ADVANCED BIOLOGY - Skeletal System: MIDTERM (2ND SEM)
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Femur
is the longest and strongest bone of the human skeleton..
Skeleton
supports the body, protects internal organs, provides for movement, sores mineral reserves, and provides site for blood cell formation.
206
How many bones are there in the adult human skeleton?
Axial Skeleton
supports the central axis of the body
8
The skull is made up of how many bones?
26
The vertebral column has ________ vertebrae with intervertebral disk between each vertebrae.
Spinal Column
protects the spinal cord.
Intervertebral disk
serves as shock absorbers between each vertebrae
5
how many pairs are false ribs?
Costae/Ribs
responsible for Hematopoiesis or the production of blood
Appendicular Skeleton
consists of the extremities of the body
Wrist Bones
comprised of 8 carpals
Hand Bones
comprised of 5 metacarpals
Finger Bones
comprised of 14 phalanges
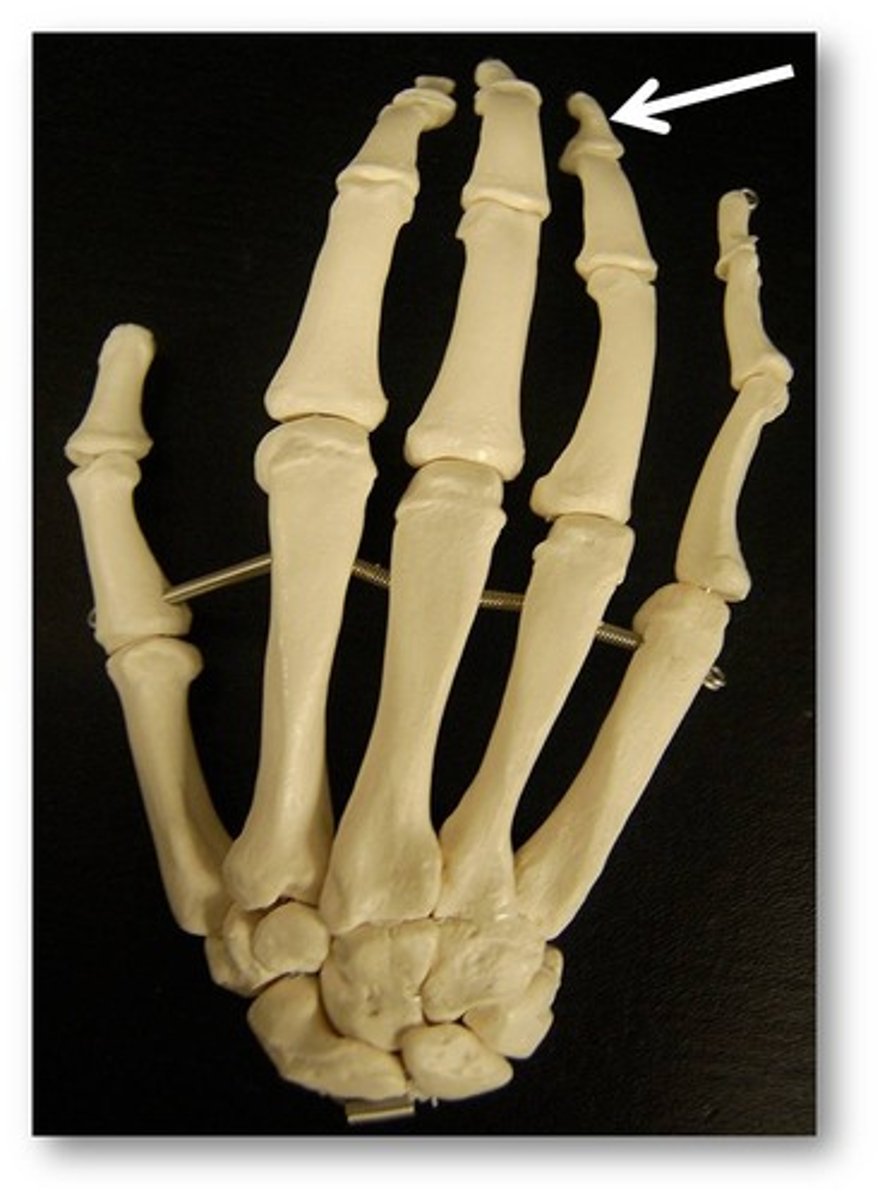
Distal Phalanx
Name the bone.
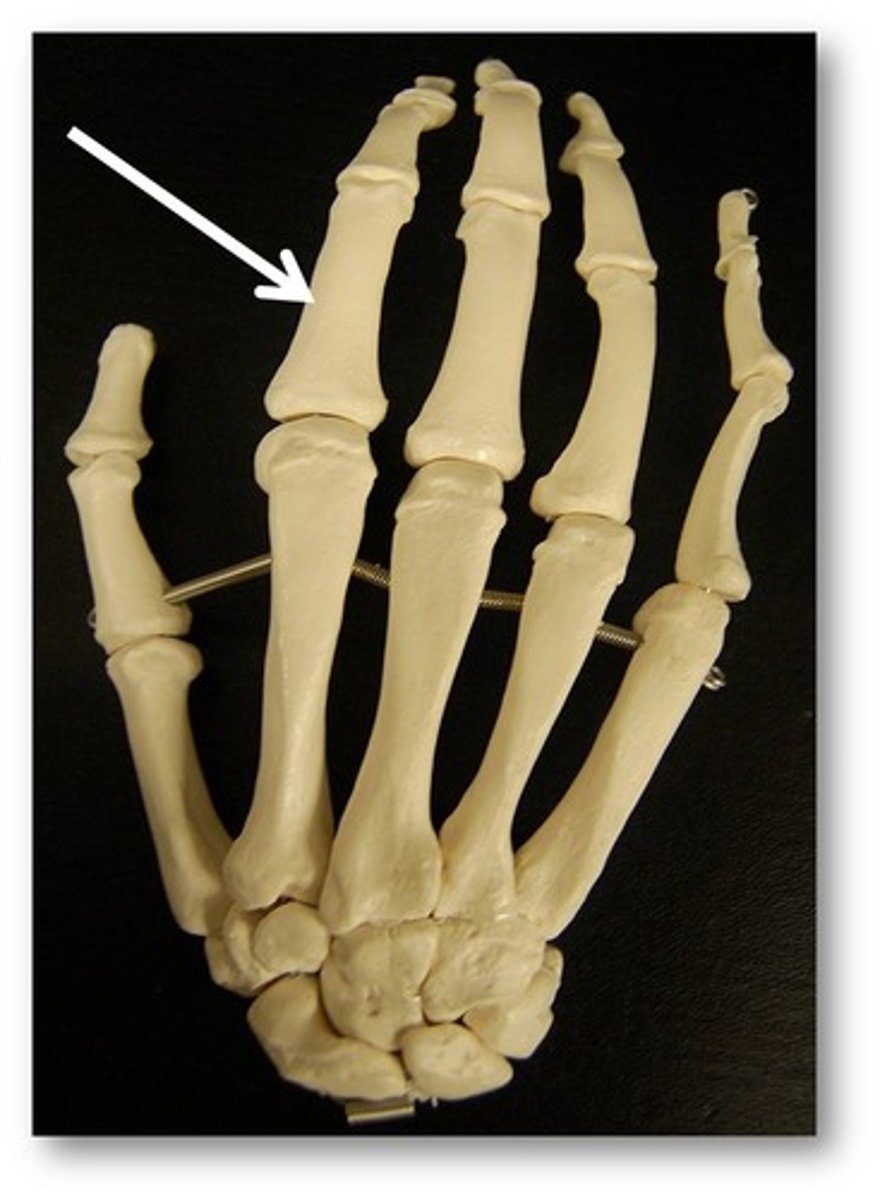
Proximal Phalanx
Name the bone.
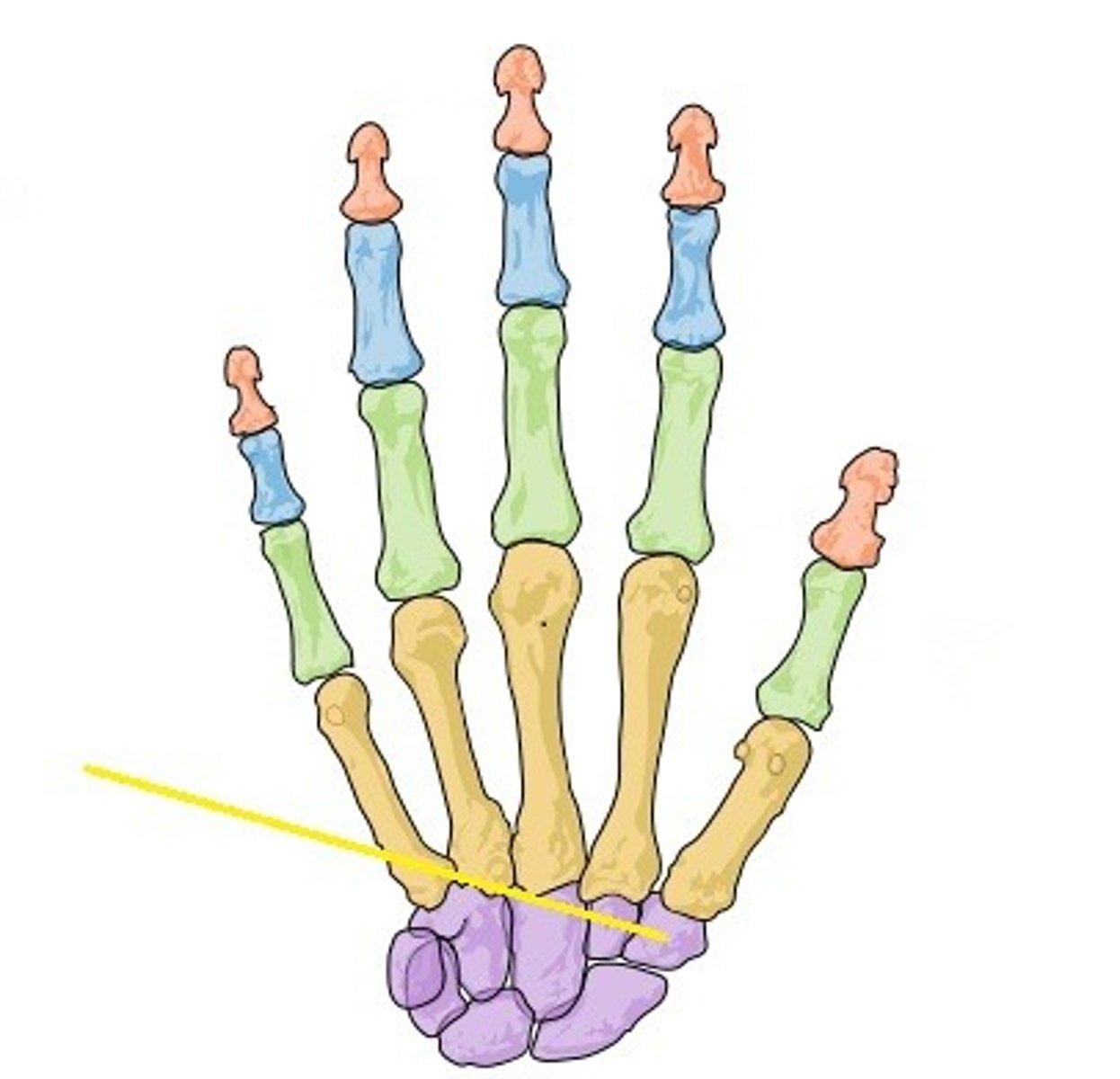
Trapezium
Name the bone.
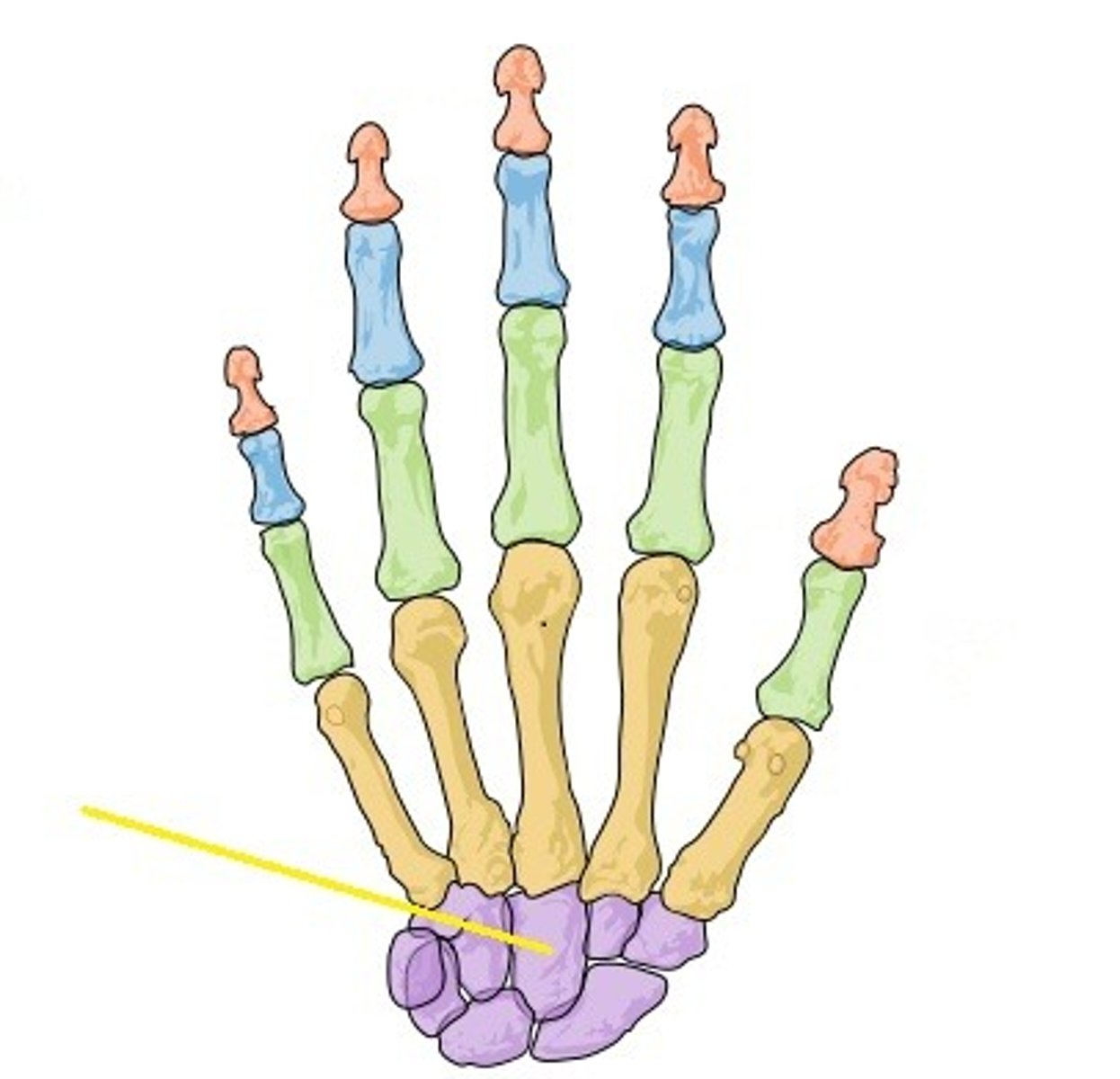
Capitate
Name the bone.
Hamate
Name the bone.
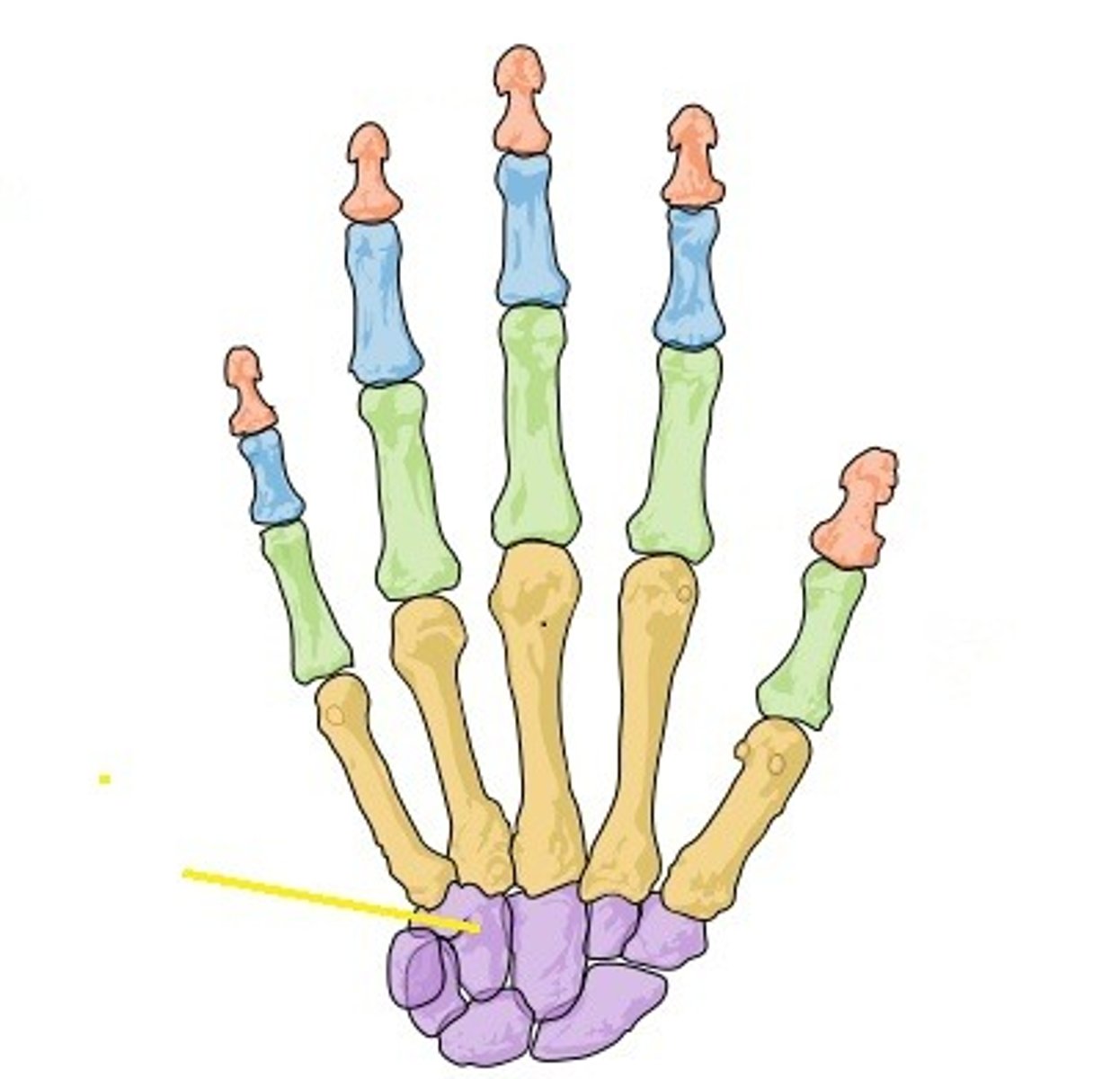
Pisiform
Name the bone.
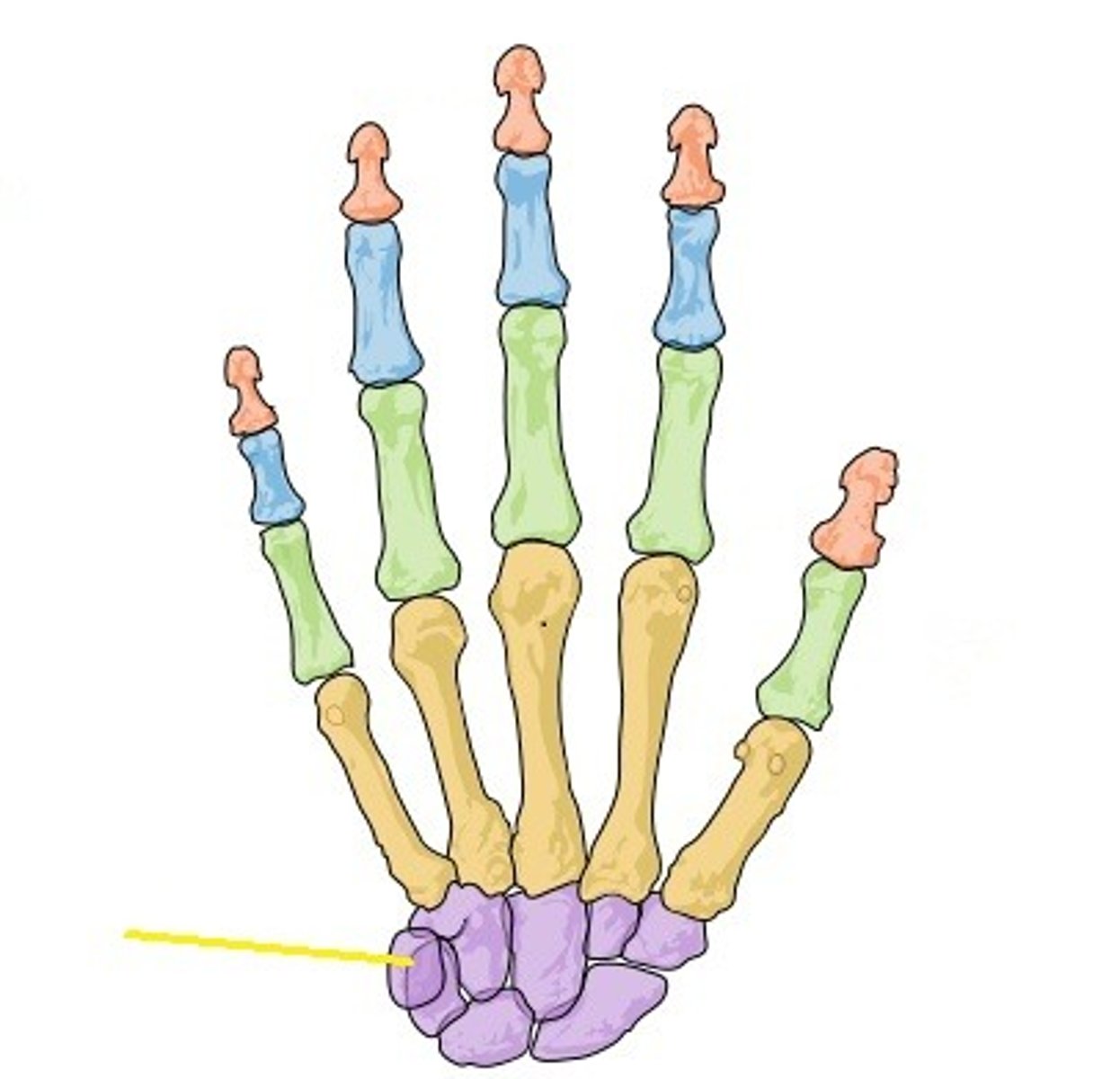
Lunate
Name the bone.
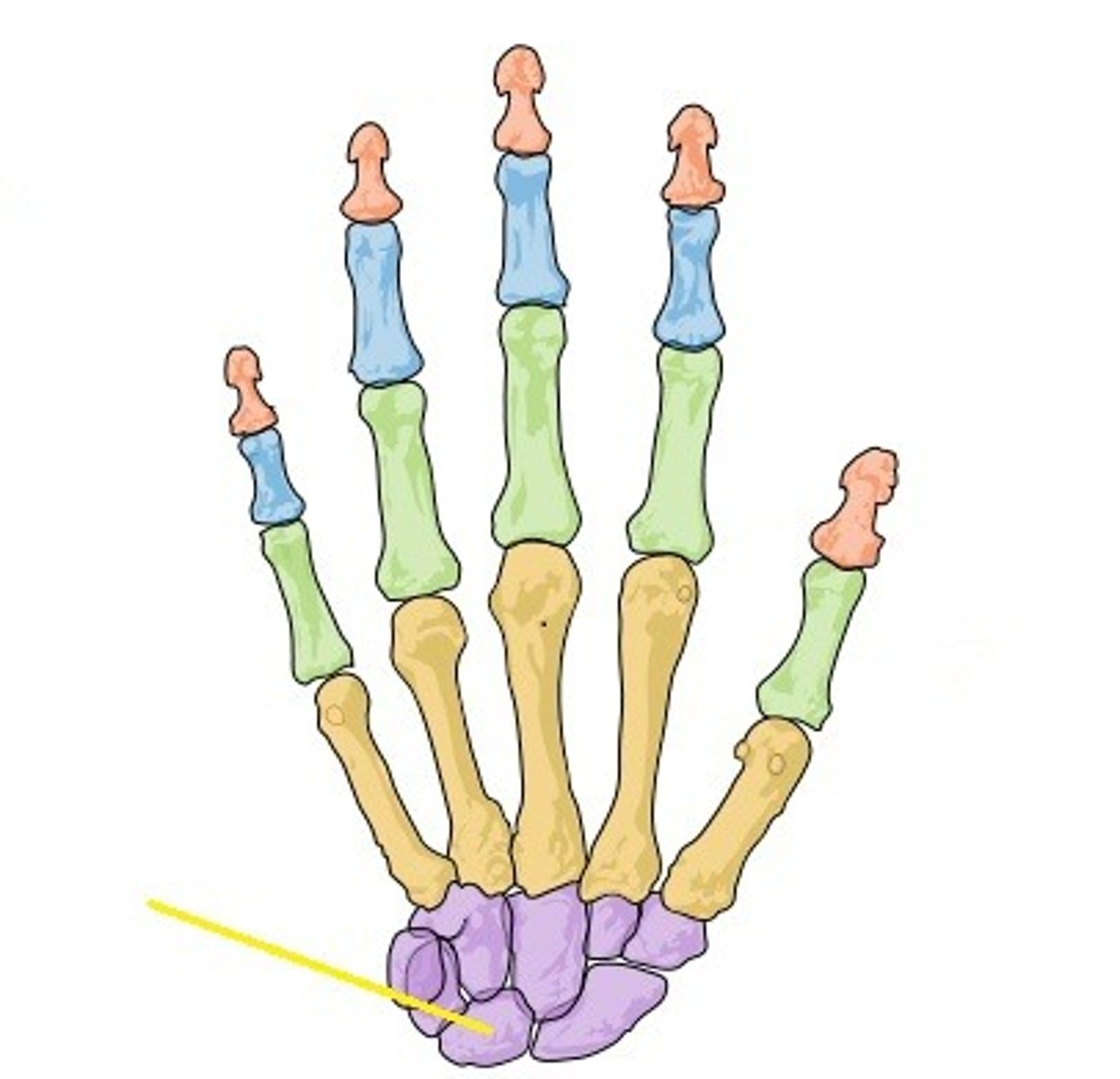
Scaphoid
Name the bone.
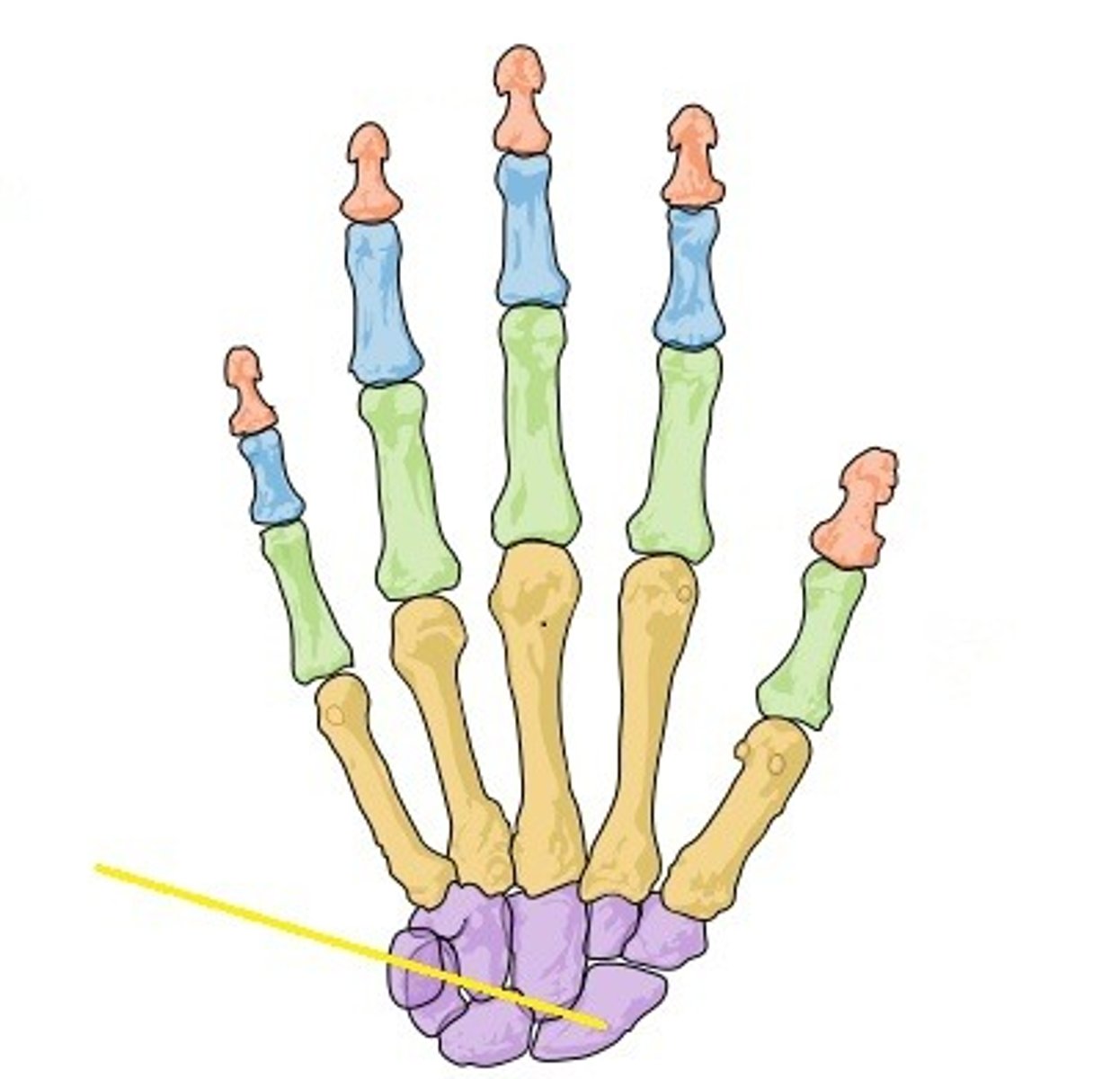
Pelvic girdle
structure to which the leg bones are attached
Patella
name the bone.
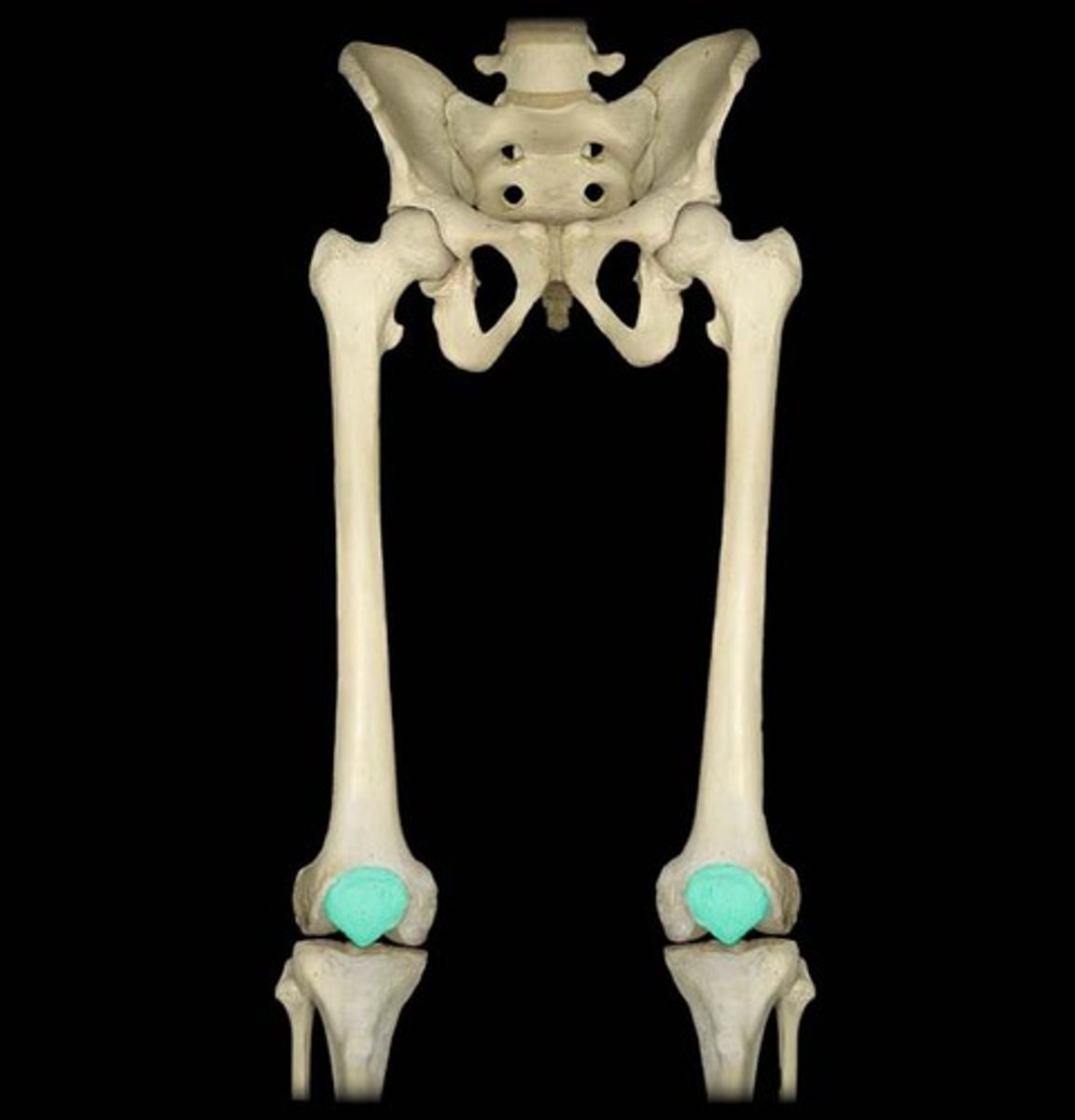
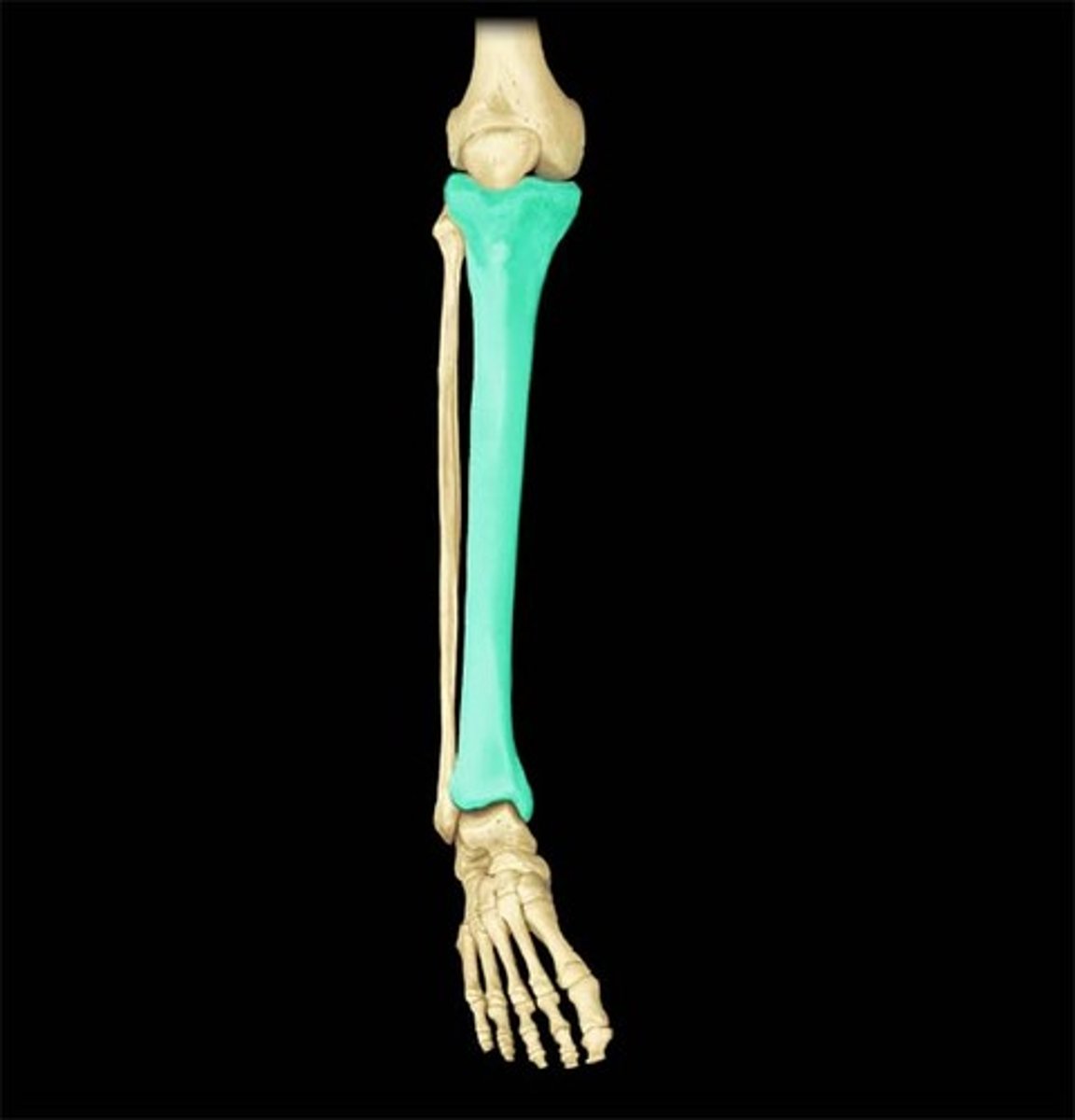
tibia
Name the bone.
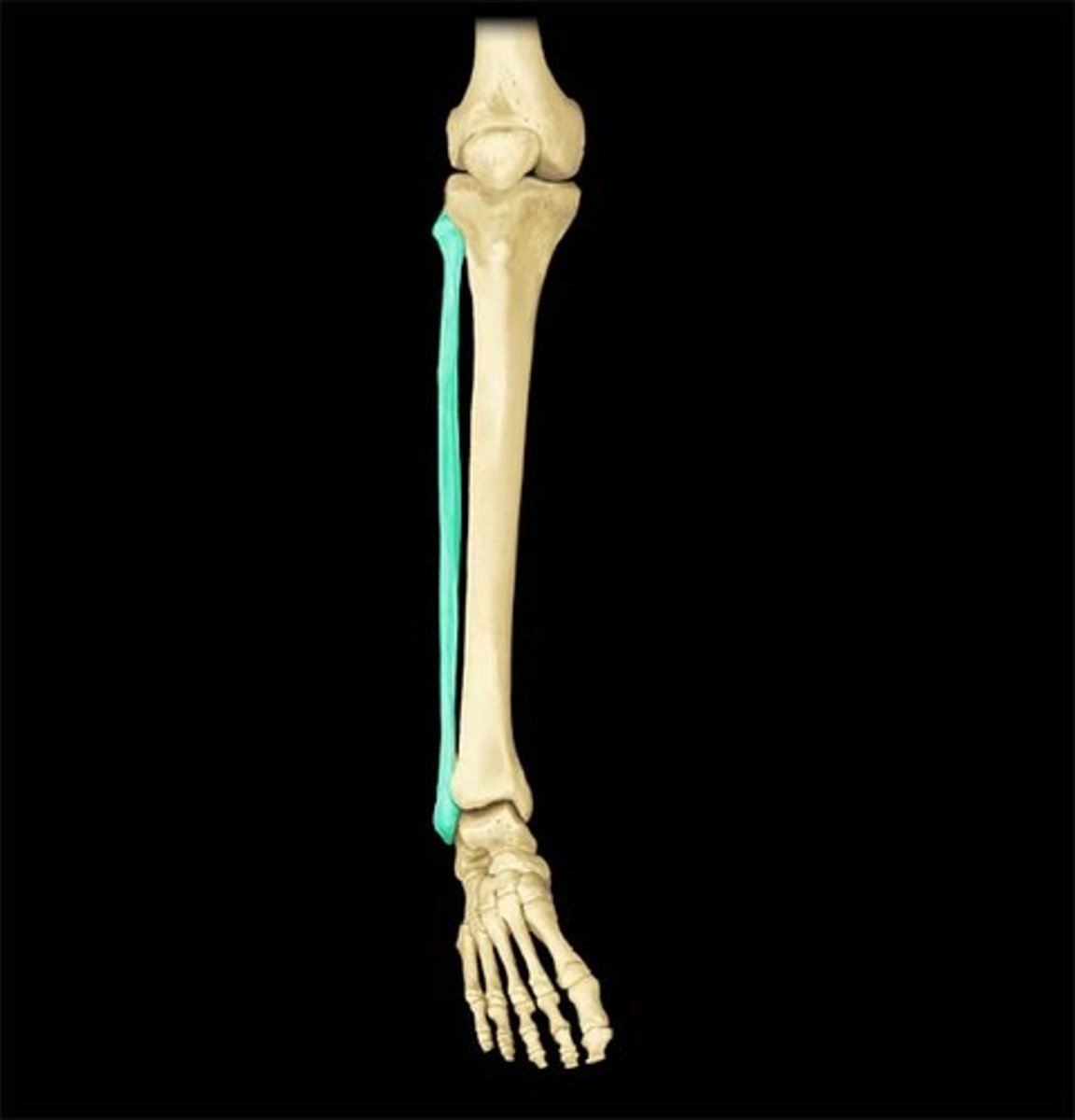
Fibula
Name the bone.
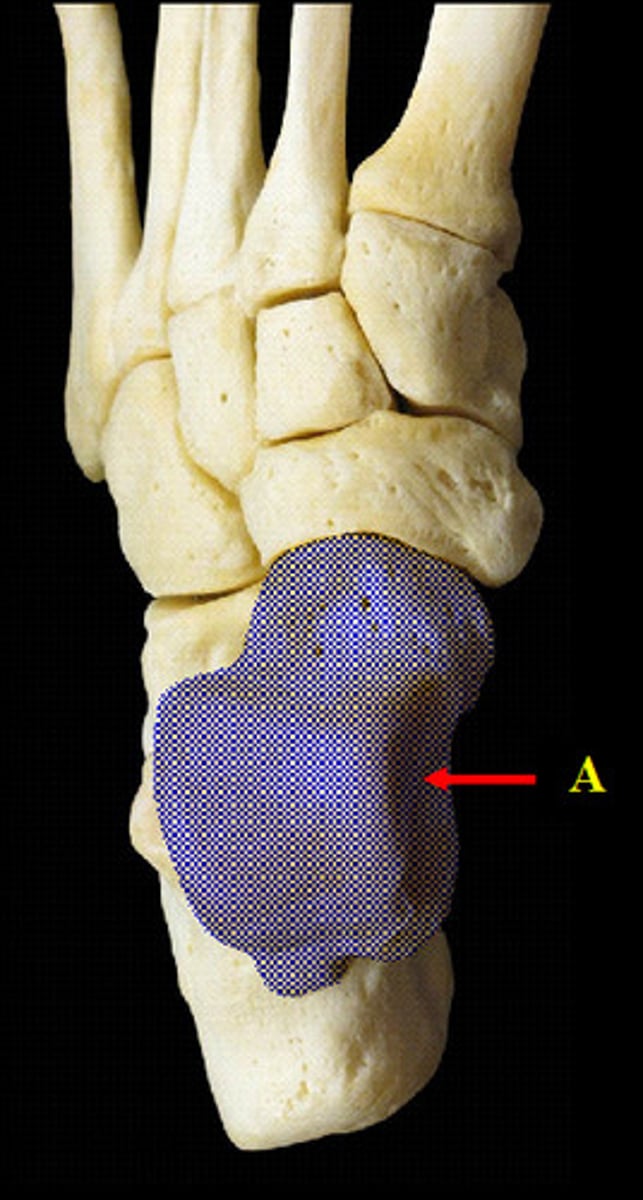
Talus
Name this specific bone of the foot.
Diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
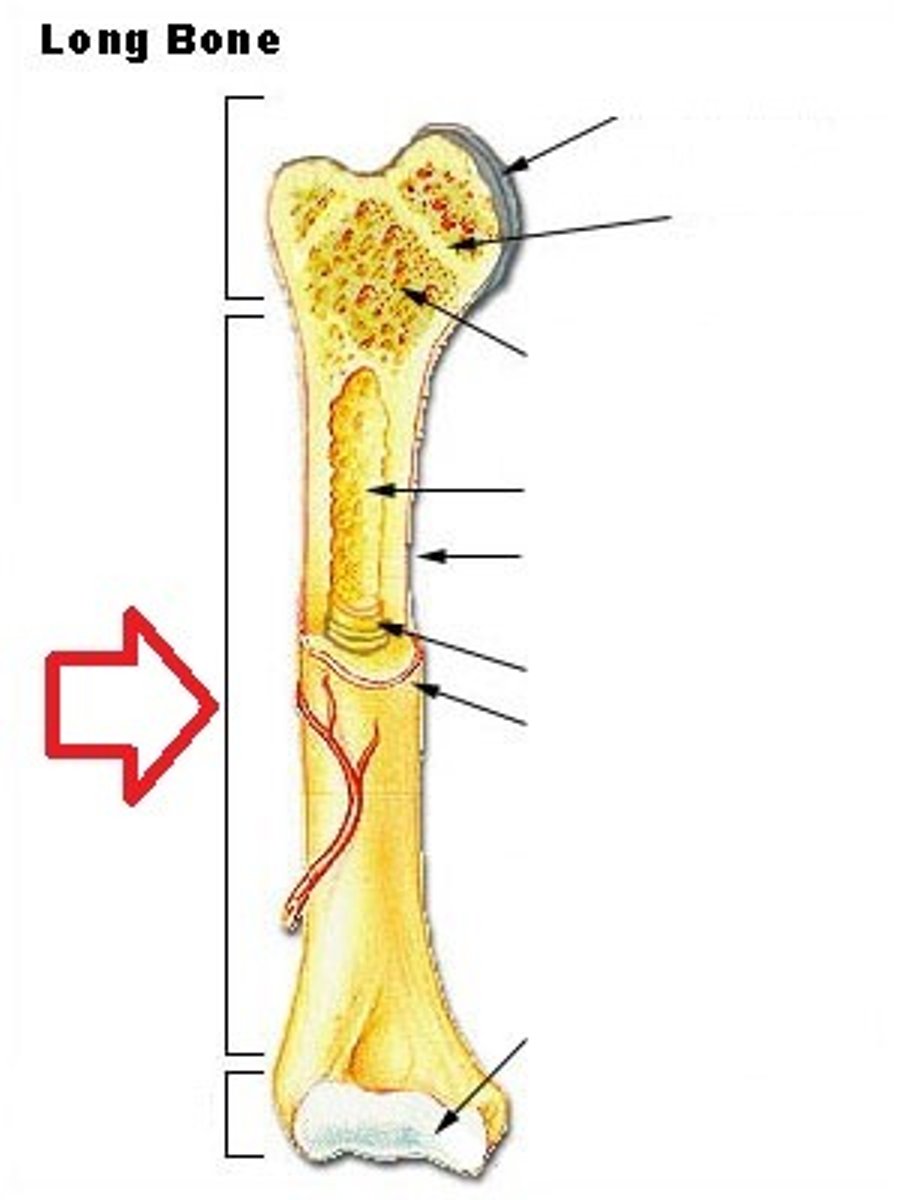
Proximal epiphysis
the end of the bone located nearest to the midline of the body
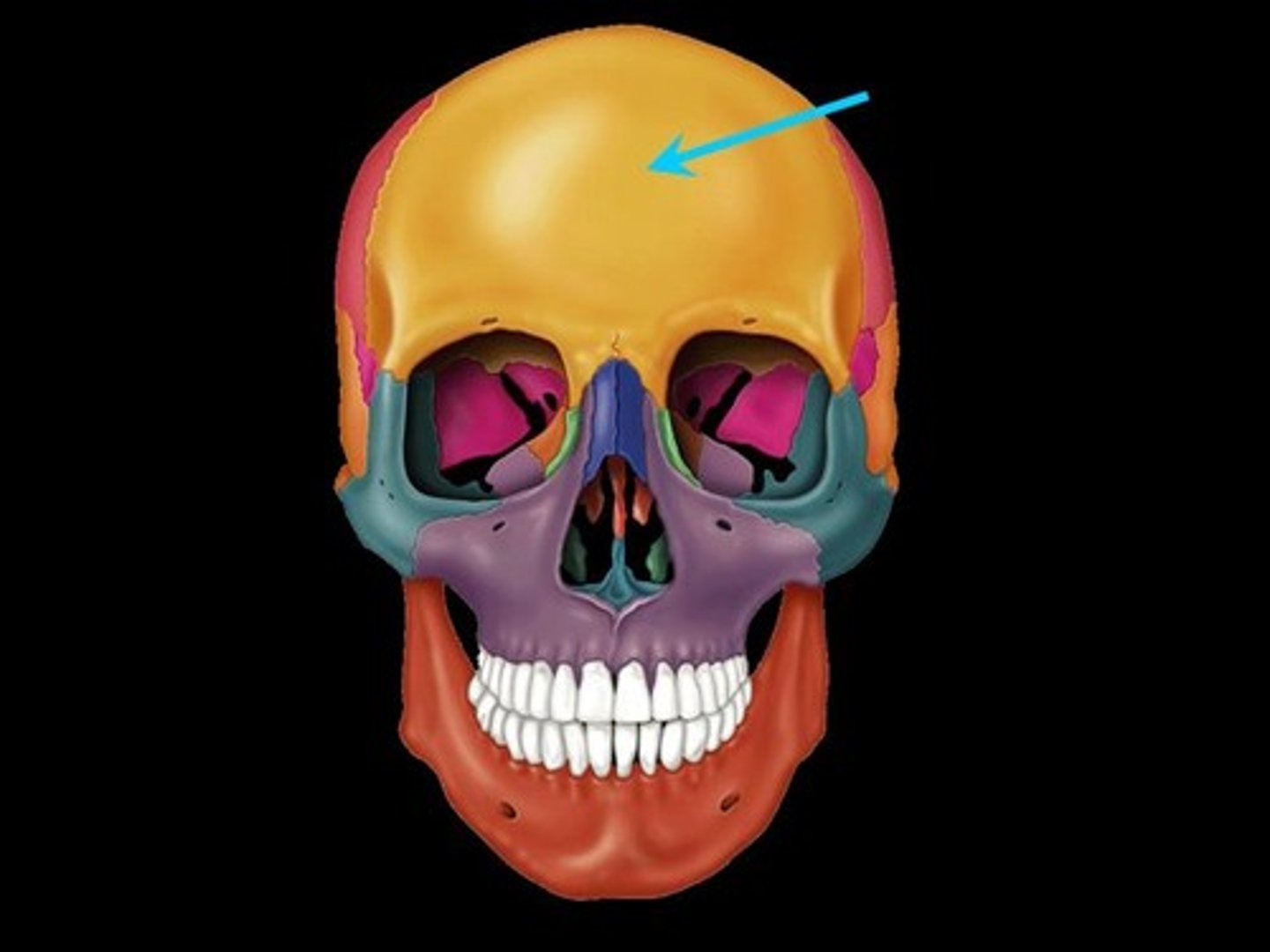
Frontal bone
Name the bone.
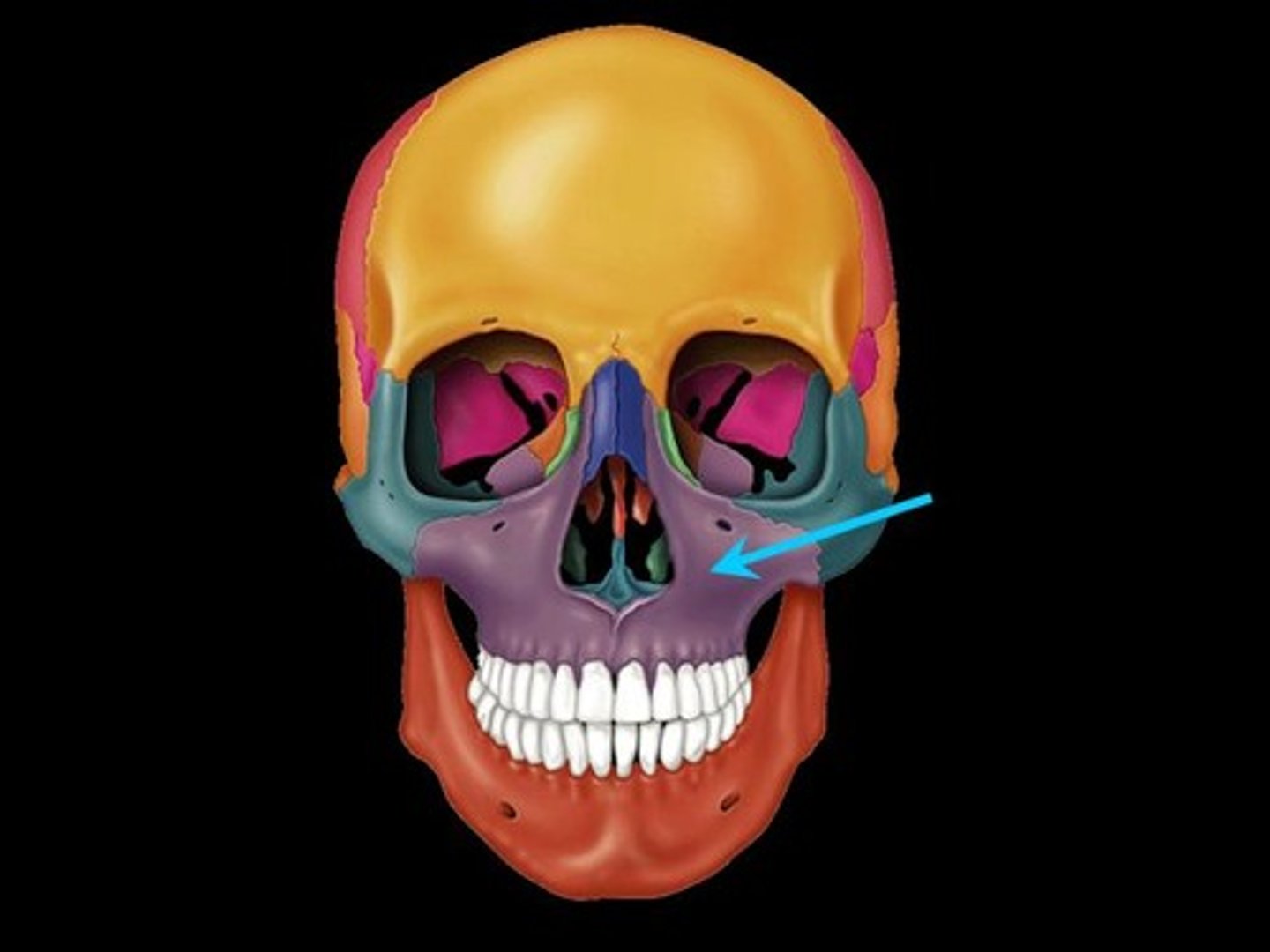
Maxilla
Name the bone.
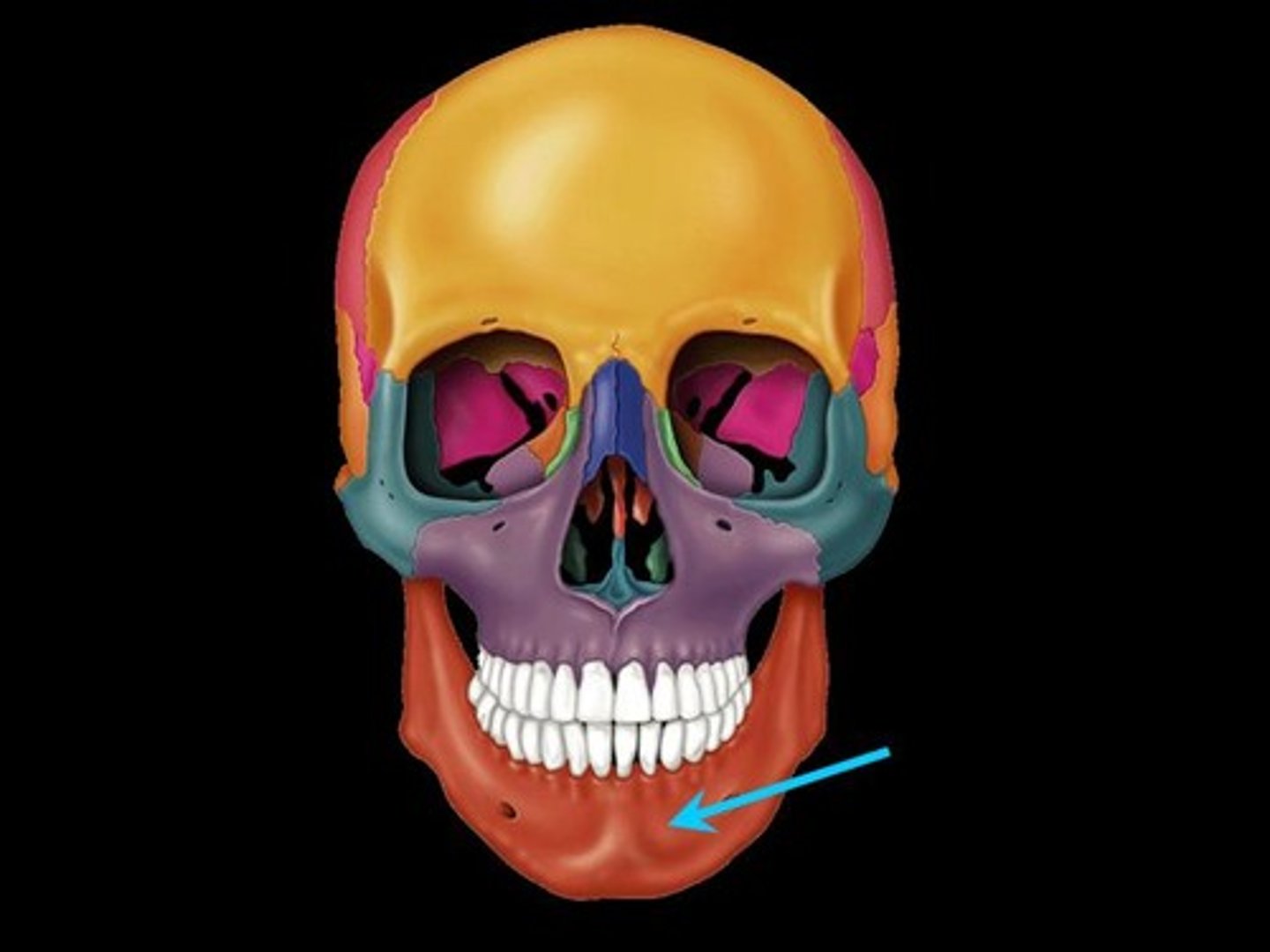
Mandible
Name the bone.
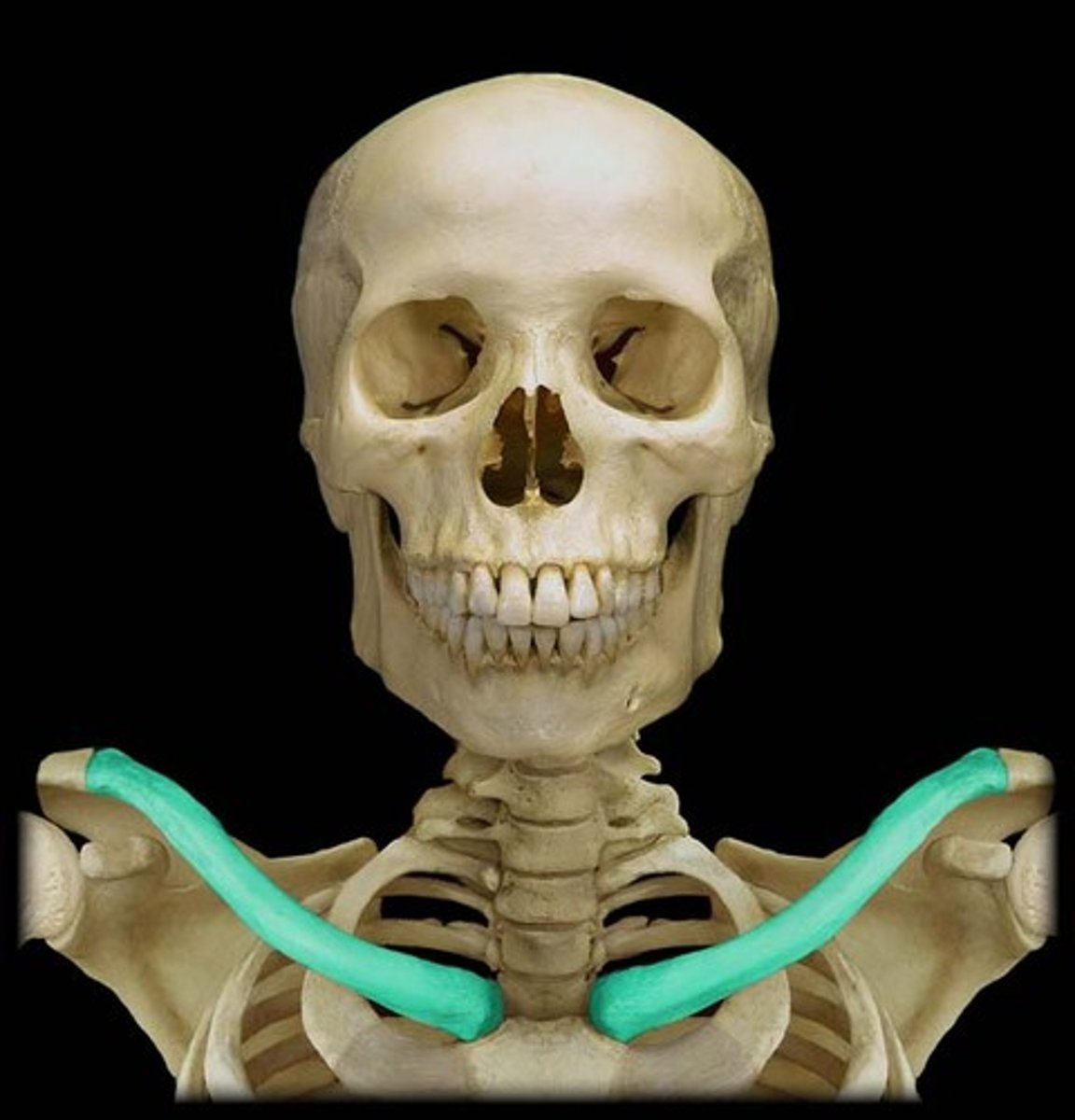
Clavicle
Name the bone.
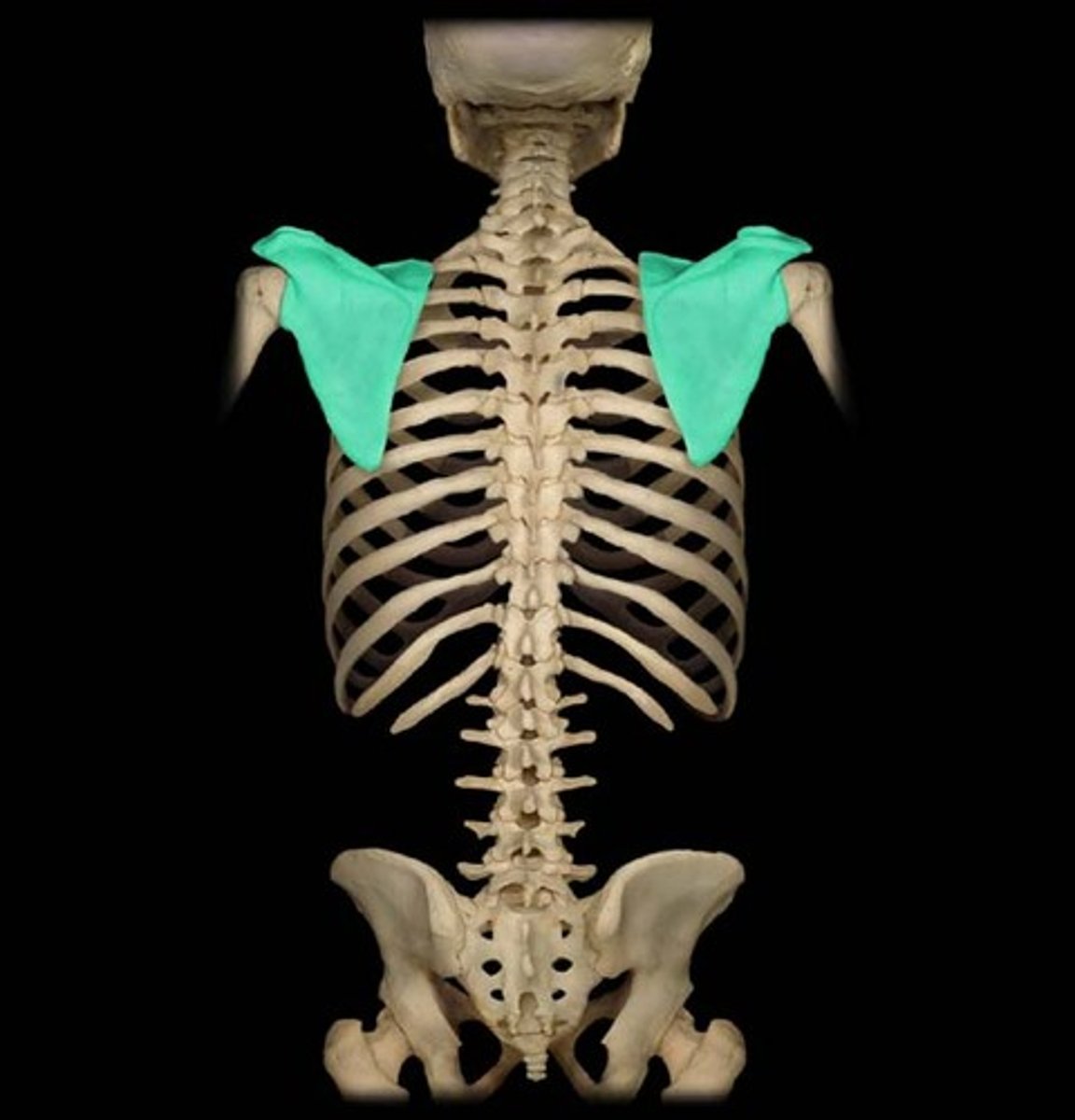
Scapula
Name the bone.
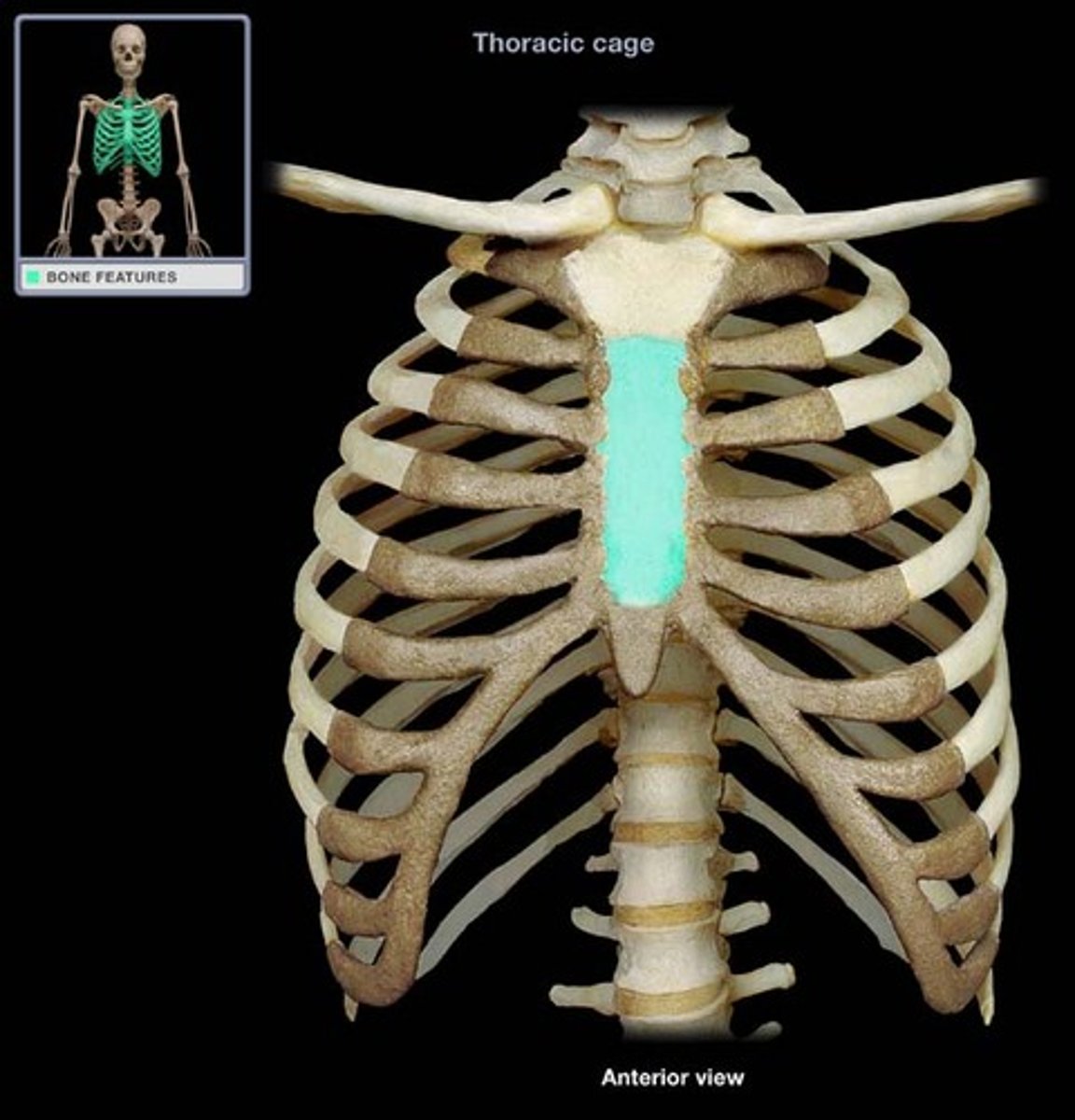
Sternum
Name the bone.
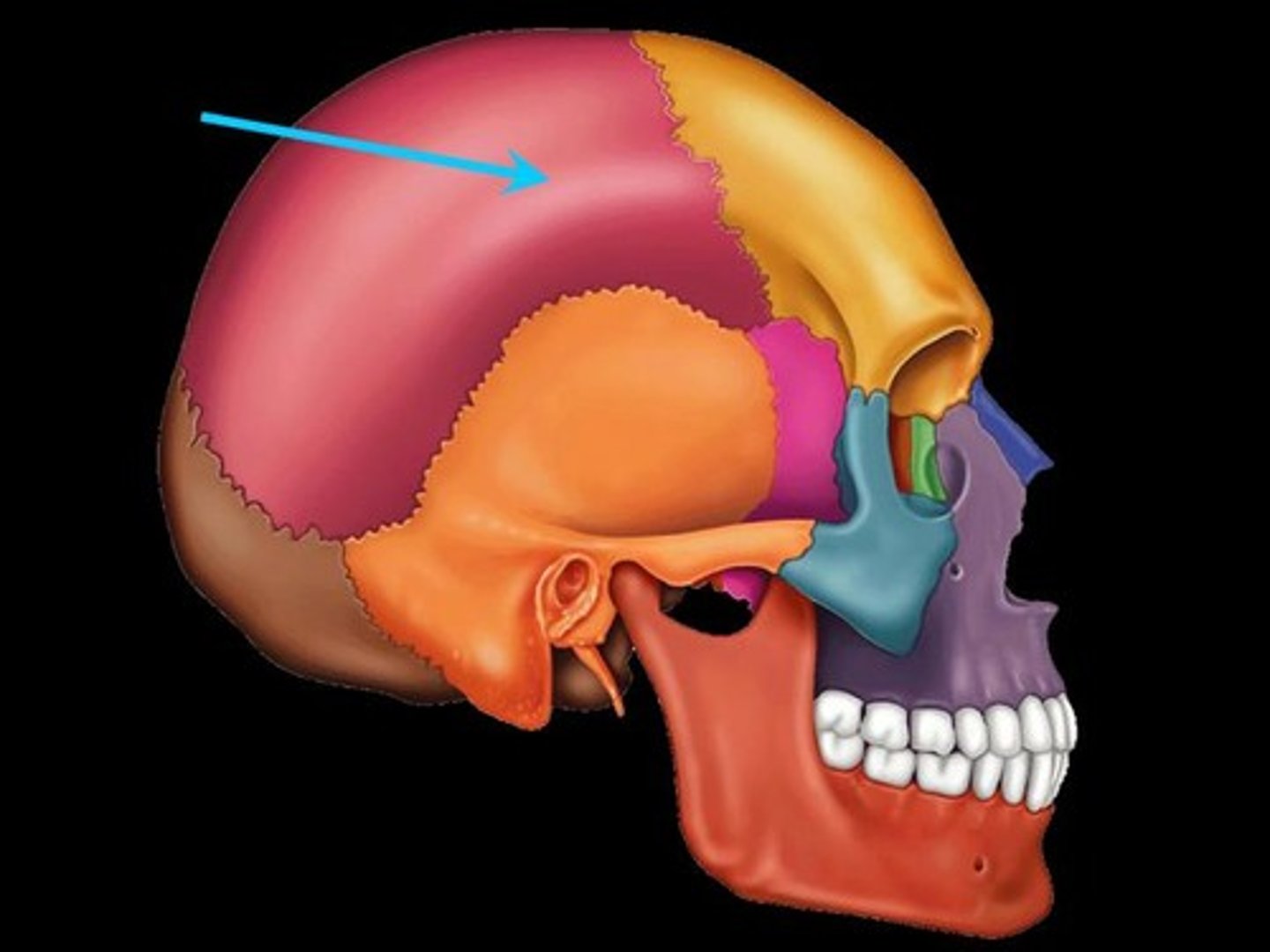
Parietal bone
Name the bone.
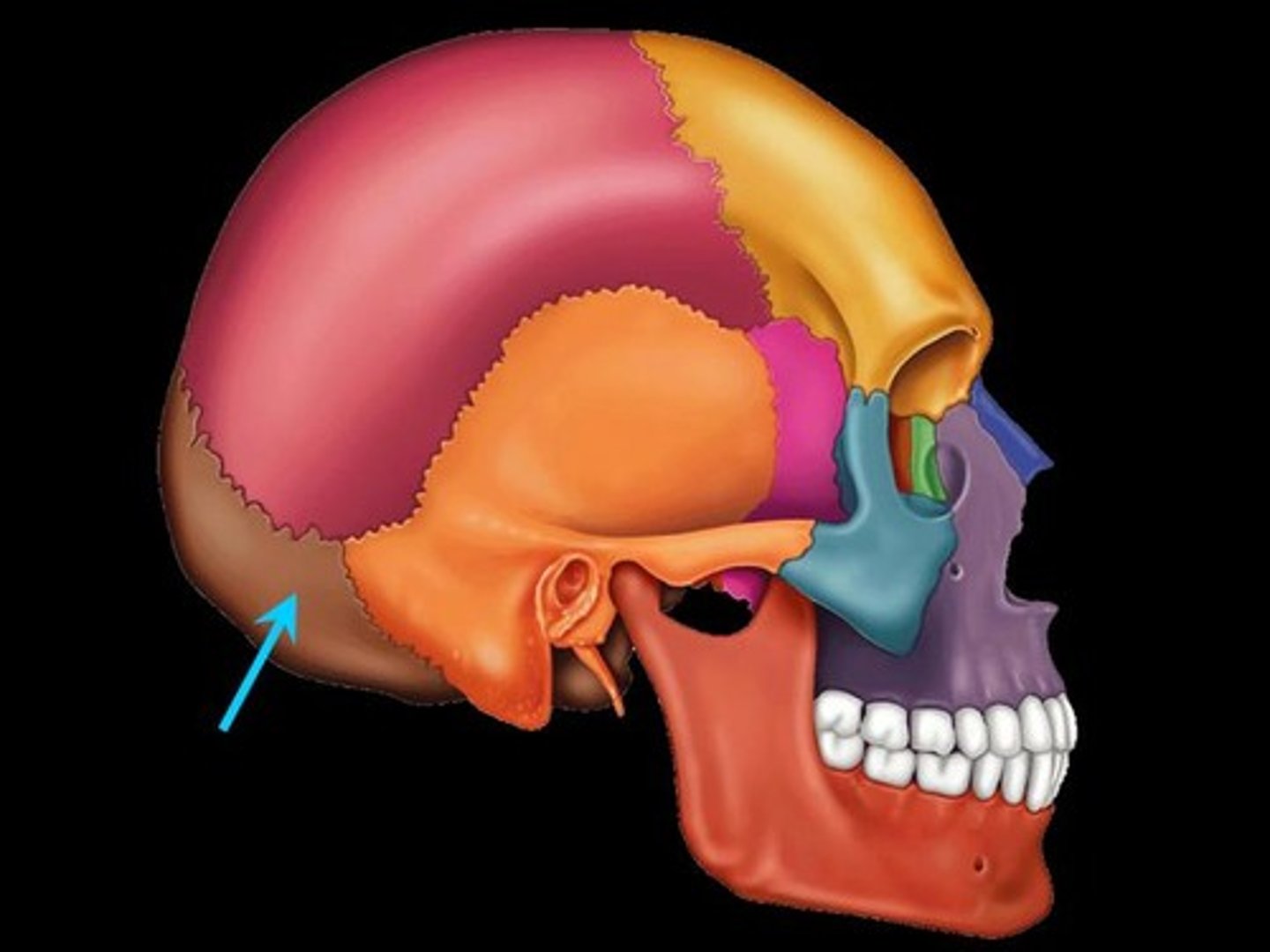
Occipital Bone
Name the bone
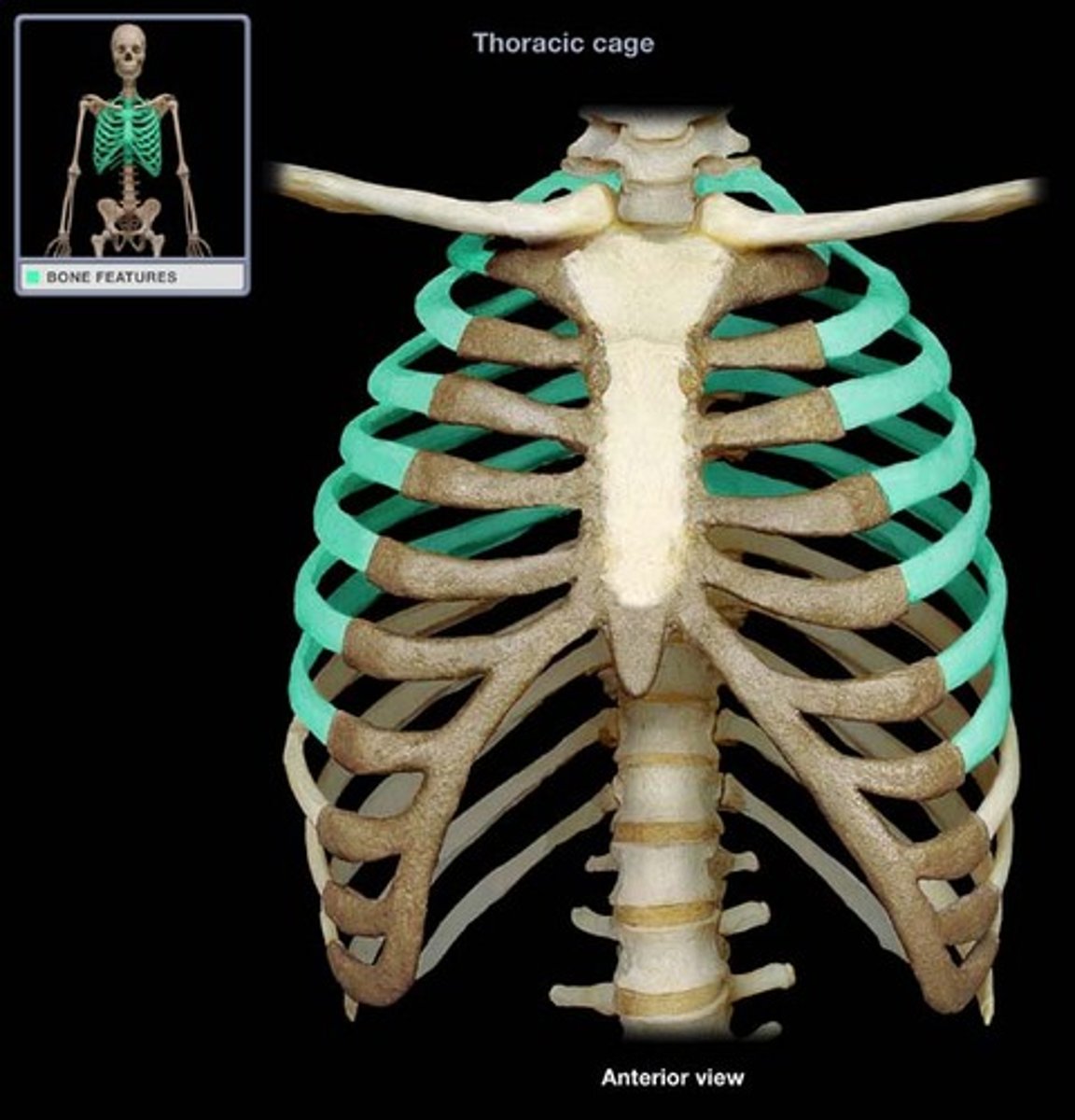
Ribs
Name the bone.
Costal Cartilage
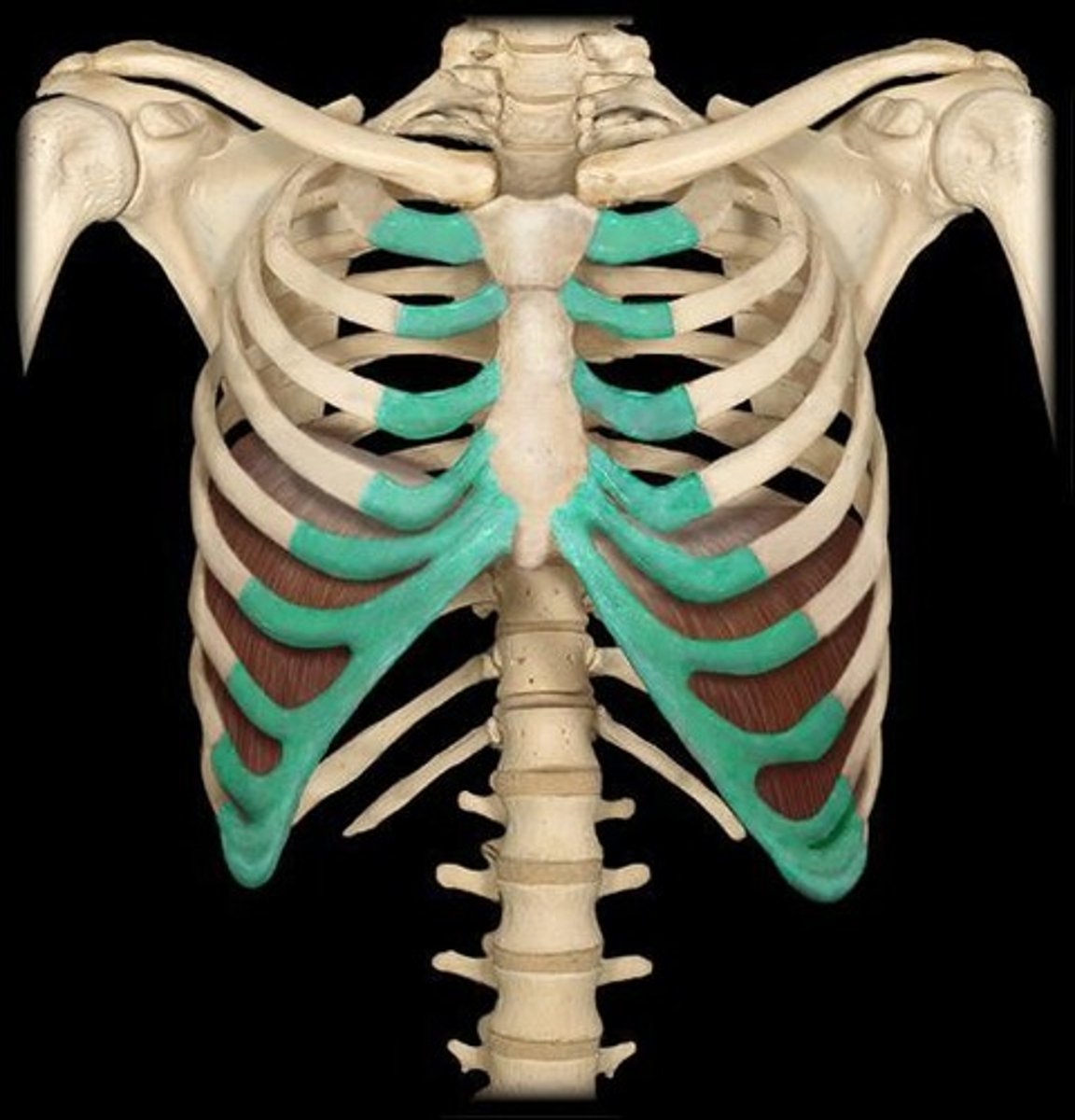
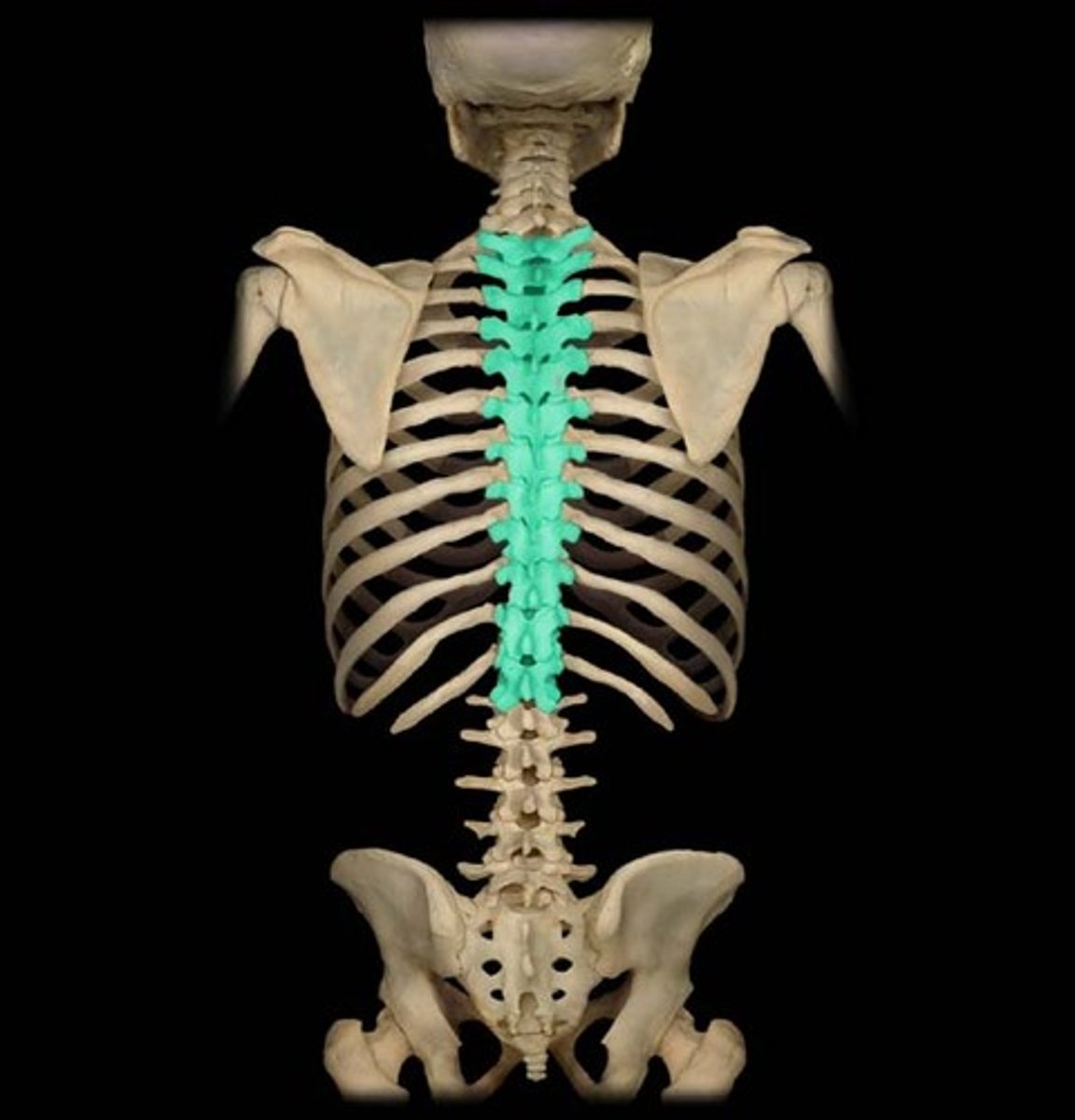
Vertebral Column
Name the bone
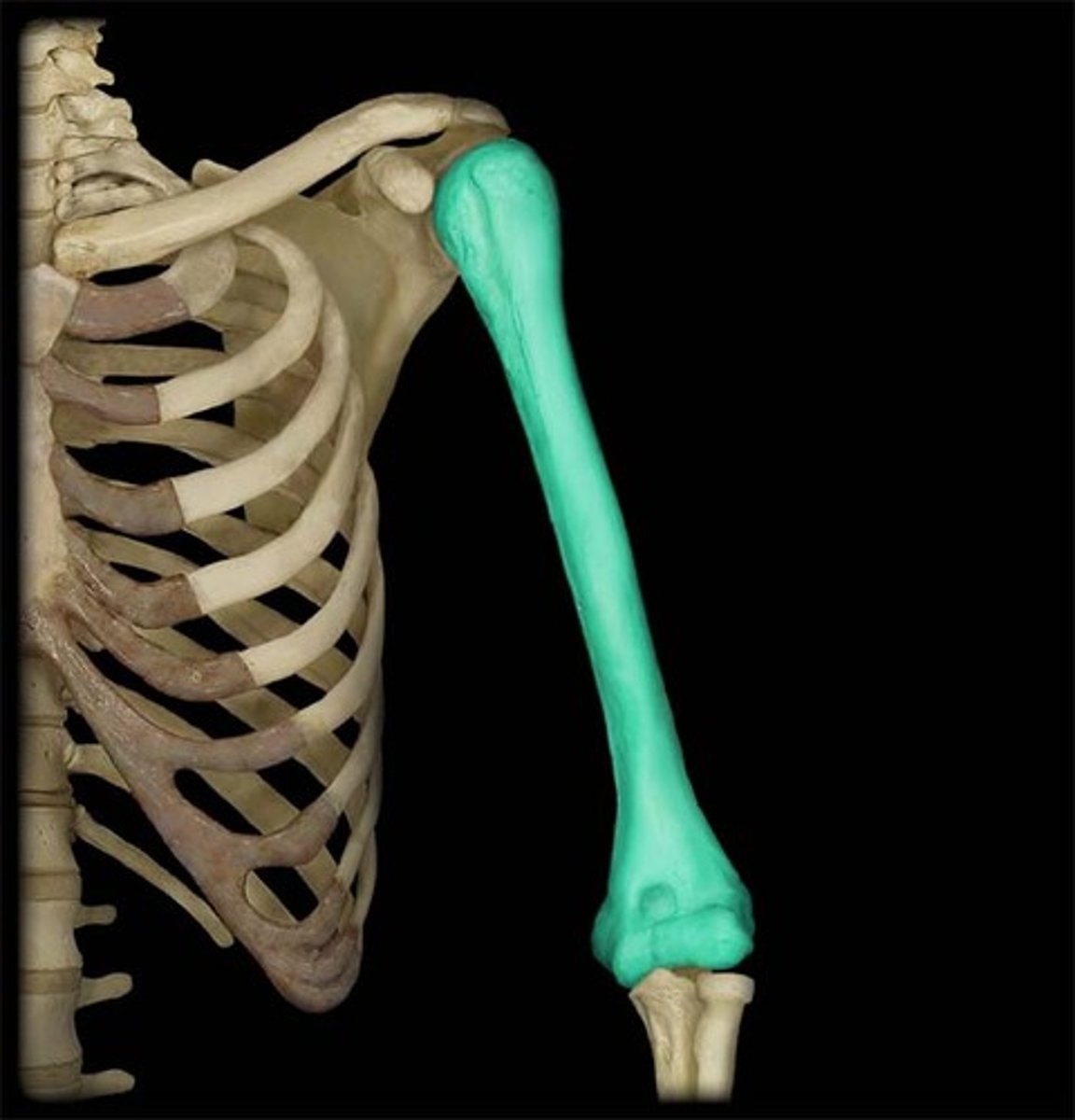
Humerus
Name the bone.
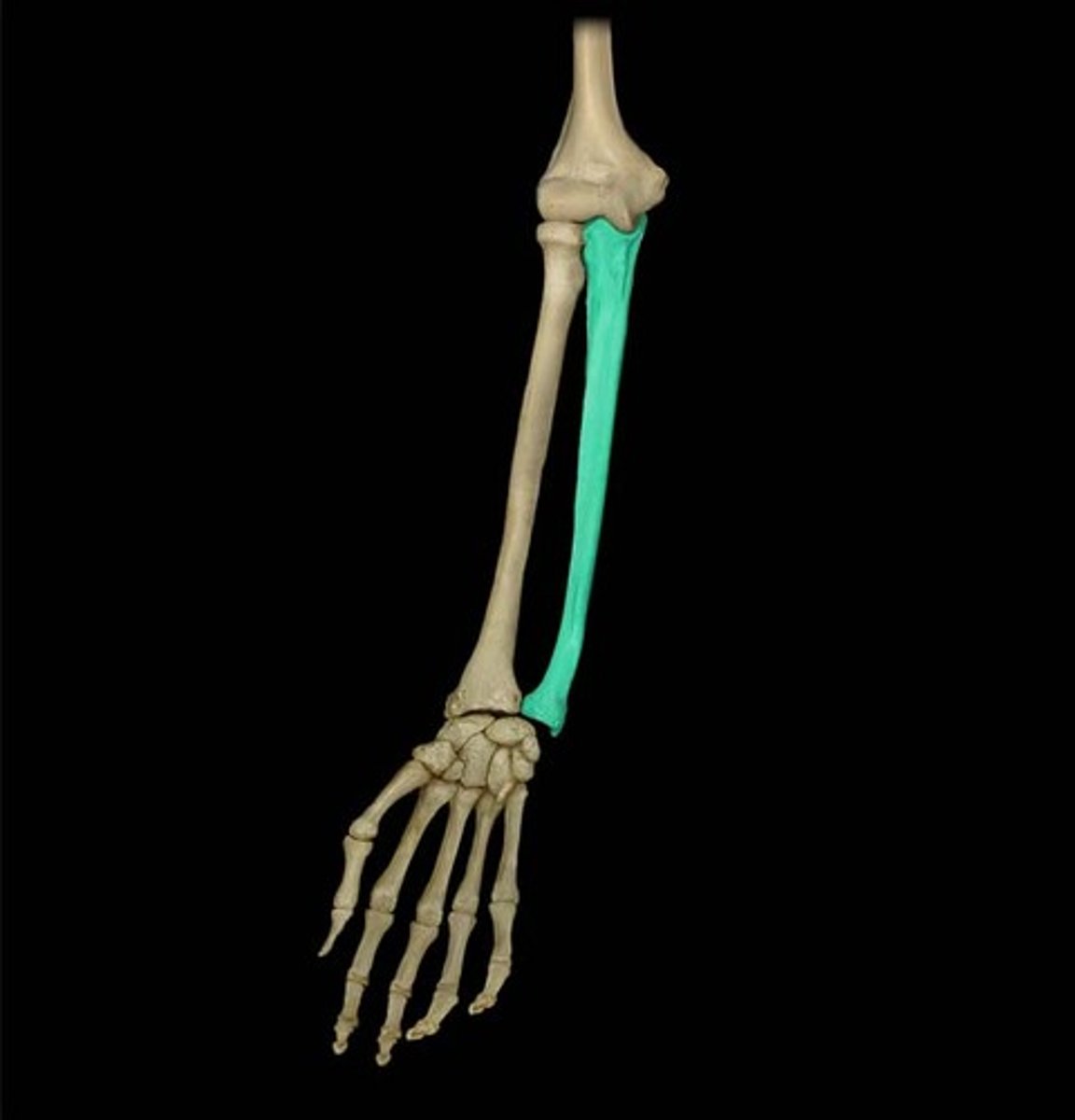
Ulna
Name the bone.
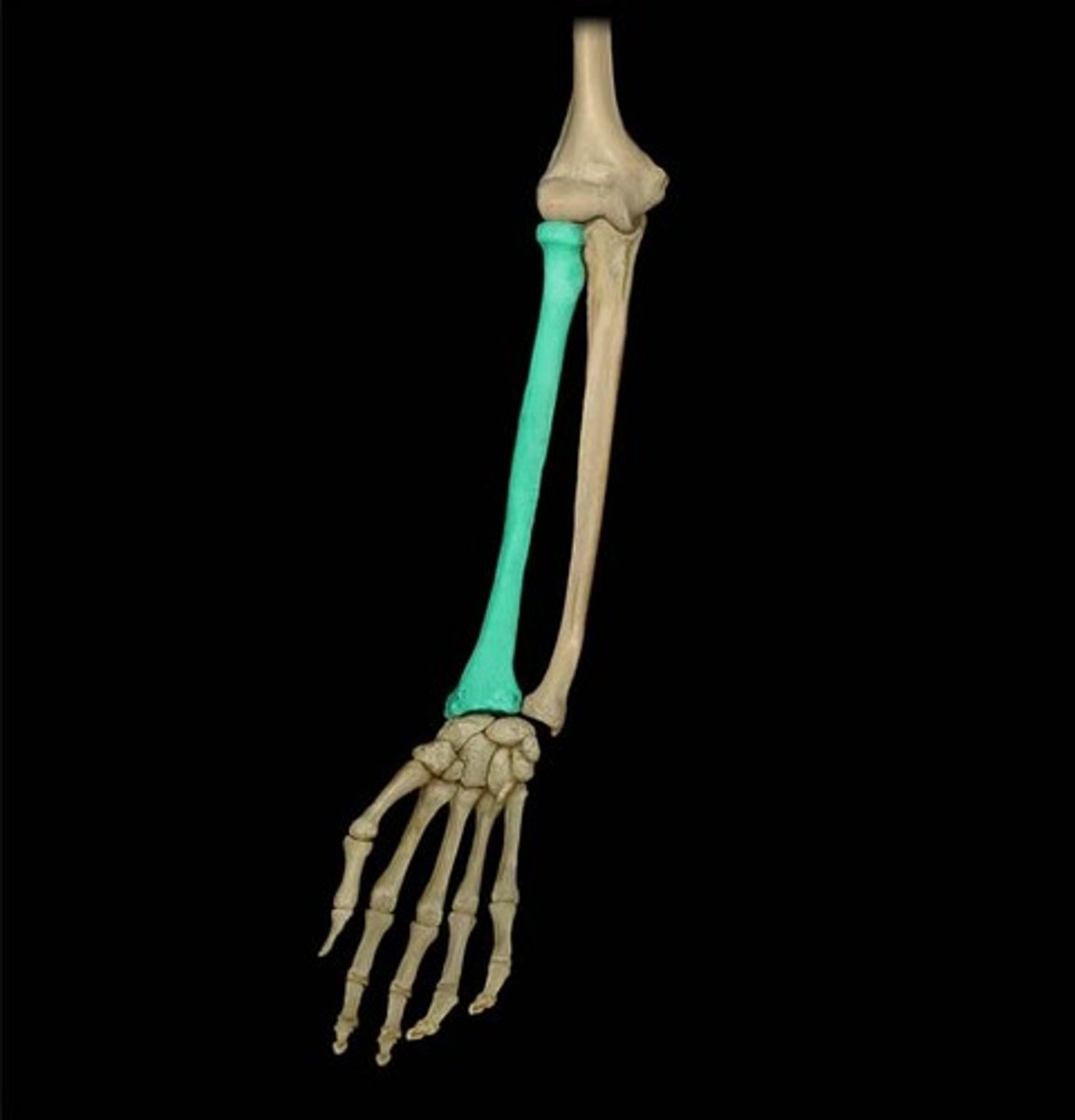
Radius
Name the bone.
phalanges
these are called?
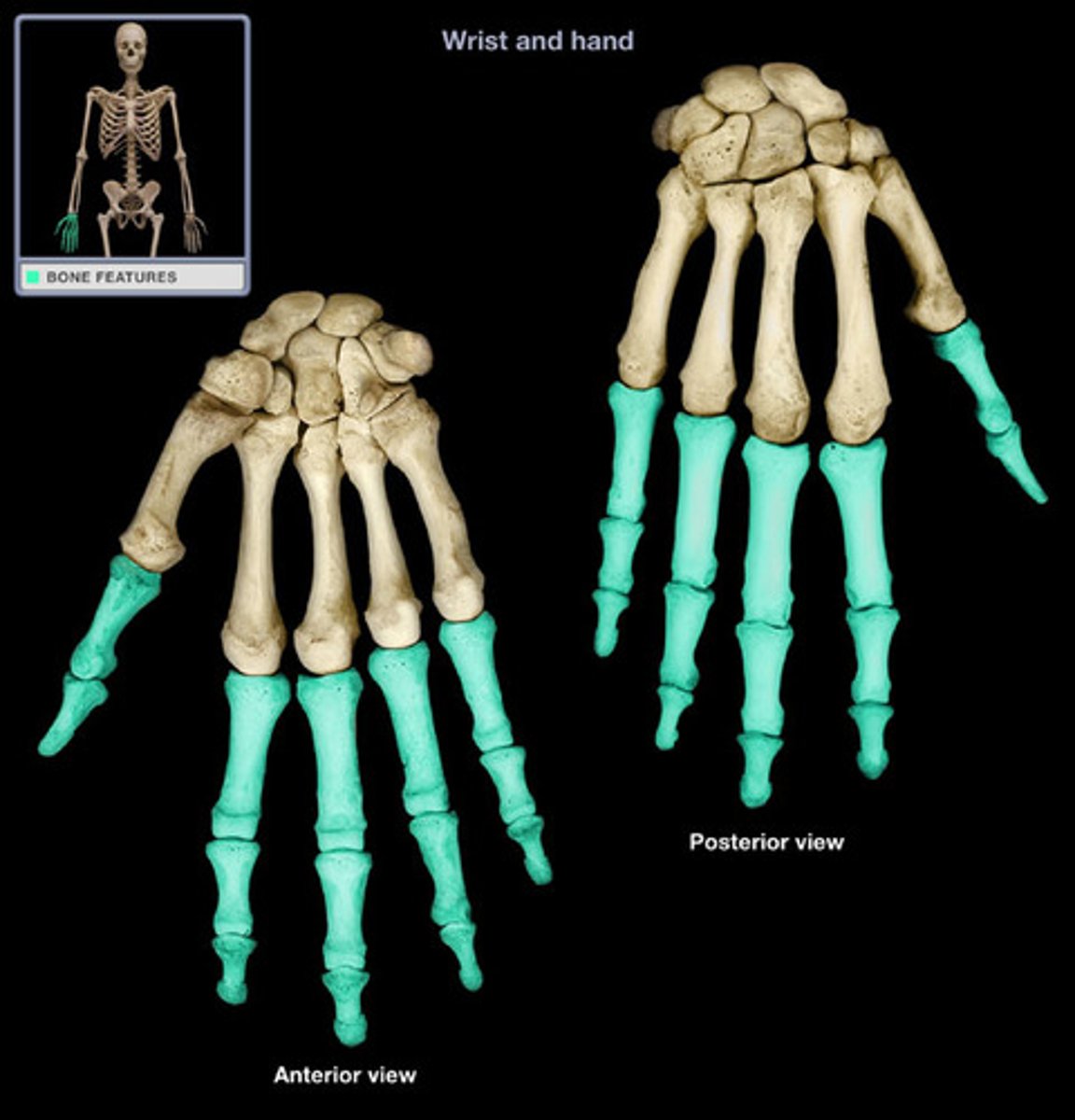
Metacarpal
these are called?
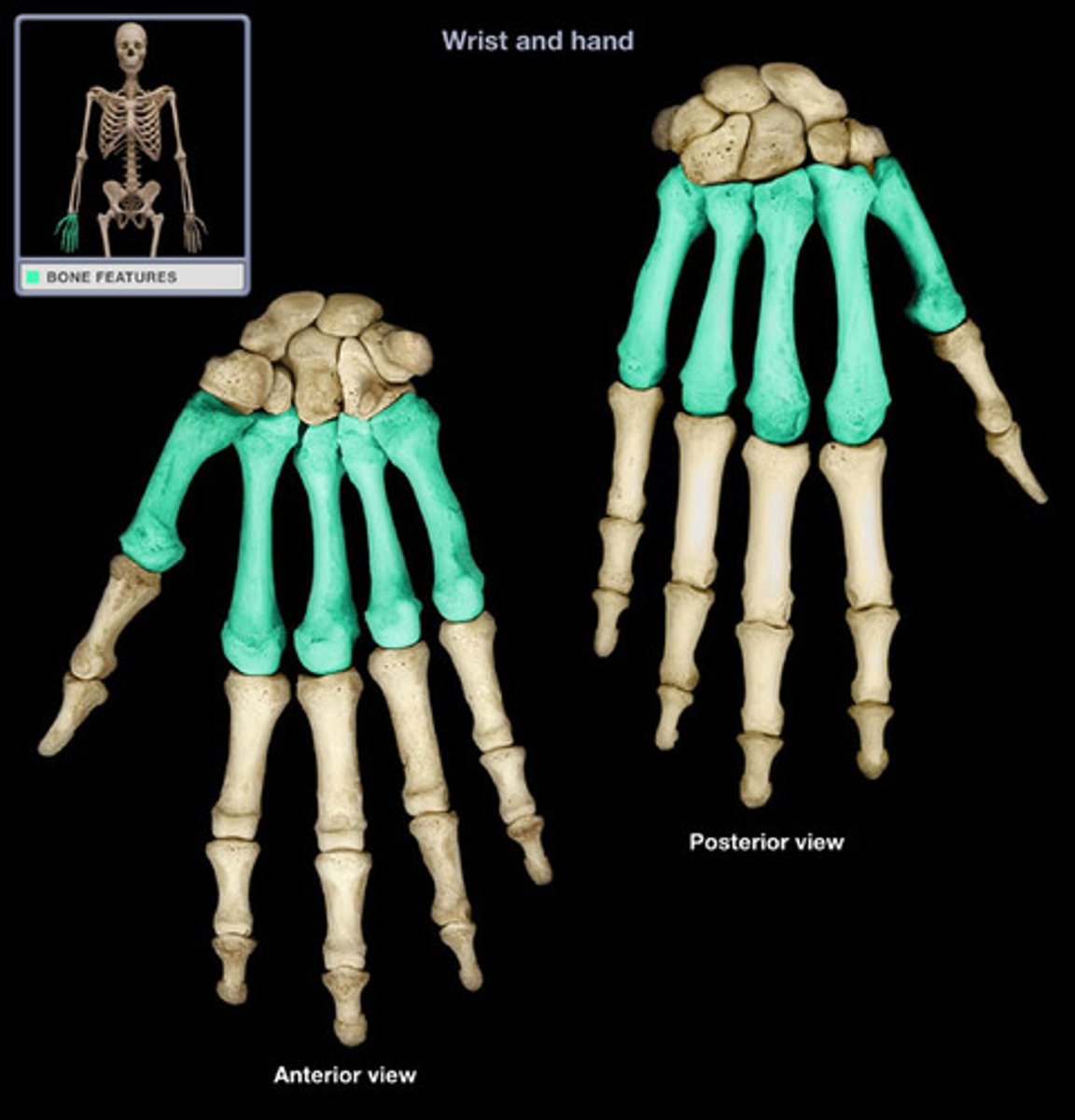
Bones
solid network of living cells and protein fibers that are surrounded by deposits of calcium salts.
Periosteum
tough layer of connective tissue surrounding the bone
Compact Bone
forms the hard, dense outer layer of bones which functions to primarily to provide strength and protection to bones.
Spongy Bone
houses the bone marrow, allow for RBCs formation or erythropoiesis, and allow bones to be less dense and more light. It also allows flexibility.
Bone Marrow
a soft tissue within bone cavities.
Yellow Marrow
made up primarily of fat cells usually found in round bones.
Red Marrow
produces red blood cells, some kinds of white blood cells, and cell fragments called platelets.
Ossification
the process of bone formation where cartilage is replaced by bone.
Osteoblast
creates bone.
Osteocytes
maintain the cellular activities of bone.
Osteoclasts
break down bone.
Joints
a place where one bone attaches to another bone.
cartilage
- a type of connective tissue scattered in a network of protein fibers - tough collagen and flexible elastin.
- does not contain blood vessels and rely on nutrients from the tiny blood vessels in surrounding tissues.
7
Ossification begins to take place up to ___________ months before birth.
Immovable Joints
-Synarthrosis
- allow no movement.
- the bones are interlocked and held together by connective tissue, or they are fused.
- the places where the bones in the skull meet are examples of immovable joints.
Slightly movable joints
-Amphiarthrosis
- permit a small amount of restricted movement
- the bones are separated from each other
- the joints between the two bones of the lower leg and the joints between adjacent vertebrae are examples of this
Freely Movable Joint
- permit movement in one or more directions
- grouped according to the shapes of the surfaces of
Ball and Socket joints
permit circular movement
Hinge Joint
Permit back and forth motion
Pivot Joints
allow one bone to rotate around another
Ligaments
attached to membranes that surround bones and hold the bones together
Synovial Fluid
produced by the cells in the other layer of the joint capsule
Inflammation
the body's response when a tissue is damaged
-Swelling, redness, heat, and pain
Kyphosis
abnormal rounding of the spine that occurs in the upper and mid back
- poor posture
- present at birth
-genetics
Rickets
bone softening disease that causes severe bowing of the legs, poor growth and sometimes causes muscle pain and weakness
- lack of Vitamin D
- not enough Calcium
- kidney and liver diseases
Arthritis
inflammation, swelling, redness of a joint
- cartilage is wearing away
- lack of Synovial fluid
Osteoporosis
bone tissue becomes brittle, thin, and spongy
- hereditary
- gender
- ethnicity
- history of broken bones lowbodyweight
Bone Tumor
abnormal growth of cells within the bone that may be non cancerous orcancerous
- hereditary
- radiation
- trauma
Scoliosis
causes the spine to curve to the left or right side
- present at birth
- hereditary
Sprain
an injury that happens when the ligaments get overstretched ortorn
Fracture
commonly occur when a person has fallen, an object has been dropped on them, or the bone has been tilted