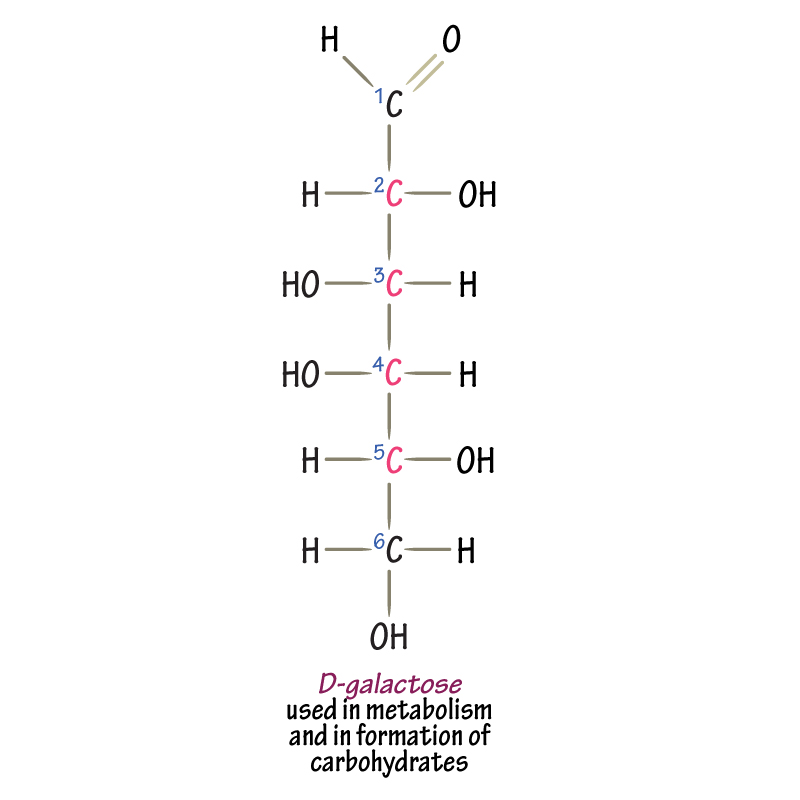
galactose
hexose sugar; monomer of lactose; aldehyde
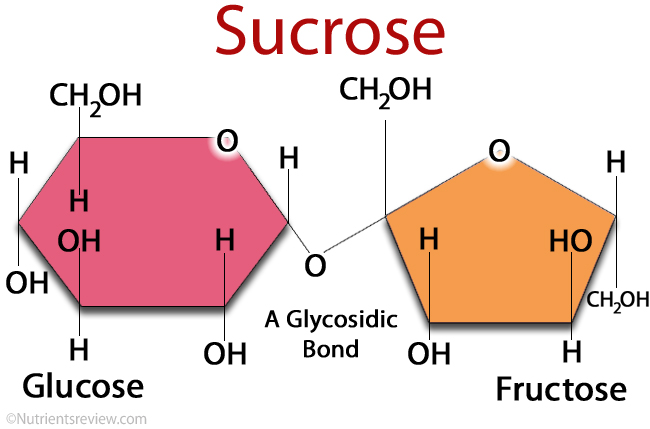
maltose
disaccharide of two glucose molecules
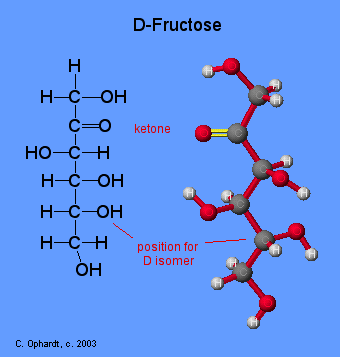
fructose
hexose sugar; monomer of sucrose; ketone
ribose
pentose sugar; component of RNA; aldehyde
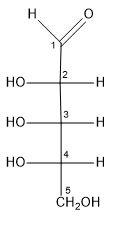
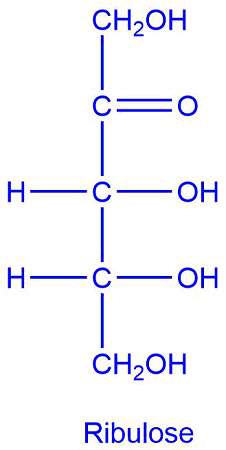
ribulose
pentose sugar; ketone
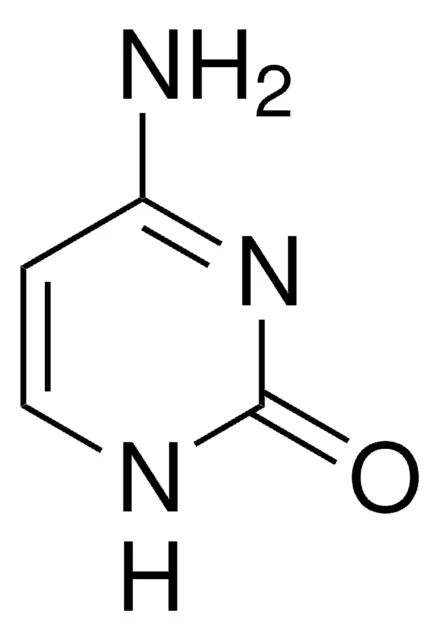
cytosine
pyrimidine group; pairs with guanine (DNA & RNA)
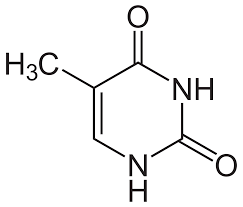
thymine
pyrimidine group; pairs with adenine (DNA)
uracil
pyrimidine group; pairs with adenine (RNA)
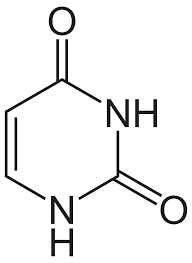
adenine
purine group; pairs with thymine/uracil (DNA & RNA)
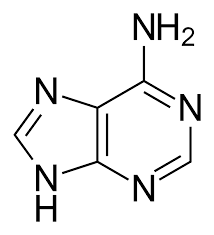
guanine
purine group; pairs with cytosine (DNA & RNA)
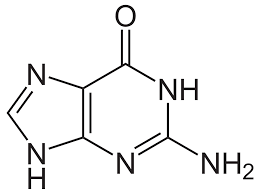
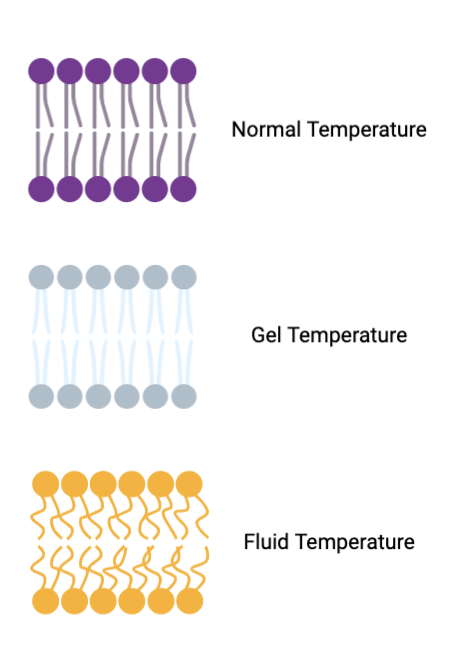
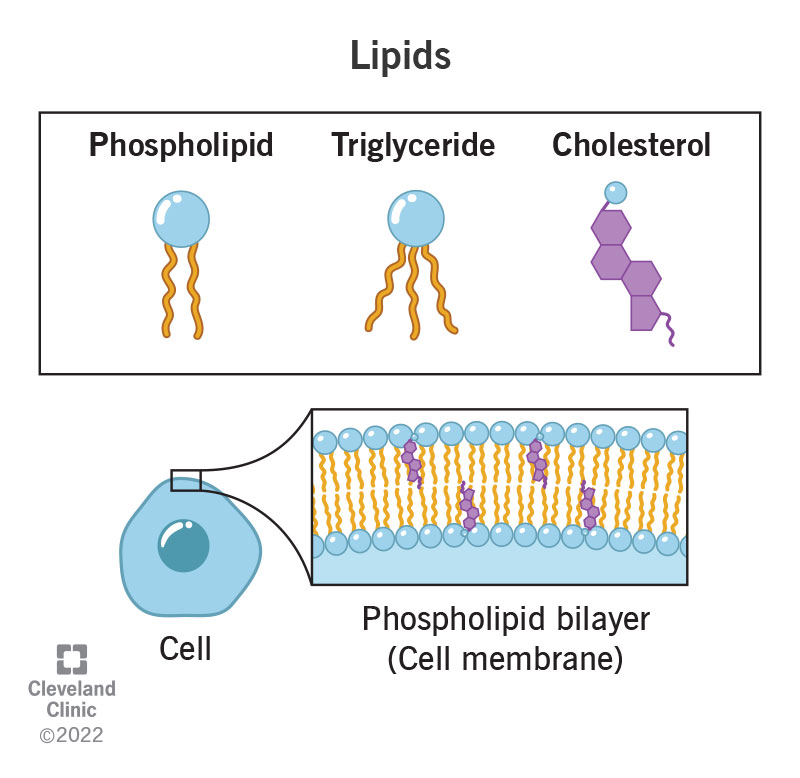
GEL (phospholipid bilayer)
temperature is colder, with no kinks in phospholipids making them more tightly packed together
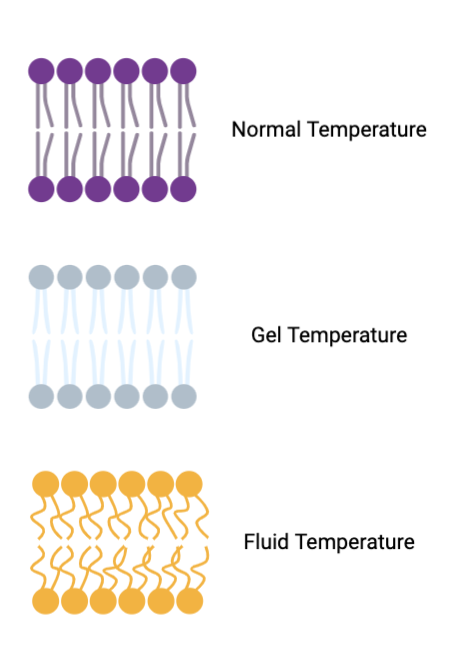
Fluidity (phospholipid bilayer)
temperature is colder, kinks within the phospholipids making them more pushed apart allowing for a more fluid membrane
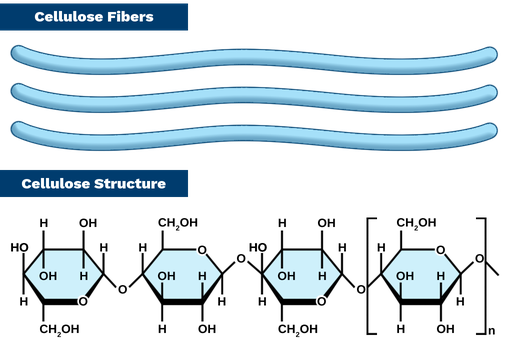
cellulose
most abundant carbon-containing organic compound on earth; found in plant cell walls (structural); b-1,4-glycosidic linkage
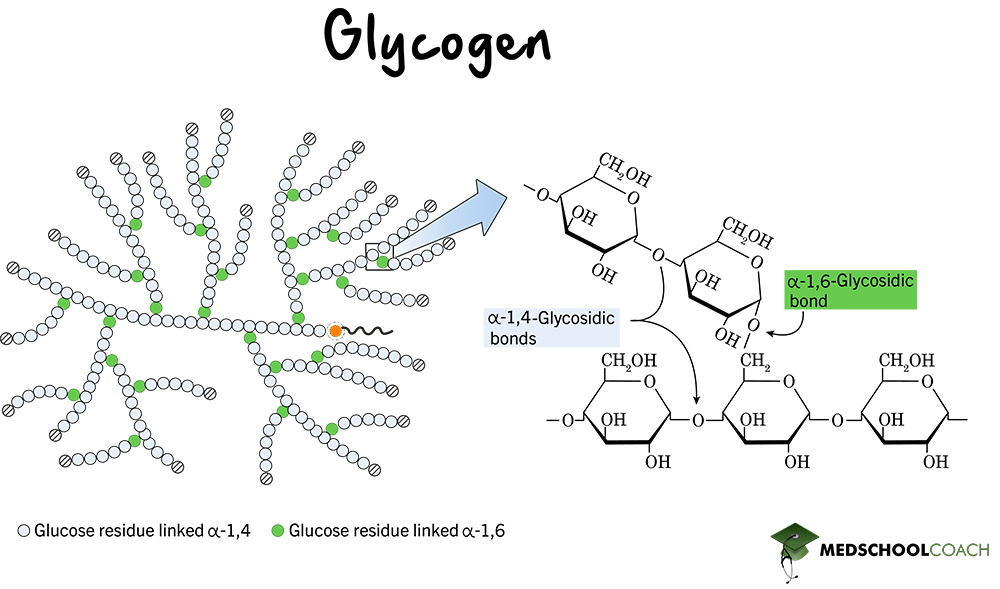
glycogen
energy storage for animals; helical (more branches); a-1.4-linkages, chained together by a-1.6-glycosidic linkages
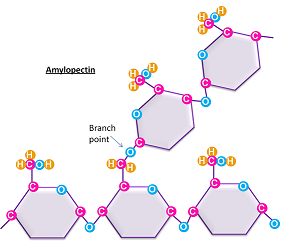
starches
energy storage for plants; how glucose is stored in plants; a-1.4-glycosidic linkage, fewer branches
amino acid
monomer of proteins (20 different versions; characterized by r group)
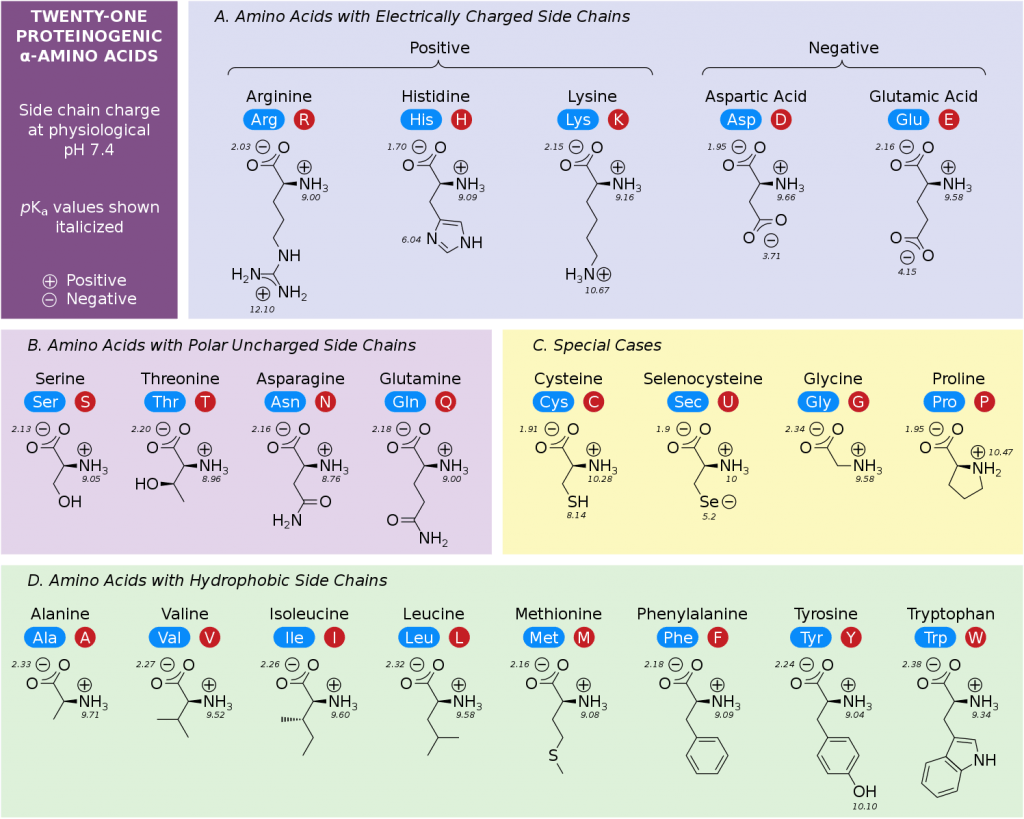
ionized amino acid
charged
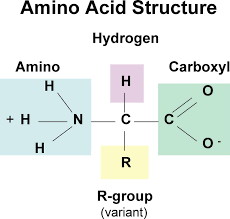
non-ionized amino acid
not charged
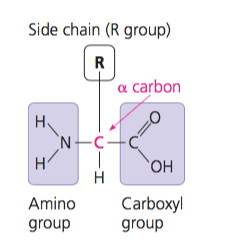
lipid
monomers are fatty acids, glycerol, fats, steroids, cholesterol
“hydrocarbon” molecule
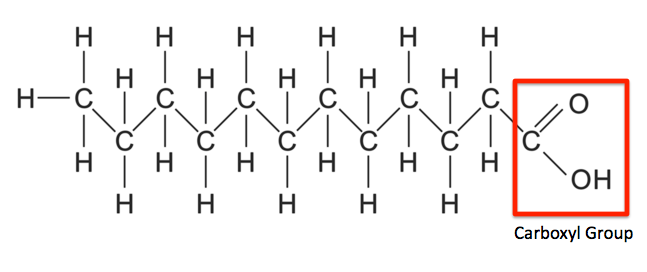
saturated fatty acid
no kinks, solid at room temperature
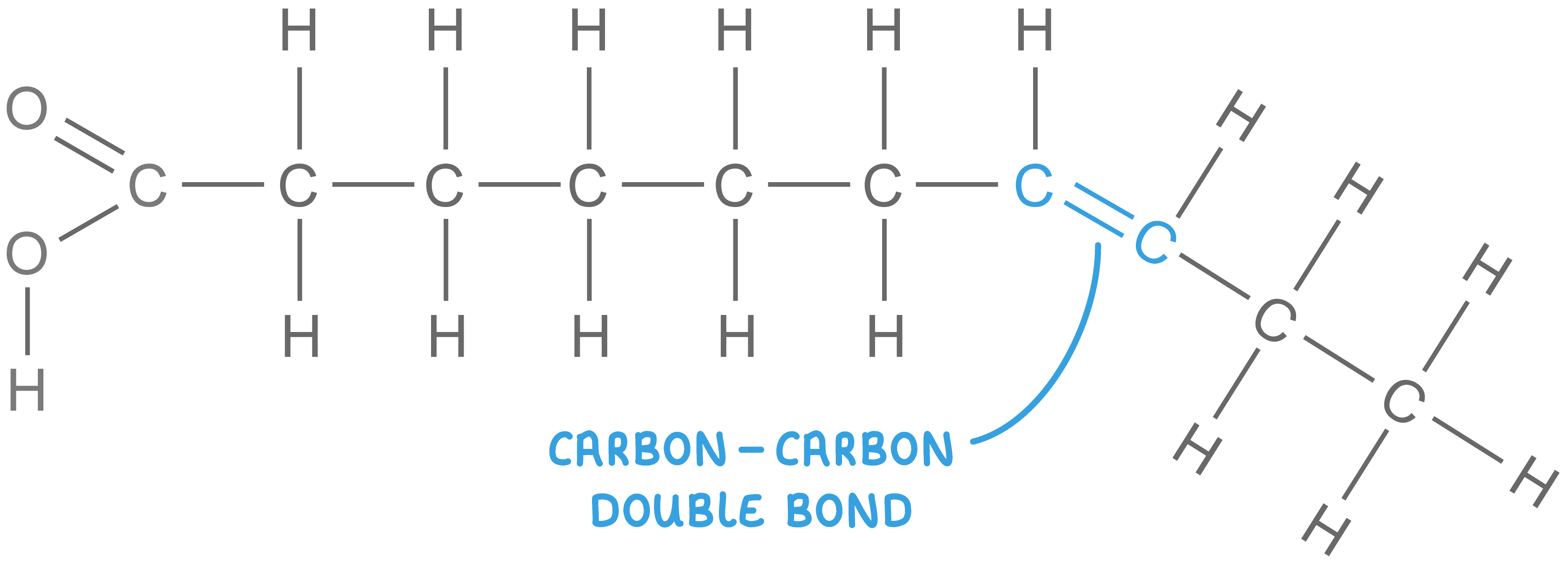
unsaturated fatty acid
kinks, liquid at room temperature
Hexose sugar formula
C12H22O11
Pentose sugar formula
C5H10O5
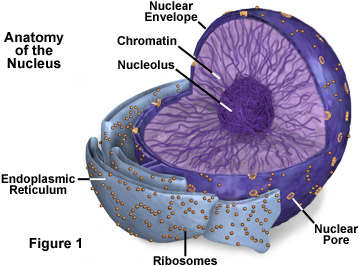
nucleus
maintenance of genetic information, location of DNA, production of ribosomal subunits, genetic information transmitted
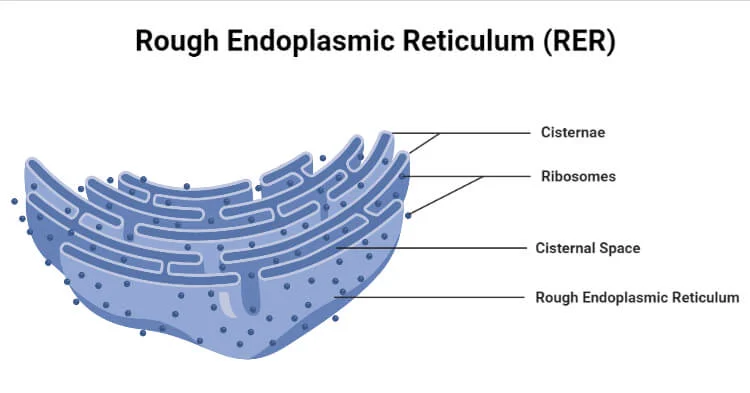
Rough ER
production of proteins within rough ER; first stop and for proteins bound for membrane
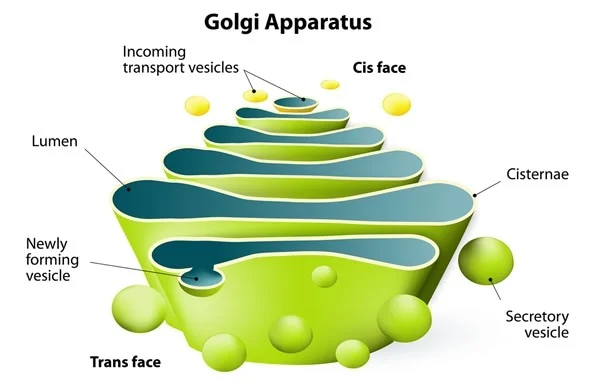
Golgi Apparatus
modifies and packages proteins from Rough ER
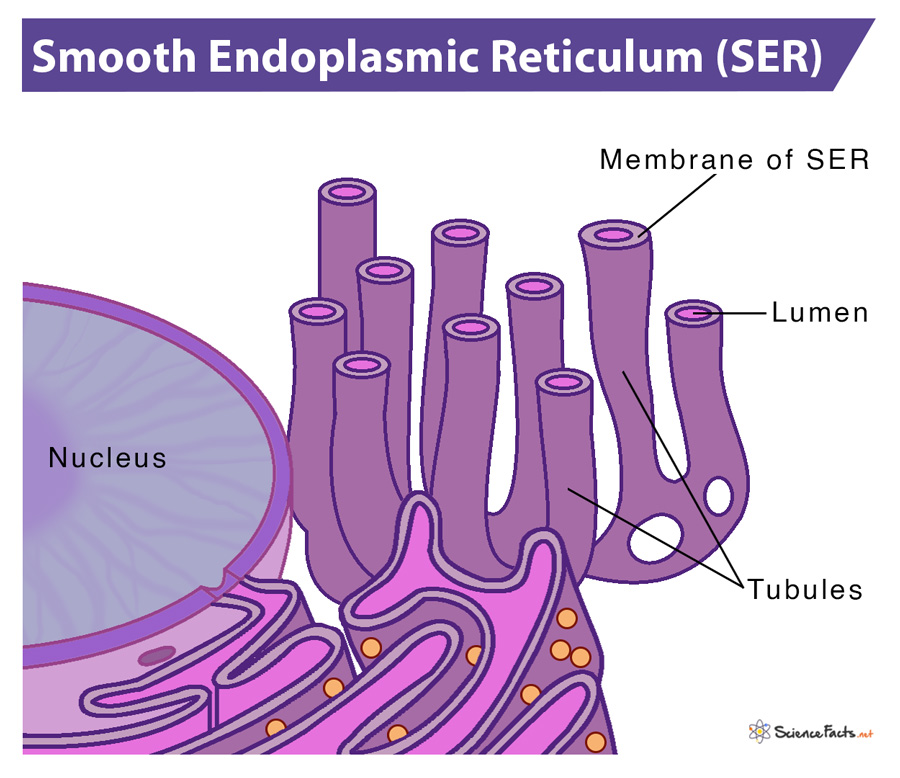
Smooth ER
detoxification of cell and lipid synthesis
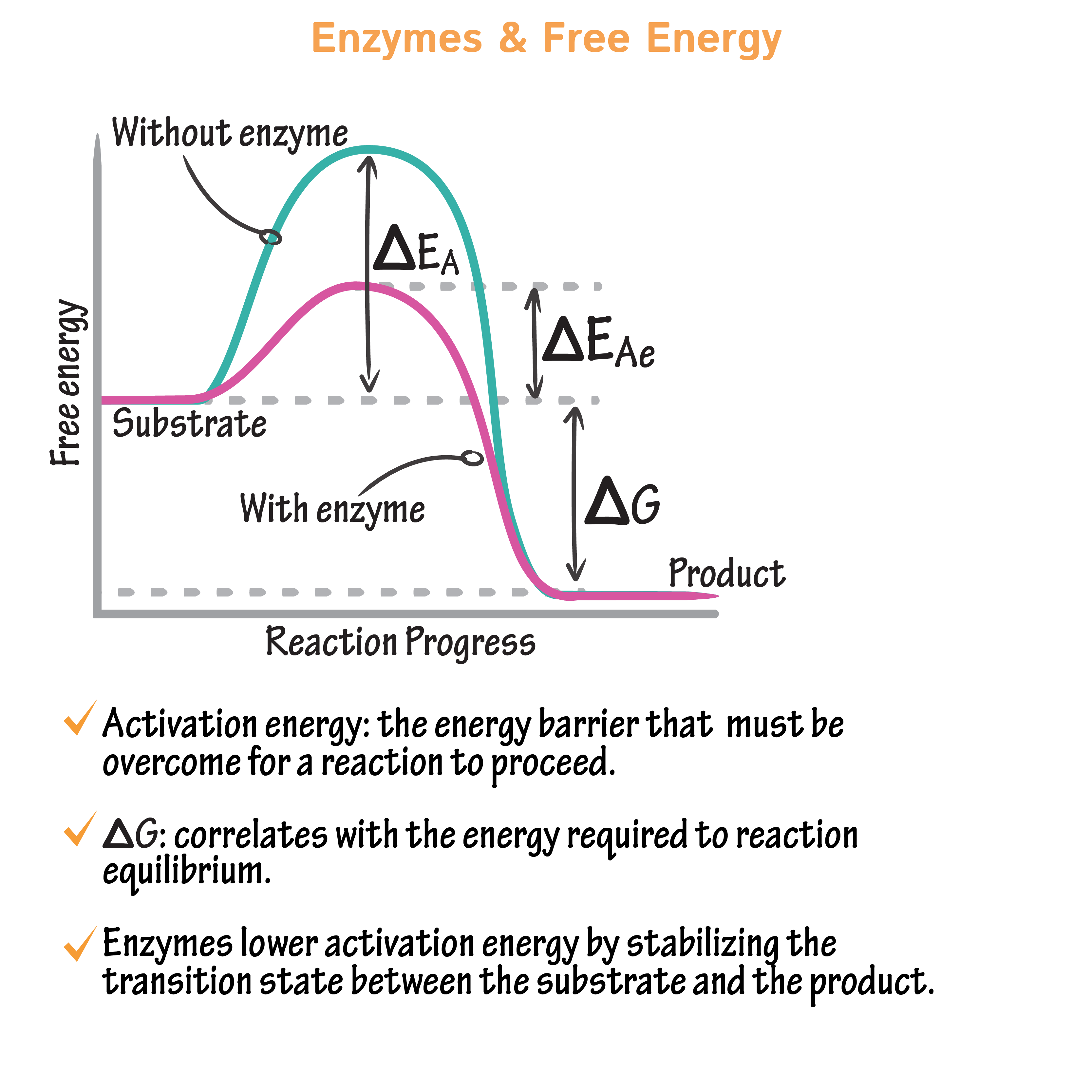
enzymes
type of protein, lowers energy of activation
entropy
amount of disorder (deltaS)
enthalpy
total energy in a molecule (deltaH)
long/weak bonds
high potential energy (nonpolar)
short/strong bonds
low potential energy (polar)
primary structure
the sequence of amino acids from N to C
secondary secondary
first level of folding; formation of a-helicies and b-pleated sheets into polypeptide, stabilized by (weak) hydrogen bonds(O-H); peptide backbone is polar
tertiary structure
unique 3D; final conformation of some proteins; due to interactions between R-groups with each other and backbone; stabilized by h-bonds of side chains, h-bonds of hydrophilic side chains and backbone, ionic bond between acidic and basic amino acid, hydrophobic clustering, and van der waals forces, disulfide linkages
quaternary structure
found in proteins with multiple polypeptide chains (subunits), called dimers; 2 identical subunits are call homodimer, and 2 different are called heterodimer
effects of misfolded proteins
prions - disease causing agents (can cause other proteins around it to also fold into prions)
-deltaG
spontaneous(exergonic) energy released from molecule
+deltaG
no spontaneous (endergonic) energy into molecule