ocular, skeletal, and periodontal drug delivery - minko
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
ocular drug delivery
cornea = protects the front of the eye
blood-retina barrier = protects the back of the eye
eye is uniquely shielded from foreign substance penetration by its natural anatomic barriers → makes effect drug delivery to the inside of the eye difficult

dry delivery by eye drops (local, topical)
limited by inefficient penetration into front of eye
virtually NO penetration to the back of the eye
systemic medications (oral tablets, IV admin)
limited by inefficient penetration into the back of the eye (blood-retina barrier)
intraocular innjection
circulatory process quickly reduces bioavailability
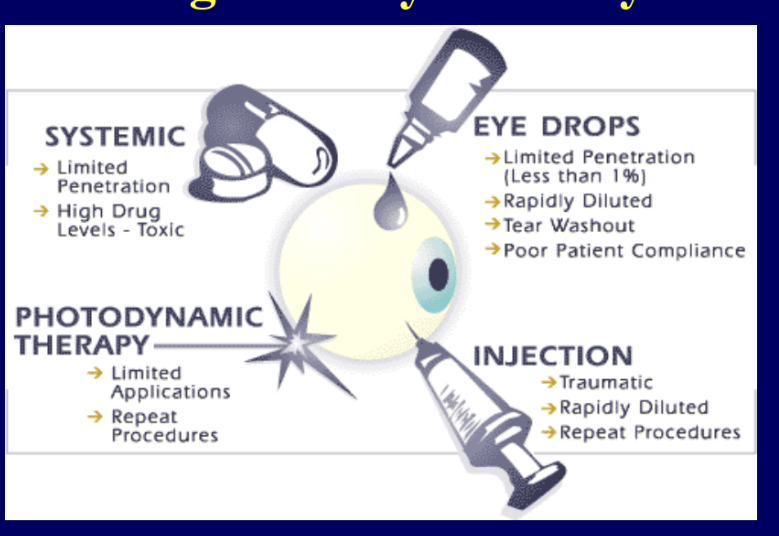
drug delivery to the eye
topical medications are frequently impeded in reaching a targeted site due to the eye’s natural protective surface
in many situations, less than 1% of the medication applied to the surface of the eye will actually reach the disease site
to achieve sufficient concentration of drug delivered to the back of the eye, medications are frequently administered systemically at very high doses → levels are necessary to overcome the blood-retina barrier than protects the eye from select molecules coming from blood stream
drug injections into the back of the eye are occasionally used but are quickly removed by the eye’s natural circulatory process, often necessitating frequent injections that can carry toxicity risks
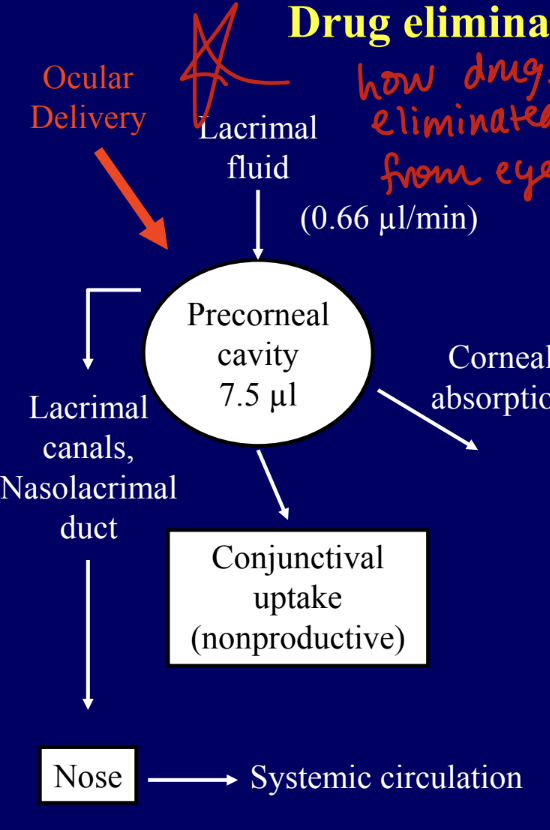
drug elimination from the eye
the solution instilled as eye drops into the ocular cavity may disappear from the pre-corneal area of the eye by any of a composite of the following routes
nasolacrimal drainage
tear turnover
productive corneal absorption
non-productve conjunctival uptake
topical ocular delivery
traditional dosage forms for delivery of drugs in the eye have been solutions and ointments; however, as a consequence of its function as the visual apparatus, mechanisms are strongly developed for the clearance offering materials from the cornea to preserve visual acuity → presents problems in the development of formulations for ophthalmic therapy
large proportion of topically applied drug is immediately diluted in the tear film and excess fluid spills over the lid margin and the remainder is rapidly drained into the nasolacrimal duct → proportion of the drug is NOT available for therapeutic action since it binds to the surrounding extraorbital tissues → these processes lead to a typical corneal contact time of about 1-2 mins in humans for all instilled solution and an ocular bioavailability that is <10%
to optimize ocular drug delivery, following characteristics are required:
good corneal penetration
prolonged contact time with corneal epithelium
simplicity of instillation for patient
a non-irritative and comfortable form (system should NOT provoke lacrymation and reflex blinking)
appropriate rheological properties
ocular drug delivery: overview
eye = logical choice for site-specific drug therapy
eye drops
limited by inefficient penetration into the front of the eye
virtually NO penetration to the back of the eye
systemic medications (oral tablets, IV injections)
limited by inefficient penetration into the back of the eye
required high doses
drug injections
circulatory process quickly reduces bioavailability
inserts and diffusion controlled systems
non-compliance, esp in elderly people
biodegradable DDS (BDD)
BDD systems are placed in the eye at the time of elective surgery
BDD systems dissolve as they release the active drug
ophthalmic gels/hydrogels
iontophoresis
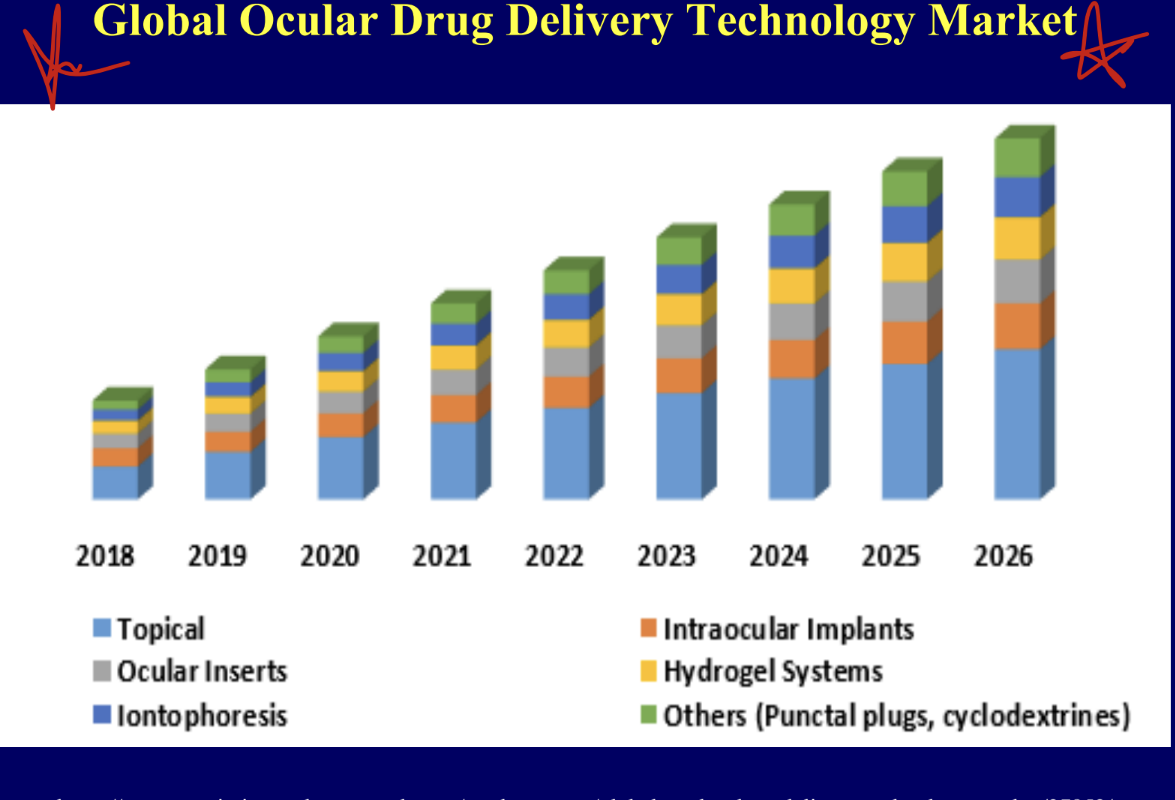
global ocular drug delivery technology market
market is mainly topical
ocular inserts, iontophoresis, intraocular implants, hydrogel systems, others = equal amounts
in general more ocular drug delivery as years go on
skeletal drug delivery
systemic drug delievry
high dose of drugs → high systemic toxicity
bone targeted drug delivery
skeletal drug delivery system (SDDS)
osteotropic drug delivery system (ODDS)
local drug delivery
sustained drug release