Cells - Vaccinations and immunity
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
What is active immunity?
When the immune system creates its own antibodies
What is natural active immunity?
When the body becomes immune after catching a disease
What is artificial active immunity?
When the body becomes immune after a vaccination
What is passive immunity?
When antibodies are donated from another organism
What is natural passive immunity?
When a baby becomes immune through antibodies it receives from its mother (usually through breast milk)
What is artificial passive immunity?
Immunity that is received after being injected with ANTIBODIES from another individual which have been collected from blood donations
Which type of immunity (a/p) requires direct exposure to an antigen?
Active
How long does it take for protection to develop in active immunity?
Over a period of time (body needs to make its own antibodies)
How long does it take for protection to develop in passive immunity.
Protection is immediate as the antibodies are already made
Which type of immunity does not produce memory cells?
Passive (because the body did not make the antibodies itself it does not know how to make them like it does in active immunity)
How long does protection last in active immunity?
A number of years as the memory cells remain in the bloodstream ready to be activated by another exposure to the complimentary antigen
How long does protection last in passive immunity?
A number of days/weeks as the antibodies break down over time and the body cannot make any more or any memory cells
When are symptoms shown during a disease?
While the body is synthesising the necessary antibodies to kill a pathogen
How do vaccines work?
They contain antigens (in the form of dead, weak or inactive pathogens) which stimulate the production of memory cells. They can also contain instructions for a body to make antibodies (e.g. mRNA covid vaccine)
What is herd immunity?
When a majority of a population are vaccinated against a disease. This means that even people who have not been vaccinated are less likely to get it because there are fewer people to catch it from
Describe the relation of animals to vaccines.
- Animal testing
- Some animal products may be in some vaccines
What are the ethical issues with vaccines?
- Animal testing
- Risks of testing on humans
- Deciding who should get the vaccine first (vaccine inequality)
What is antigenic variation?
When pathogens change their surface antigens due to changes in the genes of a pathogen
Why is antigenic variation an issue?
- Memory cells do not recognise the pathogens so instead of the secondary response being initiated the primary response has to be started
- It also makes it hard to make vaccines
What are monoclonal antibodies?
Antibodies produced from a single group of genetically identical B-cells
What is special about our use of monoclonal antibodies?
We can design them to bind to specific substances e.g. an antigen or toxin
How can monoclonal antibodies be used for cancer cells?
Cancer cells contain antigens called tumour markers. Antibodies which compliment this marker can have anti-cancer drugs attached to them. This allows for targeting of cancer cells and decreased side effects from the treatment
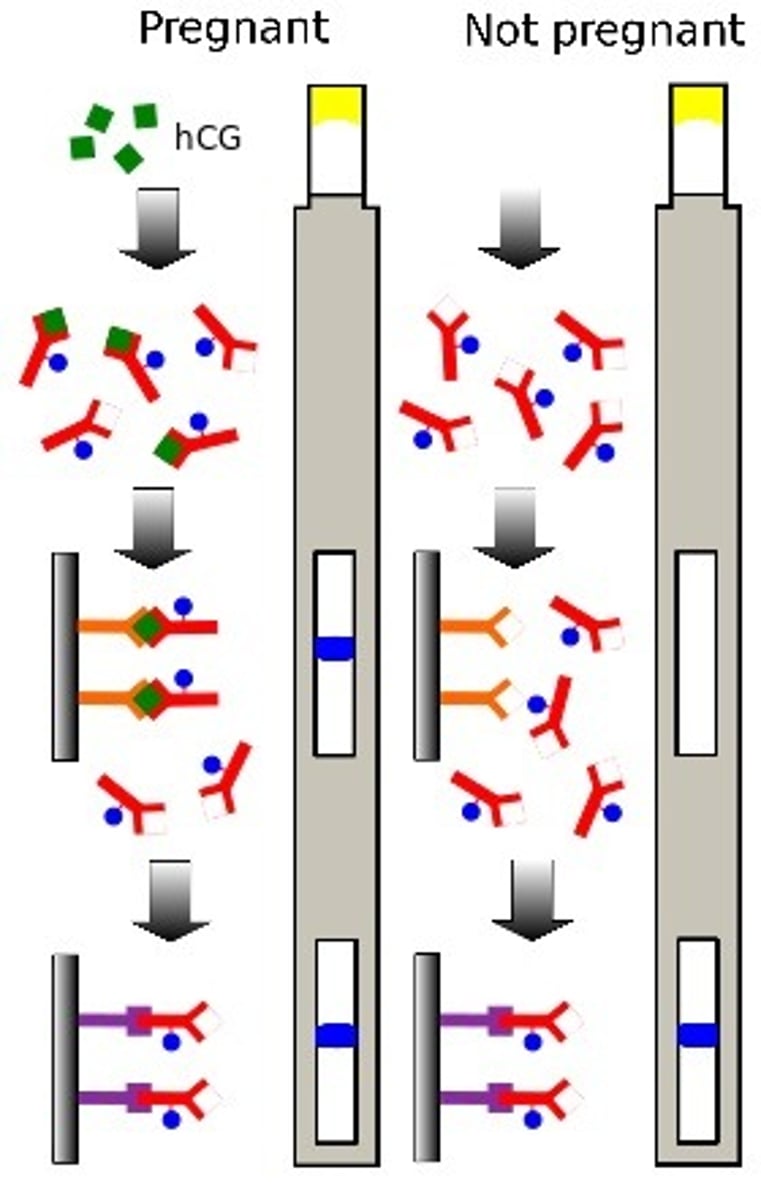
Describe the use of antibodies in pregnancy testing.
1. The application area contains antibodies which compliment the hCG antigen (which women have when pregs)
2. This antibody has a coloured bead attached which moves up the test
3. The antigen-antibody complex binds to an immobilised antigen forming a coloured line
4. The rest of the antibodies continue past this to form a second control line to show the test is valid.
Diagram showing how antibodies help in pregnancy testing.
What does ELISA stand for?
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
What does ELISA testing do?
Tests for the presence of specific antibodies
Who is ELISA testing often used for?
- Pt suffering from a pathogenic infection
- Tests for allergies
What are the two types of ELISA?
- Direct
- Indirect
What is different about the antibodies used in ELISA testing?
They have enzymes bound to them which will react when a substrate is added causing a colour change
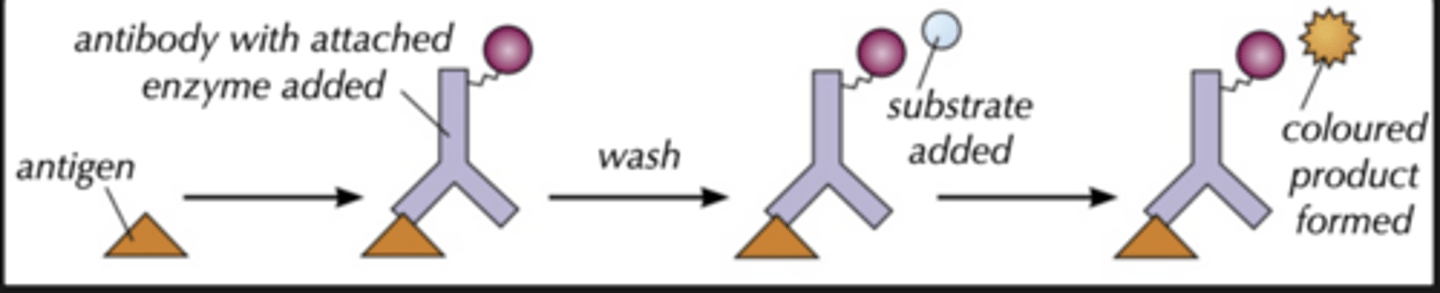
Describe the direct ELISA.
1. Antigens are isolated from a pt sample and bound to a plastic well
2. Monoclonal antibodies (with enzyme attached) which compliment the antigen are added
3. If the antigen is present the antibodies will attach
4. The well is washed to remove all unbound antibodies
5. A coloured substrate solution is added which is broken down by the attached enzymes on the antibodies if they have bound to the antigen. This colour change indicates the presence of the antigen
What is commonly used to obtain a pt sample?
Urine or blood
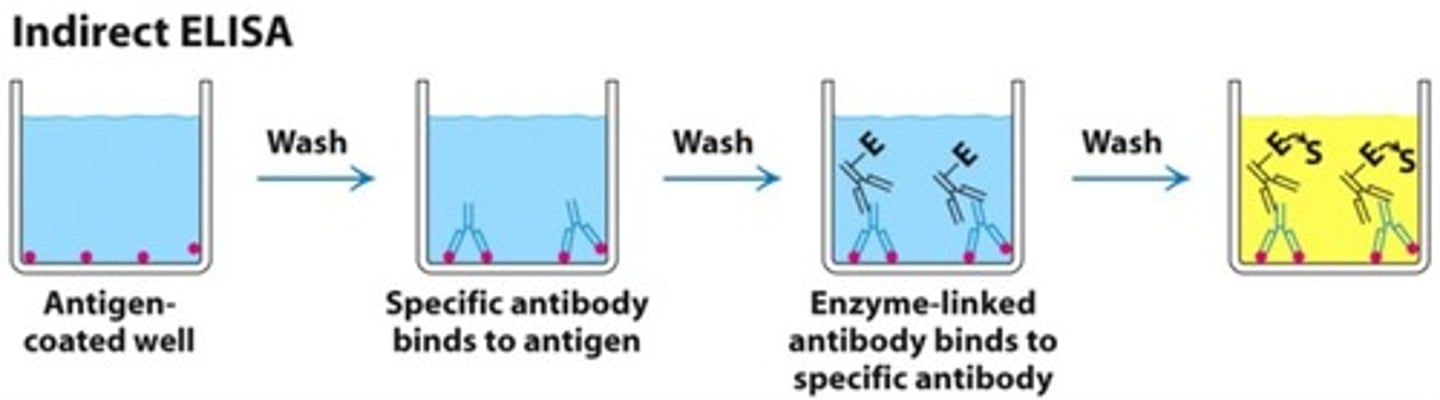
Describe the indirect ELISA.
1. Antigen is attached to a well plate along with the individuals blood serum
2. Any antibodies in the pt sample will attached to the antigen
3. The well is washed to remove any unbound antibodies
4. A second lab made antibody is added with an enzyme attached which binds to the pt sample antibody
5. The well is washed again
6. A substrate solution is added and if there is a colour change the antibody is present
What is the indirect ELISA often used to test for?
HIV
What is the main difference between a direct and indirect ELISA?
- Direct only uses one antibody while indirect uses 2
- Direct occurs after screening for an antigen to confirm the diagnosis
- Direct tests for presence of antigen in pt using lab made antibodies while indirect tests for antibodies in pt while using lab made antigens
Direct ELISA diagram.
Indirect ELISA diagram.
Where are monoclonal antibodies obtained from?
Using animals
How are monoclonal antibodies made?
A rodent is injected with an antigen and the antibodies it produces are removed by surgery
What are the ethical issues surrounding monoclonal antibodies?
Animal cruelty issues
How can monoclonal antibodies be used for cancer cells?