Business Paper 1 - Revenue, Costs and Profit (108)
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Revenue
money a business makes from its sales
formula: selling price x quantity sold
Profit
amount left over once a business subtracts its total costs from the total revenue they generate from selling goods/services to customers
formula: total revenue - total costs
Fixed Costs
do not vary with output - only change in long-term e.g rent, insurance
Variable Costs
costs that change in direct proportion to changes in output e.g raw materials, stock
Semi-Variable Costs
costs that include both fixed and variable cost-components e.g a business will pay its employees a monthly salary (fixed) but may pay them overtime if they have a lot of orders (variable)
Direct Costs
costs that can be identified directly with the production of a good or service e.g raw materials
Indirect Costs
costs that can’t be matched against each product as they need to be paid whether or not the production of a good/service takes place e.g rent on the premises
Total Costs
Total fixed costs + Total variable costs
Contribution
allows an organisation to analyse whether each of its products can cover their own variable costs
formula: selling price - variable cost per unit
Break-even
a diagram that shows level of output in a business where they don’t make a profit nor a loss
formula: fixed costs/contribution
Margin of Safety
how much a product can reduce output before the business starts to make a loss
formula: output - break-even output
Break-even chart (describe)
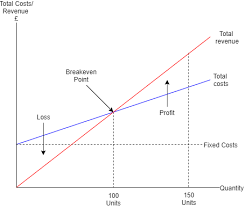
Break-even (Advantages + Disadvantages)
Advantages:
used to secure finance (part of the business plan)
simple and easily understood representation of revenue, costs and potential profit
Disadvantages:
assumes all products are sold and are sold at one price - doesn’t account for damaged or wasted stock - some can be sold at a lower selling price
assumes only one product is sold - businesses normally have a range goods which all vary in variable costs depending on the size, complexity etc.
Usefulness to Stakeholders
Stakeholders:
owners - both advantages
employees - job security, enough payment (based on potential success shown in the diagram)