IB Bio: Topic 6 (Human Physiology) (6.1, 6.2, 6.3)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/67
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
1
New cards
Peristalsis
Process involving wave-like involuntary muscle contractions to move and mix digested materials through the alimentary canal (digestive tract)
2
New cards
Circular Muscle
* Outer muscle of the muscularis
* Contracts behind the digested food to ensure a one-way direction.
* Contracts behind the digested food to ensure a one-way direction.
3
New cards
Longitudinal muscle
* Inner muscle of the muscularis
* Contracts WITH the digested food.
* Pushes digested food along the digestive tract.
* Contracts WITH the digested food.
* Pushes digested food along the digestive tract.
4
New cards
Gut Wall
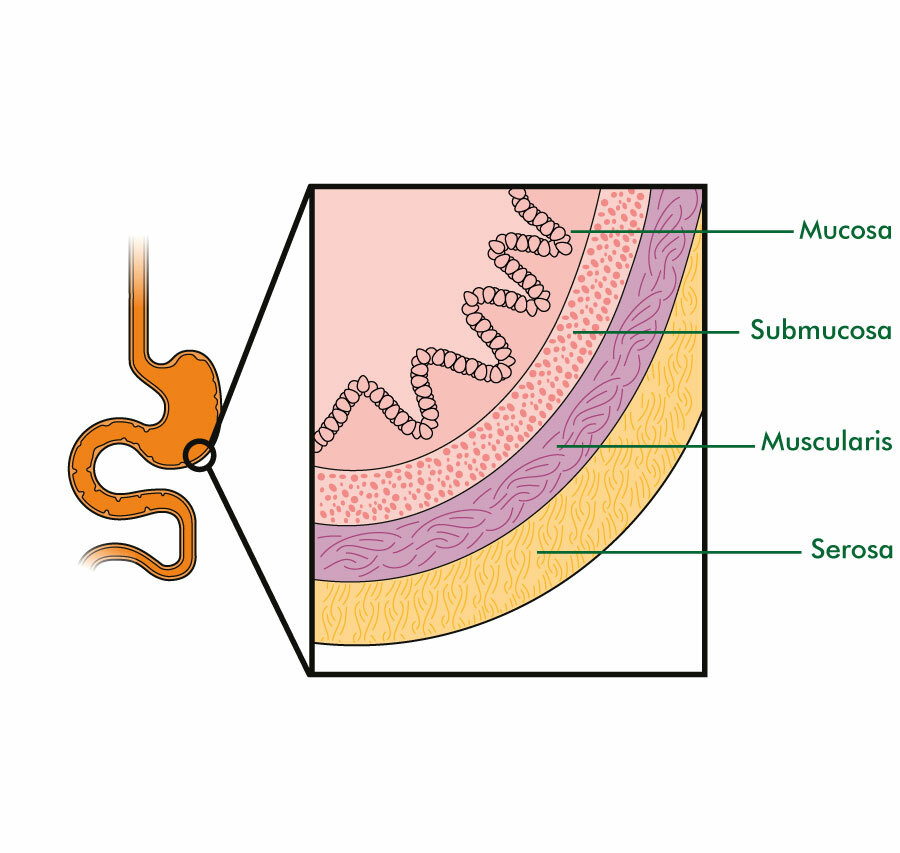
5
New cards
Peristalsis speeds
Esophagus: FAST
Intestines: SLOW
Intestines: SLOW
6
New cards
Vomiting
* Digested food returns from the stomach to the mouth.
* Process involves abdominal muscles to push digested food back up to the mouth.
* Process involves abdominal muscles to push digested food back up to the mouth.
7
New cards
Pancreatic juice
* Digestive enzymes that the pancreas secretes into gut lumen.
* Consists of Amylase (starch), Lipase (fats) and protease (proteins)
* Consists of Amylase (starch), Lipase (fats) and protease (proteins)
8
New cards
Cellulose
* Poly-saccharide made of chained glucose molecules.
* Found in plant cell walls.
* Found in plant cell walls.
9
New cards
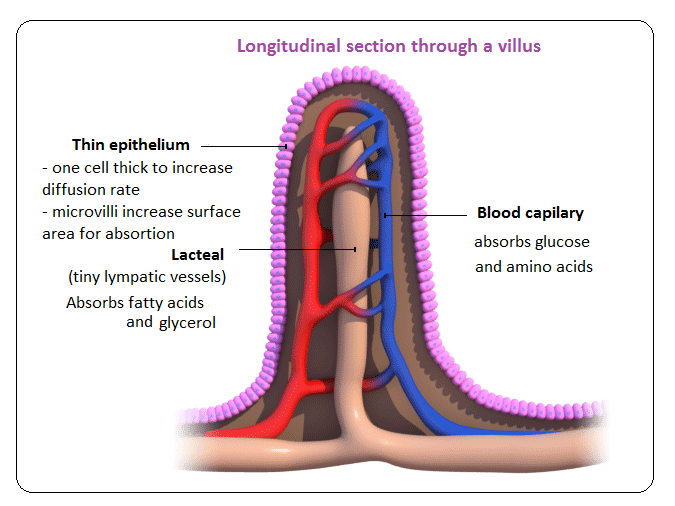
Villi and Surface area
Increased surface area helps to absorb nutrients quickly and efficiently.
10
New cards
Villi
* Tiny hair-like projections that line the inside of the small intestine. They contain blood vessels and help absorb nutrients.
* Villi are lined with Microvilli to increase surface area further.
* Villi absorb materials such as:
* Macromolecule building blocks (amino acids and monosaccharides)
* Nucleotide bases
* Minerals
* Vitamins
* Villi are lined with Microvilli to increase surface area further.
* Villi absorb materials such as:
* Macromolecule building blocks (amino acids and monosaccharides)
* Nucleotide bases
* Minerals
* Vitamins
11
New cards
Methods of absorption in Villi
* Different nutrients are absorbed differently as it depends on size and polarity
* Nutrients such as amino acids and glucose are diffused into the blood vessels.
* Fatty acids and glycerol are diffused into the lacteal and will rejoin the blood stream later.
* Nutrients such as amino acids and glucose are diffused into the blood vessels.
* Fatty acids and glycerol are diffused into the lacteal and will rejoin the blood stream later.
12
New cards
3 types of blood vessels
Arteries, Veins, and Capillaries.
13
New cards
Arteries
Send blood away from the heart (A for Away)
14
New cards
Veins
Returns blood back to the heart
15
New cards
Capillaries
* Smallest blood vessels
* connect arterioles and venules
* 1 cell thick, blood cells travel in a single file.
* Material exchange occurs here.
* connect arterioles and venules
* 1 cell thick, blood cells travel in a single file.
* Material exchange occurs here.
16
New cards
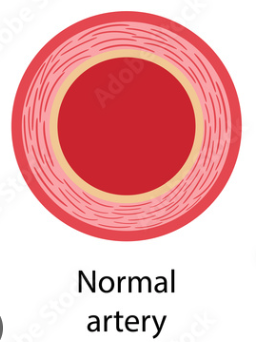
Artery Walls
* Work with heart to control blood flow
* Strong, tough tissue to withstand changing blood pressure.
* Elastin: enables arteries to stretch during maximum flow.
* Smooth muscle: contractions from muscle control diameter of lumen.
* Strong, tough tissue to withstand changing blood pressure.
* Elastin: enables arteries to stretch during maximum flow.
* Smooth muscle: contractions from muscle control diameter of lumen.
17
New cards
Arterial Blood Pressure
* Blood entering from pumping heart causes HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE in arteries.
* Arterial walls help to regulate blood pressure.
* Arterial walls help to regulate blood pressure.
18
New cards
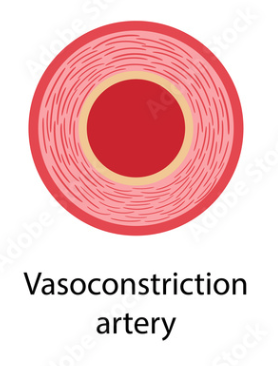
Systolic Pressure
* Maximum Arterial pressure
* Occurs when the heart pumps
* Vasoconstriction occurs
* Occurs when the heart pumps
* Vasoconstriction occurs
19
New cards
Diastolic Pressure
* Minimum Arterial pressure
* Occurs when the heart relaxes
* Vasodilation occurs
* Occurs when the heart relaxes
* Vasodilation occurs
20
New cards
Veins and Blood Pressure
* Collects blood returning from capillaries at LOW BLOOD PRESSURE
* Blood flow is assisted by gravity and general body muscle movements
* Blood flow is assisted by gravity and general body muscle movements
21
New cards
Veins and Valves
* Valves are ONLY found in veins
* They allow for a one-way movement of blood flow
* Stops deoxygenated blood from flowing in the wrong direction
* They allow for a one-way movement of blood flow
* Stops deoxygenated blood from flowing in the wrong direction
22
New cards
Steps of blood vessels used:
1) Aorta
2) Arteries
3) Arterioles
4) Capillaries
5) Venules
6) Veins
7) Vena Cava
2) Arteries
3) Arterioles
4) Capillaries
5) Venules
6) Veins
7) Vena Cava
23
New cards
Systemic Blood Circulation
Supplying nourishment to all tissues in the body (everywhere)
24
New cards
Coronary Blood Circulation
Supplying nourishment to heart tissues (heart)
25
New cards
Pulmonary Blood Circulation
Movement of blood between the heart and lungs for gas exchange (heart and lungs)
26
New cards
Renal Blood Circulation
Movement of blood to and through the kidneys for filtration of wastes.
27
New cards
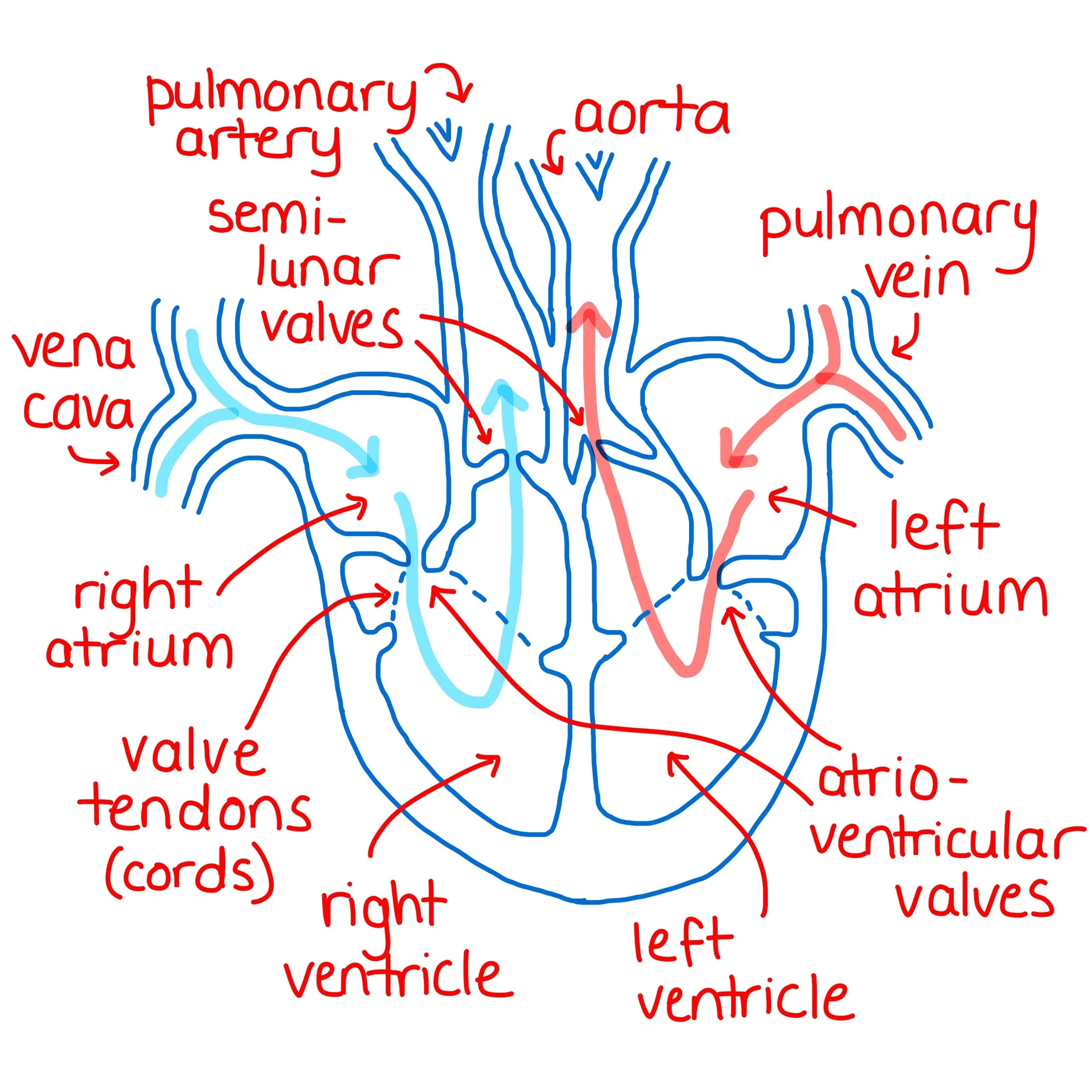
Heart Chambers
* Right Atrium and Right Ventricle
* Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
* Left Atrium and Left Ventricle
* Pumps oxygenated blood to body
* Pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
* Left Atrium and Left Ventricle
* Pumps oxygenated blood to body
28
New cards
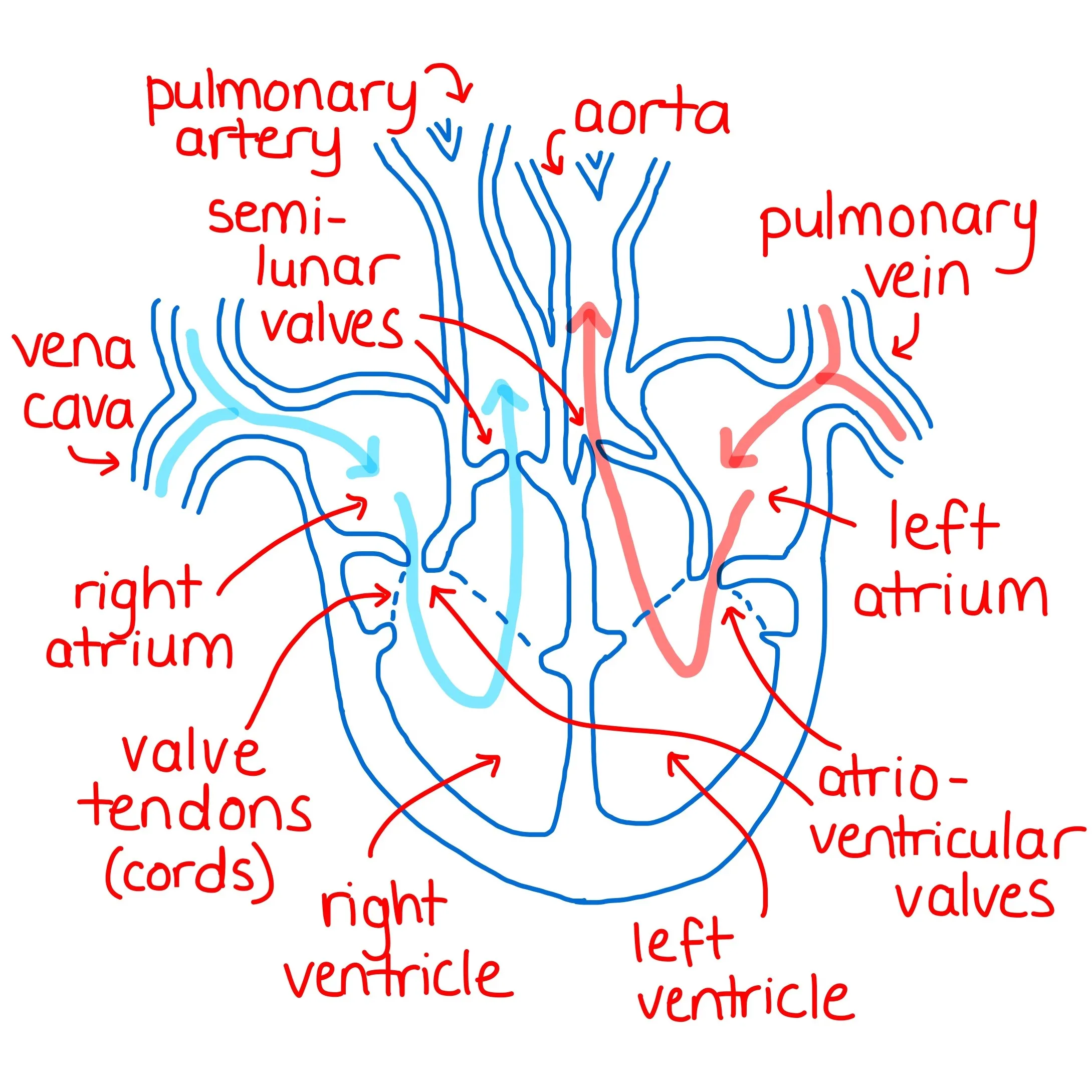
Heart Valves
* 2 types
* Atrioventricular Valves
* Between Atria and Ventricles
* Tricuspid and Mitral
* Semilunar Valves
* Between ventricles and exiting the heart
* Pulmonary and Aortic
* Atrioventricular Valves
* Between Atria and Ventricles
* Tricuspid and Mitral
* Semilunar Valves
* Between ventricles and exiting the heart
* Pulmonary and Aortic
29
New cards
Cardiac Cycle
Rhythmic contraction of heart muscles to pump blood throughout the body (the heart beat)
30
New cards
Heart Beat
The sounds of heart beats come from valves opening and closing.
31
New cards
2 phases of Cardiac Cycle
Systole and Diastole
32
New cards
Systole Phase
* Pumping phase
* Atria relax and fill with blood from vena cava and lungs
* Ventricles contract and blood is being pumped into lungs and the rest of the body
* Valves
* Semilunar Valves: Open
* Atrioventricular Valves: Closed
* Atria relax and fill with blood from vena cava and lungs
* Ventricles contract and blood is being pumped into lungs and the rest of the body
* Valves
* Semilunar Valves: Open
* Atrioventricular Valves: Closed
33
New cards
Diastole phase
* Refilling phase
* Atria contract and pump blood into ventricles
* Ventricles relax and fill with blood
* Valves
* Semilunar Valves: Closed
* Atrioventricular Valves: Open
* Atria contract and pump blood into ventricles
* Ventricles relax and fill with blood
* Valves
* Semilunar Valves: Closed
* Atrioventricular Valves: Open
34
New cards
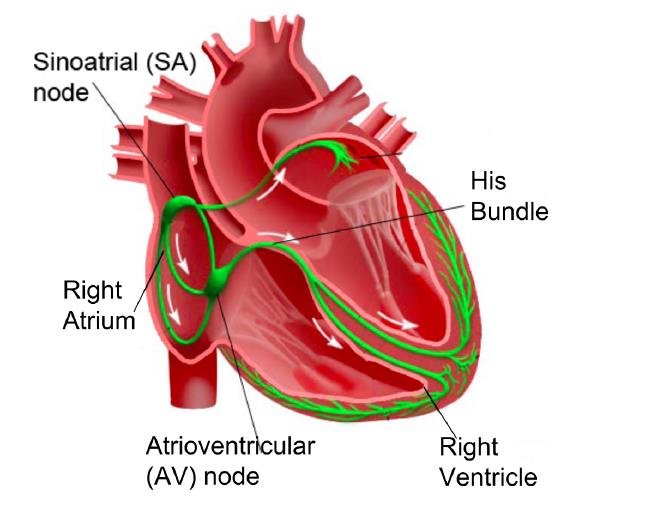
Nervous control of heart beat
* Heart beat normally controlled by electrical activity
* Consist of 3 main parts: Sinoatrial (SA) Node, Atrioventricular (AV) Node and the His-Purkinje System
* Consist of 3 main parts: Sinoatrial (SA) Node, Atrioventricular (AV) Node and the His-Purkinje System
35
New cards
Steps of nervous control of heart beat
* Blood fills right atrium
* SA node sends electrical signal
* Atria contract and start filling ventricles with blood.
* Signals reach AV node
* Blood continues to fill ventricles
* Signal reaches His-Perkinje System in ventricles
* Ventricles contract to pump blood.
* Signal finishes
* heart muscles relax
* Heart Muscles wait for next signal
* SA node sends electrical signal
* Atria contract and start filling ventricles with blood.
* Signals reach AV node
* Blood continues to fill ventricles
* Signal reaches His-Perkinje System in ventricles
* Ventricles contract to pump blood.
* Signal finishes
* heart muscles relax
* Heart Muscles wait for next signal
36
New cards
Chemical control of heart beat
Controlled by Adrenaline, the hormone increases heart rate.
37
New cards
Artherosclerosis
* Hardening (plaques) and narrowing of the arteries
* slowly block arteries and blood flow
* Cause of heart attacks and strokes.
* Causes:
* Bad Cholesterol
* High blood glucose levels
* slowly block arteries and blood flow
* Cause of heart attacks and strokes.
* Causes:
* Bad Cholesterol
* High blood glucose levels
38
New cards
Occlusion
Stoppage or blockage of a blood vessel
39
New cards
Surface Barriers
The first line of defence against infectious disease are the surface barriers that present the entry of pathogens into the body
40
New cards
Skin
* Protects external structures when intact (outer body area)
* Consists of a dry, thick and tough region composed of deadly cells.
* Consists of a dry, thick and tough region composed of deadly cells.
41
New cards
Mucous Membranes
* Protects internal Structures
* Consists of a thin region of living surface cells that release fluids to wash away pathogens
* Mucus, saliva, tears, etc…
* Contacts biochemical defence agents.
* Consists of a thin region of living surface cells that release fluids to wash away pathogens
* Mucus, saliva, tears, etc…
* Contacts biochemical defence agents.
42
New cards
Clotting
* Process to stop bleeding when skin is cut
* Liquid blood changes to semi-solid form
* seals injured wound
* stops further blood loss
* stops pathogen entry
* protects new tissue while healing
* Liquid blood changes to semi-solid form
* seals injured wound
* stops further blood loss
* stops pathogen entry
* protects new tissue while healing
43
New cards
Scab
Hard and dried clot that is a protective crust forming over a wound during healing.
44
New cards
Platelets
* Blood cells that help with clotting process
* Gather at damaged area/blood vessel and create a plug.
* Releases clotting factors which begins clotting process.
* Gather at damaged area/blood vessel and create a plug.
* Releases clotting factors which begins clotting process.
45
New cards
Fibrin Production
* Clotting factors leads to the production of the enzyme Thrombin
* Changes soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin.
* Changes soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin.
46
New cards
Fibrin
Forms a mesh that traps more blood cells, hardening into a scab once oxidized.
47
New cards
Coronary Thrombosis
* Blood clots forming in coronary arteries of the heart
* Reduces heart function
* Reduces oxygen capacity of cells
* Reduces ATP synthesis for cells
* Causes:
* Smoking, high B.P, diabetes, obesity…
* Reduces heart function
* Reduces oxygen capacity of cells
* Reduces ATP synthesis for cells
* Causes:
* Smoking, high B.P, diabetes, obesity…
48
New cards
Phagocytes
* Part of the NONSPECIFIC immune response
* Destroy pathogens by ingesting them through phagocytosis (cell-eating)
* Chemicals released from damaged cells attract phagocytes to area.
* Destroy pathogens by ingesting them through phagocytosis (cell-eating)
* Chemicals released from damaged cells attract phagocytes to area.
49
New cards
Lymphocytes
* Part of the specific immune response
* Destroy pathogens by producing chemicals called ANTIBODIES
* Can distinguish between body cells (self) and foreign cells (non-self)
* Destroy pathogens by producing chemicals called ANTIBODIES
* Can distinguish between body cells (self) and foreign cells (non-self)
50
New cards
Phagocytic WBC
* Variety of WBC that eat pathogens by endocytosis.
* eat everything (nonspecific)
* digest using lysozyme
* eat everything (nonspecific)
* digest using lysozyme
51
New cards
Pus
White liquid formed when large numbers of phagocytes are attracted to a wound.
52
New cards
WBC movement
WBC are able to squeeze through cells to get to an infected area.
53
New cards
Antibodies
* Proteins produced by special WBCs
* Lymphocytes
* Plasma cells (Clones of lymphocytes)
* Specific Immunity
* Attach to pathogen’s antigens
* Act as a marker that tells WBCs to “eat” pathogens by phagocytic endocytosis
* Inhibits pathogen from attacking to other healthy tissue cells; neutralizing it.
* Lymphocytes
* Plasma cells (Clones of lymphocytes)
* Specific Immunity
* Attach to pathogen’s antigens
* Act as a marker that tells WBCs to “eat” pathogens by phagocytic endocytosis
* Inhibits pathogen from attacking to other healthy tissue cells; neutralizing it.
54
New cards
Antigens
* Protein/ carbohydrate coat surrounding cells
* specific shape of pathogenic antigens can be detected by the immune system.
* specific shape of pathogenic antigens can be detected by the immune system.
55
New cards
Lymphocyte differentiation
* Lymphocyte attaches to antigen and either
* 1) changes into plasma cells and makes many clones of itself
* releases antibodies to help kill pathogens.
* 2) becomes a memory cell
* remembers pathogen and is ready for future invasions.
* 1) changes into plasma cells and makes many clones of itself
* releases antibodies to help kill pathogens.
* 2) becomes a memory cell
* remembers pathogen and is ready for future invasions.
56
New cards
Antibody specificity
* lymphocytes can make different kinds of antibodies
* Shape of “variable region” of antibody determines what antigen it can attach to.
* Shape of “variable region” of antibody determines what antigen it can attach to.
57
New cards
Virus
Reproduction:
* Cannot reproduce by itself
* needs help from living host cell
\
* Cannot reproduce by itself
* needs help from living host cell
\
58
New cards
Steps of viral infection
1) Virus attaches or goes inside the cell
2) Virus DNA replaces all DNA
3) Cell produces LOTS of virus copies
4) Cell dies (explodes) due to large amount of viruses
5) New viruses are released
2) Virus DNA replaces all DNA
3) Cell produces LOTS of virus copies
4) Cell dies (explodes) due to large amount of viruses
5) New viruses are released
59
New cards
HIV
* Human Immunodeficiency Virus
* Specifically targets lymphocytes (helper-T cells) and destroys them.
* Decrease in immune response
* Decreased antibody production, and number of active lymphocytes.
* Infection of HIV can lead to AIDS
* Opportunistic infections take advantage of weakened immune system.
* Specifically targets lymphocytes (helper-T cells) and destroys them.
* Decrease in immune response
* Decreased antibody production, and number of active lymphocytes.
* Infection of HIV can lead to AIDS
* Opportunistic infections take advantage of weakened immune system.
60
New cards
Antibiotics
* Chemical that stops microorganism growth
* Usually specific for prokaryotes (bacteria)
* Eukaryotic cells are not affected.
* Processes stopped in bacteria:
* DNA replication
* Transcription
* Translation
* Ribosome function
* Cell wall formation
* Usually specific for prokaryotes (bacteria)
* Eukaryotic cells are not affected.
* Processes stopped in bacteria:
* DNA replication
* Transcription
* Translation
* Ribosome function
* Cell wall formation
61
New cards
Antibiotics VS Virus
* Antibiotics have NO effect on viruses
* Viruses have no cellular metabolism
* uses a host cell’s own process for reproduction
* Viruses have no cellular metabolism
* uses a host cell’s own process for reproduction
62
New cards
Blood Type A
* Has “A” Antigens
* Has “B” Antibodies
* Has “B” Antibodies
63
New cards
Blood Type B
* Has “B” Antigens
* Has “A” Antibodies
* Has “A” Antibodies
64
New cards
Blood Type AB
* Has “A” & “B” Antigens
* Has NO antibodies
* Has NO antibodies
65
New cards
Blood Type O
* Has NO Antigens
* Has “A” & “B” Antibodies
* Has “A” & “B” Antibodies
66
New cards
rH factor
* A third kind of antigen found on RBC
* When you have an rH antigen
* rH positive (rH+)
* When you have NO rH antigens
* rH negative (rH-)
* When you have an rH antigen
* rH positive (rH+)
* When you have NO rH antigens
* rH negative (rH-)
67
New cards
Agglutination
* Immune response
* Clumping of blood cells due to antibodies attacking antigens in blood.
* Leads to hemolysis (the destruction of blood cells)
* Clumping of blood cells due to antibodies attacking antigens in blood.
* Leads to hemolysis (the destruction of blood cells)
68
New cards
Blood Typing
* Method used to figure out the blood type of a person
* Blood type depends on the observed combination of agglutination or non-agglutination
* Blood type depends on the observed combination of agglutination or non-agglutination