Earth Systems
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
f= force
G= gravitational constant (6.6743×10−11 m3 kg−1 s−2)
m1= mass of object 1
m2= mass of object 2
r= distance between centres of the masses
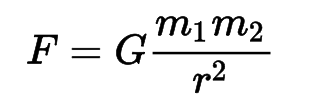
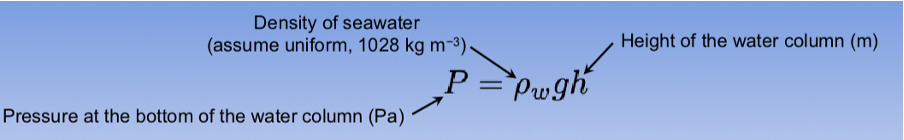
Hydrostatic Equation
P= pressure at bottom of water column
Pw= density of seawater (assuming uniform; 1028kg m-3
gh= height of water column (m)
What are meteorites?
Natural objects originating in outer space that survive an impact with the Earth’s surface.
What are xenolith?
Rock fragments that are transported by a magma and subsequently found within it.
They provide important information about the otherwise inaccessible mantle.
Moment of Inertia of Earth
How difficult it is to spin.

Preliminary Reference Earth Model (PREM)
Crust to Core:
1) The Moho: crust-mantle boundary- a sharp discontinuity in seismic velocity where igneous and metamorphic crustal rocks are underlain by mantle peridotite. 7-11/12 km
2) The Low-Velocity Zone: ~100km depth with evidence that part of the upper mantle is less rigid and may be partly molten. This is the top of the asthenosphere, below the rigid lithosphere (crust and upper mantle)
3) Mantle transition zone: a change from mainly peridotite above to rock with higher density minerals below.
4) Lower mantle: gradual increase in vp and vs- increasing rigidity of minerals with increasing pressure.
5) The Core: probably dominated by iron or nickel-iron. The outer core is molten and the inner core is solid. The outer core must have ~10% lighter elements (O, S, Si, K, H) to match the calculated seismic velocities.
What does the magnetic field do?
Deflects charged particles of the solar wind that would otherwise strike Earth and destroy the atmosphere.
Key changes through geological time
1) Amount and distribution of solar radiation received by Earth’s surface
2) Surface character of the Earth and distribution of continental plates
3) Composition of the atmosphere
4) Living things on Earth
5) Magnetic field
What are cyanobacteria?
Photosynthetic bacteria that appeared on Earth about 2.5 billion years ago
What was the Great Oxidation Event?
When oxygen levels in the atmosphere increased to appreciable levels.
Characteristics of Hardness
Resistant to scratching and indentation- measured on Mohs Relative Hardness Scale
Ionic bonds
Moderate strength- ± poles stick togetheroC
Covalent bonds
Atoms share electrons in the outermost shell, strong
Metallic bonds
Electrons are ‘free’ / delocalised making them electrically conductive
What bonds do calcite have?
Covalent and ionic
Mineral Group 1
Silicates- contain SiO4
Feldspars are the most common crustal mineral
Mineral group 2
Silicates containing Fe and Mg- Olivine, Amphibole and Pyroxene
What does viscosity affect?
Gas escape
Lava flow velocity
Eruptive style
Crystal growth
Bubble rise/crystal settling
Magma ascent rate through crustS
Strombolian eruptions
Short-lived
Explosive
Can form scoria coneB
Vulcanian eruptions
Canon-like explosions
Short-lived
High velocity
Compressive stress
Stefan Boltzmann Equation
E = σ T4
σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant
(5.673 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4 )
What does the Stefan Boltzmann Equation calculate?
The total energy radiated per unit area per unit time (or power) by a black body at a given temperature.
What is temperature in K?
Temp in C + 273K
Sun’s surface temperature in K
6000K
Lapse rate
The rate of change in atmospheric temperature as it decreases with height.
Lapse rate of dry air (DALR)
9.8oC/km
Stratosphere
10km-50km above Earth
Temperature increases through this layer due to ozone.
Mesosphere
50km-100km above Earth
Strong atmospheric tides
Little moisture
Coldest place in Earth’s atmosphere (low as -140o)
Thermosphere
100km-500km
Temperature increases with height due to absorption of solar radiation by atmospheric molecules
Exosphere
Gas molecules are not gravitationally bound to Earth near the bottom of the exosphere
Thin envelope of lightest gases (hydrogen/helium)
Ocean surface temperature is increased by…
Short-wave solar radiation absorbed by the surface ocean
Conduction between a warm atmosphere and a cold ocean
Ocean surface is decreased by…
Long-wave back radiation emitted by the ocean surface
Conduction between warm ocean and cold atmosphere
Evaporation
Salinity of surface ocean is increased by…
Evaporation
Sea ice formation
Salinity of surface ocean is decreased by…
Precipitation
Sea ice melting
Input of freshwater by rivers
Ideal Gas Equation
P= pRT
Pressure- gradient force
This causes air to move from regions of high pressure to regions of low pressure
Isobaric surfaces
Surfaces of constant pressure
Why doesn’t Earth have a single cell convection?
Earth rotates and Coriolis force causes moving air and water to turn
Coriolis parameter
This describes the magnitude of the effect of Coriolis force at a specific location
f = 2 * Ω * sin(φ), where Ω is the Earth's angular velocity and φ is the latitude.In the N hemisphere, f is positive because latitude is positive
At the equator f is zero
In the S hemisphere, f is negative because latitude is negative
Coriolis force
CF= 2Ω sin θ v
To understand how the movement of Earth effects moving objects in the atmosphere and oceans.
Processes of poleward heat transport in the atmosphere
1) Latent heat
2) Hurricanes
3) Baroclinic waves
Ekman spiral- consequence of Coriolis effect
Where winds exert a frictional force (wind stress) on the surface layer of the ocean.
Initially the surface layer is pushed in the same direction of the wind.
As soon as water starts to move, Coriolis force acts upon it and the curren turns to the right (in NH)
Surface layer exerts a frictional force on layer beneath, causing this to also turn right and so on…
Ekman transport
Net transport in the Ekman layer is perpendicular to the wind (right in NH and left in SH)
Causes either upwelling or downwelling dependent on wind direction in relation to coastline and which hemisphere you are in
Importance of Upwelling
Brings nutrient rich water from deep layer to the surface in the photic zone.
These can be utilised by phytoplankton, increasing primary productivity and biomass up the food chain.
These regions are commercially important for fisheries (especially sardines and anchovies.
Anti-cyclone (high pressure)
Atmospheric pressure distribution in which there is a high central pressure relative to the surroundings.
Characterised by large areas of stagnant weather conditions which are often dry and settled.
Closed isobars on a synoptic weather chart
Mid-latitude cyclones (low pressure)
Air is generally rising vertically through the atmosphere- as it rises and cools water vapour condenses to form clouds and can often lead to precipiation
Weather is often cloudy, wet and windy
Cold front typical weather conditions
Sharp wind veer
Band of rain ahead and along
Cold and dry conditions follow as front passes
Warm front typical weather conditions
Cool with increasing cloud
Winds often ‘back’ from an easterly to southerly direction
Warmer, more humid air after it passes
What are Eddies?
The oceans’ weather- longer lasting than atmospheric systems, for months to years.
Sometimes referred to as rings
Why are Eddies important?
Contain a different water mass (temp and salinity) to surrounding water
This means that they are a form of transport of heat and salt between water masses (aka. Eddie mixing)
May also contain different nutrients and plankton species to surrounding water leading to plankton blooms
High cloud examples
Cirrus
Cirrostratus
Cirrocumulus
Medium cloud examples
Altostratus
Nimbostratus
Altocumulus
Low cloud examples
Stratus
Cumulus
Cumulonimbus
Tritiu, (3H)
Radioactive isotope of hydrogen with two neutrons and one proton
Half-life of ~12 years
What generates tsunamis?
Undersea earthquakes or landslides
Vertical movement of the seabed causes a displacement of the sea surface that ravels away as a surface gravity wave
Examples of tsunami warning systems
Seismometers to detect
Model simulators help predict their path and size
Sirens and public alarms for evacuation
Land-based temperature observations
Stevenson screen (1.25m above ground level, wet and dry bulbs)
Land-based rainfall observations
Tipping bucket rain gauge (copper gauge about 450mm above ground level)
Sunshine/solar radiation observations
Campbell-stokes sunshine recorder and pyranometers
Wave properties
Height
Amplitude
Wavelength
Phase speed