GI Nutrition in Eating Disorders (Dr. Kane)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
___________ is a critical period that includes...
• Development of lifelong nutritional habits
• Prevention of adult diet-related chronic diseases (Cardiovascular disease, cancer, osteoporosis)
Adolescence

what are some strategies to help optimize nutrition intake in anorexia pts?
safe foods (fruits, veggies, tofu, low fat/fat-free foods, plain tuna, plain chicken)
add small amounts of higher calorie foods (salad dressing, avocado, oils, mayo, peanut butter)
avoid high fiber (slow gastric emptying = more filling + worse constipation)
What are nutritional needs of adolescents?
- Energy and protein (Higher total calories and protein grams per day)
- Vitamins and minerals of concern (Vit A, D, Iron, Calcium)

When do boys begin their growth spurt?
12-13 years old

When do girls begin their growth spurt?
10-11 years old

What is an average range of what females could gain during puberty?
15-55 lbs

What is an average range of what males could gain during puberty?
15-65 lbs

Define the following:
Variety of atypical eating behaviors used to reduce weight
disordered eating

Examples of ____________ include:
- Going on and off diets
- Refusing to eat specific macronutrients
- Usually does not make a person seriously ill
disordered eating

Define the following:
Increase risk of health-compromising behaviors
- Excessive caloric restriction
- Frequent dieting
- Use of diet pills/laxatives
- Severe body image distortions
- Eating disorders (ED)
weight/body dissatisfaction

Define the following:
A psychiatric condition involving extreme body dissatisfaction and long-term eating patterns harming the body
-highest incidence in Caucasian female population
-typically includes severe food restriction, obsessive exercising, self induced vomiting, laxative abuse
eating disorder

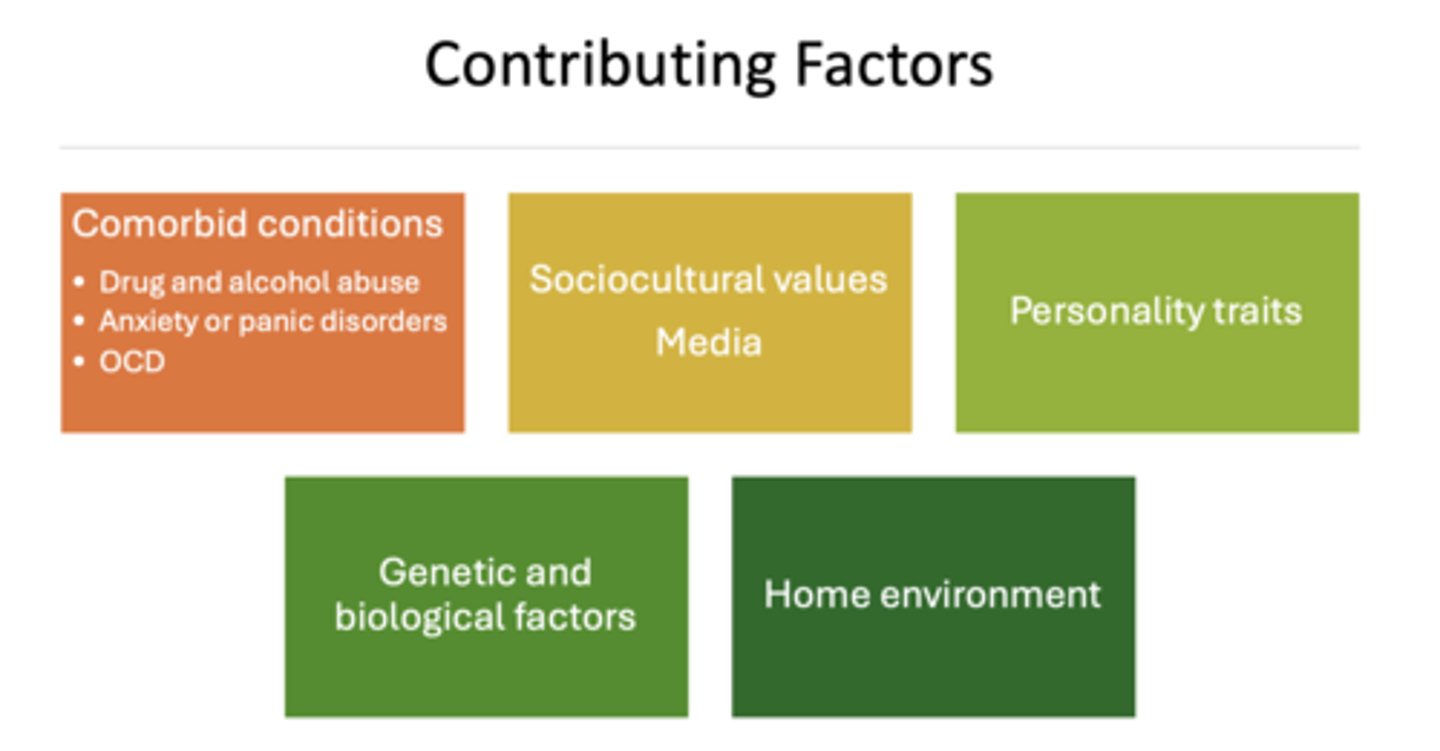
What are the main contributing factors to eating disorders?
- Comorbid conditions (Drug/alcohol, anxiety, OCD)
- Socialcultural values
- Media
- Personality traits
- Genetic and biological factors
- Home environment
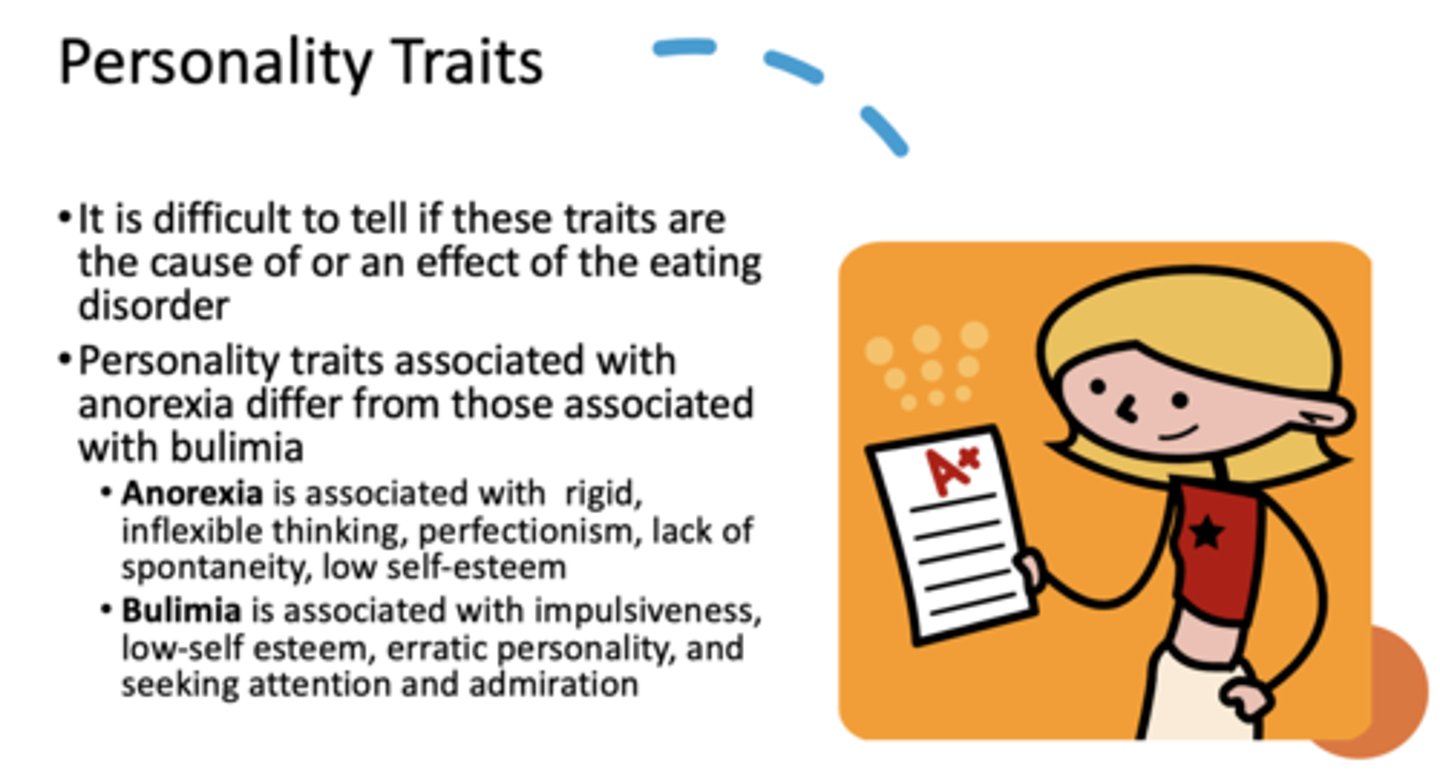
what personality traits are associated with anorexia vs bulimia?
• Anorexia is associated with rigid, inflexible thinking, perfectionism, lack of spontaneity, low self-esteem
• Bulimia is associated with impulsiveness, low-self esteem, erratic personality, and seeking attention and admiration
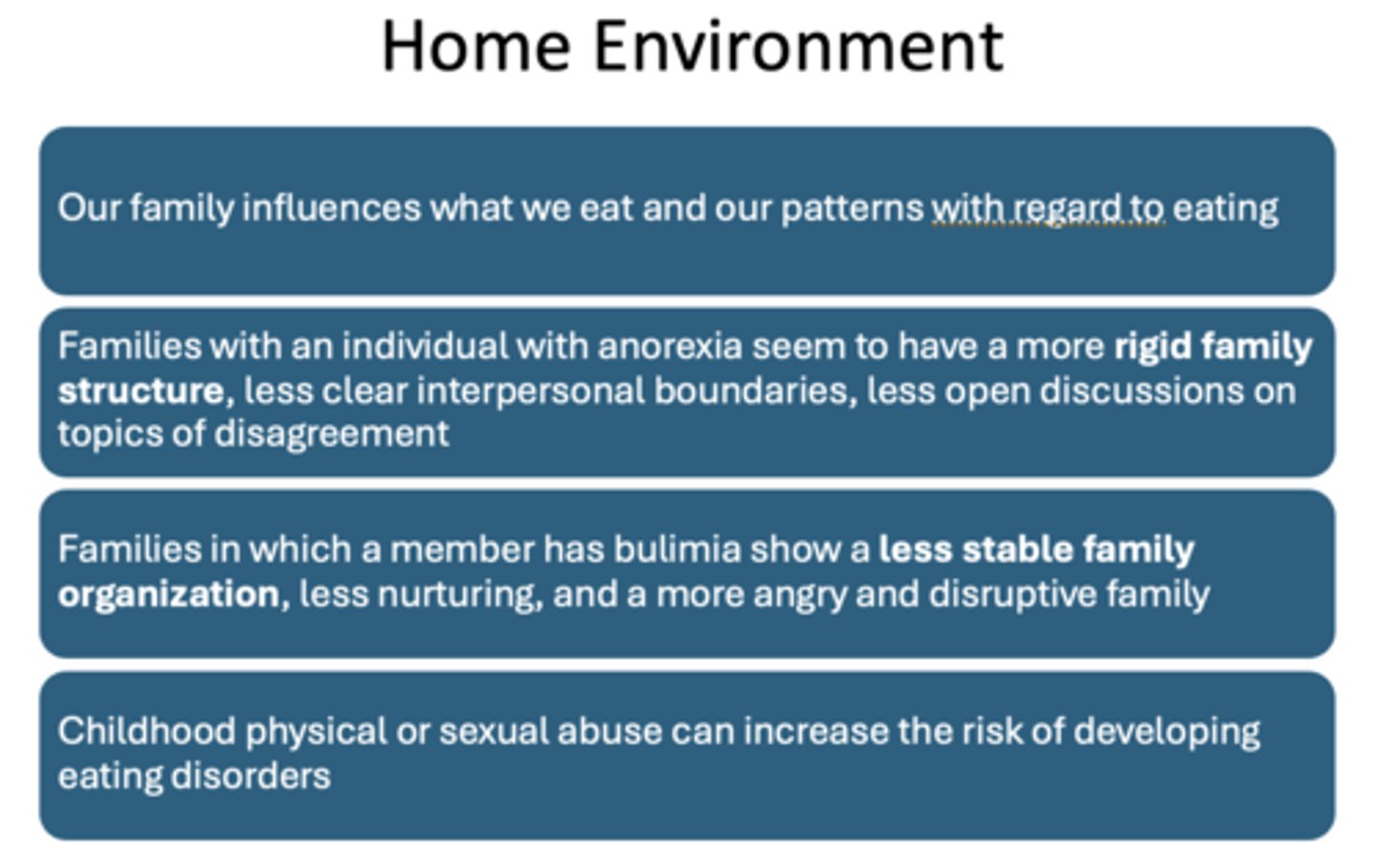
how is home environmetn associated with anorexia vs bulimia?
anorexia → rigid family strucutre, less clear interpersonal boundaries, less open discussions on disagreements
bulimia → less stable family organization, less nurturing, more angry/disruptive
childhood physical/sexual abuse increase risk of ED
what are some genetic/biologic factors that may contribute to eating disorders?
first degree biological relatives
alterations in brain serotonin levels, neuropeptide systems, brain neurocircuitry
(difficult to separate genetic/environmental influences)
Define the following:
• Energy intake restriction resulting in significantly low body weight for age, gender, development, and health.
• Intense fear of gaining weight or becoming fat or engaging in behavior that interferes with weight gain even at a low weight
• Disturbance in the way one’s body weight or shape is experienced, increased influence of body weight or shape on self evaluation, lack of recognition of seriousness of low body weight
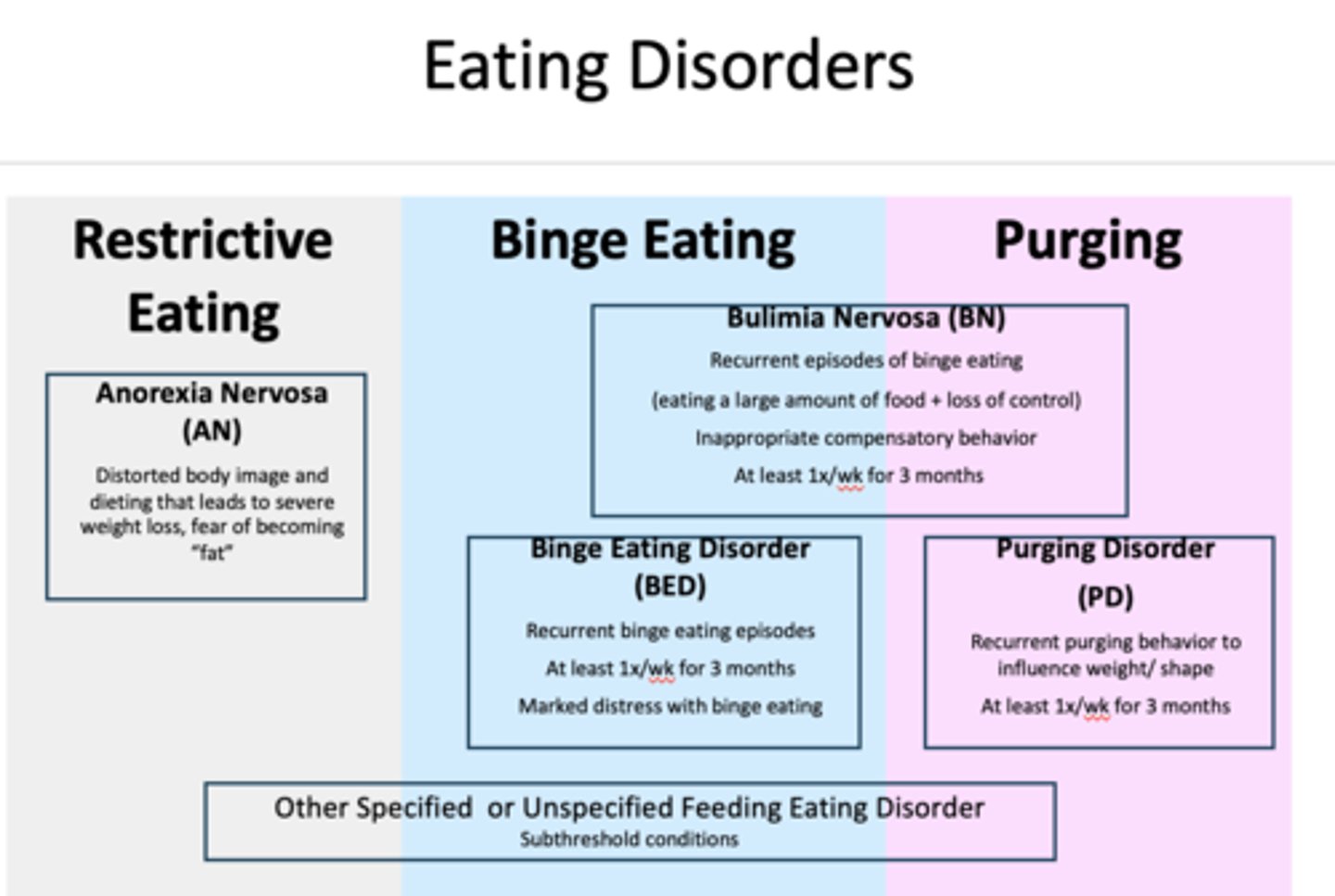
Anorexia Nervosa (AN)

what are the 2 types of anorexia nervosa?
restricting type: Significant weight loss through diet, fasting, excessive exercise
binge eating/purging type: Significant weight loss through diet AND engagement in recurrent episodes of binge eating / purging behavior in the previous 3 month
what are behaviors that attempt to rid the body of unwanted food through means such as vomiting, laxatives, diuretics, enemas, or other means called?
purging behaviors
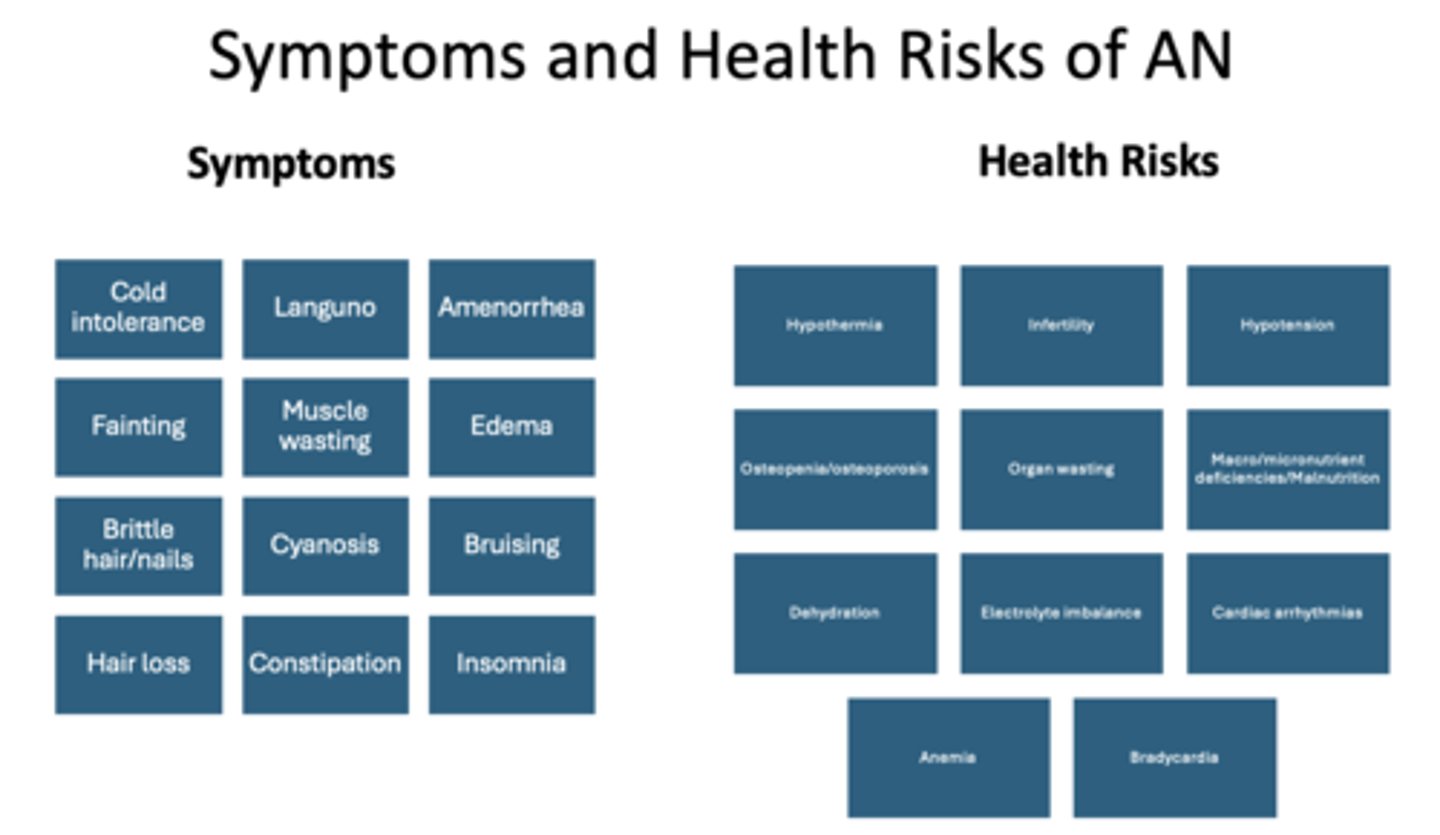
what are some symptoms of anorexia nervosa?
cold intolerance
fainting
brittle hair/nails
hair loss
languno
muscle wasting
cyanosis
constipation
amenorrhea
edema
bruising
insomnia
what are some health risks of anorexia nervosa?
hypothermia
infertility
hypotension
osetopenia/osteoporosis
organ wasting
nutrient deficiencies + malnutrition
dehydration
electrolyte imbalance
cardaic arrhythmias
anemia
bradycardia
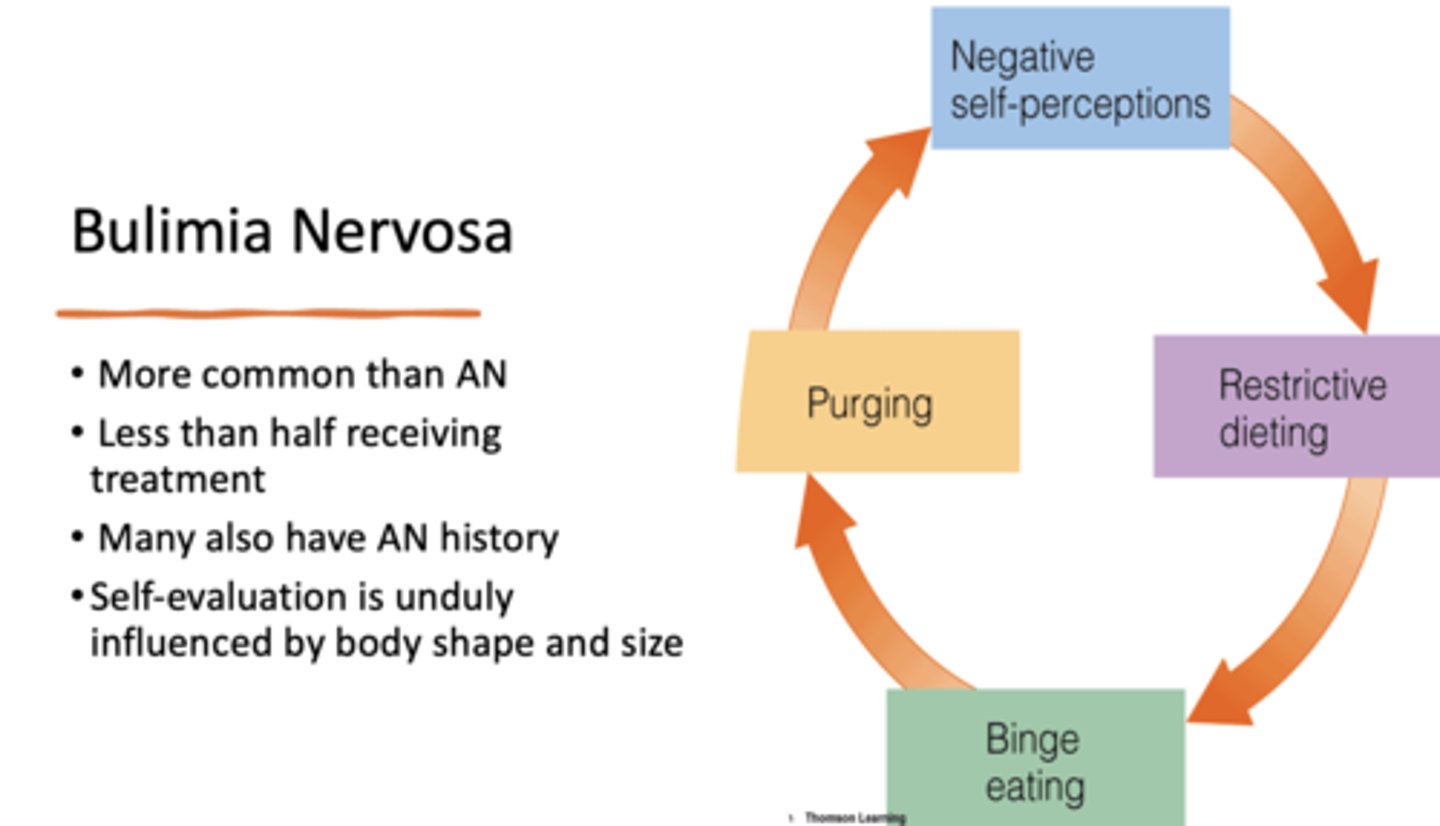
What has the following characteristics?
- Recurrent episodes of binge eating
(eating a large amount of food + loss of control) followed by compensatory behavior
- At least 1x/wk for 3 months
- Eating disorder characterized by binge eating followed by purging behaviors
Bulimia Nervosa (BN)

What is more common: anorexia nervosa or bulimia nervosa?
Bulimia nervosa
What has the following characteristics?
- Recurrent binge eating episodes
- At least 1x/wk for 3 months
- Marked distress
Binge Eating Disorder (BED)
-Recurrent purging behavior to influence weight/ shape
-At least 1x/wk for 3 months
Purging Disorder (PD)
Basic yet reliable set of five questions that help assess whether an eating disorder exists.
The questions are
1. Do you make yourself sick because you feel uncomfortably full?
2. Do you worry you have lost control over how much you eat
3. Have you recently lost more than one stone (14 pounds or 6.35 kg) in a three month period?
4. Do you believe yourself to be fat when others say you are too thin?
5. Would you say that food dominates your life?
SCOFF questionnaire

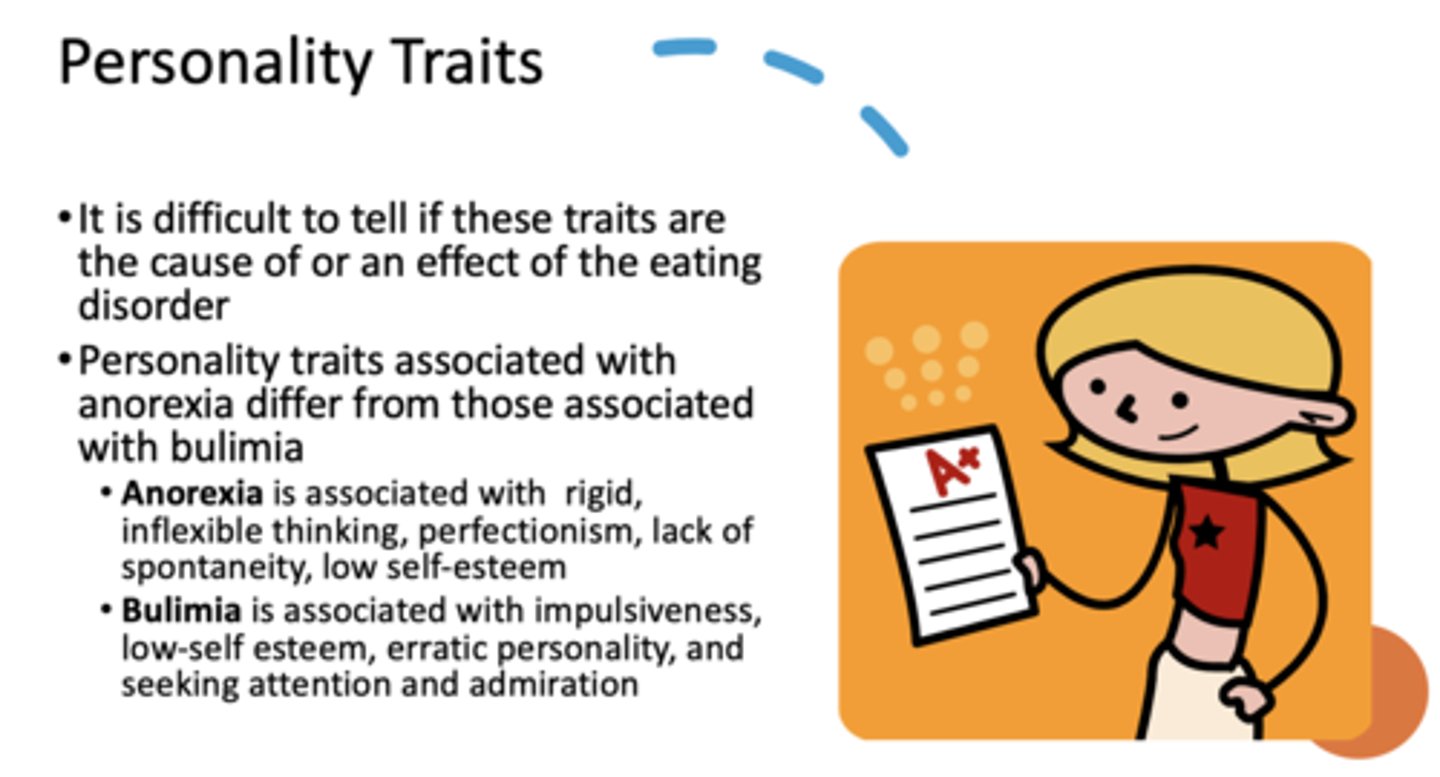
this eating disorder is associated with personality traits of rigidity, inflexible thinking, perfectionism, lack of spontaneity, low self-esteem:
Anorexia Nervosa (AN)
this eating disorder is associated with personality traits of impulsiveness, low-self esteem, erratic personality, and seeking attention and admiration:
Bulimia Nervosa (BN)
t/f: The likelihood of developing an ED is significantly increased in first-degree biological relatives of individuals with EDs
true
t/f: eating disorders do not affect brain/chemical compositions
false
Families with a member that suffers from _______ seem to have a more rigid family structure, less clear interpersonal boundaries, less open discussions on topics of disagreement
Anorexia Nervosa (AN)
Families in which a member has _______ show a less stable family organization, less nurturing, and a more angry and disruptive family
Bulimia Nervosa (BN)
t/f: Childhood physical or sexual abuse can increase the risk of developing eating disorders
true
Anorexia Nervosa (AN) is much more prevalent in which gender?
females
What type of Anorexia Nervosa (AN)?
- Significant weight loss through diet, fasting, excessive excercise
- During the last three months, the individual has not engaged in recurrent episodes of binge eating or purging behavior (i.e., self-induced vomiting or the misuse of laxative, diuretics, or enemas.)
restricting type

What type of Anorexia Nervosa (AN)?
-During the last three months, the individual has engaged in significant weight loss through diet AND recurrent episodes of binge eating or purging behavior (i.e., self-induced vomiting or the misuse of laxatives, diuretics, or enemas.)
Binge-eating/purging type

an attempt to rid the body of unwanted food through means such as vomiting, laxatives, diuretics, enemas, subsequent excessive exercise, or other means
purging behaviors

What is the difference between the binge eating/purging type of anorexia nervosa and bulemia?
Anorexia is associated with a low body weight
what type of drugs are prescribed for patients with eating disorders?
-Antidepressants: SSRIs (selectively inhibit serotonin reuptake)
-Olanzipine (SSNRIs - dopamine + serotonin receptors)
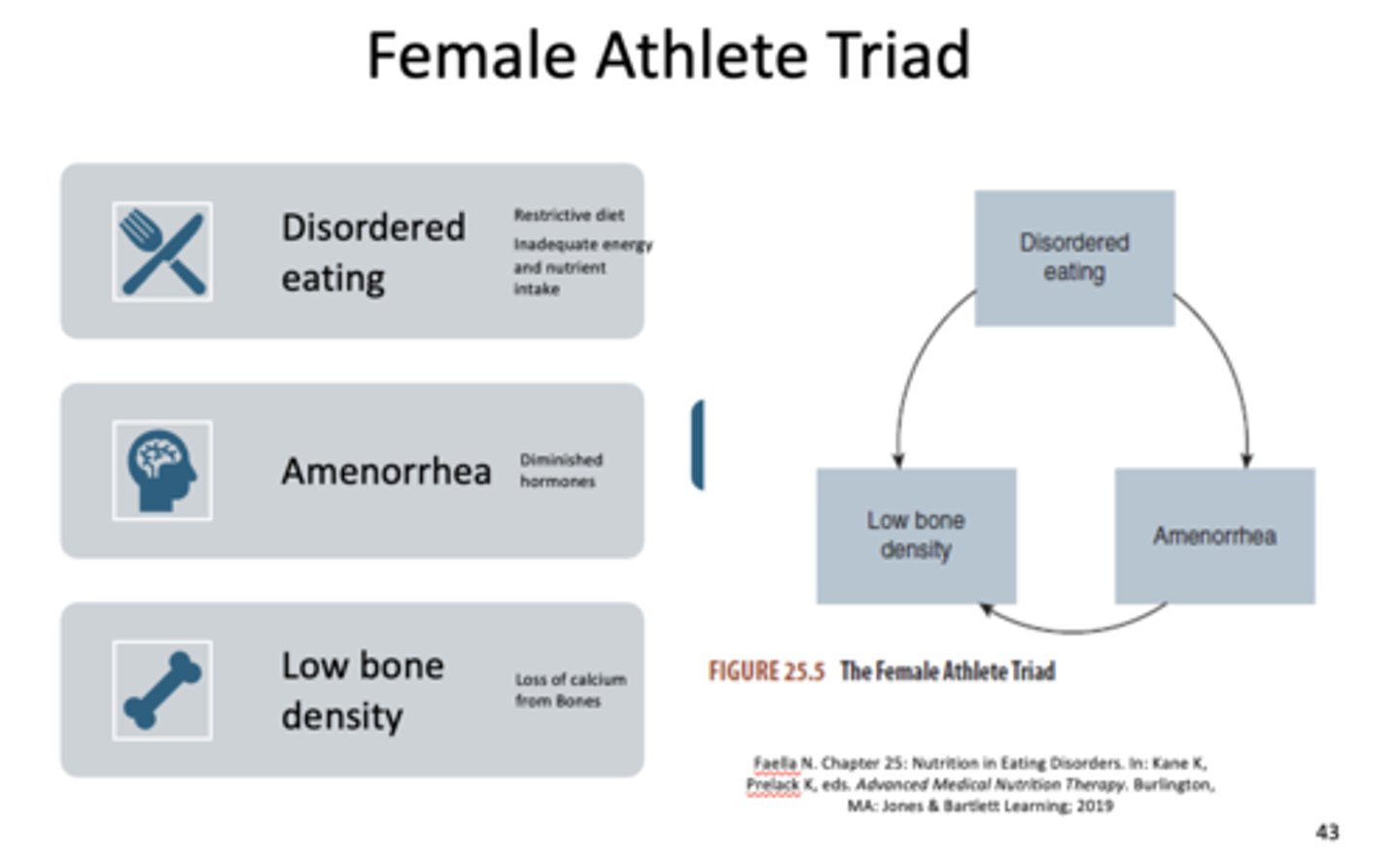
the female athlete triad is associated with elite performance requiring a low BMI and consist of a triad of:
- Disordered eating
- Amenorrhea (diminished hormone)
- Low bone density (loss of calcium from bones)
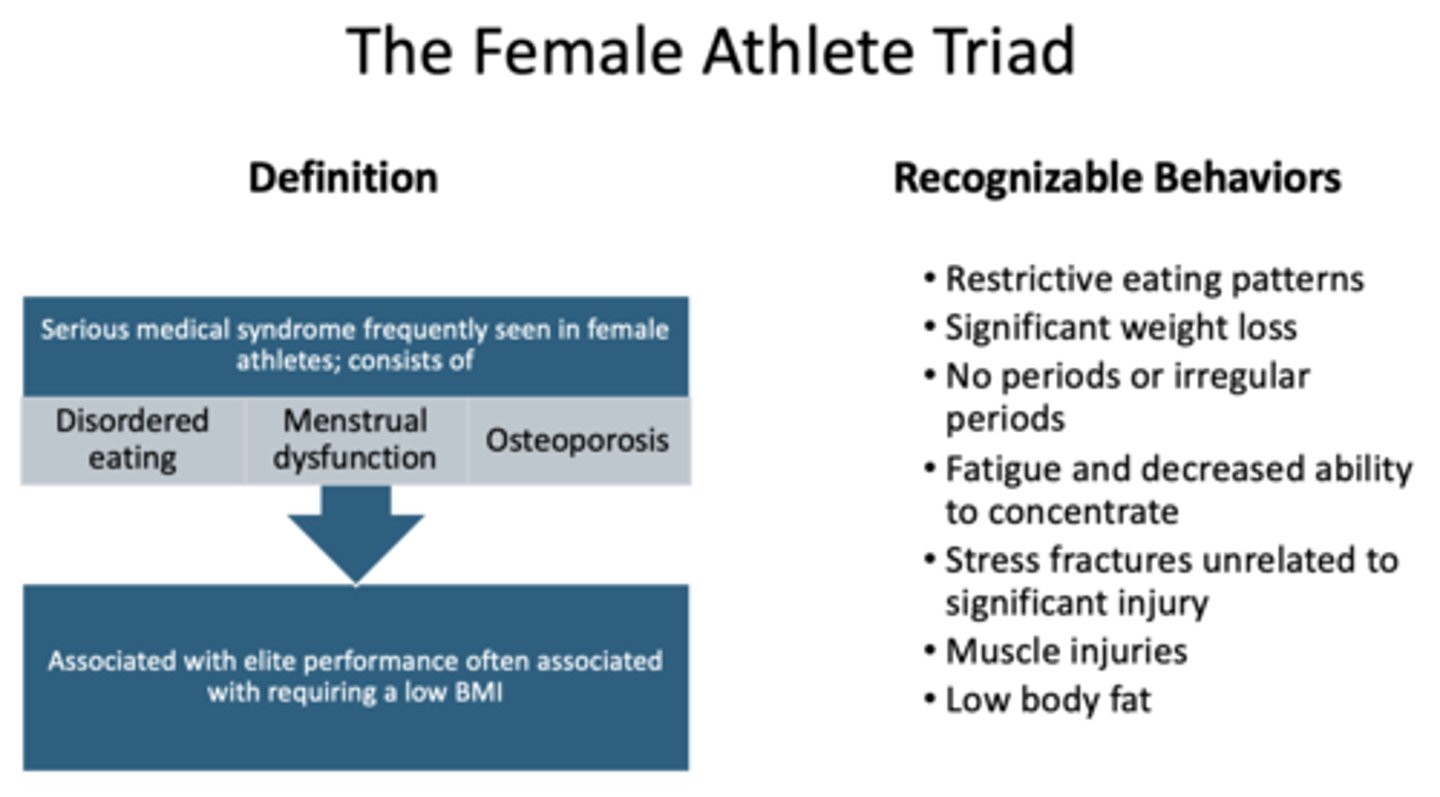
The following are recognizable behaviors of what?
• Restrictive eating patterns
• Significant weight loss
• No periods or irregular periods
• Fatigue and decreased ability to concentrate
• Stress fractures unrelated to significant injury
• Muscle injuries
• Low body fat
Female athlete triad
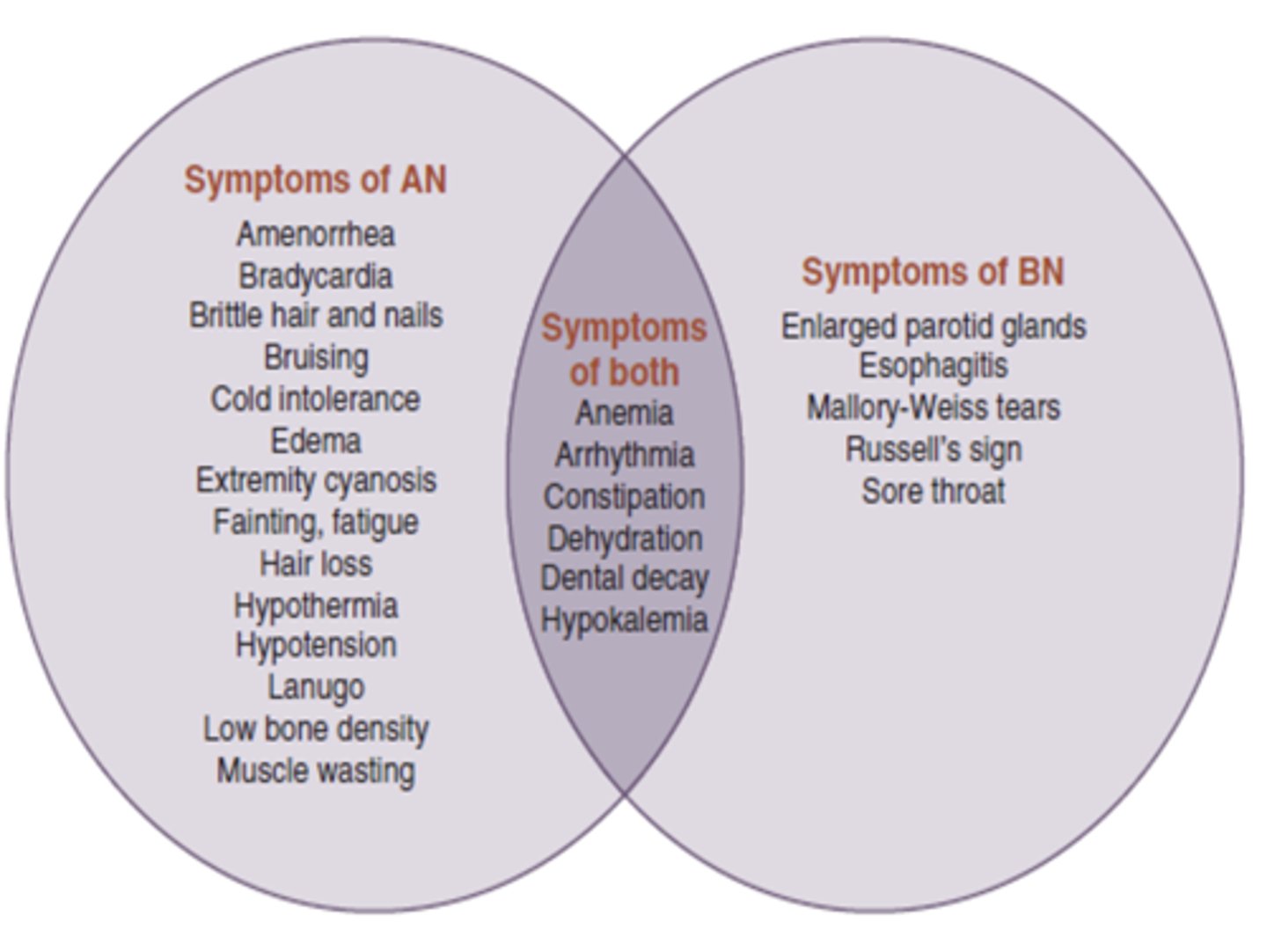
Are the following symptoms related to anorexia, bulimia, or both?
• Cold intolerance
• Lanugo
• Amenorrhea
• Fainting
• Muscle wasting
• Edema
• Brittle hair/nails
• Cyanosis
• Bruising
• Hair loss
• Constipation
• Insomnia
Anorexia Nervosa (AN)
Are the following symptoms related to anorexia, bulimia, or both?
- Enlarged parotid gland
- Esophagitis
- Mallory-weiss tears
- Russell's signs
- Sore throat
Bulimia Nervosa (BN)
Are the following symptoms related to anorexia, bulimia, or both?
- anemia
- arrhythmia
- constipation
- dehydration
- dental decay
- hypokalemia
both
What has the following characteristics?
• May develop in malnourished patients with the initiation of concentrated carbohydrate delivery.
• Characterized by the derangements in phosphorus, potassium, and, to a lesser extent, magnesium
refeeding syndrome
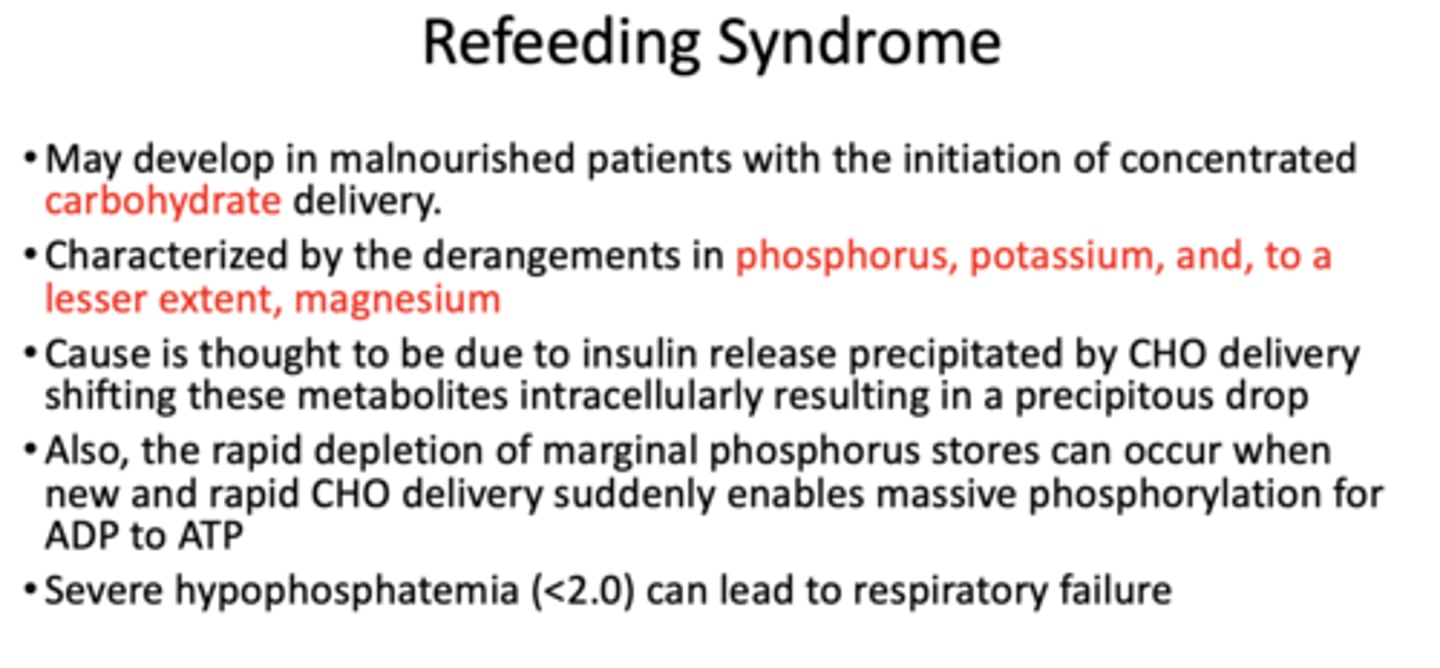
What is thought to be the cause of refeeding syndrome?
Thought to be due to insulin release precipitated by CHO delivery shifting these metabolites intracellularly resulting in a precipitous drop
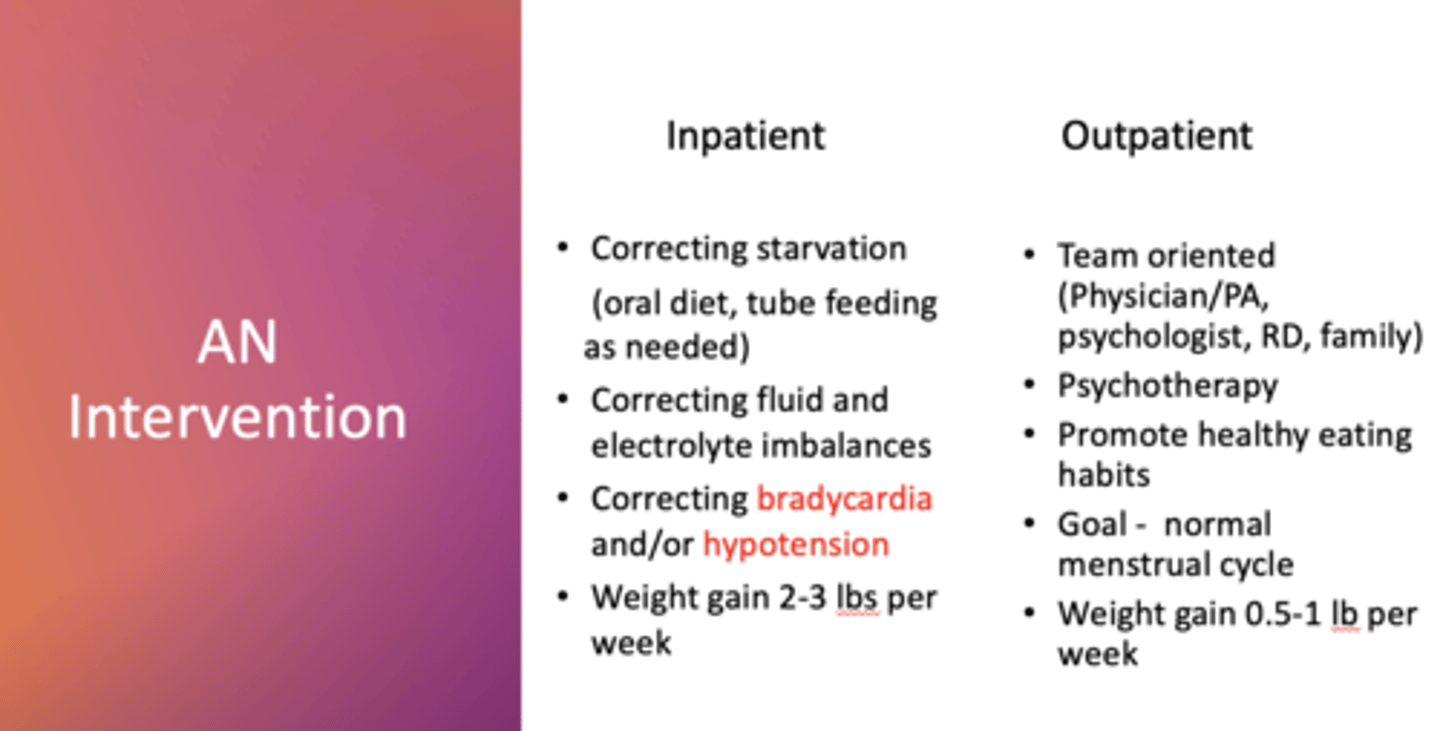
What kind of AN intervention is this (inpatient/outpatient)
-correct starvation
-correcting fluid/electrolyte imbalances
-correcting bradycardia/hypotension
-weight gain 2-3lbs/week
inpatient
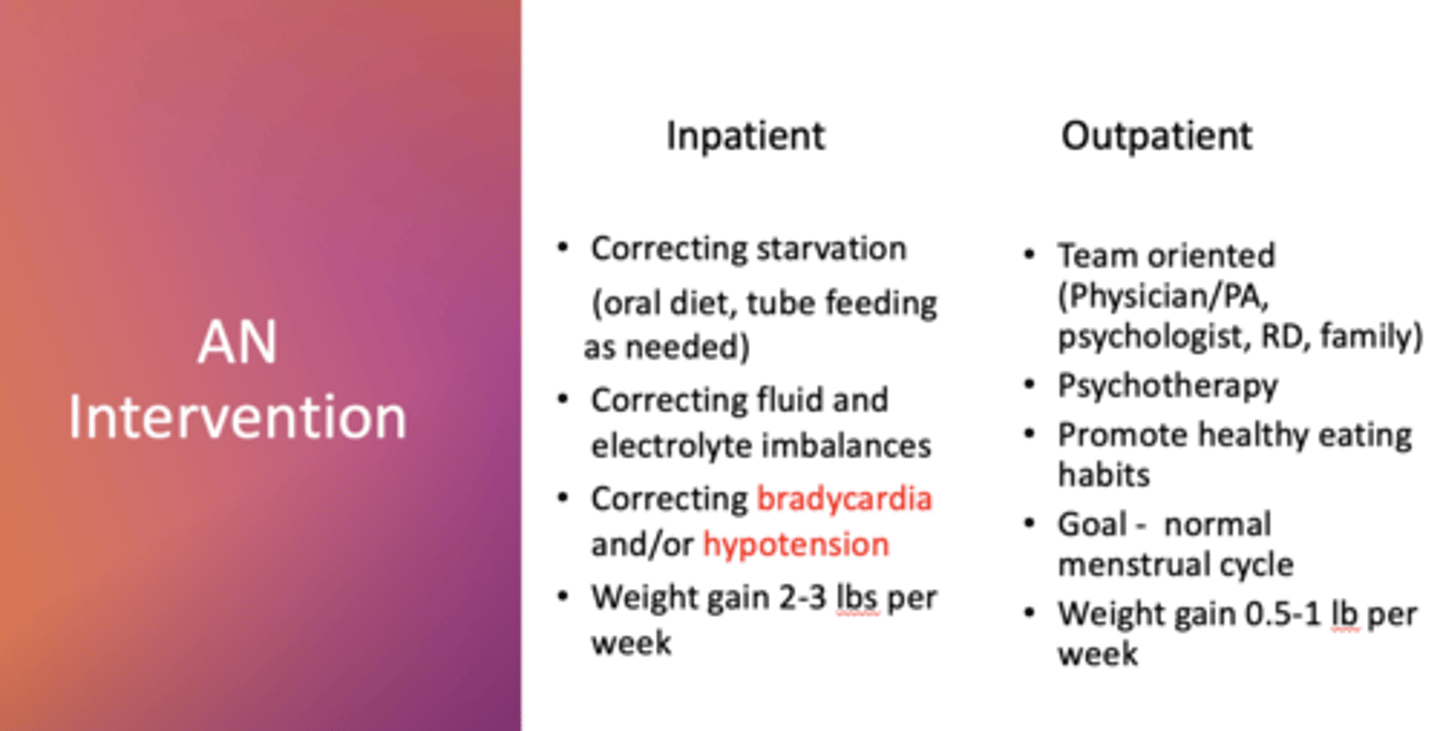
What kind of AN intervention is this (inpatient/outpatient):
• Team oriented (Physician/PA, psychologist, RD, family)
• Psychotherapy
• Promote healthy eating habits
• Goal - normal menstrual cycle
• Weight gain 0.5-1 lb per week
Outpatient
What are the four caloric needs for weight gain?
• 30-40 kcal/kg initially or 1000-1600 kcal/day
• Increase 200-300 kcal daily
• May require up to 70-100 kcal/kg for wt gain
• Females may need 3500+ kcal and males 4000+ kcal daily

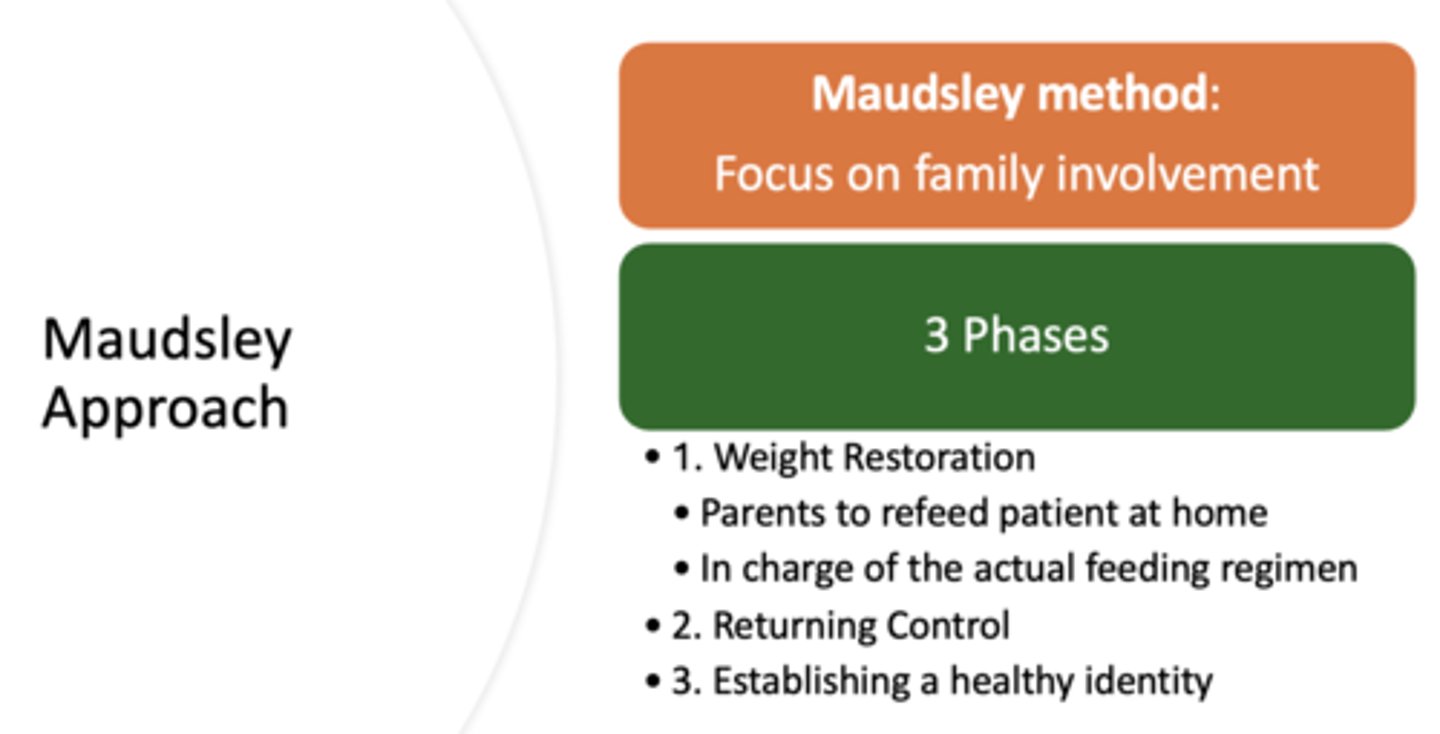
The Maudsley approach has a focus on family involvement. What are the 3 phases?
- Weight restoration
- Returning control
- Establishing a healthy identity
how can we prevent refeeding syndrome?
- Identify high risk patients
- Replete all electrolytes prior to initiation of nutrition
- Initiate and advance nutrition slowly
- Monitor and replete phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, and thiamine

Which of the following is not considered an intervention for Bulimia Nervosa?
a. stabilize fluid/electrolyte balance
b. correct nutrient deficiencies
c. stress management
d. healthy weight maintenance
e. oral health
f. quick introduction of fatty foods
g. team approach
f. quick introduction of fatty foods
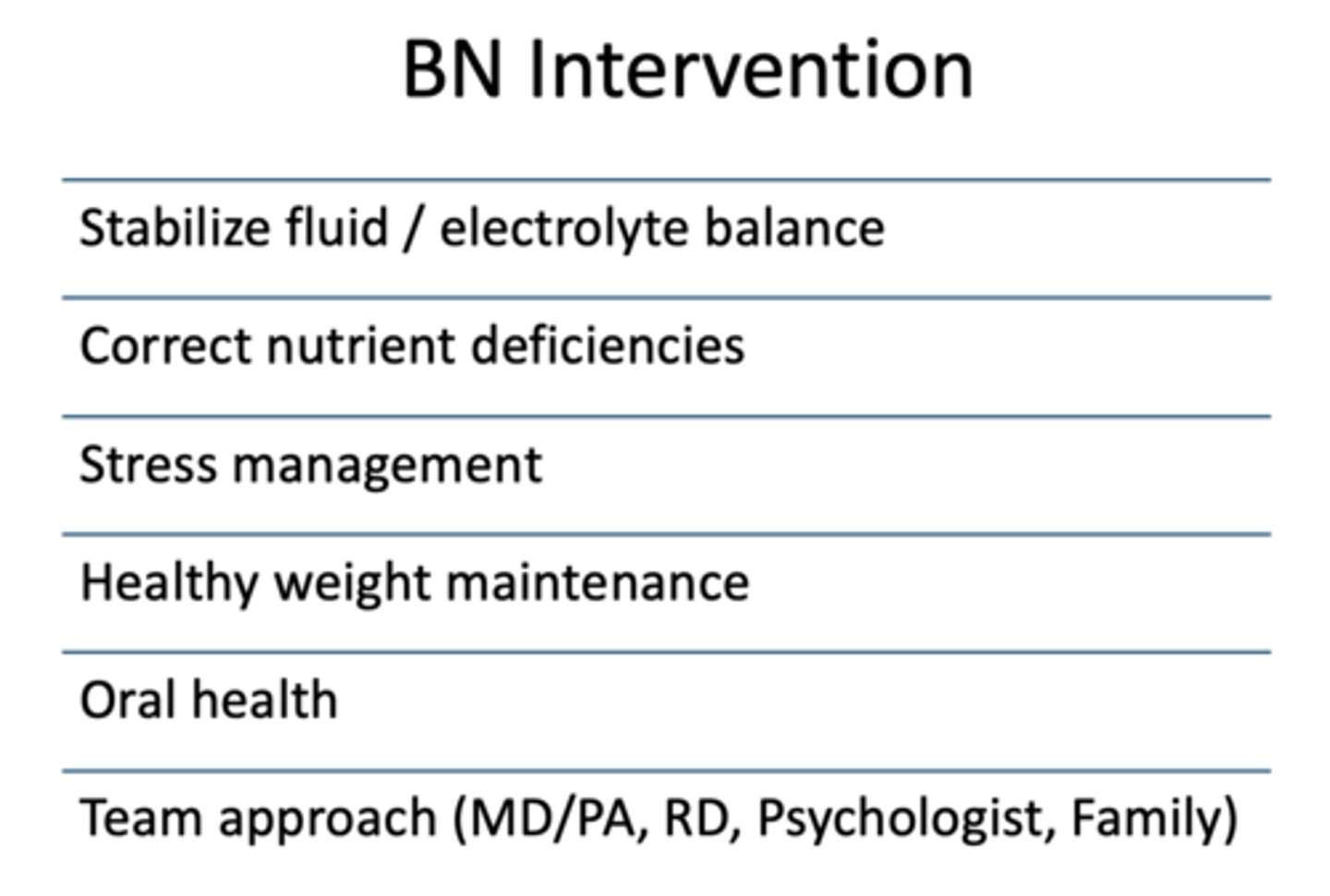
What are the treatments for bulimia nervosa?
• Cessation of binge-purge cycle
• Maintain weight
• Restore stable eating behavior
• Correct nutrient deficiencies/ balance levels
• Treat medical complications
• Monitor and alter thought patterns related to food and body image

What has the following characteristics?
- Binge eating without purging or other compensating
- Frequency: 1x weekly for 3 months
- Risk factors: obese, overweight, substance abuse, depression, anxiety, chronic stress
- Chaotic eating behaviors, negative self esteem, poor body image, guilt
binge eating disorder
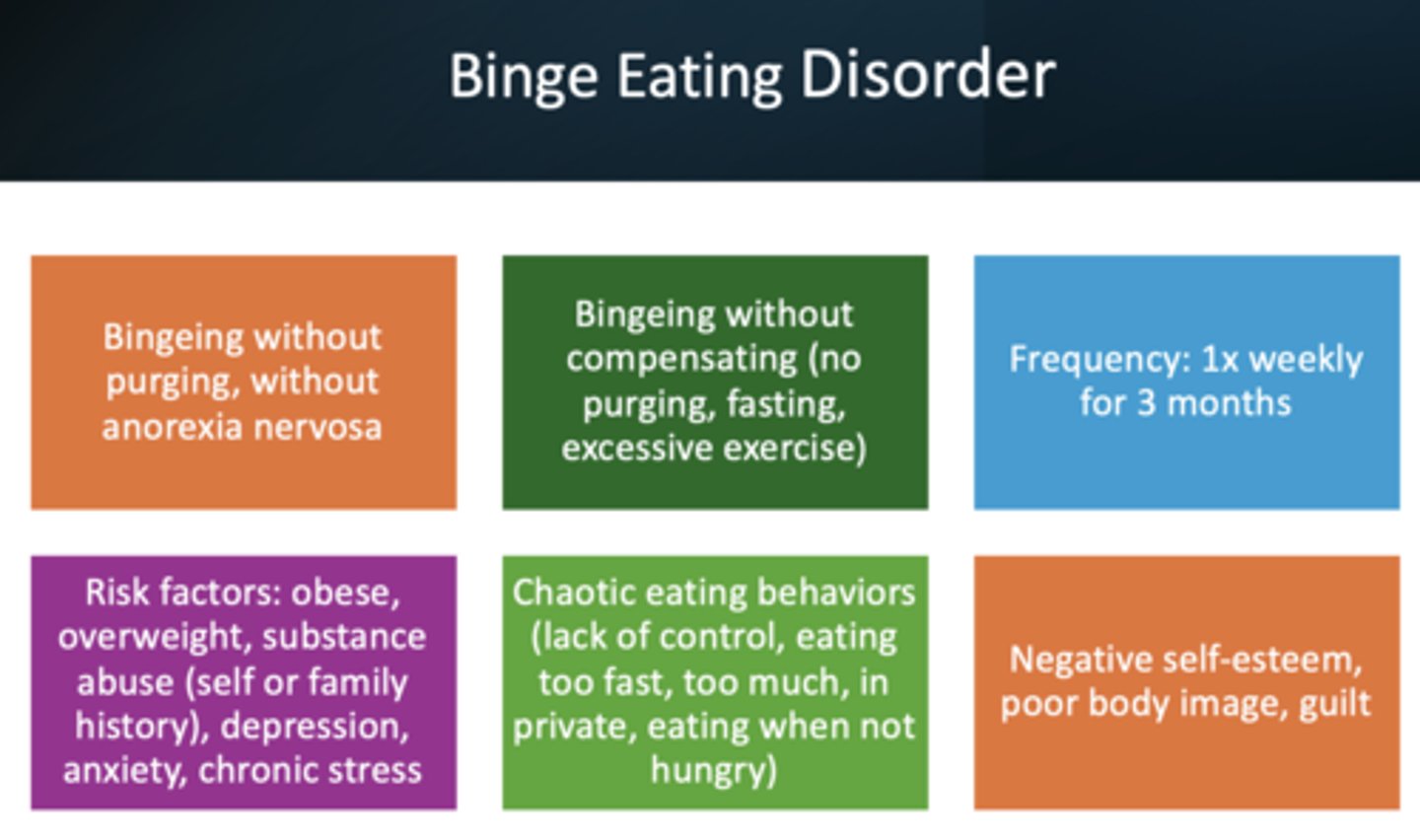
What has the following symptoms?
- Disappearance of large amounts of food
- Eating quickly
And health risks?
- Overweight/obesity
- Stress/psychological impacts
binge eating disorder

What are the treatment goals for individuals with binge eating disorders?
- Interrupt binge eating behaviors
- Improve body image
- Improve nutrition status
- Increase physical activity
- Promoting self-acceptance

What is the gold standard of treatment for eating disorders?
interprofessional approach

What are four tips for working with individuals with eating disorders?
1. Individualize recommendation based on each patient’s specific needs
2. Become aware of safe and unsafe foods and “trigger” foods and work with patients to demystify these foods
3. Address patients’ concerns (constipation, bloating) – gradually introduce fiber
4. Be consistent, beware of manipulation

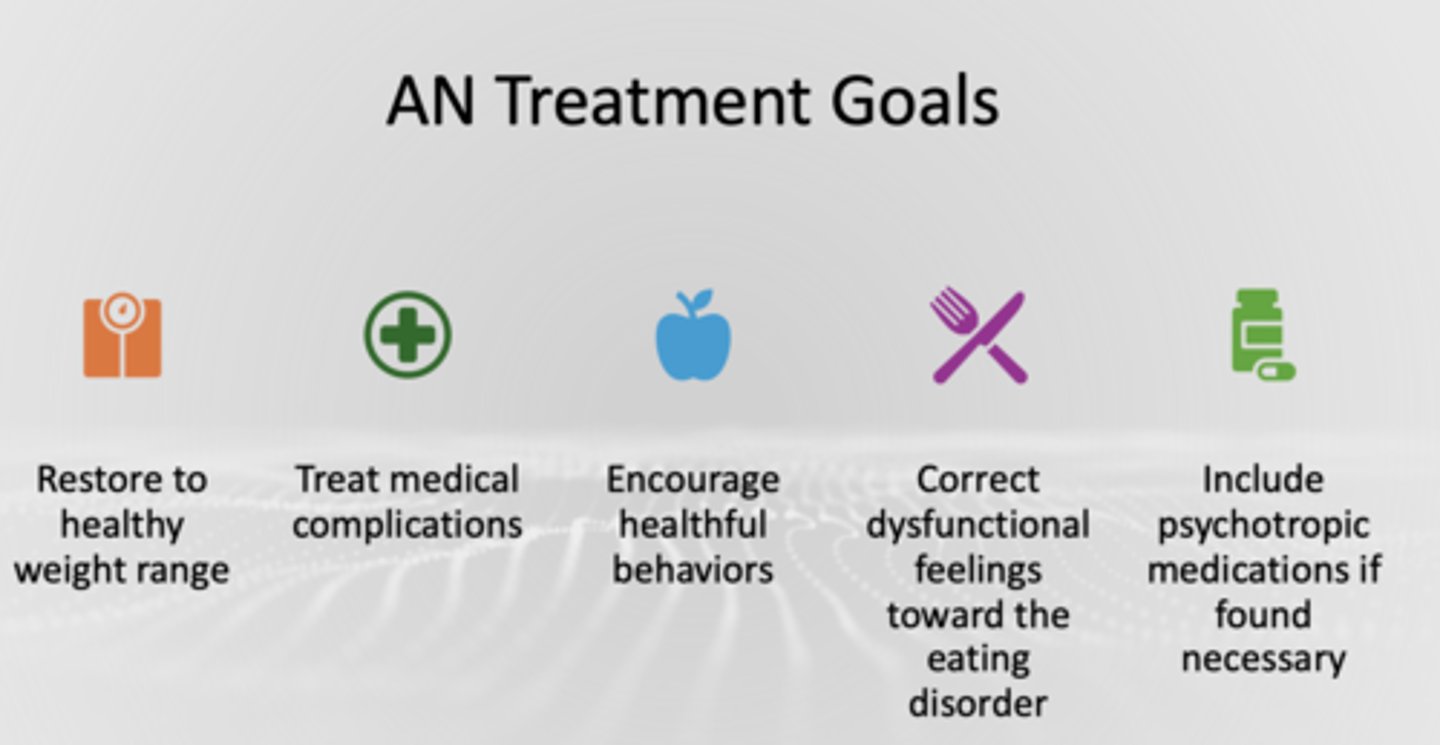
What are the goals of treating individuals with anorexia nervosa?
• Restore to healthy weight range
• Treat medical complications
• Encourage healthful behaviors
• Correct dysfunctional feelings toward the eating disorder
• Include psychotropic medications if found necessary
What are common safe foods for individuals with anorexia nervosa?
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Tofu
- Low fat/fat free foods
- Plain tuna
- Plain chicken

Fiber can _________ gastric emptying
Slow

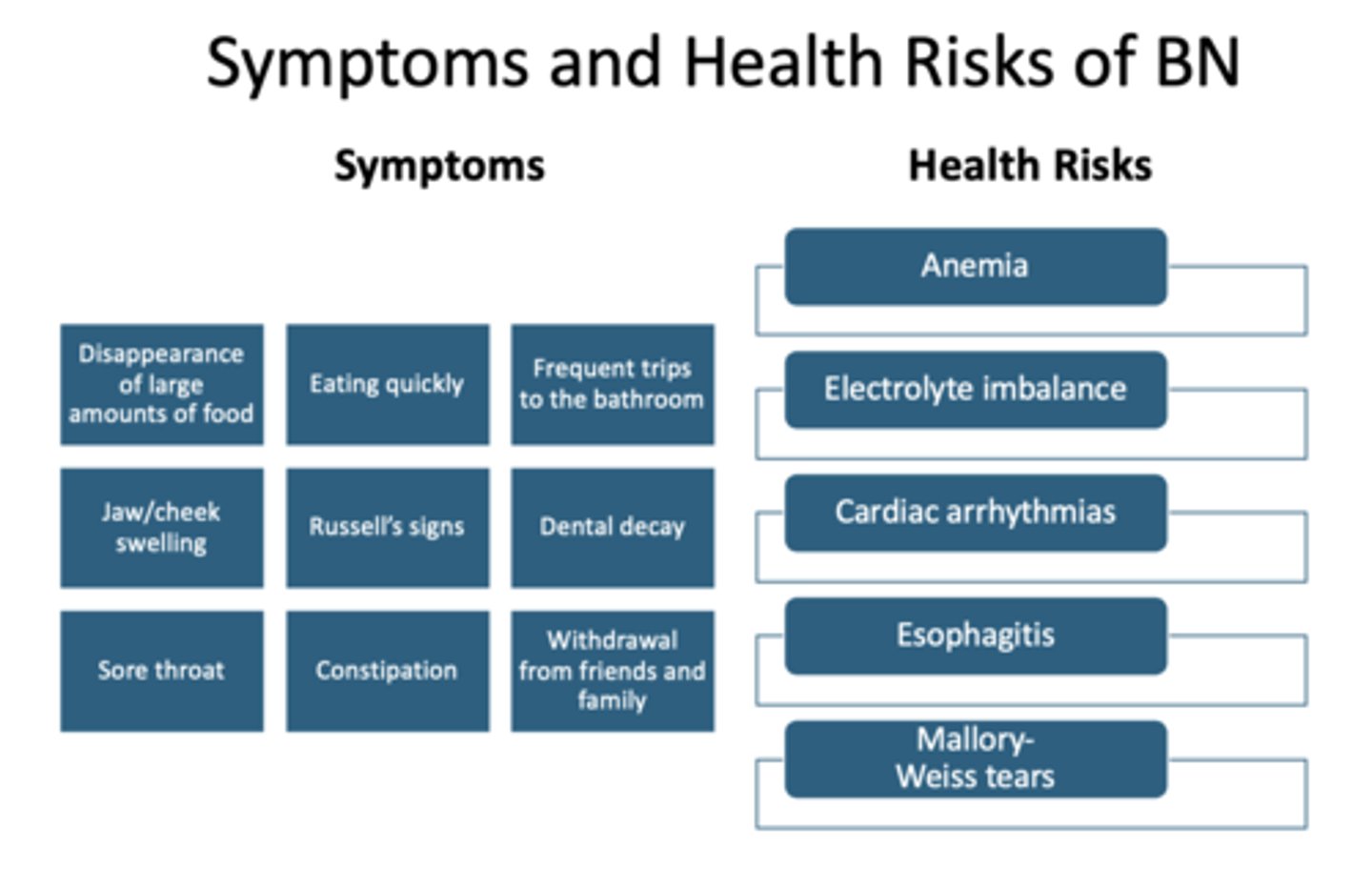
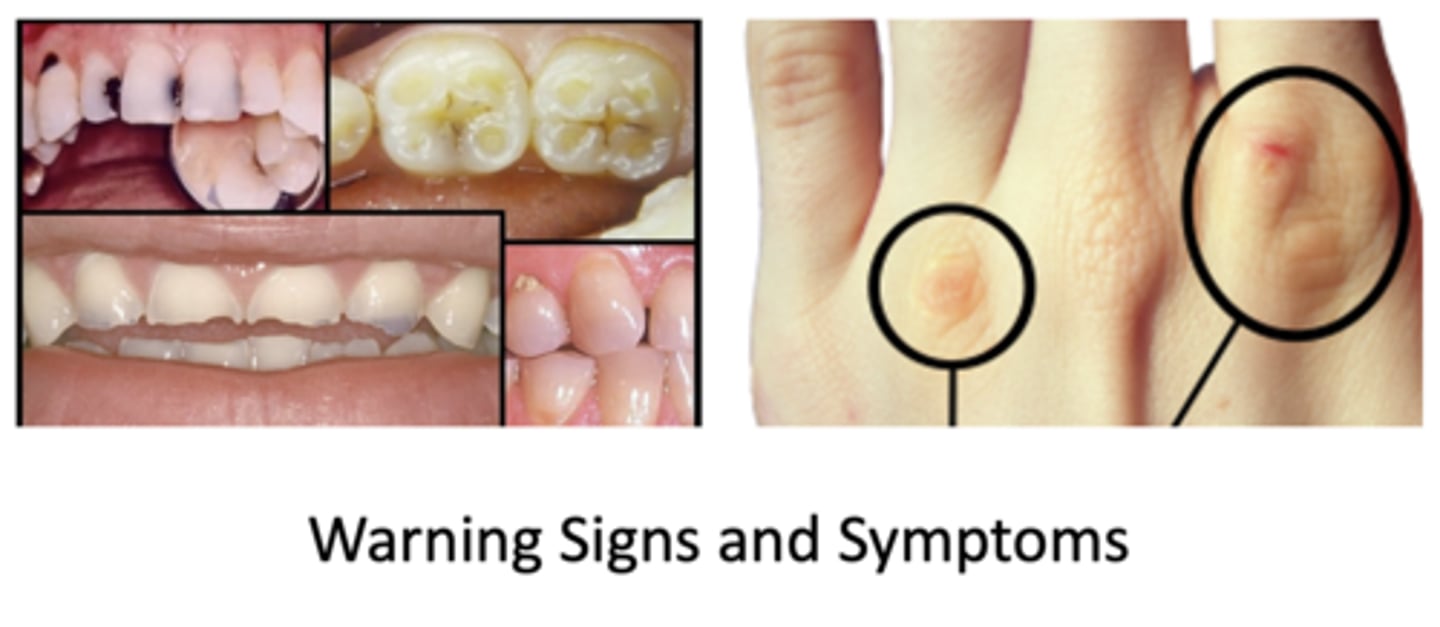
What are two warning signs and symptoms of bulimia nervosa?
- Russel's signs (sores/scars on knuckles/hands)
- Dental erosion
Changes in body composition occur in puberty leading to greater ________ body mass in males and greater ________ mass in females
lean, fat

T/F: Vegetarianism is a red flag for early adolescents
True (Need to ask why)

T/F: Eating disorders are multifactorial conditions associated with physical and psychological morbidities.
True
