Microbiology Exam 3
1/170
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
Catabolism is ________ whereas anabolism is _________
break down; synthesis
How many parts of the nitrogen cycle are done solely by microbes?
4
How many parts of the nitrogen cycle are microbes a part of?
8
1 cal = _____ J
4.184
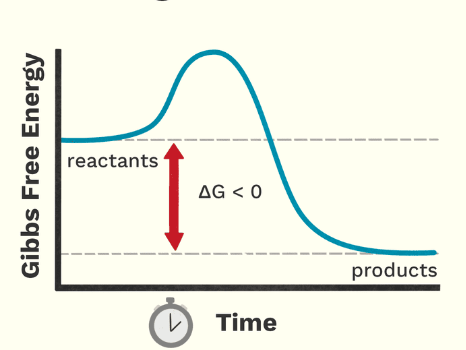
What type of reaction is this?
exergonic
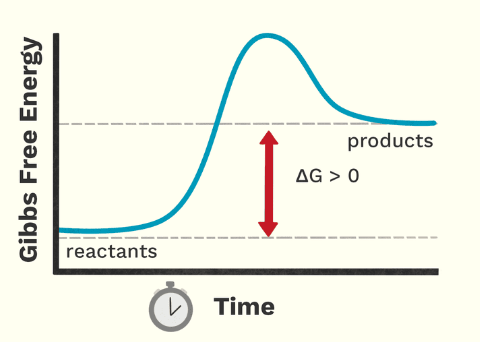
What type of reaction is this?
endergonic
ΔG for an exergonic reaction is positive. True or False
false it is negative
Are endergonic reactions spontaneous or nonspontaneous?
nonspontaneous
Where is the energy stored in an endergonic reaction?
in the bonds
Exergonic reactions
-ΔG
spontaneous
energy released
Endergonic reactions
+ΔG
nonspotaneous
energy entering
GTP is involved in ______ synthesis
protein
Lipid synthesis uses ____
CTP
UTP is involved in what synthesis?
peptidoglycan
What is -ΔG for ATP hydrolysis?
-7.3 kcal/mol
ATP has the highest phosphate transfer potential. True or False
false it is not the highest but it is still high
You have two redox potentials -0.68 and 0.84 which one is the electron donor and electron acceptor?
-0.68 = electron donor (oxidation)
0.84 = electron acceptor (reduction)
What are all the names of oxidation?
electron donor, reductant, reducing agent
What are all the names of reduction?
electron acceptor, oxidant, oxidizing agent
What are the 2 rules of redox pairs?
reduced member that is more negative donates electrons to the oxidized member that is more positive
greater the difference in redox potential the greater amount of energy available
When ΔG is less than 0 what is the redox potential and direction of reaction?
redox potential is greater than 0
reaction is spontaneous is forward direction
When ΔG is greater than 0 what is the redox potential and direction of reaction?
redox potential is less than 0
reaction is spontaneous is reverse direction
What is Faraday’s constant?
23 kcal/volt
96.5 kJ/volt
What is the Nernst equation?
ΔG0' = -nFEo ‘
Where is the ETC in prokaryotes versus eukaryotes?
eukaryotes = mitochondria
prokaryotes = cell membrane
What electron carrier in the ETC is the most negative redox potential?
the first electron carrier, NADH
Which of the electron carriers accepts two electrons and one proton?
NADH and NADPH
What are the flavoproteins and how many electrons and protons do they accept?
FAD and FMN
carry 2 electrons and 2 protons
What is a lipid that transports two electrons and two protons?
CoQ/ubiquinone
Which electron transport carrier uses iron and is part of a heme group that carries 1 electron?
cytochromes
Ferredoxin is an example of _________
nonheme iron-sulfur protein
Nonheme iron-sulfur protein carry _____ electron
1
What is the difference in binding for prosthetic groups and coenzymes?
prosthetic group = covalently bound to enzyme
coenzyme = loosely bound to enzyme
What is a holoenzyme composed of?
apoenzyme + cofactor
What is the transition state complex?
when the reactants come together; at the top of the graph
How do enzymes lower activation energy?
increasing substrate concentration at active site
orienting substrates properly
Reaction rate _______ as [substrate] increases
increases
A higher Km means what?
higher [substrate]
Would amylase work in the stomach?
no because pH is specific to each enzyme and have their own optimum pH
Sulfa drugs are an example of a ________ inhibitor. Why?
competitive; they resemble PABA
What is an example of a noncompetitive inhibtor?
poisons like cyanide
What are ribozymes made up of?
RNA
What are functions of ribozymes?
catalyze peptide bond formation
self splicing
involved in self replication
How do cells regulate metabolism?
compartmentation
transcriptional & translational
post-translational
Prokaryotes don’t have compartmentation. True or False
false they do
What are examples of reversible post-translational mechanisms?
allosteric regulation
covalent modification
What are isoenzymes?
different forms of enzymes that bind to same substrate
Pacemaker enzymes are the first enzyme of the pathway. True or False
false they usually are but not always
What are the carbon, electron, and energy source for a photolithoautotroph?
carbon = CO2
energy = light
electron = inorganic electron donor
Plants are an example of what type of nutritional organism?
photolithoautotrophs
What type of organism uses organic carbon, light, and organic electron donor?
photoorganoheterotroph
CO2, inorganic materials, and inorganic electron donor are for what organism?
chemolithoautotroph
What does a chemolithoheterotroph use?
organic carbon, inorganic chemicals, inorganic electron donor
What is the difference between heterotrophs and autotrophs?
heterotroph = use organic molecules
autotroph = use single carbon molecule, CO2
Which of the microorganisms are primary producers?
photolithoautotrophs/photoautotrophs & chemolithoautotrophs
The majority of pathogens are ________
chemoorganoheterotrophs '
What are the basic needs of all living organisms?
ATP as an energy currency
reducing power to supply electrons for chemical reactions
precursor metabolites for biosynthesis
Oxygen is the difference between fermentation and respiration. True or False
false
What can chemoorganotrophs do that chemolithotophs can’t?
fermentation
What is the difference between fermentation and respiration?
ETC = respiration
no ETC = fermentation
What are the 6 requirements for all life?
CHONPS
Where are electrons donated in fermentation?
to an endogenous acceptor
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
the final electron acceptor differs
aerobic = oxygen
anaerobic = not oxygen, an exogenous acceptors
Where is the ATP made through respiration?
SLP and oxidative phosphorylation
What is an example of an endogenous electron acceptor?
pyruvate
What is the pacemaker enzyme in glycolysis?
phosphofructokinase
What are the routes of glycolysis?
EMP (most common)
ED
PPP
Are archaea able to go through beta-oxidation? Why?
no because beta oxidation uses fatty acids which archaea do not have, they have isoprene units
What is an commonality between all 3 glycolysis routes?
all convert glucose to G3P
What is the net gain of ATP from the EMP pathway?
2 ATP
How many NADHs are made from glycolysis?
2 NADH
The EMP pathway functions only in the presence of oxygen. True or False
false it works with or without O2
What is the order of glycolysis?
glucose, G6P, F6P, F1,6-BP, G3P, 3-phosphoglycerate, PEP, pryuvate
What type of bacteria use the ED pathway? Give an example.
soil bacteria and a few gram (-) bacteria; ex = Bacillus
Would yeast use the ED pathway? Why or why not?
no because yeast is a type of fungi which is eukaryotic and eukaryotes don’t use ED pathway
What is major difference between the EMP and ED pathway in terms of the pathway intermediates?
the ED pathway produces 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate (KDPG)
Why does the ED pathway produce 1 ATP while EMP produces 2?
because only 1 G3P is made; KDPG becomes pyruvate and G3P
PPP is a major source of what electron carrier?
NADPH
What is important about E4P and ribose-5-phosphate?
make RNA nucleotides
PPP works at the same time as EMP. True or False
true
Does the Kreb’s cycle work in anaerobic bacteria?
no
What is yield of TCA?
6 NADH
2 FADH2
2 ATP
What is the role of pyruvate dehydrogenase?
oxidizes and cleaves pyruvate into acetyl-CoA and CO2
What type of bond is present in acetyl-CoA?
thioester bond, which yields a lot of energy
The ATP produced after succinyl-CoA is due to what?
SLP
Why is alpha-ketoglutarate important in TCA?
important in the making of amino acids
What is overall occurring in TCA?
the carbons from glucose are getting oxidized while NADH is getting reduced through gaining those electrons
What 2 places in the Kreb’s cycle are the thioester bond found?
succinyl-CoA and acetyl-CoA
Where is the ETC located in bacteria vs eukaryotes?
bacteria = cell membrane
eukaryotes = inner mitochondrial membrane
Where does the NADH come from in the ETC?
from TCA and glycolysis
Complex I in the has a negative or positive reduction potential? Why?
negative because the higher the reduction potential is the more likely it is to be reduced so the first complex has to be the lowest so the other ones can accept the electrons
If there is a high concentration of cytochrome c outside the mitochondria what does that mean about the cell?
the cell is not healthy
Glucose is a better _____ and ½ O2 is a better ______
glucose = electron donor (oxidized)
½ O2 = electron acceptor (reduced)
What is a coupling site and which of the complexes does not do this?
coupling site = where protons are being pumped
complex II is NOT a coupling site
What does CoQ connect?
connects complex I to III and complex II to III
What does cytochrome c connect?
complex III to IV
Complex II participates in pmf. True or False
false since it does not pump H+
If rotenone and malonate were given how many ATP would be created?
4 ATP (2 from glycolysis +2 from TCA)
What happens when rotenone is given?
it inhibits complex I so NADH accumulates and there is no NAD+ so glycolysis can’t move forward and the cell dies
Where are protons present in gram (-) bacteria?
periplasmic space