EKG IVF hemodynamics
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
hemodynamic monitoring
Monitoring of blood as it moves through the body and the measurement of the pressures it creates
where does the transducer need to be?
at zero level, level of right atrium, also known as phlebostatic axis
where can you find phlebostatic axis?
4th Intercostal Space, Midaxillary
Anytime you reposition pt ; check transducer to make sure it is still at phlebostatic axis or you will get
false readings
Arterial lines (ART lines) are usually found in which arteries ?
radial and femoral
what is purpose of ART line?
BP monitoring and ABG testing
Only type of fluid that can be used with art line is the
fluid flush that is used to keep line from clotting off
what is most common art line spot?
radial artery
how do you get labs from ART line?
discard first 5-10 ml of blood
why do we need ART lines?
to have an accurate BP for vasoactive drugs
Why do we occasionally compare ART line BP to NIBP?
to see if numbers correlate
can a nurse place ART line?
no
what does nursing care of ART line entail?
dressing changes, ensuring patency, removal
if ART line is removed from radial artery how long do you hold pressure ?
5 min
if ART line is removed from femoral artery how long do you hold pressure ?
20 min
what does allens test tell us ?
if we have good arterial blood flow in hand
how is wrist usually positioned for ART line placement ?
hyperextended
what are CMS checks?
checks for circulation , motion , and sensation on extremity with ART line
If arterial line is obstructing perfusion to extremity, it must be
discontinued
what do you do with negative CMS checks?
report to provider
potential complications of ART lines include :
infection, loss of limb, bleeding
what is important to know before ART line removal ?
if pt is on anticoagulants/ blood thinners
what do you do after removing ART line?
place clear dressing over removal site so you can reassess later
Swan Ganz Catheter (SGC) is also called
pulmonary artery catheter
Swan Ganz Catheter (SGC) sits in the ------- artery
pulmonary
Swan Ganz Catheter (SGC) gathers what data?
CVP: Central Venous Pressure
PAP: Pulmonary Artery Pressure
PCWP: Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure
CO: Cardiac Output
CI: Cardiac Index
SVO2: Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation
Swan Ganz Catheter ; for every place in heart there is a different ----------- so provider can know where tip of catheter is
waveform
Swan Ganz Catheter : every area in heart has a different ---------- associated
pressure
How do we verify placement of Swan Ganz Catheter?
Chest x ray
normal central venous pressure (CVP)
2-8
CVP measures
right atrial pressure , amount of fluid returning to the right side of the heart
how do we obtain central venous pressure ?
PA catheter or central line
Pulmonary Artery Pressure (PAP) measures :
PA systolic , PA diastolic , Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
normal PA systolic
15-30 mm Hg
normal PA diastolic
8-15 mmHg
Normal pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP)
8-15 mmHG
Causes of increased PAP (Pulmonary Artery Pressure):
pulmonary HTN
How do we obtain Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure (PCWP)?
Swan Ganz is passed into pulmonary artery , balloon inflated, when waveform flattens catheter is "wedged"
Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure (PCWP) is a reliable indirect measurement of :
left atrial pressure
Pulmonary Capillary Wedge Pressure (PCWP) is only thing that tells us about left side of heart with which catheter ?
Swan Ganz
right sided HF
CVP elevated, PAP- normal, PCWP- normal
left sided HF
CVP, PAP, PCWP- all elevated
pulmonary HTN
CVP- normal, PAP- elevated, PCWP- normal in absence of L-sided HF
hypovolemia
CVP- decreased. PAP- decreased, PCWP- increased
lung issues
CVP- elevated, PAP- elevated, PCWP- normal
SVO2 Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation is the % of ------ in the blood returning to the right side of the heart
o2
SVO2 Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation reflects
the body's overall o2 utilization by the tissues
normal SVO2 Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation value
60-80% (average 75%)
right sided HF
CVP elevated, PAP- normal, PCWP- normal
left sided HF
CVP, PAP, PCWP- all elevated
pulmonary HTN
CVP- normal, PAP- elevated, PCWP- normal
hypovolemia
CVP- decreased. PAP- decreased, PCWP- increased
lung issues - copd , ards, pneumonia
CVP- elevated, PAP- elevated, PCWP- normal
SVO2 Mixed Venous Oxygen Saturation
normal value 60-80% (average 75%)
percentage of 02 in the blood returning to the right side of the heart
Reflects the body's overall O2 utilization by the tissues.
svo2 number will fluctuate based on patients
activity
How often must a central line be flushed?
every 8-12 hours
CVL uses
CVP monitoring, IV fluids, TPN, PPN
how do we confirm CVL placement?
CXR
what is preferred access site for CVL?
subclavian
what CVL site has highest infection risk?
femoral
PICC lines are inserted ---------- , but are still a type of central line
peripherally
Can a PICC line or CVL be used longer ?
PICC Line
PICC line long term uses
abx, TPN
implanted central line
entirely under skin , surgically implanted, useful for long term chronic patients
what type of needle is used to access implanted central line?
huber

how do you dress and clean implanted central line?
sterilely , with central line kit, clear dressing
dialysis catheter
red and blue cap for DIALYSIS Only
high infection risk
trialysis catheter
purple port can be used for fluids and CT contrast
crystalloids
•Intravenous electrolyte solution
•Moves freely between intravascular compartment and interstitial space
colloids
Blood substitutes
Large particles assist fluid to stay within the vascular space
primary fluids run -------
continually
secondary fluids run -----
for a limited period of time
do your secondary fluids go above or below primary?
above
isotonic fluids
NS LR
little to no fluids shift
hypotonic fluids
0.45% NS
fluid moves from vascular space into the cells
what type pts need hypotonic fluids?
DKA, hypernatremia
what are s/s of intravascular collapse
low bp high hr neuro changes
how does intravascular collapse occur?
if hypotonic fluids are given roo fast
what is an indicator of non compilable meds?
precipitation in the lines
SA node
bodys normal pacemaker 60-100 bpm
AV node
"Back-up" if the SA node fails (40-60 bpm)
bundle of HIS
Can also initiate impulses (40-60 bpm)
purkinje fibers
Network of fibers
Carry electrical impulses directly to ventricular muscle cells (20-40 bpm)
p wave
Electrical stimulation of atria to fire (depolorization)
QRS complex
The electrical current signaling ventricles to fire (depolarization)
Much larger than P wave
T wave
Resting phase of the ventricles (repolarization)
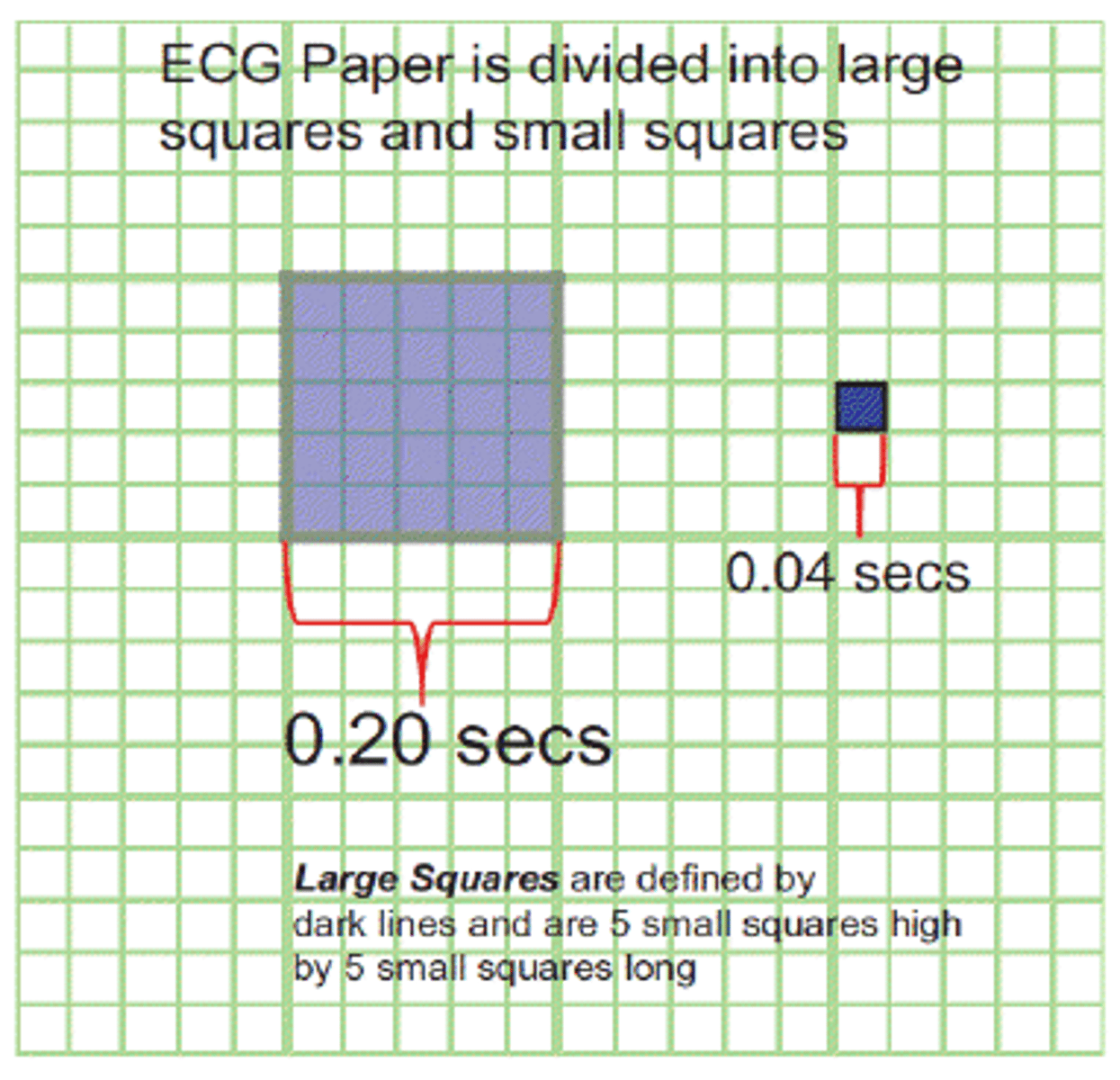
smallest boxes
0.04 seconds
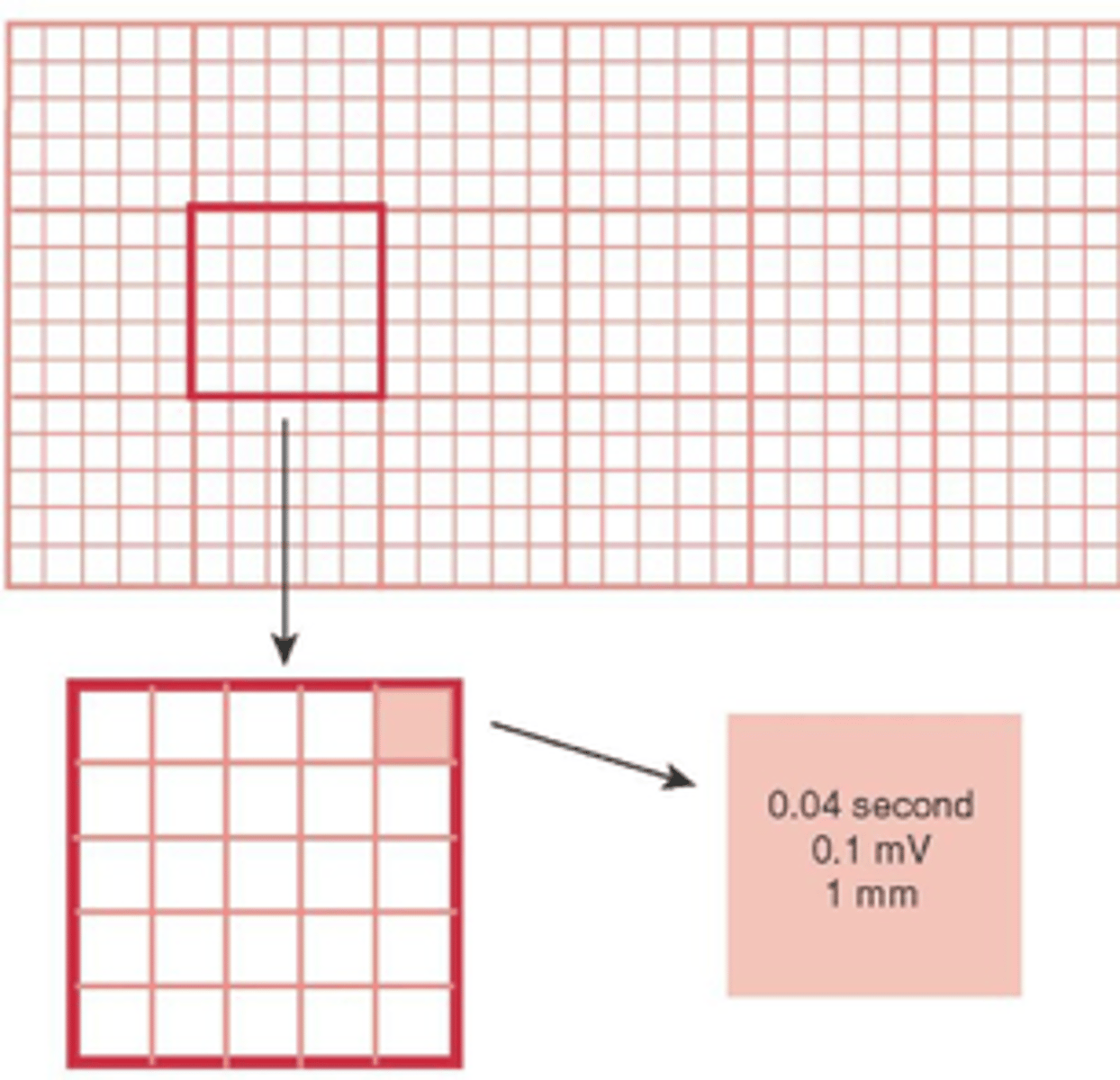
larger boxes
0.20 seconds
5 large boxes
1 second strip
15 large boxes
3 seconds
30 large boxes
6 seconds
300 large boxes
1 min
PR interval
time between beginning of the p wave until the beginning of the QRS
typically 0.12 and 0.20 seconds
What does it mean if the PRI is prolonged or >0.20 seconds
Some sort of diseased pathway and there is a delay in impulse travelling from SA node to AV node
QRS
The beginning of the QRS complex to the end of the QRS complex
Normally less than 0.12 seconds in length
Prolongation indicates a diseased normal pathway
problem in AV to bundle of HIS if QRS wider than 0.12 seconds
how many seconds trip do we use to get heart rate?
6 second strip
atrial rate
count p waves
ventricular rate
count QRS complexes
normal hr
60-100
bradycardic rate
<60