Biochem Exam 4
1/228
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
229 Terms
lysine ; leucine
only _ and _ are purely ketogenic AA’s
glucogenic
can be catabolized to
TCA intermediate
glucose in gluconeogenesis
ketogenesis
pathway that can be catabolyzed to acetyl-CoA
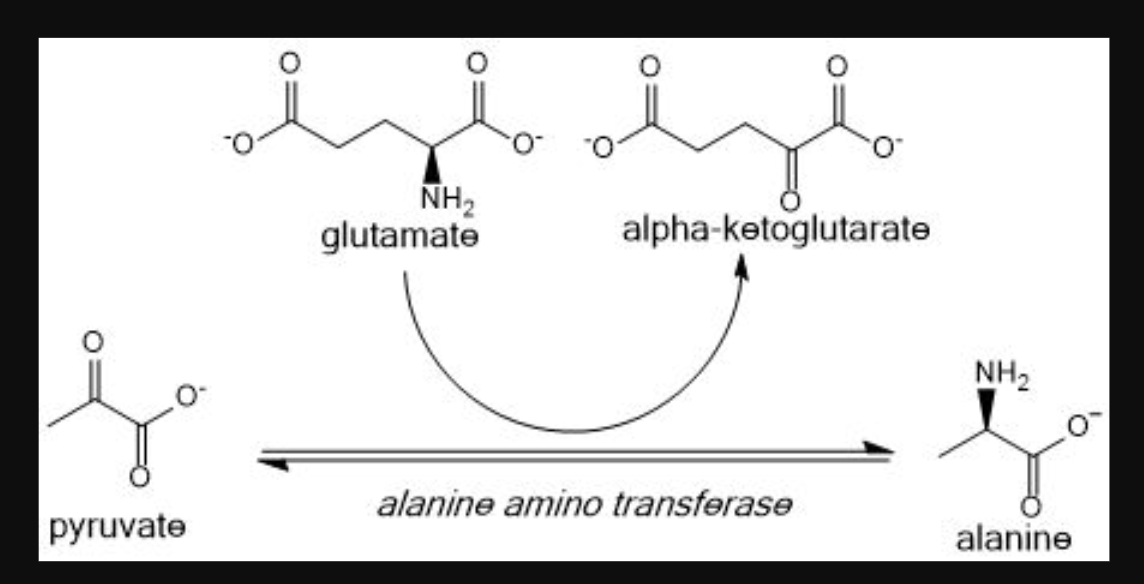
alanine
one of the most abundant AA in blood
(pyruvate analog, ammonia carrier)
glutamate ; alpha ketoglutarate
If making an AA, the universal donor is _ to generate _
nitrogen
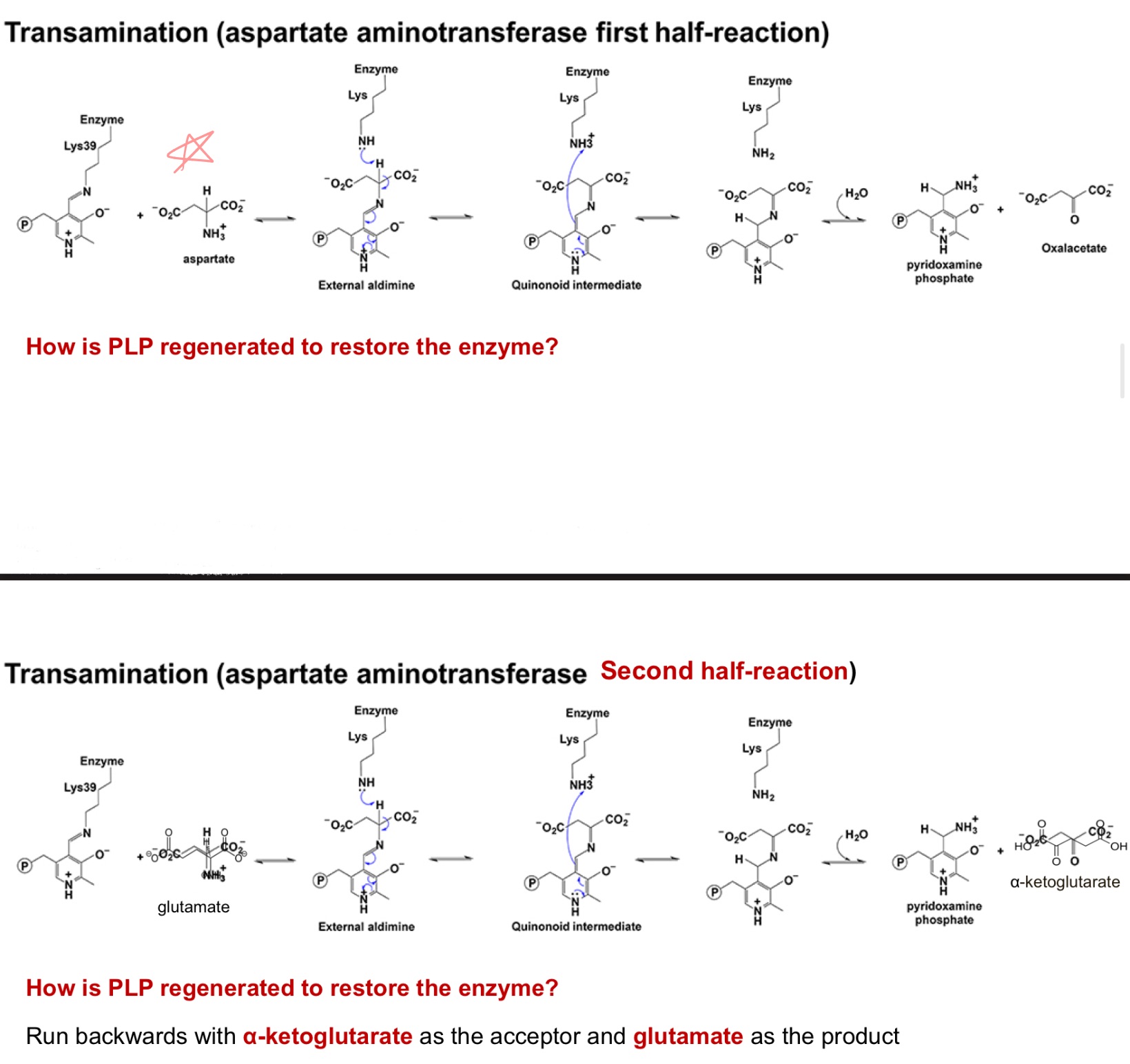
PLP goes through this altered enzyme intermediate to hold onto a _ as a transamination is done.
removing nitrogen
First step of catabllozying AA is …
pyruvate ; glutamate
PLP
Alanine becomes _ by giving up it's nitrogen to alpha ketoglutarate to make _.
Using _ cofactor
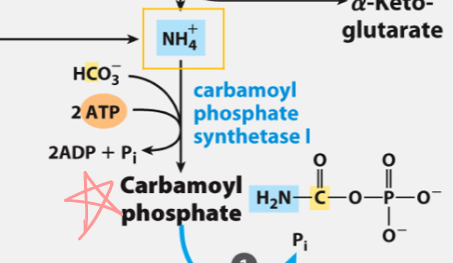
k
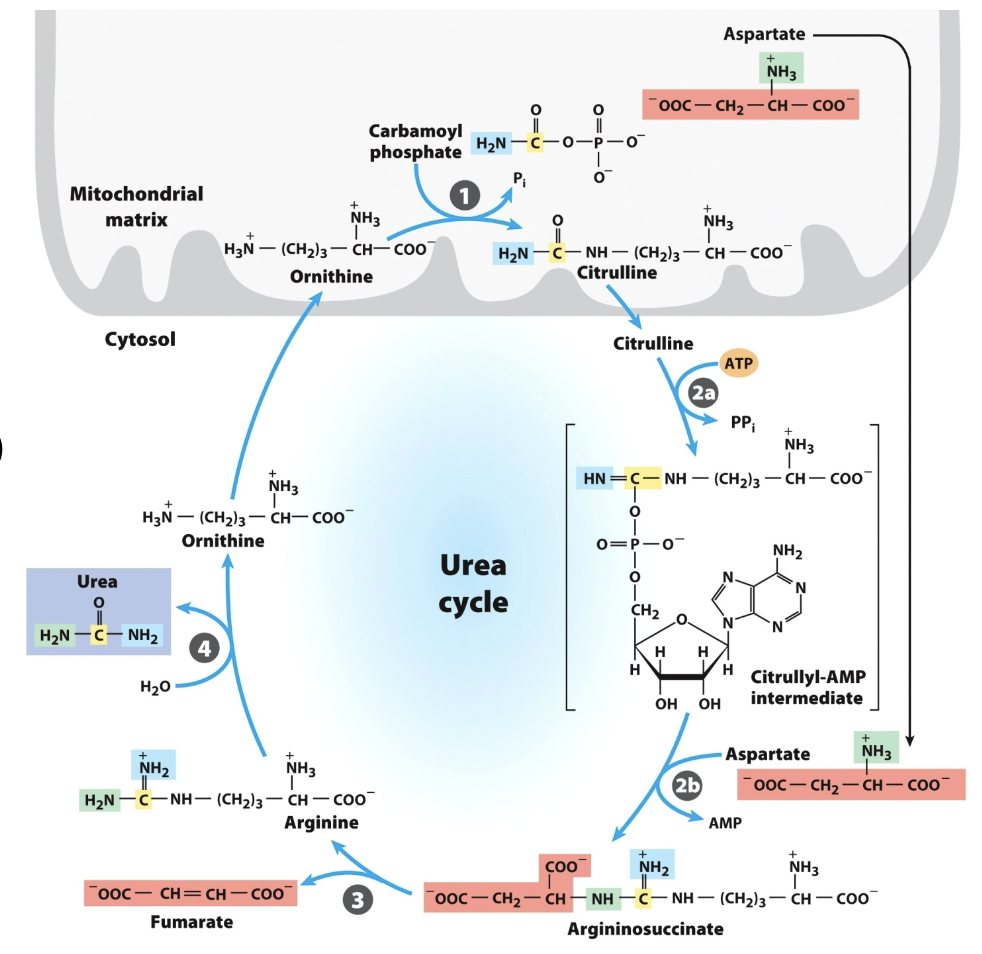
Draw the rxn catalyzed by Carbamoyl Phosphate I
First one was to make bicarbonate attackable, then second phosphate is actual donor.
In rxn catalyzed by Carbamoyl Phosphate I
Only one phosphate on the product, why did it use 2 (ATPs)?
Ornithine transcarbamylase
Argininosuccinate synthetase
Argininosuccinase
Arginase
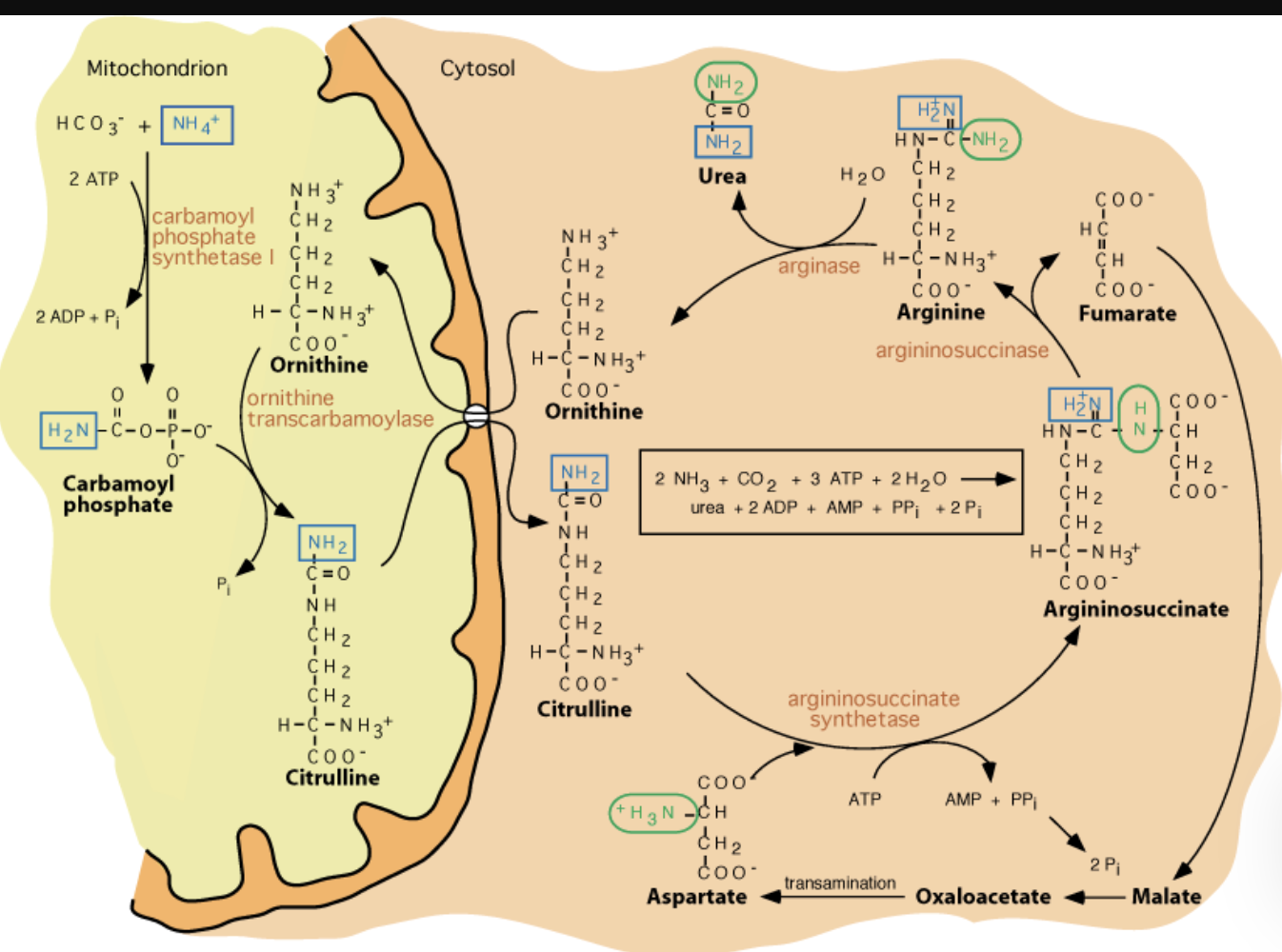
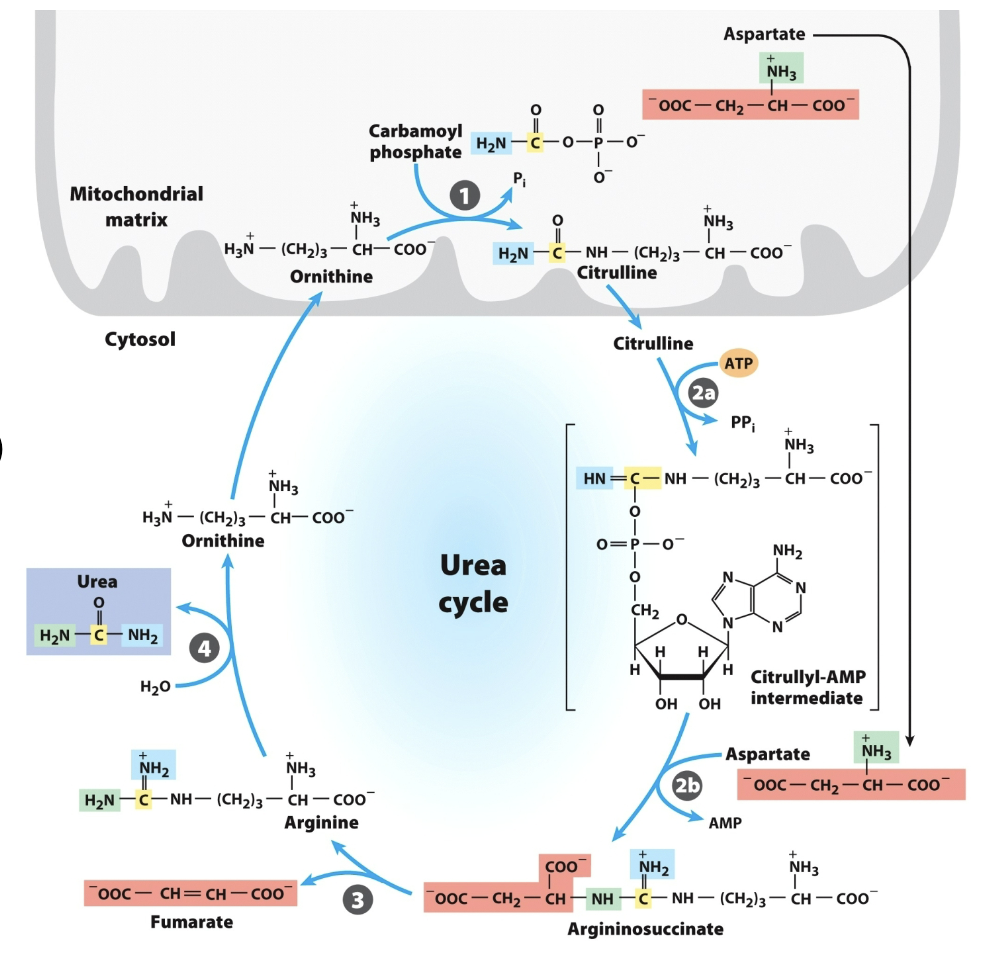
Urea Cycle 4 Enzymes:
Don’t draw any reactions, but recognize/be able to put in order
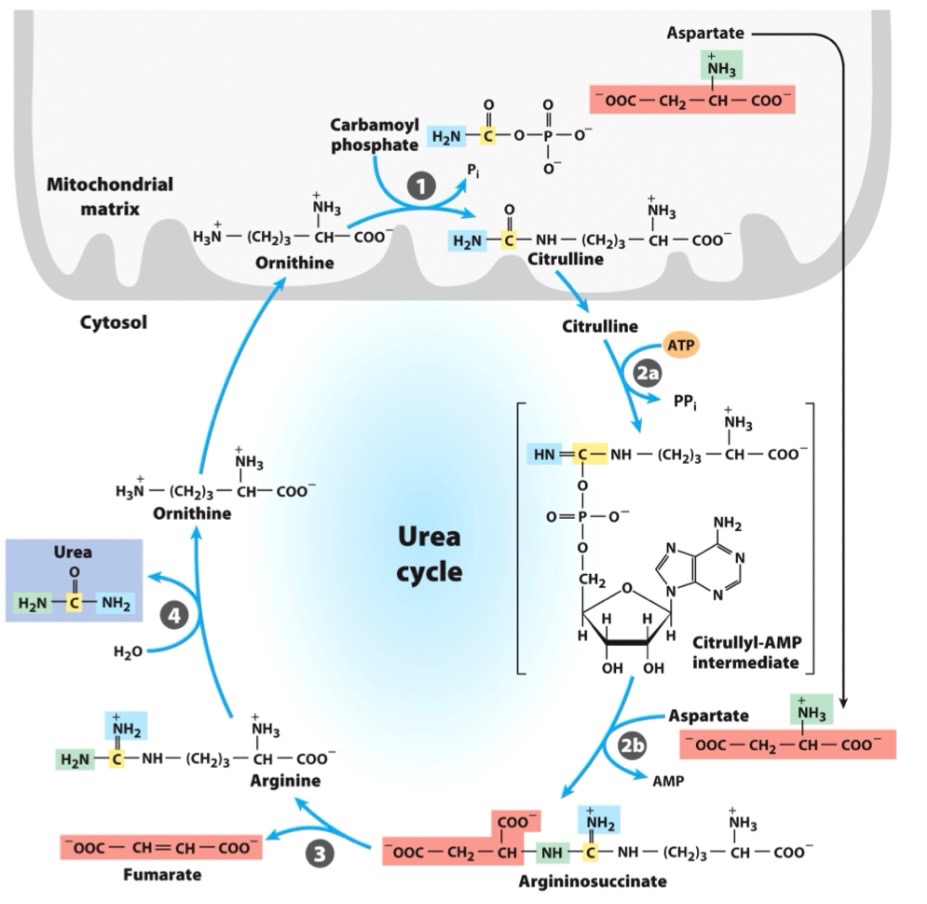
Ornithine transcarbamylase
_ is the only Urea Cycle reaction in the mitochondria
Lysine
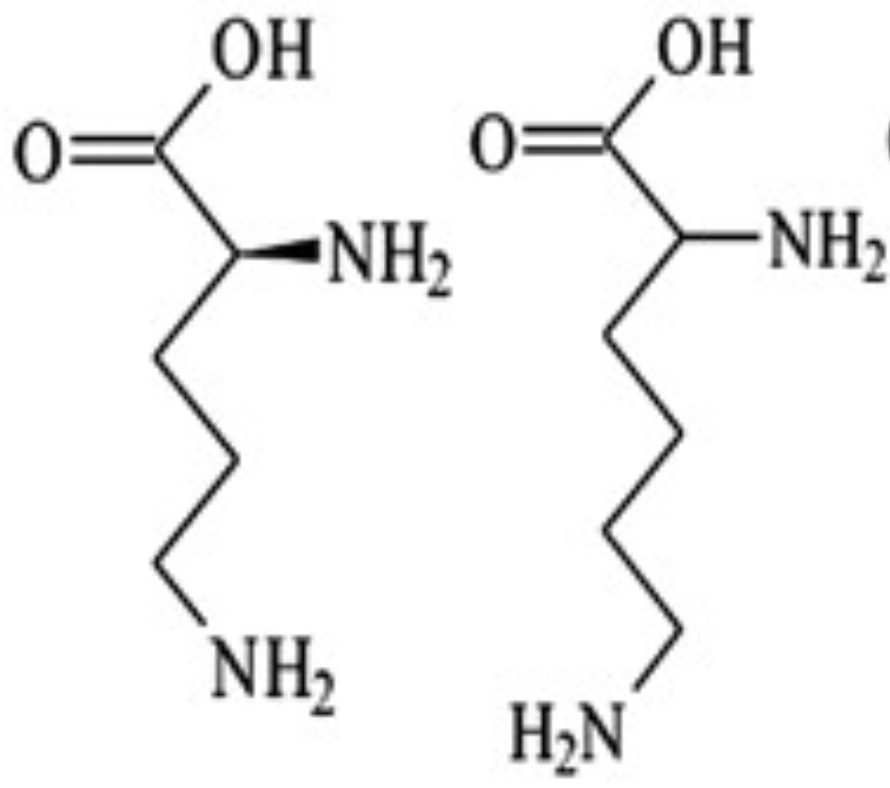
Ornithine is _ with one less carbon
Argininosuccinate synthetase
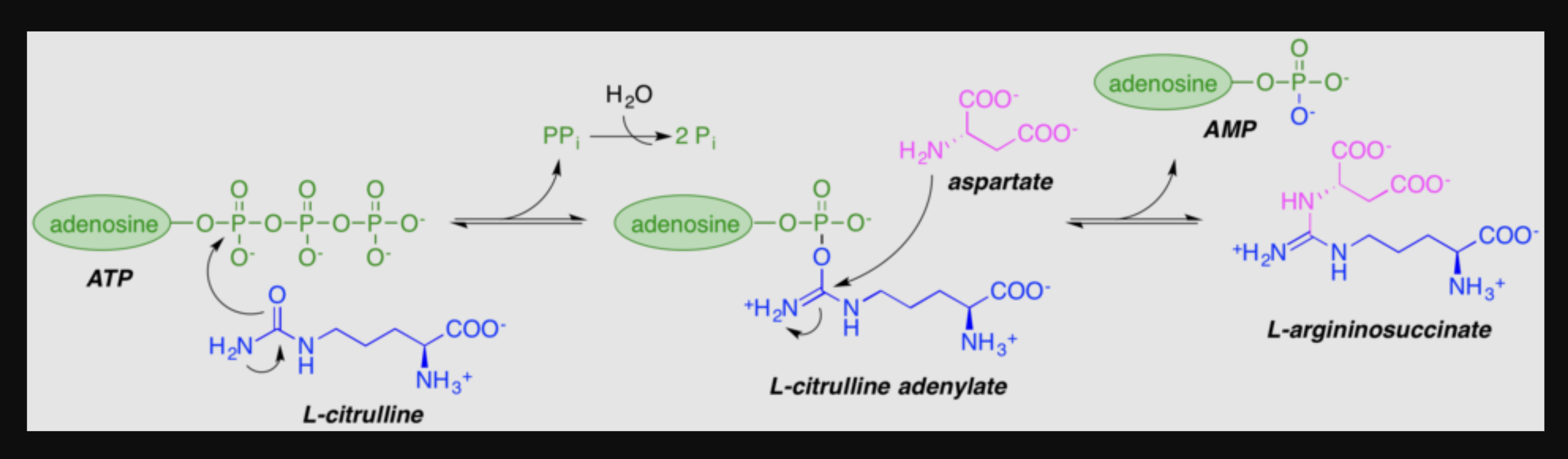
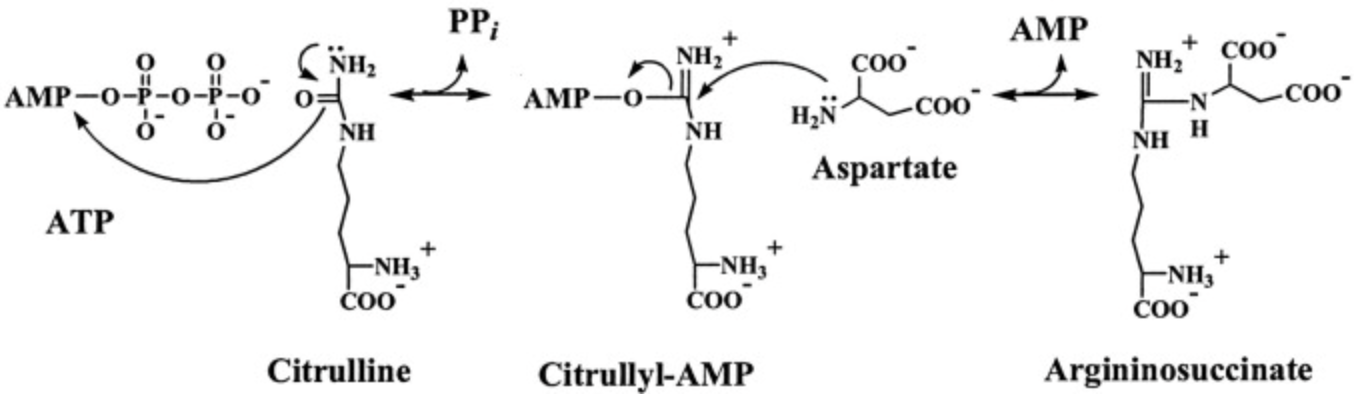
What adenylates citrulline to allow attack from aspartate?
Argininosuccinate
in urea cycle,
the big molecule u dont wanna memorize
(citrulline + aspartate)
citrullyl-AMP intermediate
urea cycle intermediate between citrulline and argininosuccinate?
bicarbonate in CPS 1
Where did yellow carbon come from?
inorganic ammonia in CPS 1
Where did blue N come from?
aspartate
Where did green N come from?
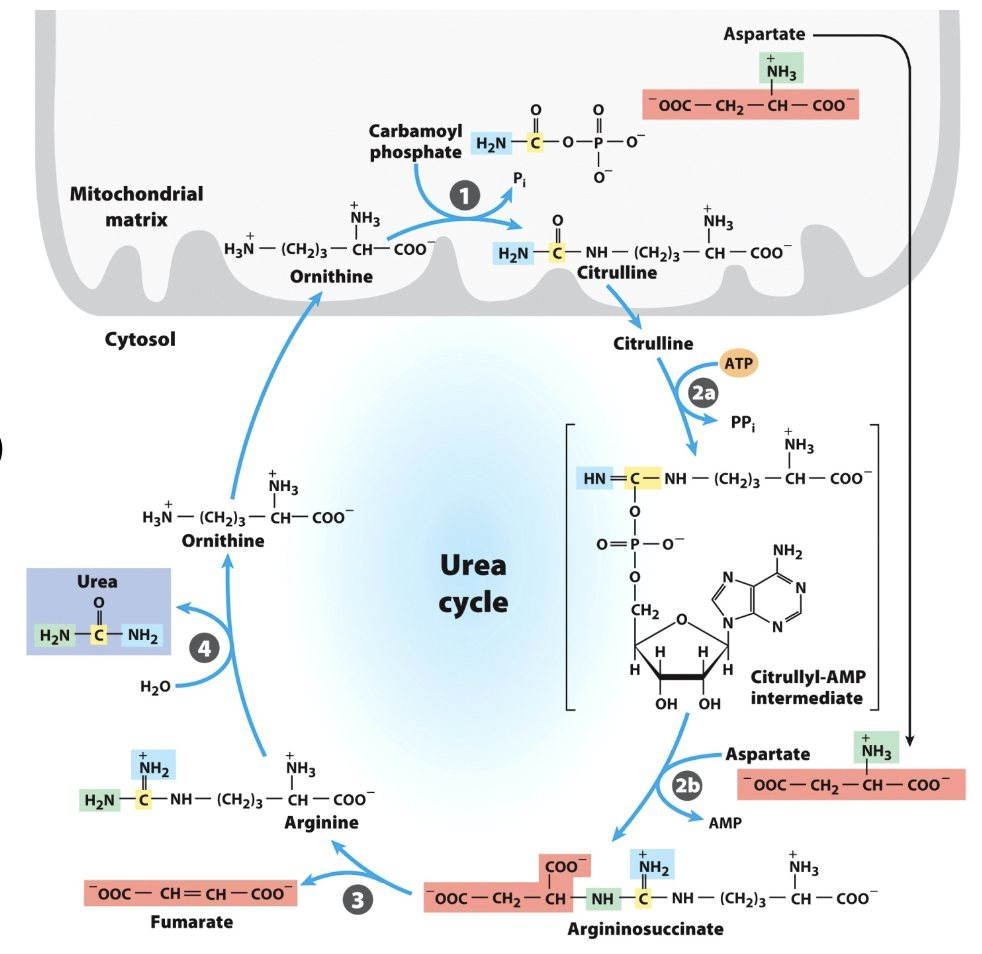
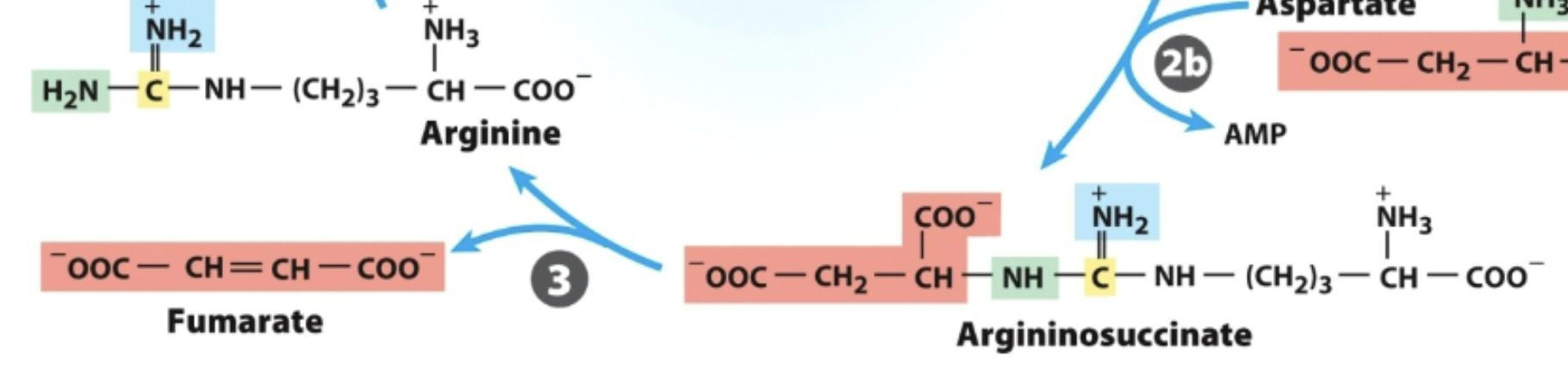
Argininosuccinase
In the urea cycle,
What breaks down argininosuccinate, generating arginine and releasing fumarate?
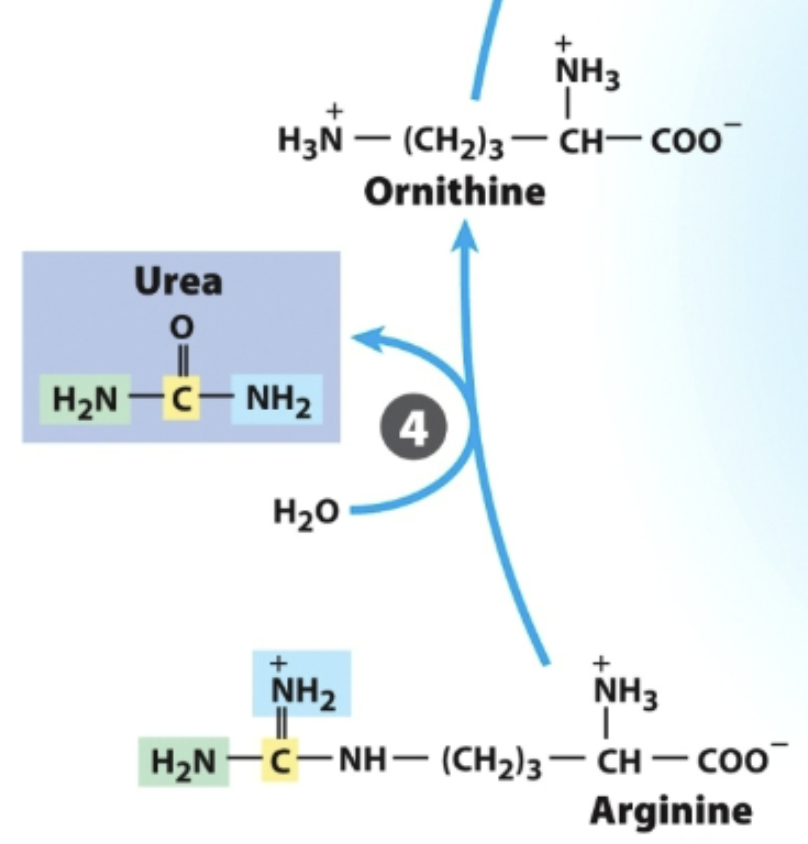
Arginase
In the urea cycle,
What breaks down arginine, generating urea and regenerating ornithine?
AA
no storage for _s
acetyl-CoA + glutamate → CoASH + N-acetylglutamate
NAG is like a “go” signal: its presence tells the liver, “There’s enough substrate (glutamate and acetyl-CoA) and nitrogen to start the urea cycle.”
CPS1 is inactive without NAG.
N-acetyl glutamate synthase (NAGS) reaction?
N-acetylglutamate
is an essential and obligatory allosteric regulator of CPSI
arginine
N-acetylglutamate is activated by _
Glutaminase, Glutamate by oxidative deamination
Aminotransferase using PLP cofactor
Bicarbonate
hydrate and then oxidize
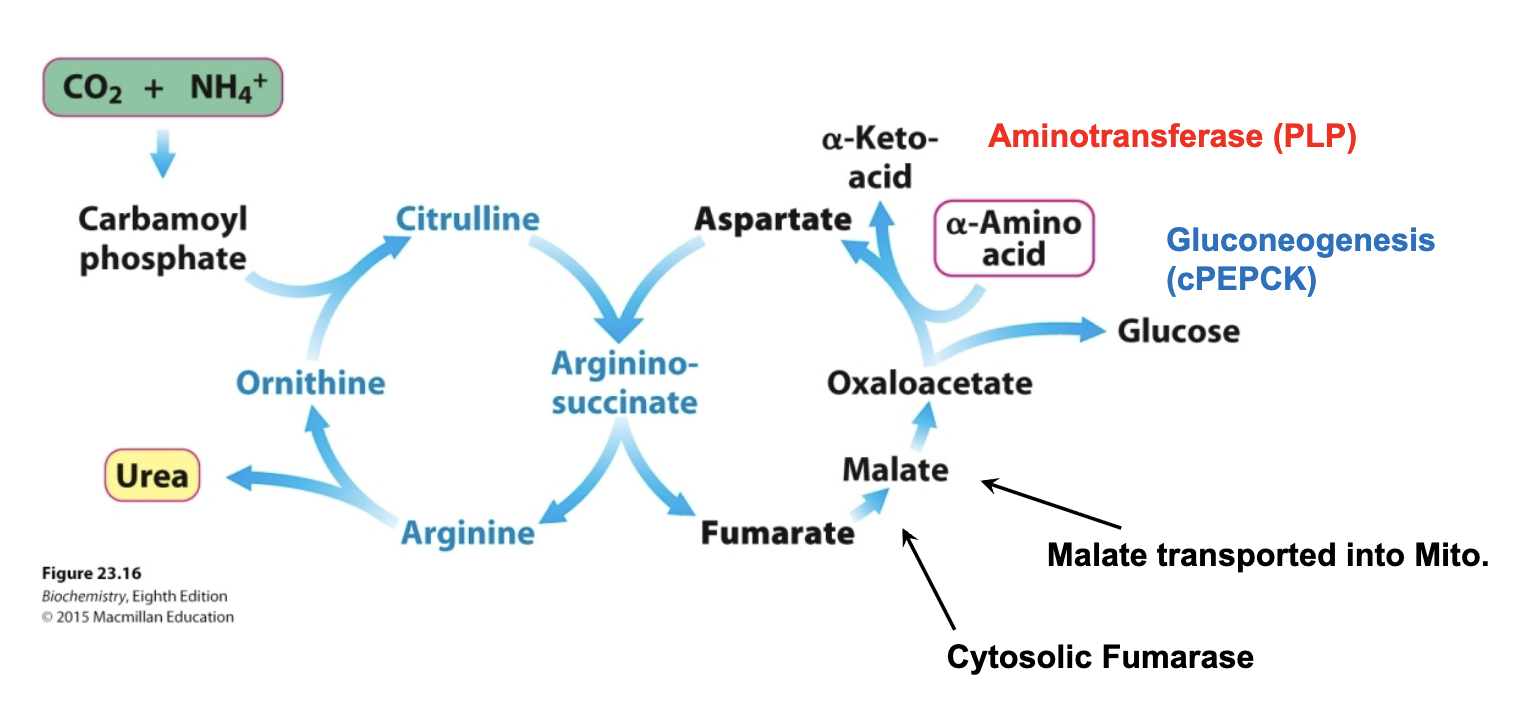
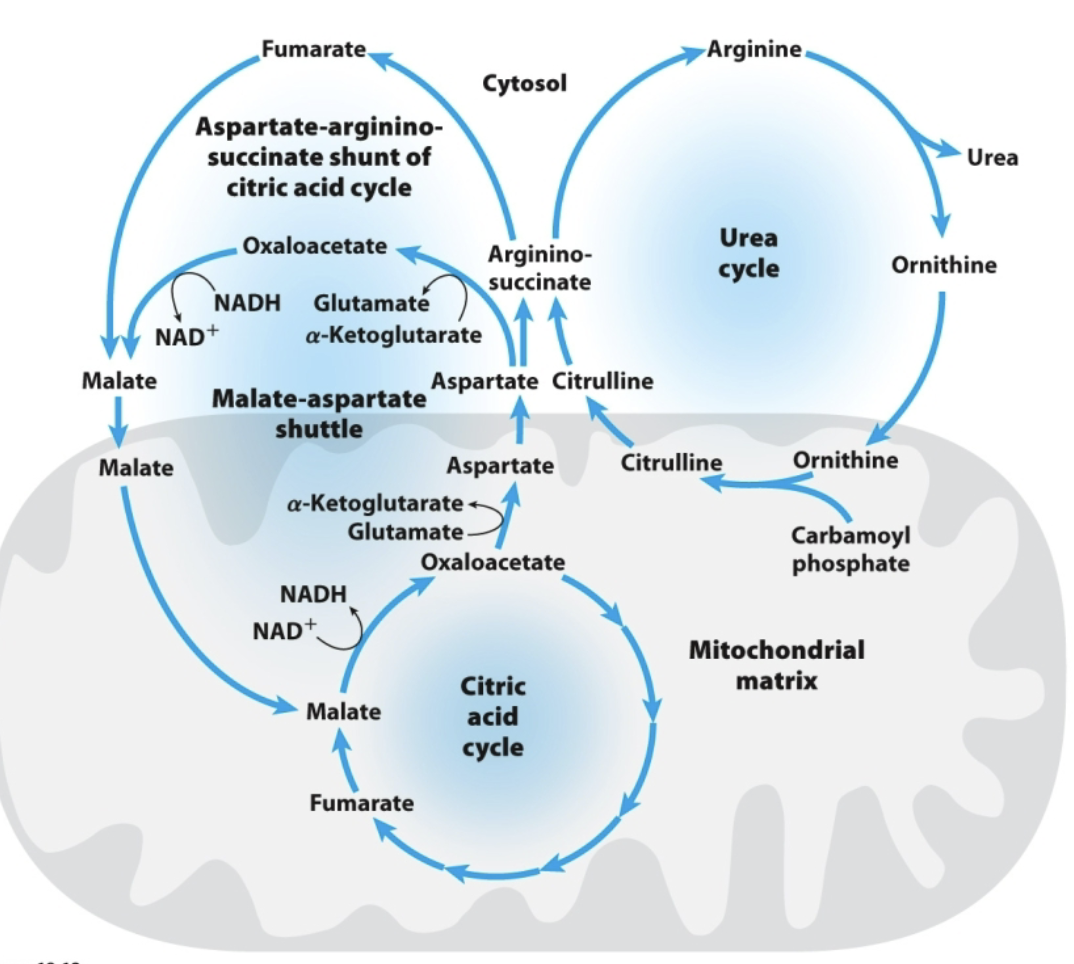
(fumarate —> malate —> OAA —> aspartate)
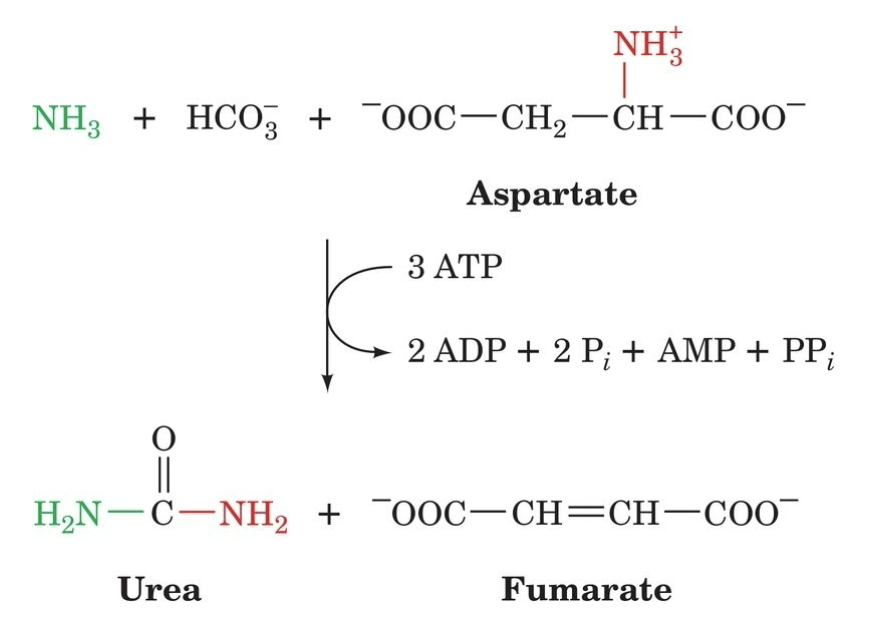
Overall Urea Cycle Reaction
Where did the green ammonia come from (if in the Liver)?
The red one?
Carbon in urea came from?
How can fumarate be converted back into aspartate (step by step)?
Glutamate
Alphaketoglutarate
What alpha AA is this?
What’s the alpha keto acid?
yea :(
got it?
glutamate
pyridoxal phosphate (PLP)
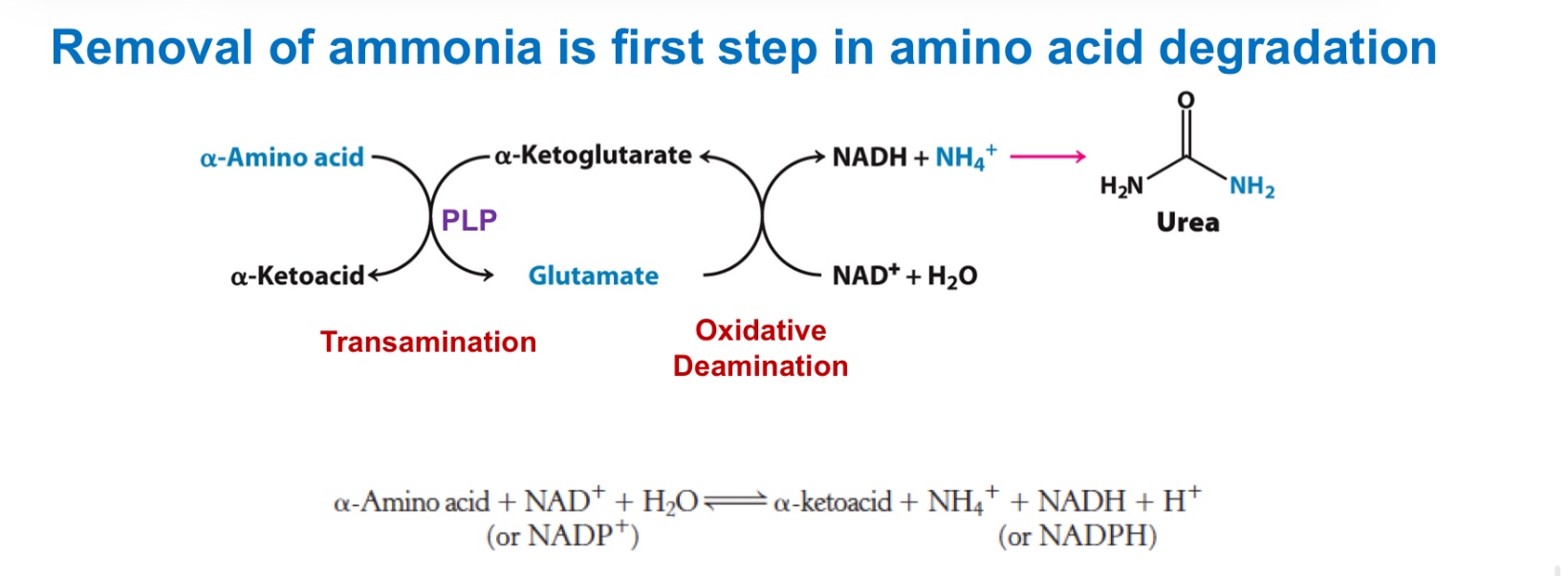
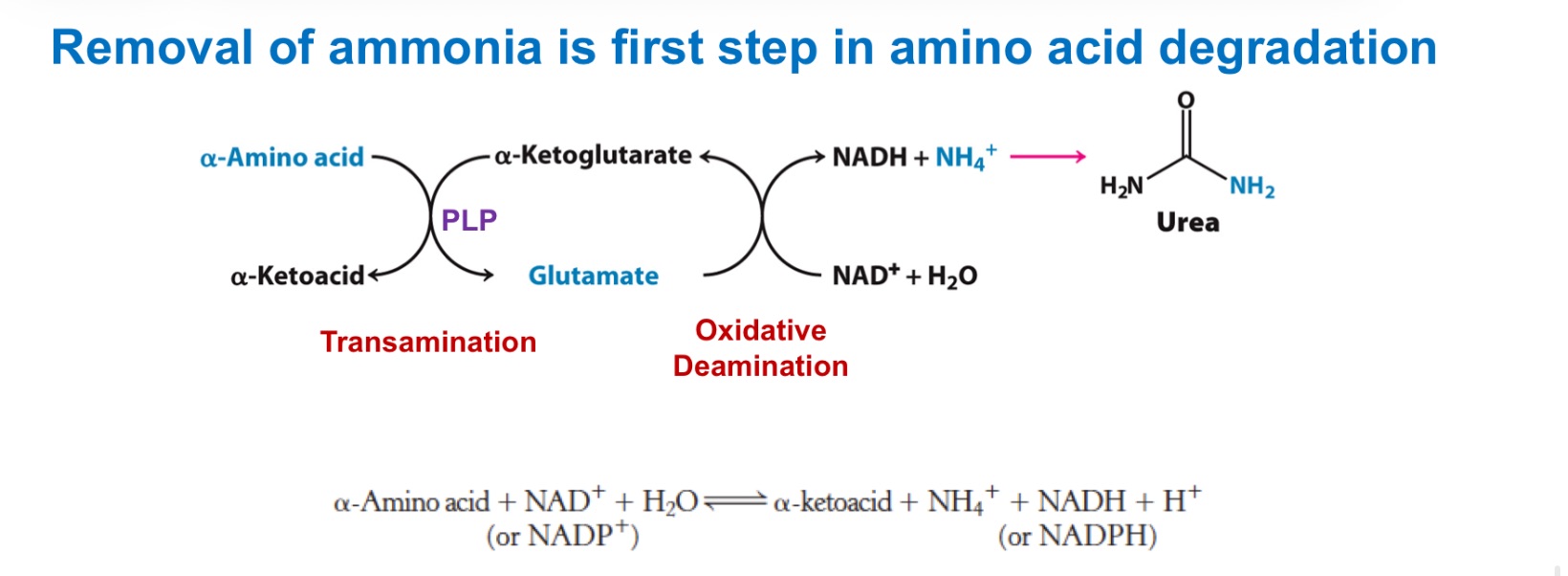
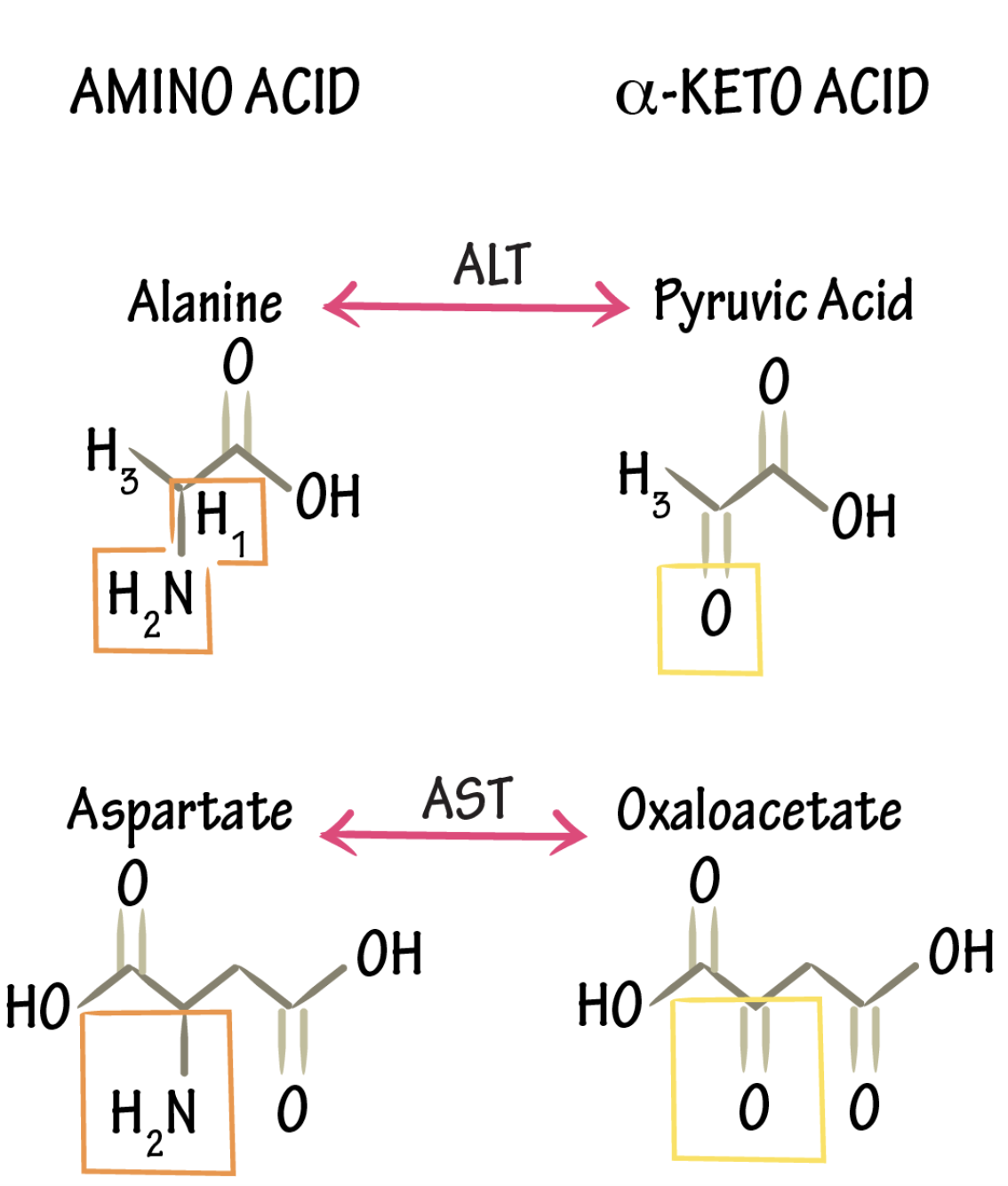
How amino groups are collected: transamination
The −NH₂ on most amino acids is moved to α-ketoglutarate → _; the original amino acid becomes its α-keto acid (its carbon skeleton).
Enzyme/cofactor: aminotransferases (a.k.a. transaminases) use _, which forms a Schiff base with the amino acid and stabilizes carbanion intermediates (acts as an “electron sink”). generally reversible
This funnels many different amino-nitrogens into a single pool (glutamate), which is then processed to release ammonia or to carry nitrogen between tissues.
glutamate
universal nitrogen carrier
alpha-ketoglutarate
universal nitrogen acceptor
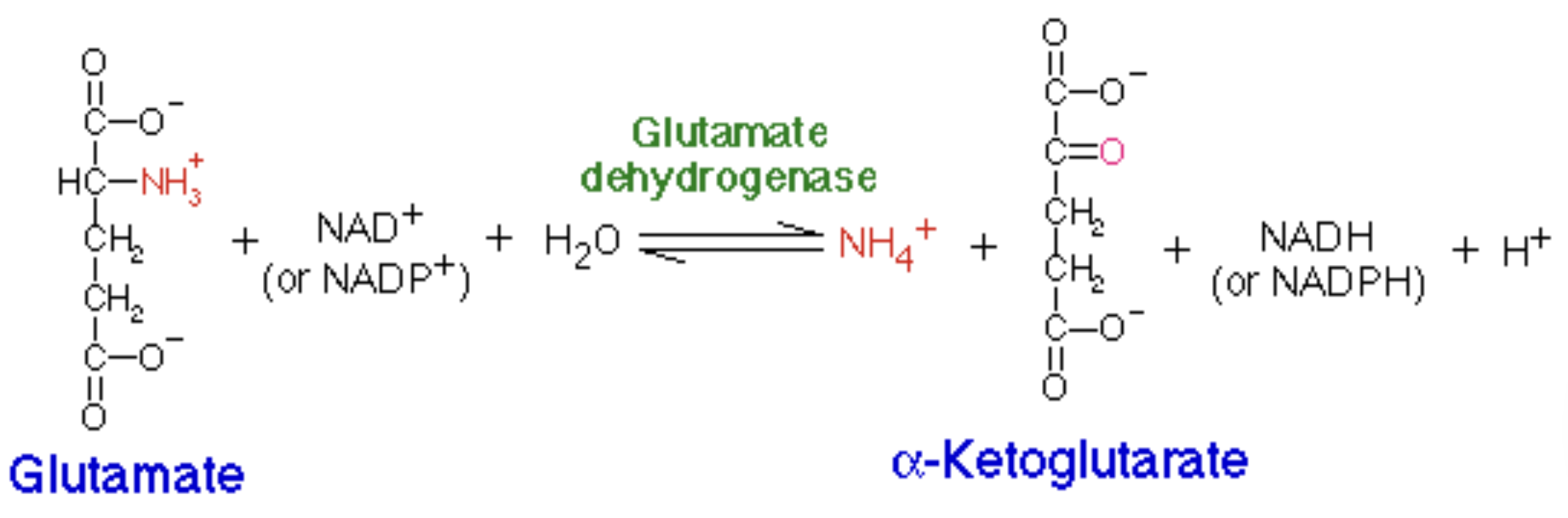
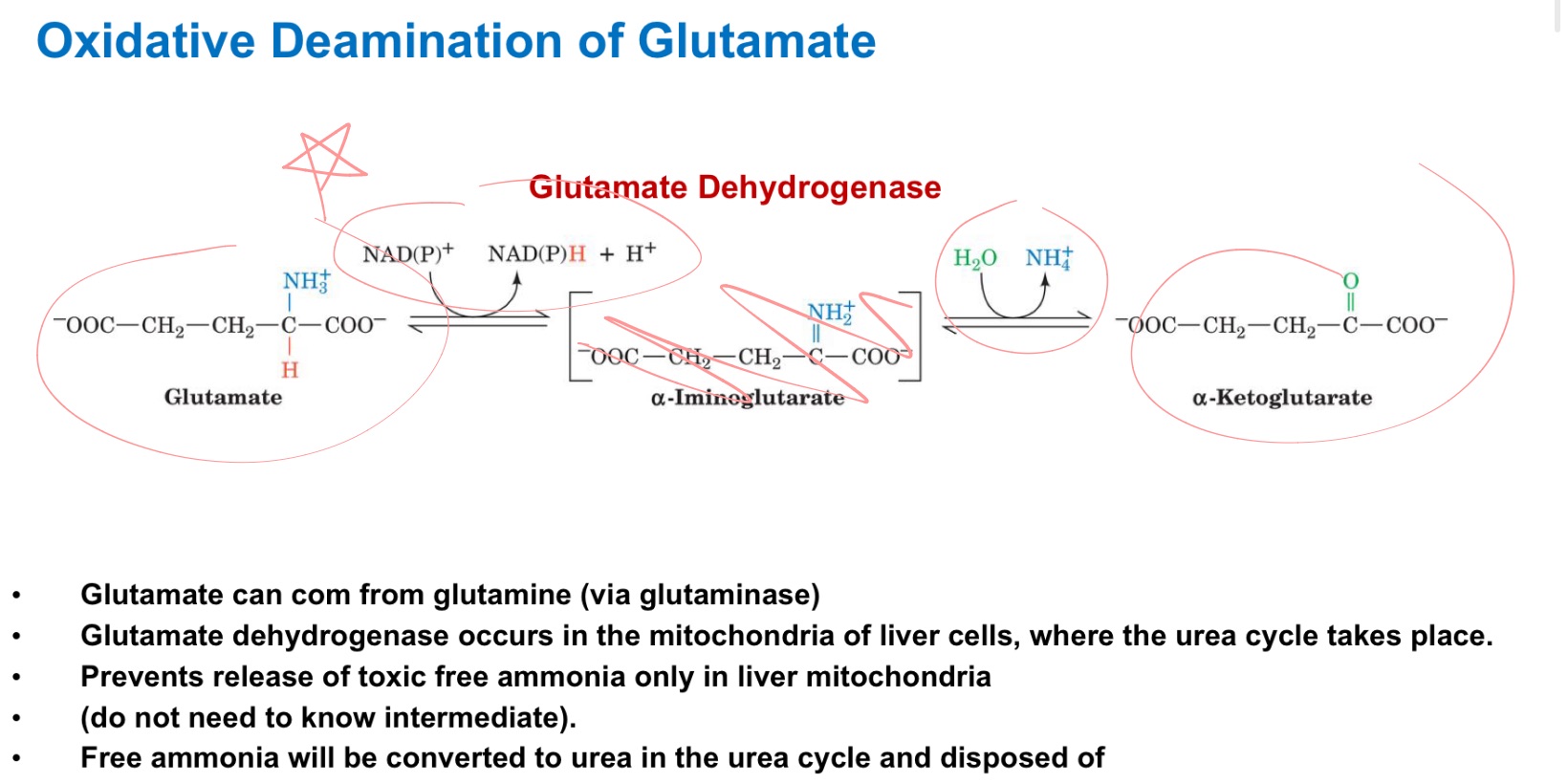
Glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH)
_ in mitochondria of liver catalyzes oxidative deamination:
glutamate → α-ketoglutarate + NH₄⁺.
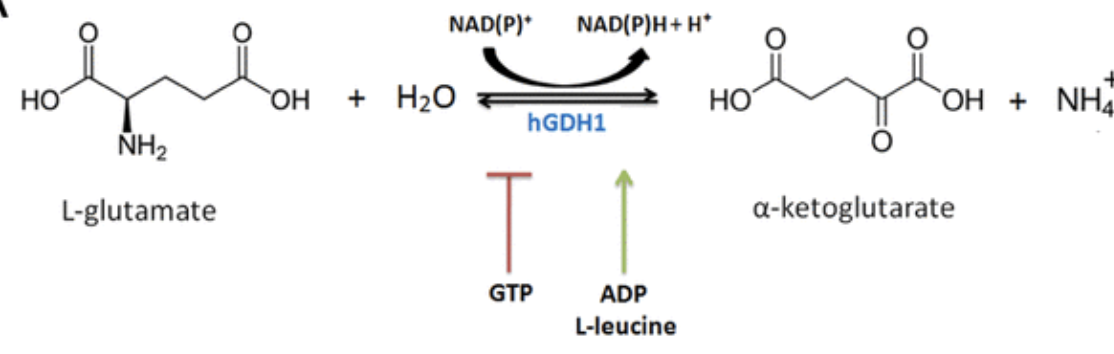
ADP ; GTP
GDH can use NAD⁺ or NADP⁺ (in mammals both work).
It’s allosterically regulated (activated by _, inhibited by _): the cell links nitrogen removal to energy status.
transamination
_ interconverts an AA and a α-ketoacid
oxidative deamination
_ of glutamate releases ammonia for disposal
run backwards with alpha-KG as the acceptor and glutamate as product
How is PLP regenerated to restore enzyme?
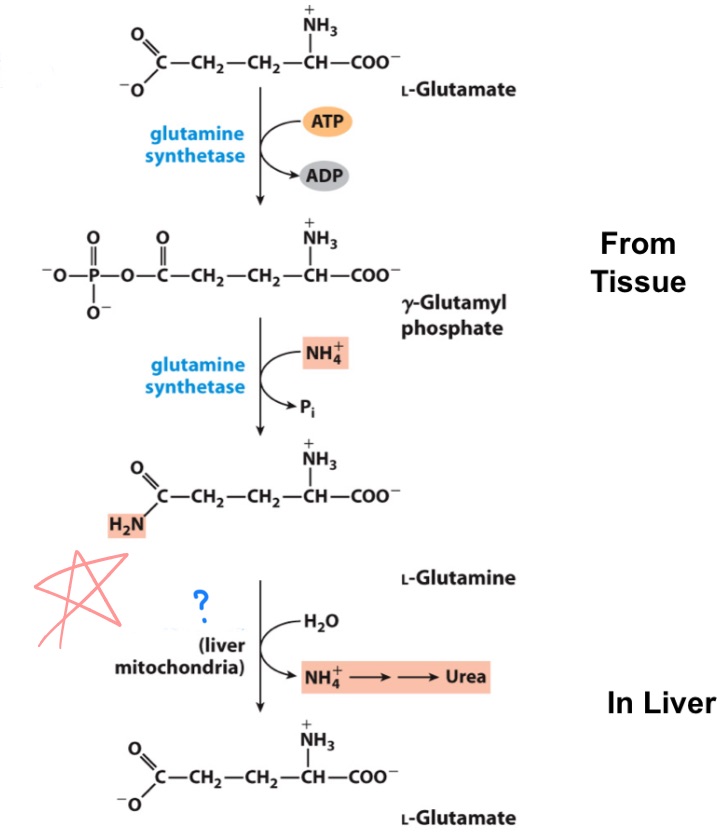
glutaminase
(Glutamine Amidotransferase: a complex of at least 2 subunits:
a glutaminase and a synthase.)
_ will remove the nitrogen on glutamine —> glutamate
fine
Draw Glutamate DH reaction
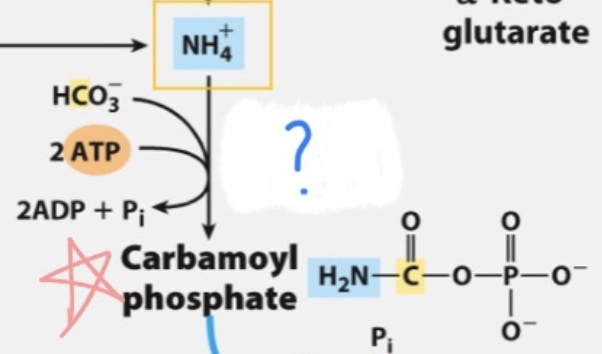
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS1)
_ is an enzyme in the mitochondria that catalyzes the first step of the urea cycle, converting ammonia and bicarbonate into carbamoyl phosphate.
draw entire reaction
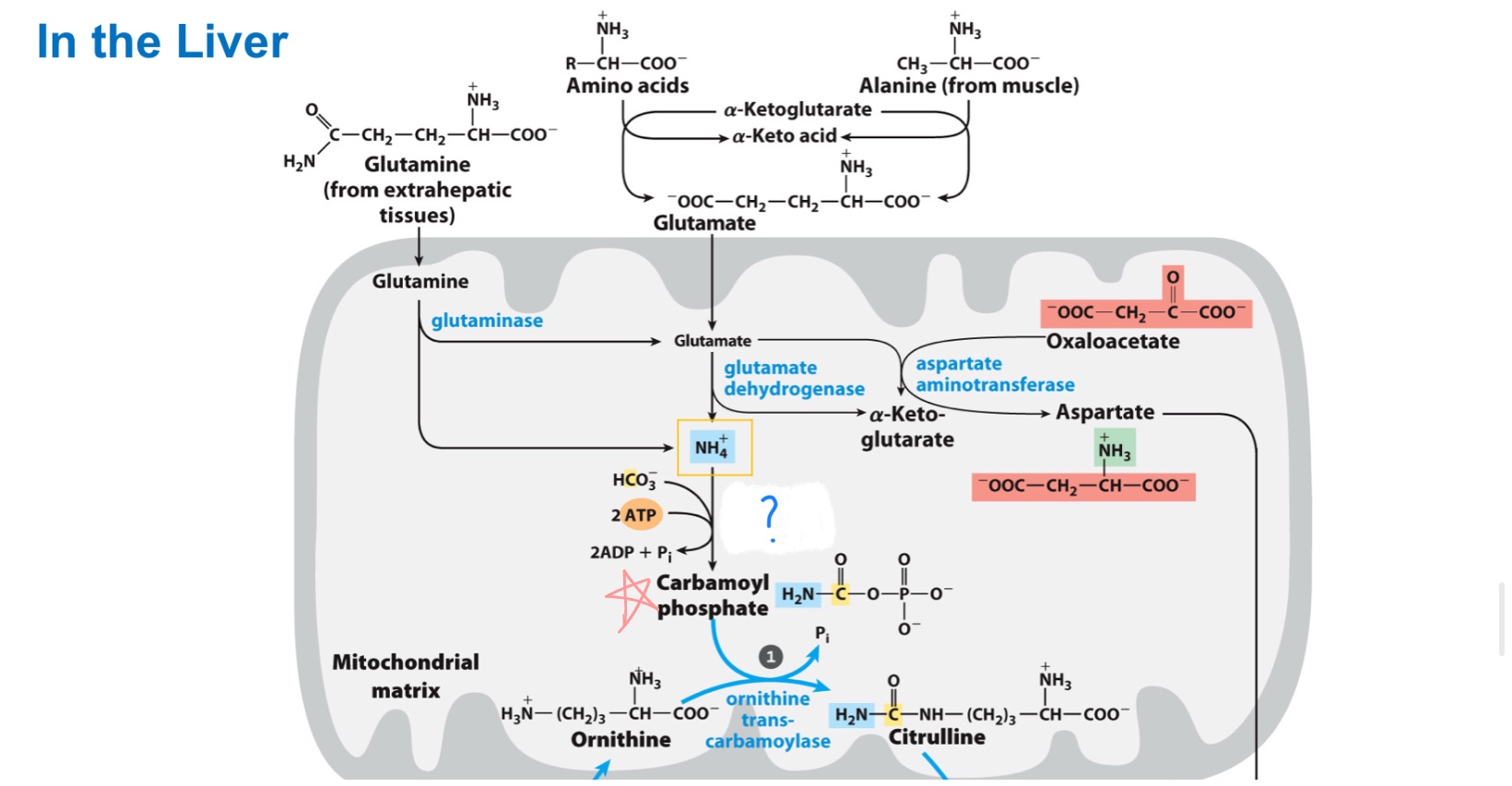
(ammonia recaptured via) synthesis of carbamoyl phosphate
First nitrogen-acquiring reaction of urea cycle …
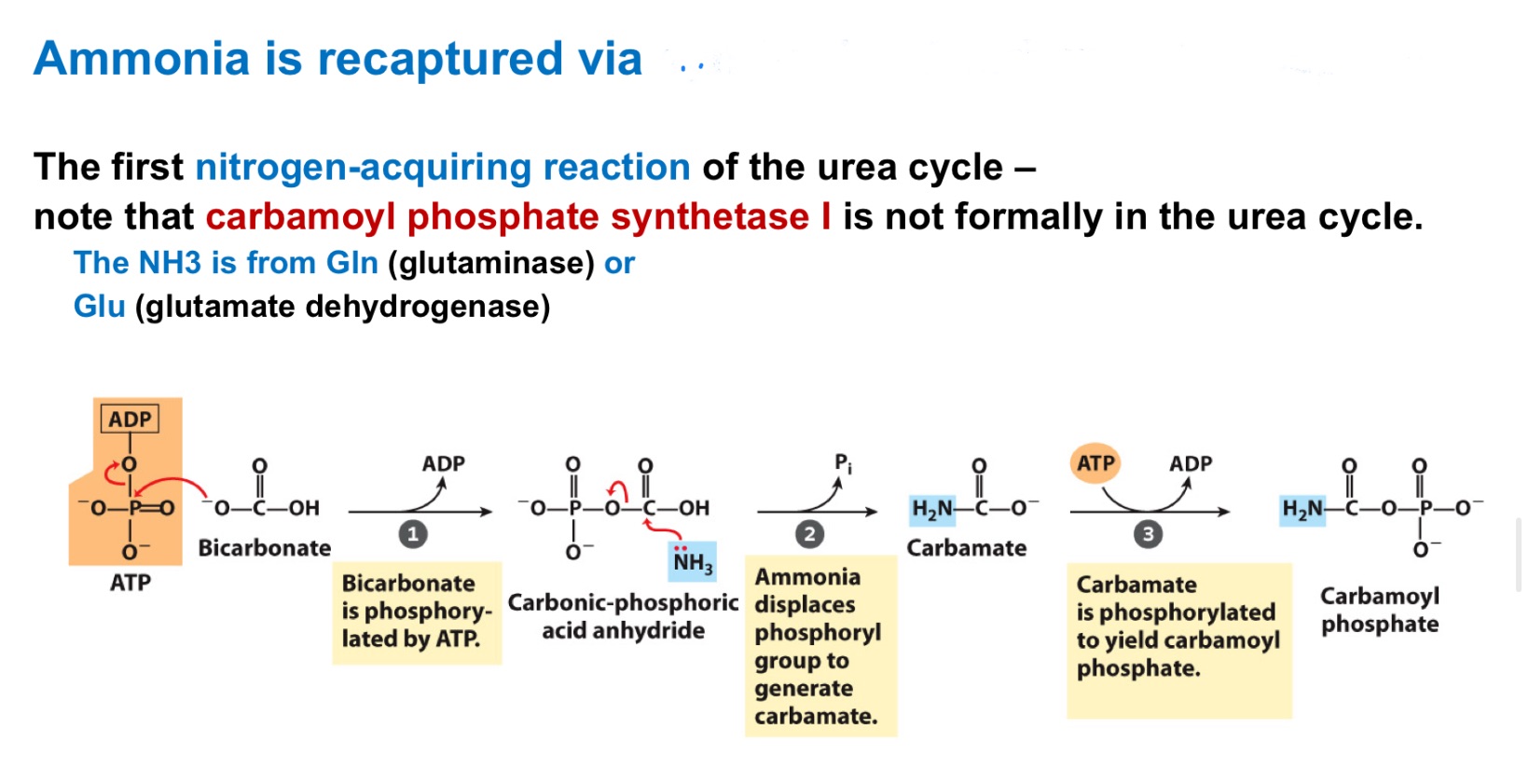
Ornithine transcarbamoylase
Argininosuccinate synthetase
Argininosuccinase
Arginase
Nitrogen from carbamoyl phosphate enters urea cycle.
Enzyme 1: _ , only rxn in mitochondria
Enzyme 2: _ , adenylates citrulline to allow attack from Asp
Enzyme 3: _, generates Arg, releases fumarate
Enzyme 4: _, generates urea, regnerates ornithine
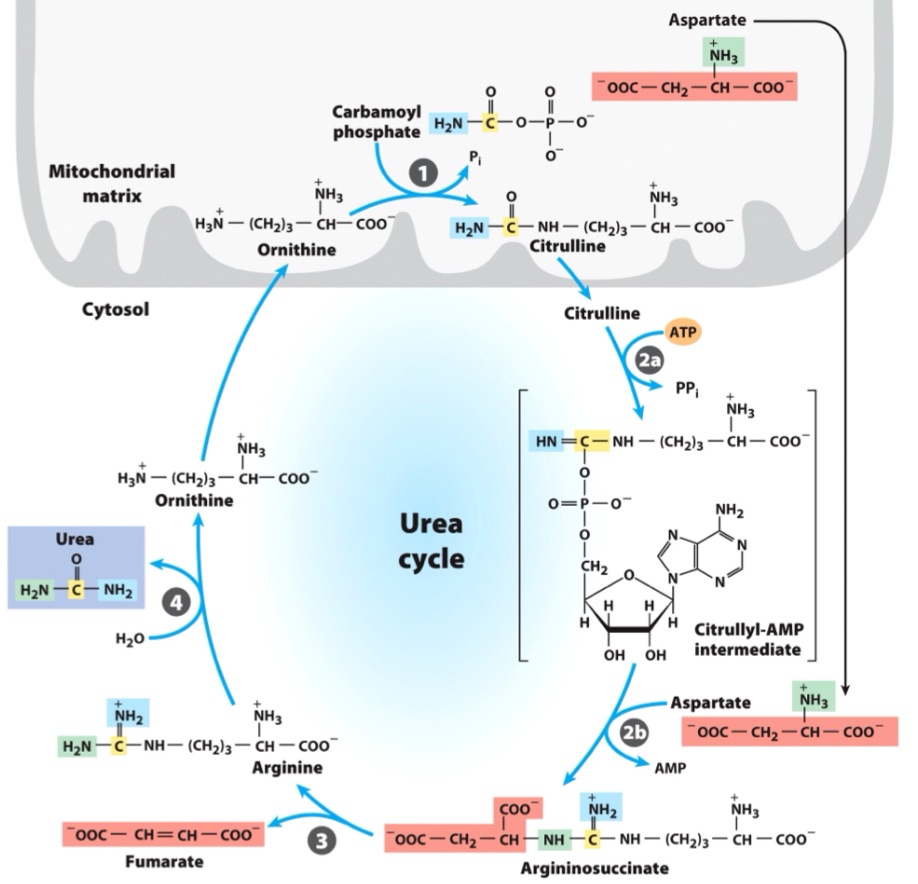
entry of aspartate (into urea cycle)
second nitrogen-acquiring reaction in urea cycle?
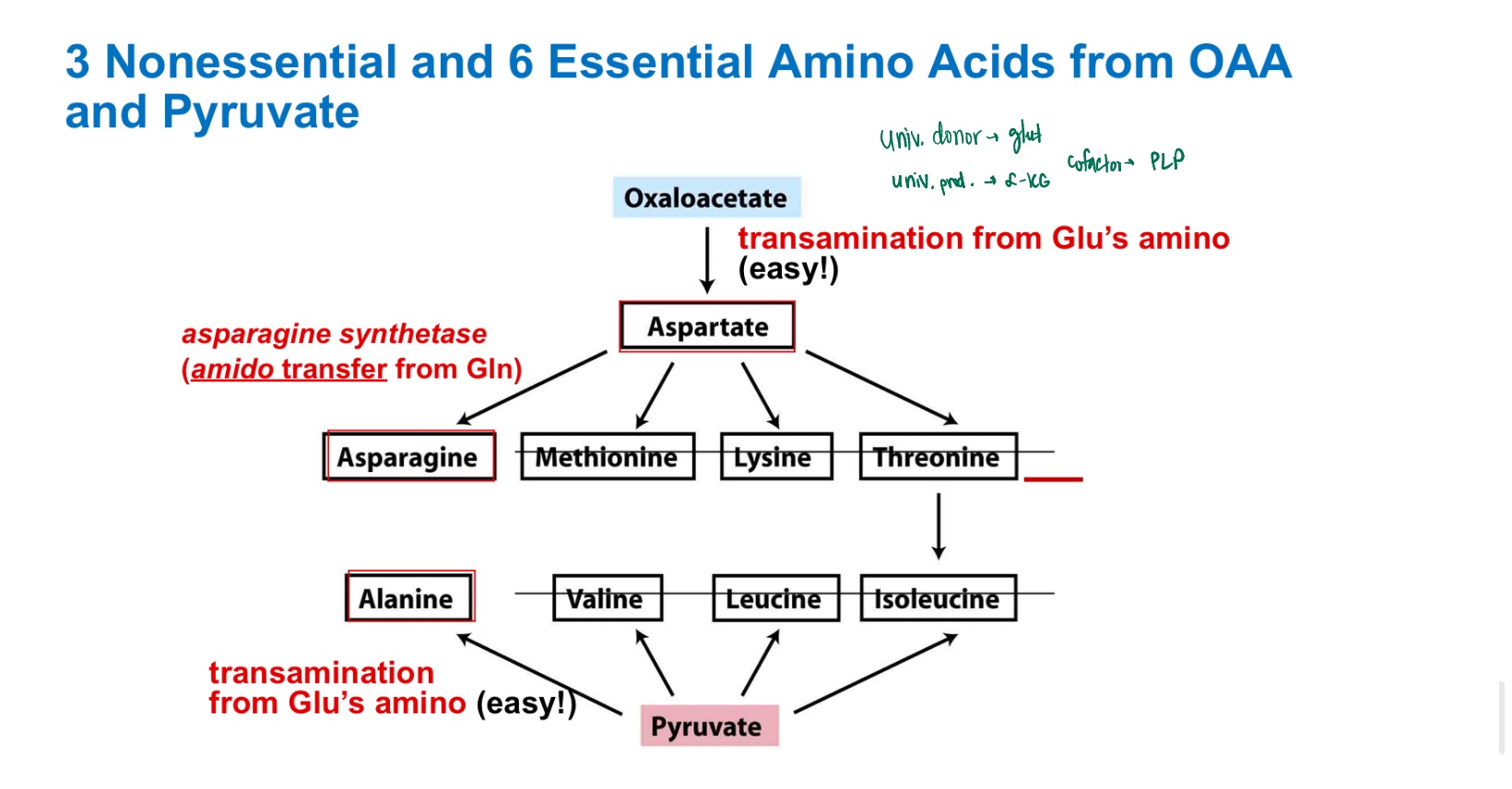
ala
asn
asp
glu
ser
Nonessential AA’s?
H, I
Leu, Lys
M, P
Thr, Trp
V
essential AA’s?
alanine
pyruvate precursor?
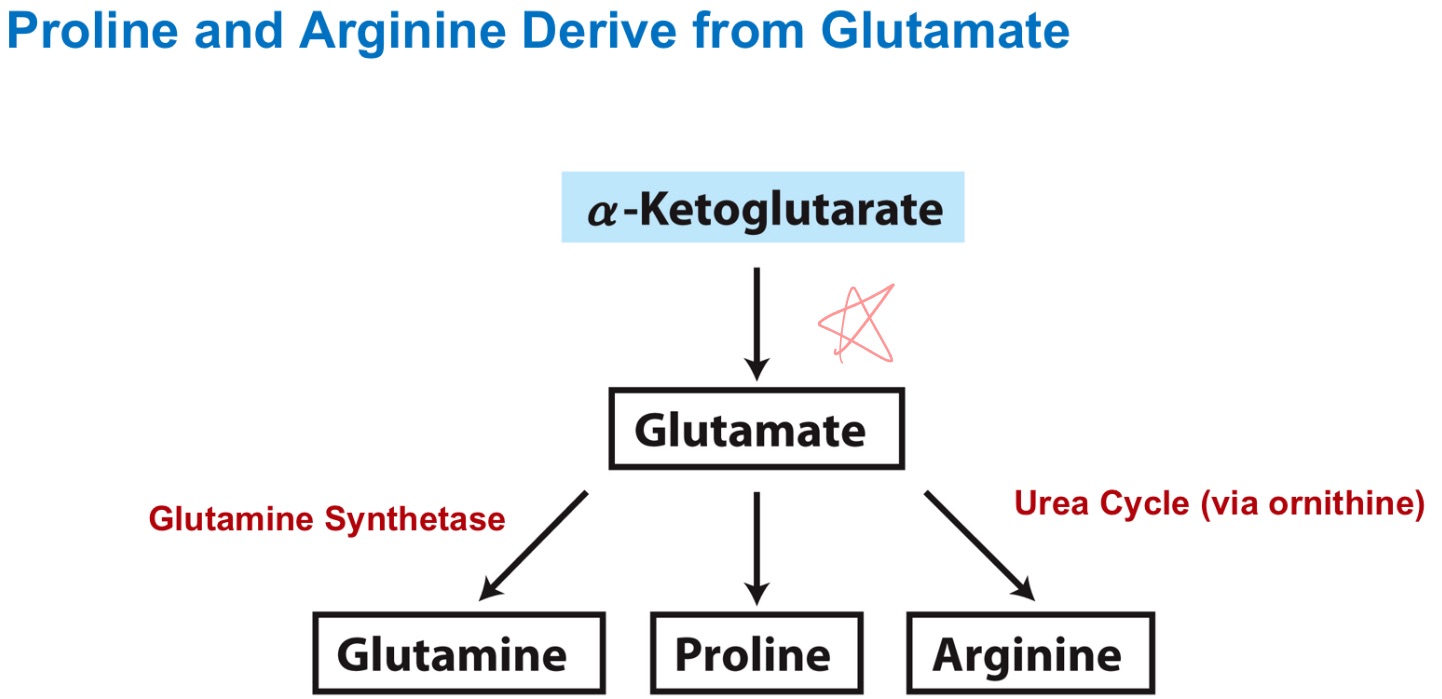
glutamate
glutamine
proline
arginine
α-Ketoglutarate precursors?
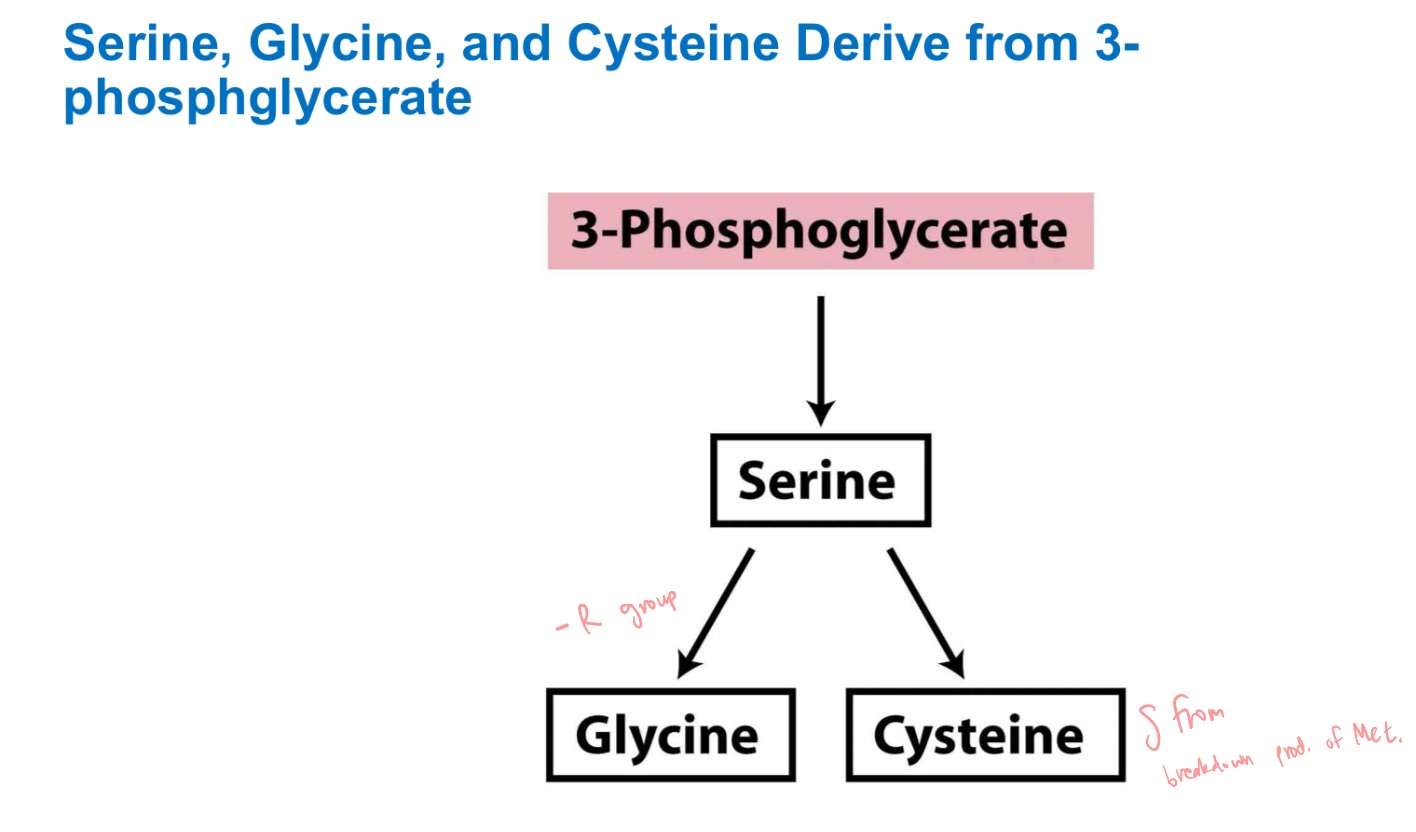
serine
glycine
cysteine
3-phosphoglycerate precursors?
aspartate
asparagine
Oxaloacetate precursors?
starving / bad diet
(insufficient AAs)
negative nitrogen balance indicative of?
growth (excess dietary AAs)
positive nitrogen balance indicate of?
acetoacetate
Leucine and Lysine are precursors of …
aspartate (via urea cycle)
fumarate precursor?
α-KG —> glutamate —> proline or arg (via urea cycle!!)
How are Pro and Arg derived from Glutamate?
Draw glutamate to proline (no int steps)
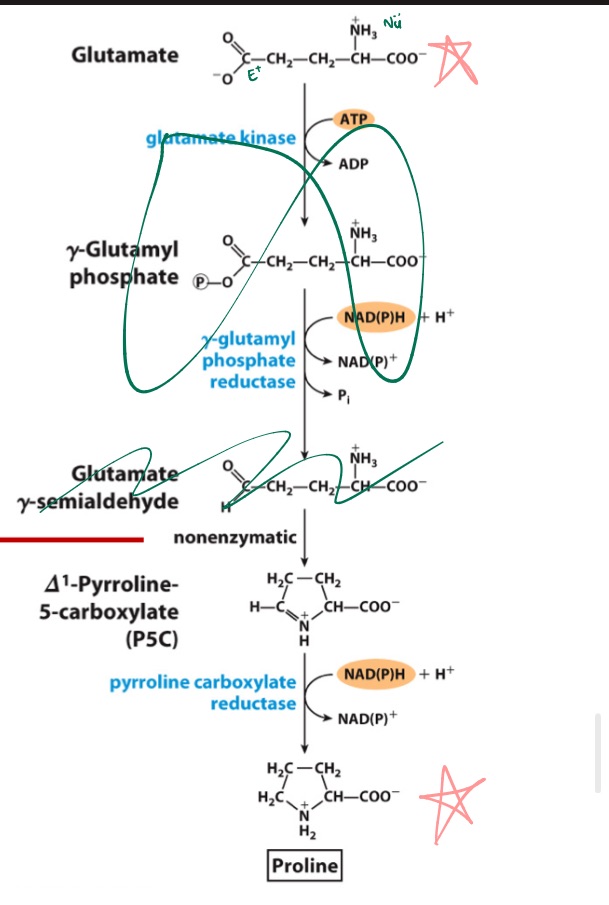
Glu
… from _
MEMORIZE PIC
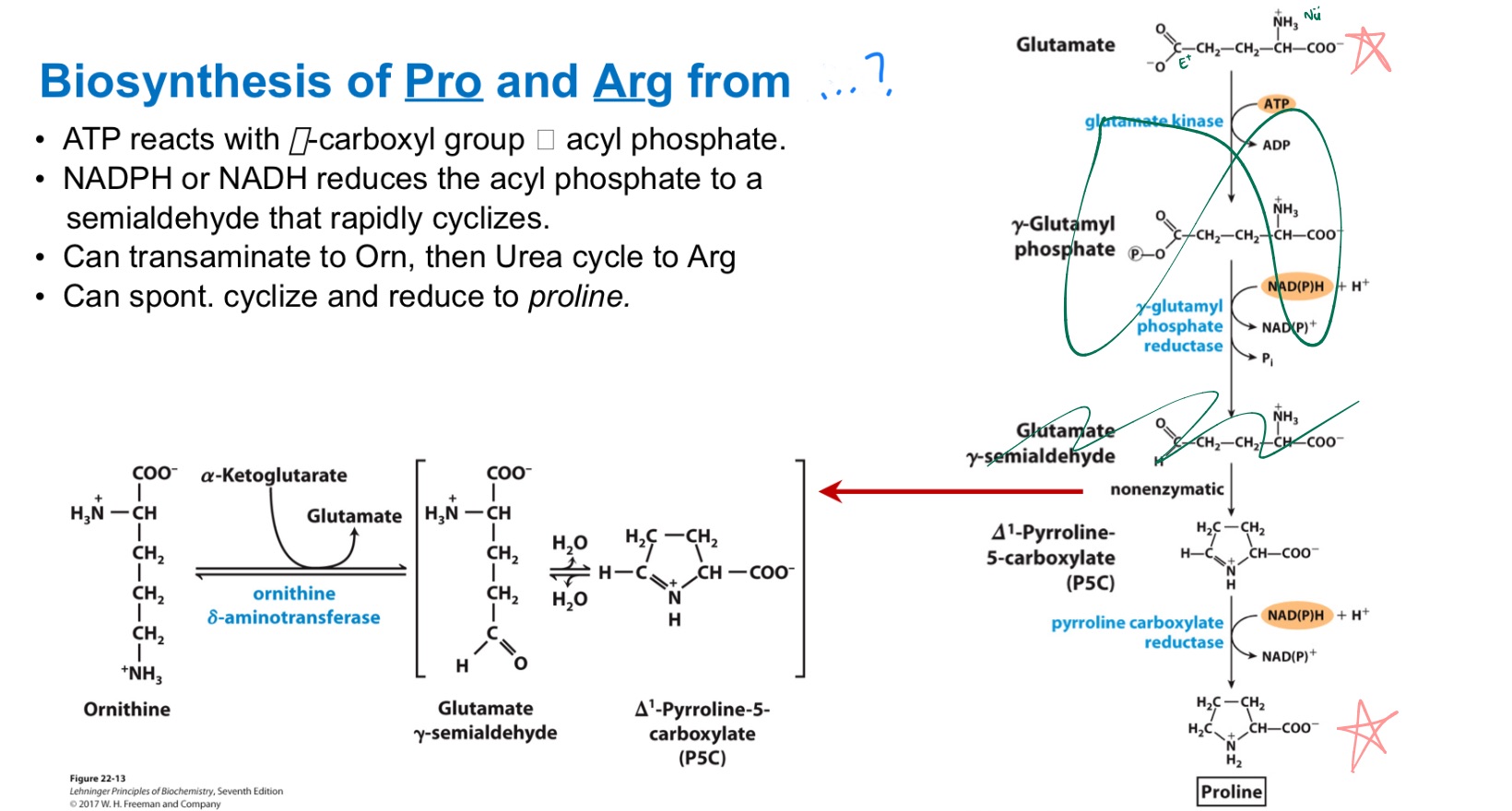
ok
Draw Asn from Asp from OAA!
and backwards!
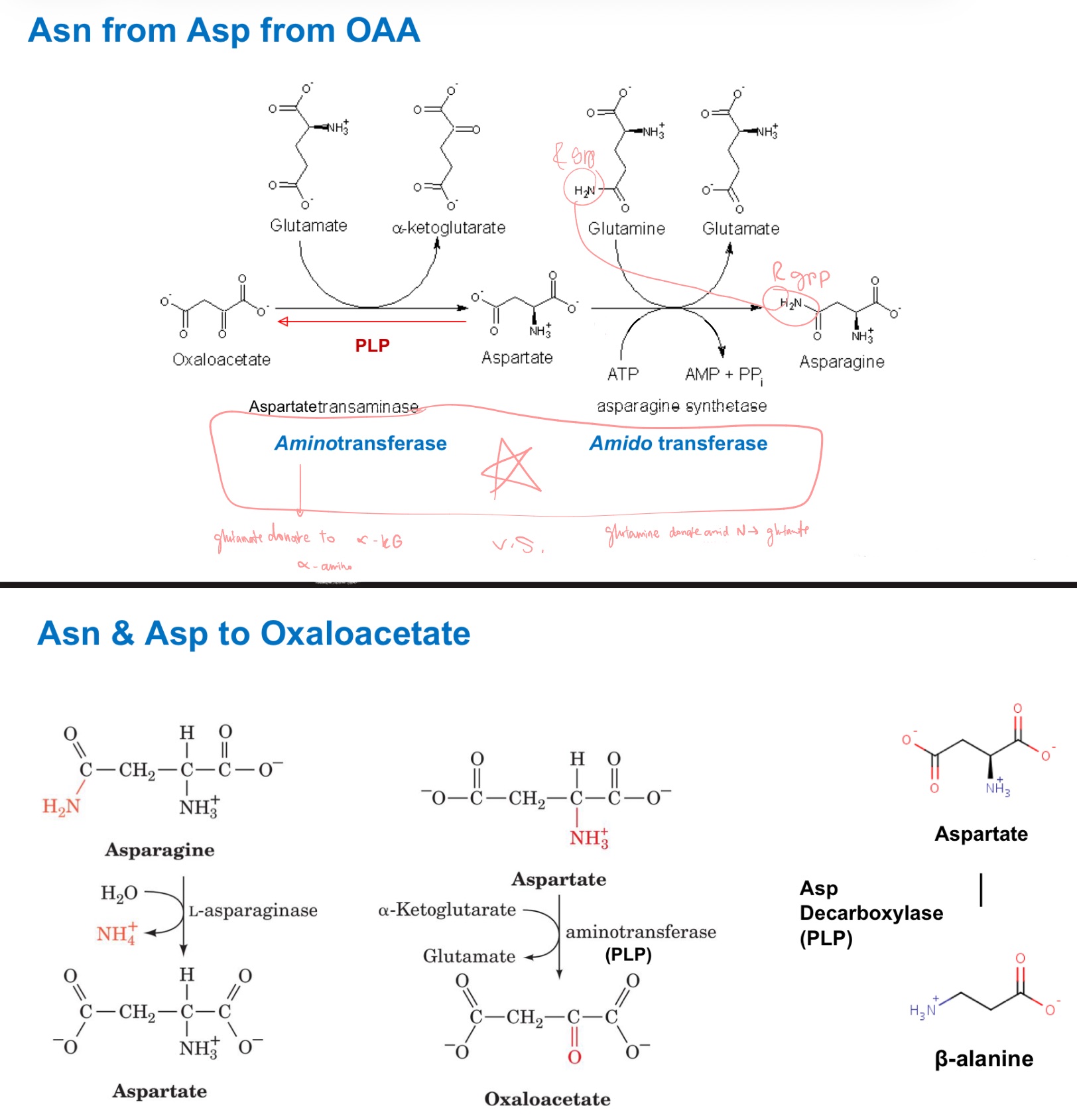
inorganic ammonia
N source of glutamine?
glutamine
N source of asparagine?
3-PG of glycolysis
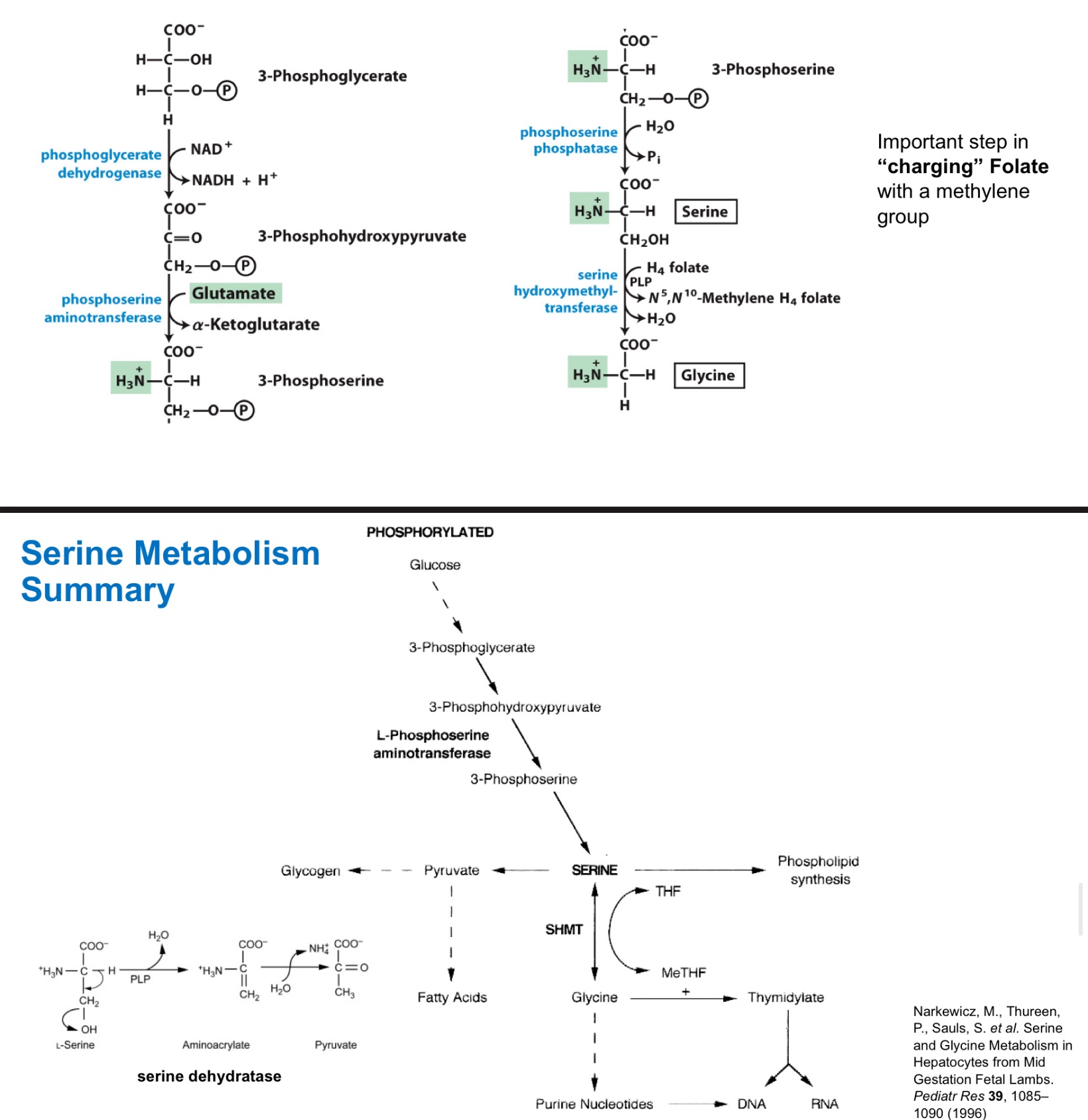
serine derives from …
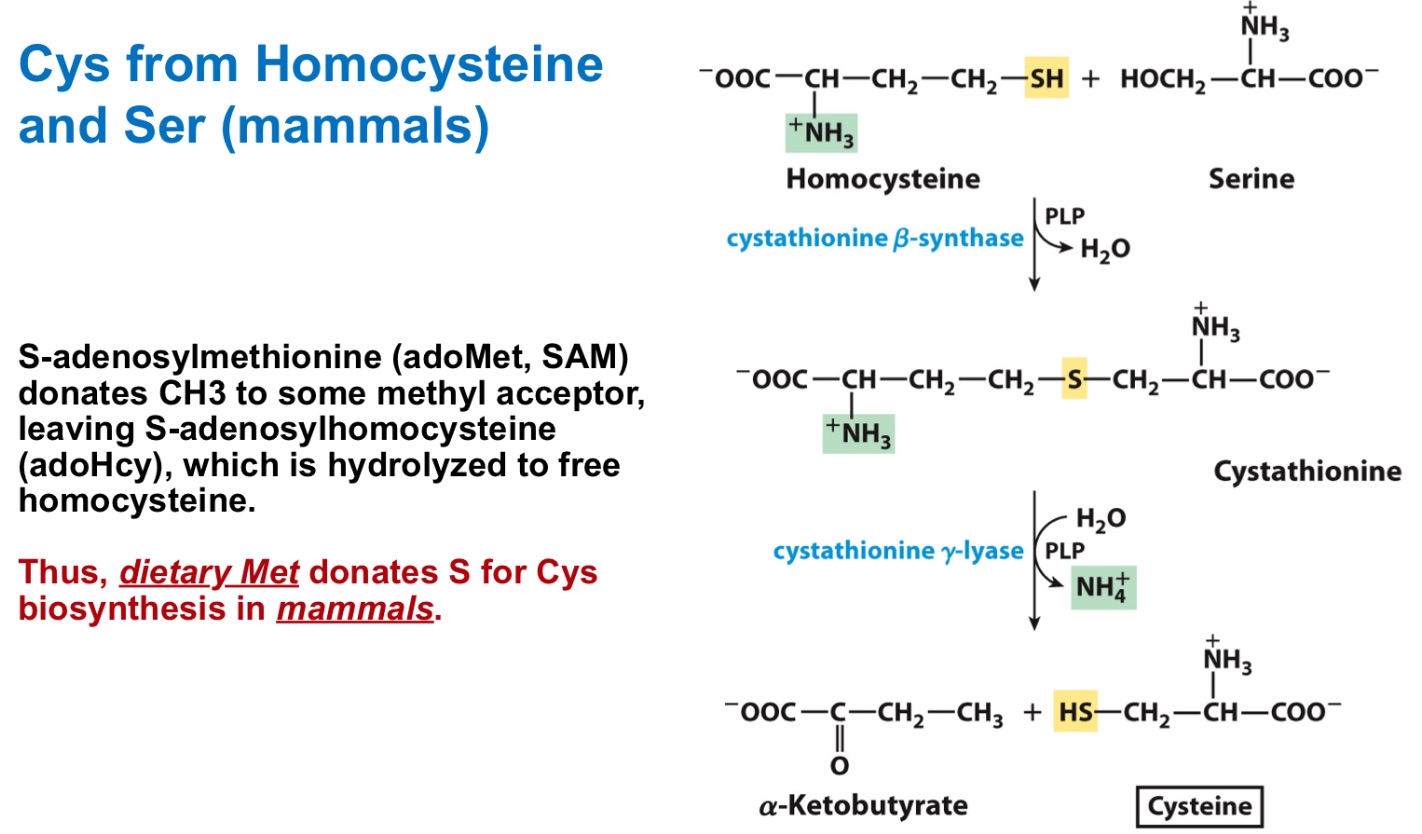
Homocysteine and Serine (in mammals)
Cysteine derives from _ + _
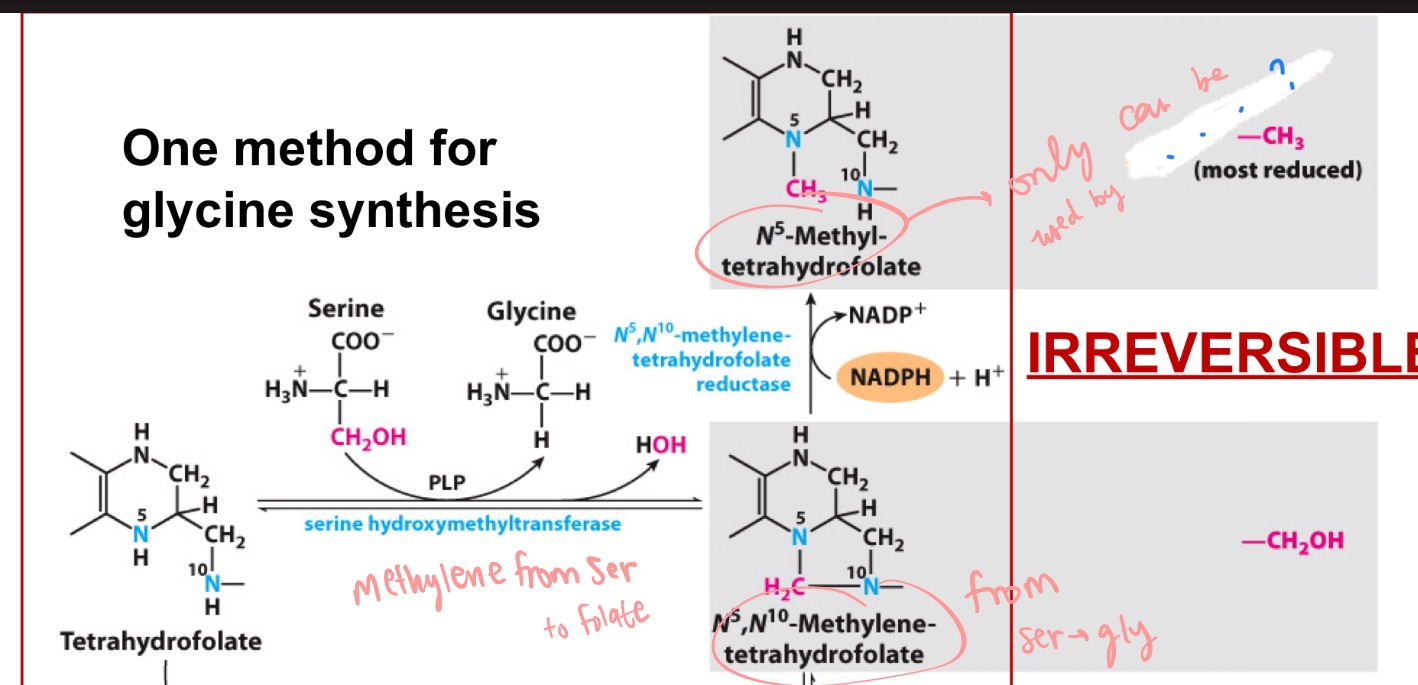
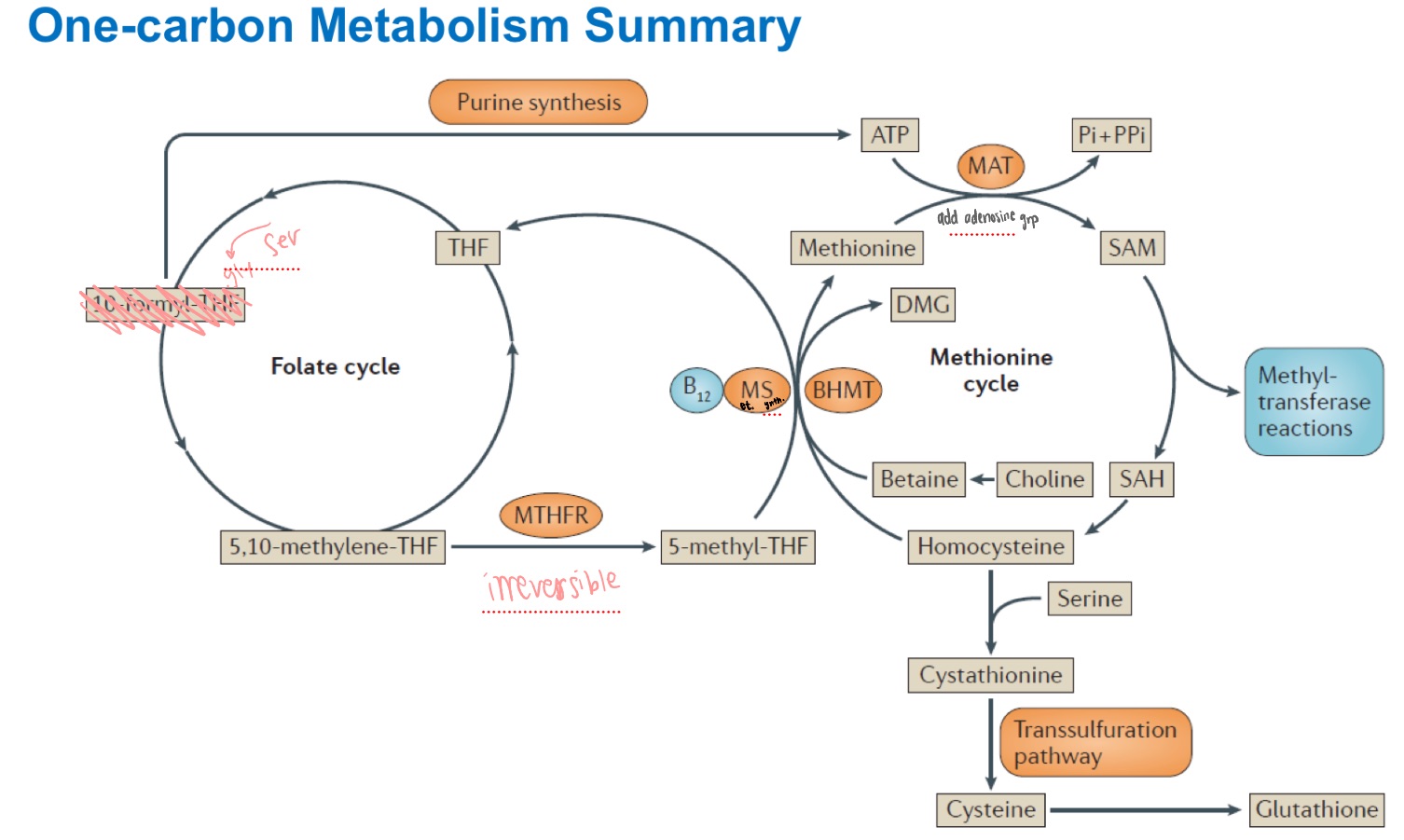
Folate is versatile but not potent/powerful
SAM is not versatile (only transfers methyls) but is very strong
Folate vs SAM?
folate
_ can transfer a carbon in many oxidation states (methyl, methylene, formal-), but is not a good transferase.
it’s a 1-C carrier
N5-methyl THF
Reduction of:
N5,N10-methylene THF —> ____
is irreversible
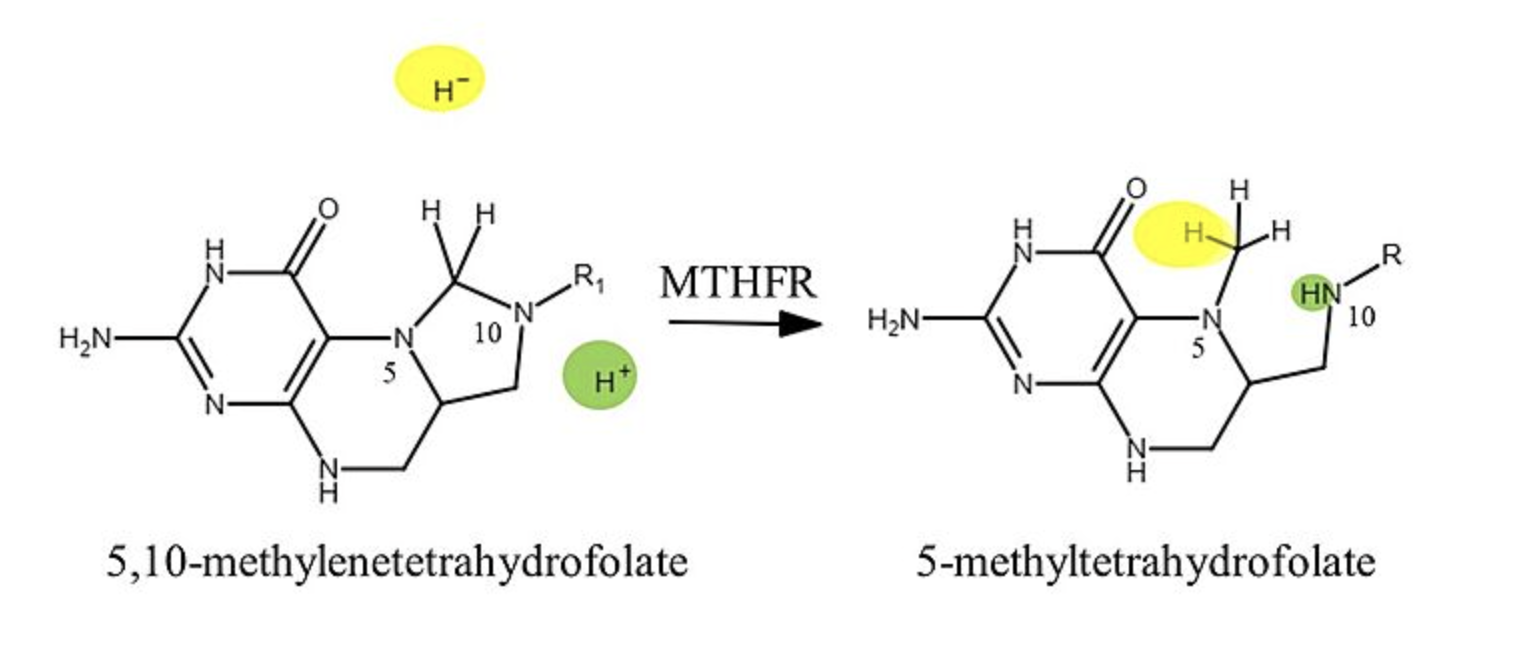
methionine synthase
N5-methyltetrahydrofolate can only be used by which enzyme?
Met. Synth. can only make methionine out of methionine
(While methionine synthase can convert homocysteine back to methionine, this conversion relies on other nutrients like folate and vitamin B12, and it's the overall balance of incoming dietary methionine and its subsequent use that determines nutritional status.)
Why is methionine an essential amino acid if Methionine Synthase is an enzyme that makes methionine in the body?!
homocysteine ; N5 THF
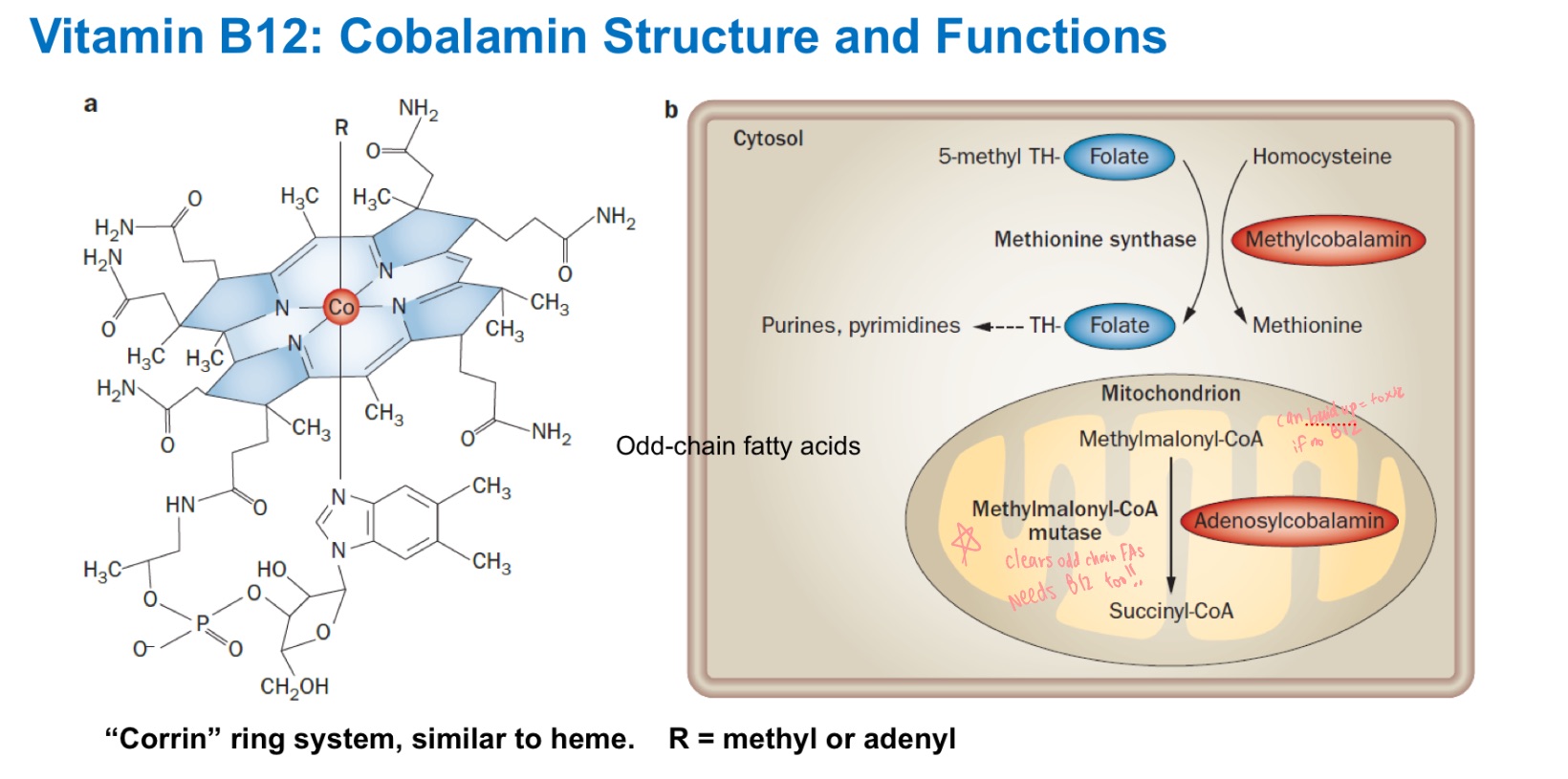
B12
Methionine Synthase requires _, _,
and _ (MOST IMPORTANT)
Homocysteine
_ is derived from methionine but is also required for Methionine production
B12
Lot of folate in diet/body, but N5 accumulates?
Deficiency in _, leading to failure to convert to Met and produce THF
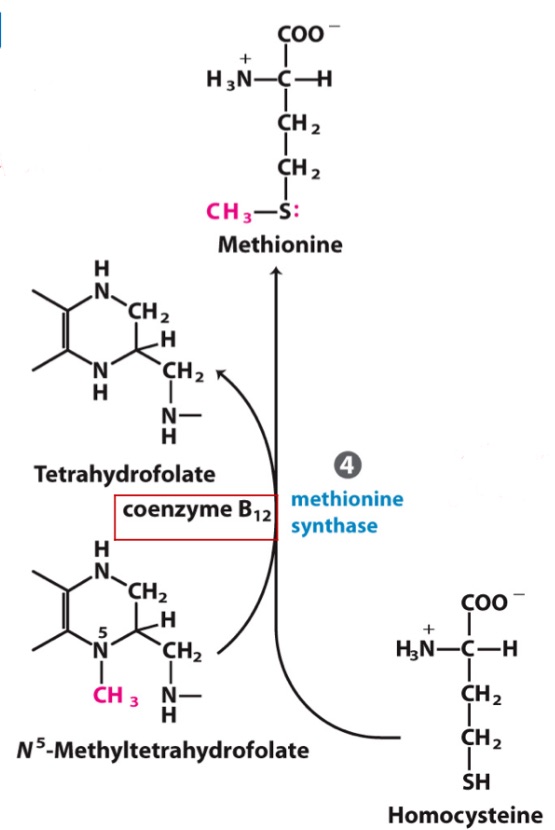
B12-dependent methionine synthase
Cysteine synthesis pathway
When homocysteine levels are high, 2 pathways to rid of?
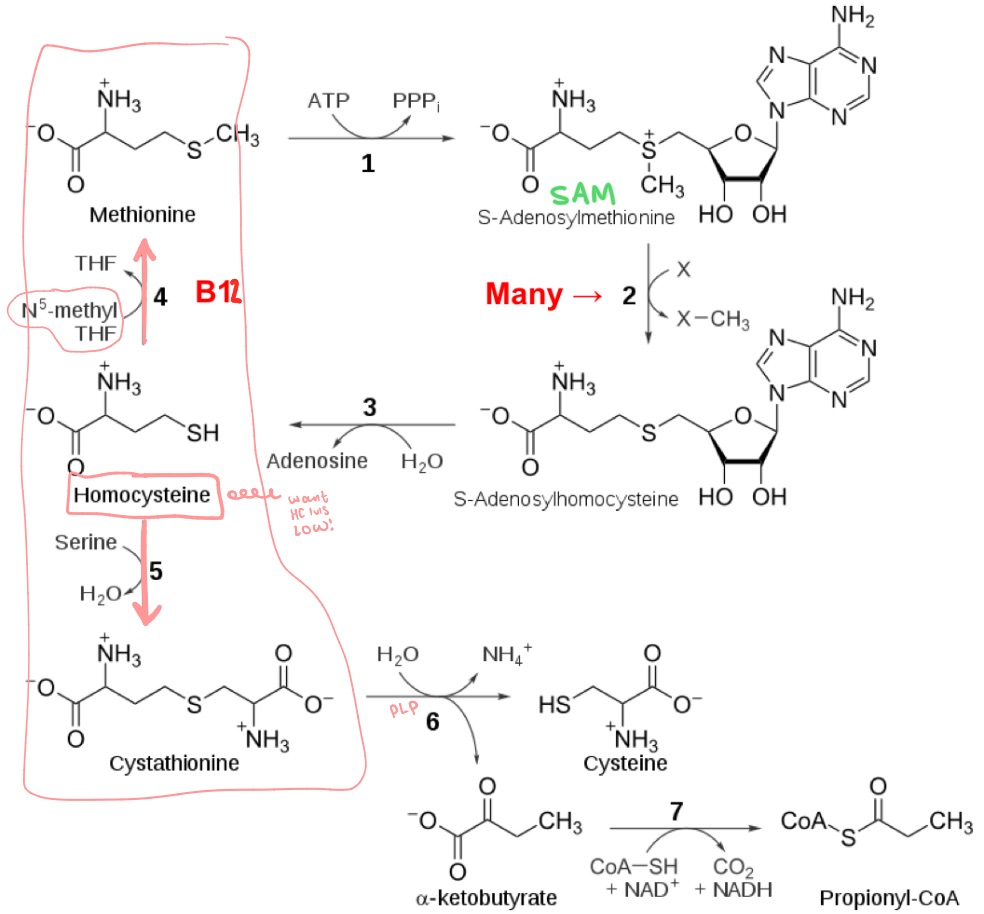
Methionine
(which came from homocysteine, which came from SAM)
Where did cysteine’s sulfur come from?
Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase
Methionine synthase enzyme requires B12. What other enzyme requires B12?
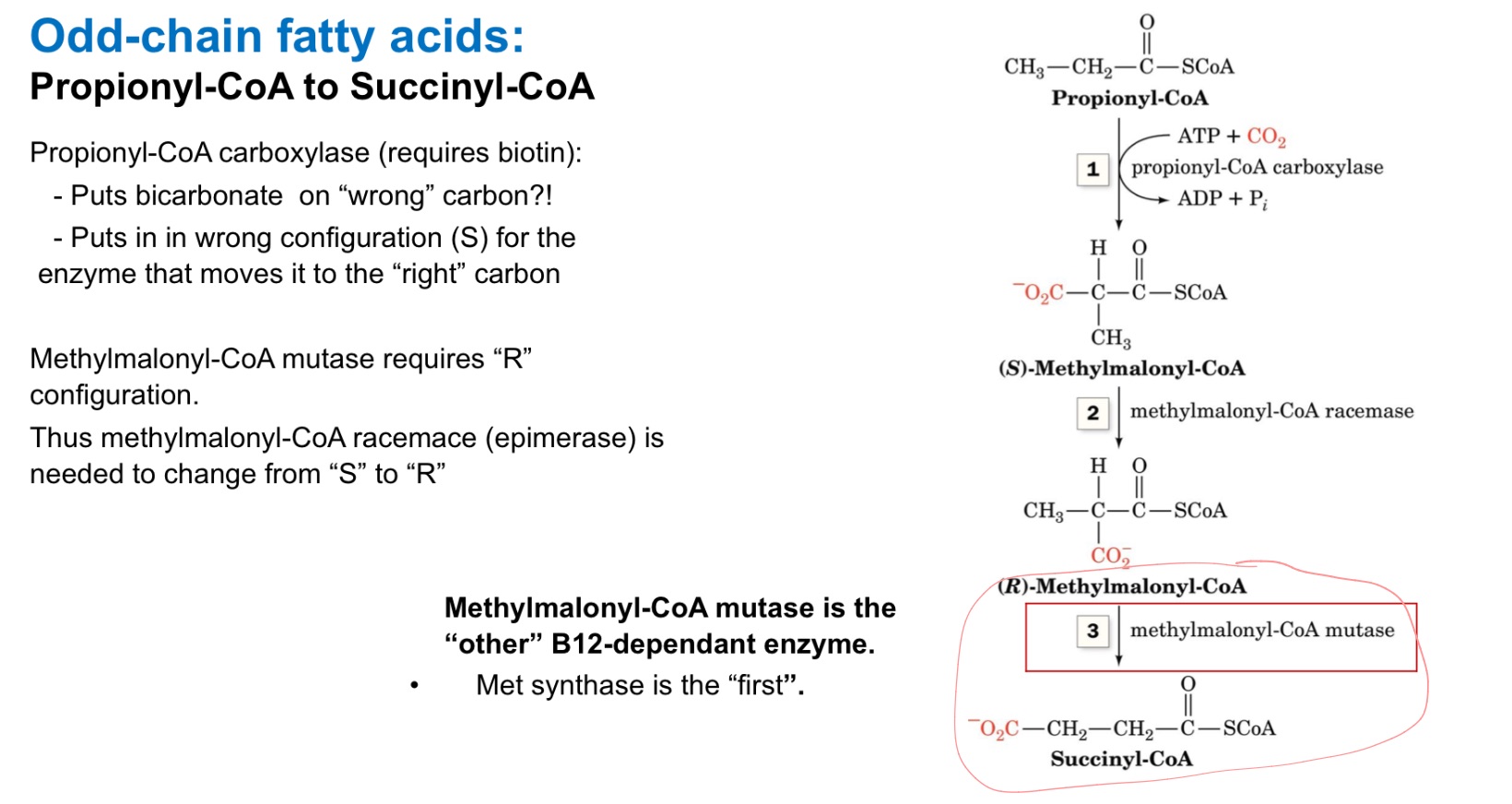
Clears odd chain FAs
(methylmalonyl-CoA —> Succinyl-CoA)if no B12, buildup —> toxic
What does methylmalonyl-CoA mutase do?
Why would it build up?
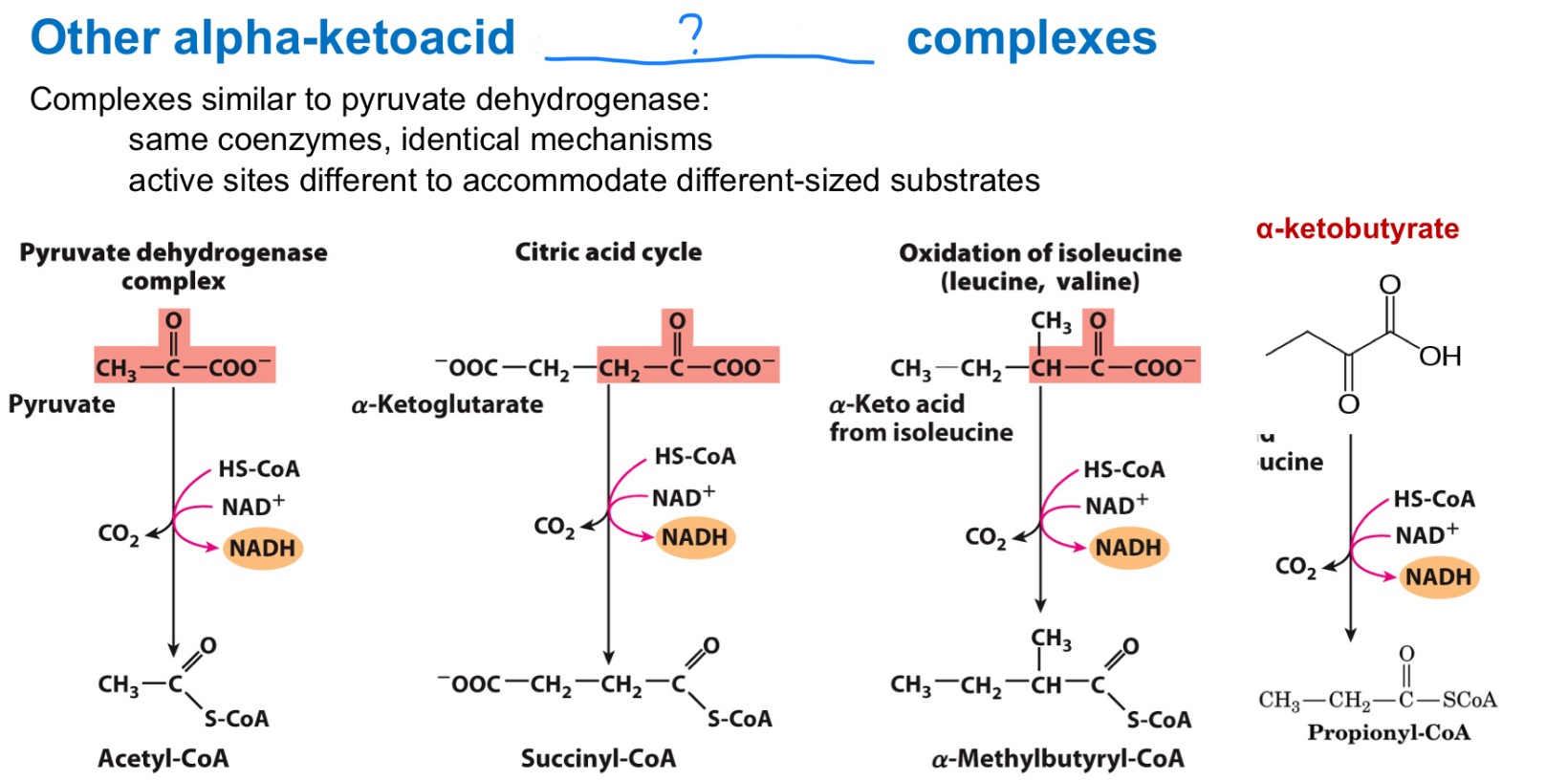
dehydrogenase
Look at all these _ complexes!
irreversible reduction
5,10methylene-THF —> 5-methyl-THF is _
Folate ; Methionine
_ and _ cycle summary
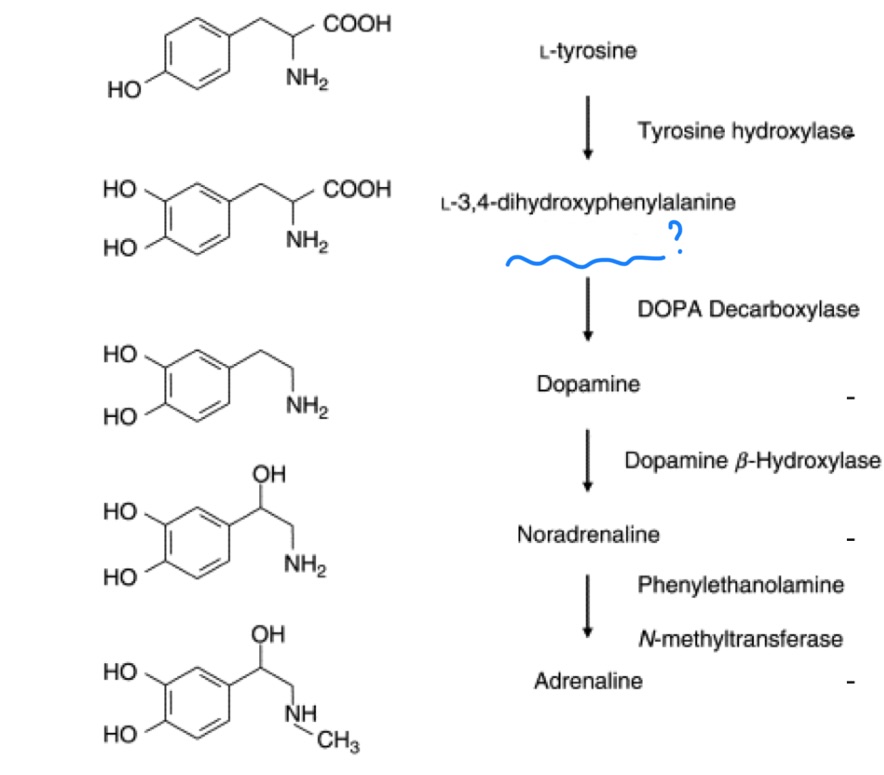
tyrosine hydroxylase
RLS enzyme of dopamine production?
uses iron intermediate
dopamine
_ is a precursor for norepinephrine and epinephrine
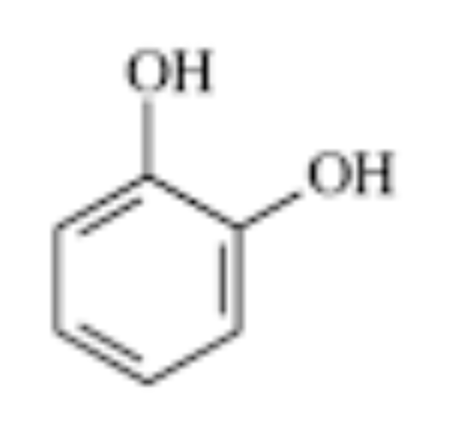
catechol
this is a _ group
L-DOPA
precursor for dopamine called?
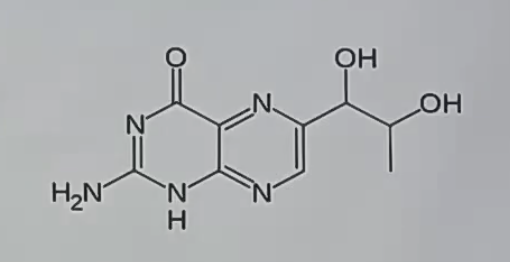
biopterin
_ is a cofactor for aromatic AA hydroxylase enzymes
ascorbate
Vitamin C = ?
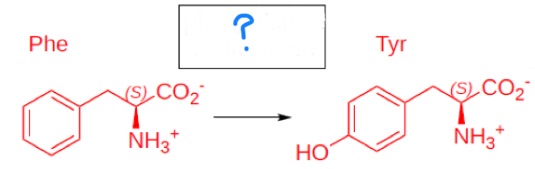
phenylalanine hydroxylase
fill in blank
PKU
phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency —> ?
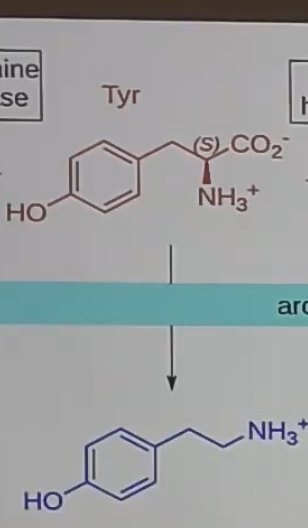
tyramine
decarboxylase tyrosine to get _
biopterin and iron
2 cofactors of tyrosine hydroxylase?
aromatic L amino acid decarboxylase (AADC)
L-DOPA —> dopamine by what enzyme?
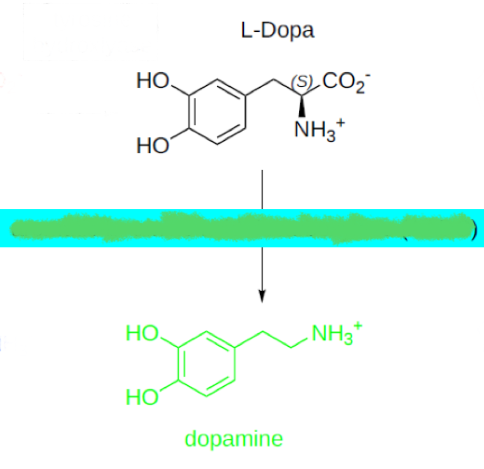
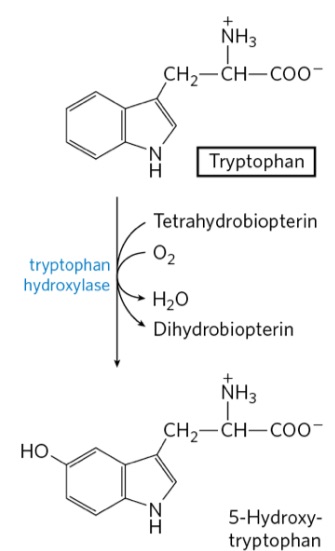
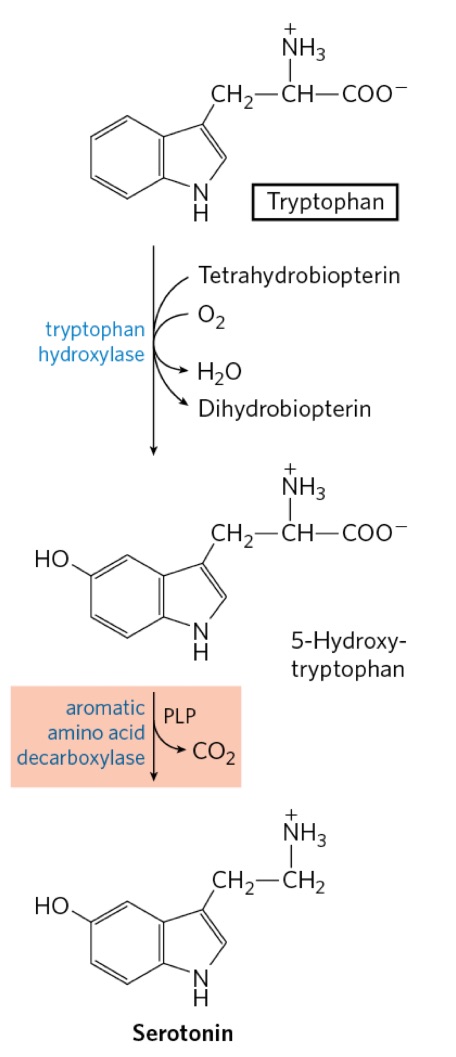
serotonin
who dis?
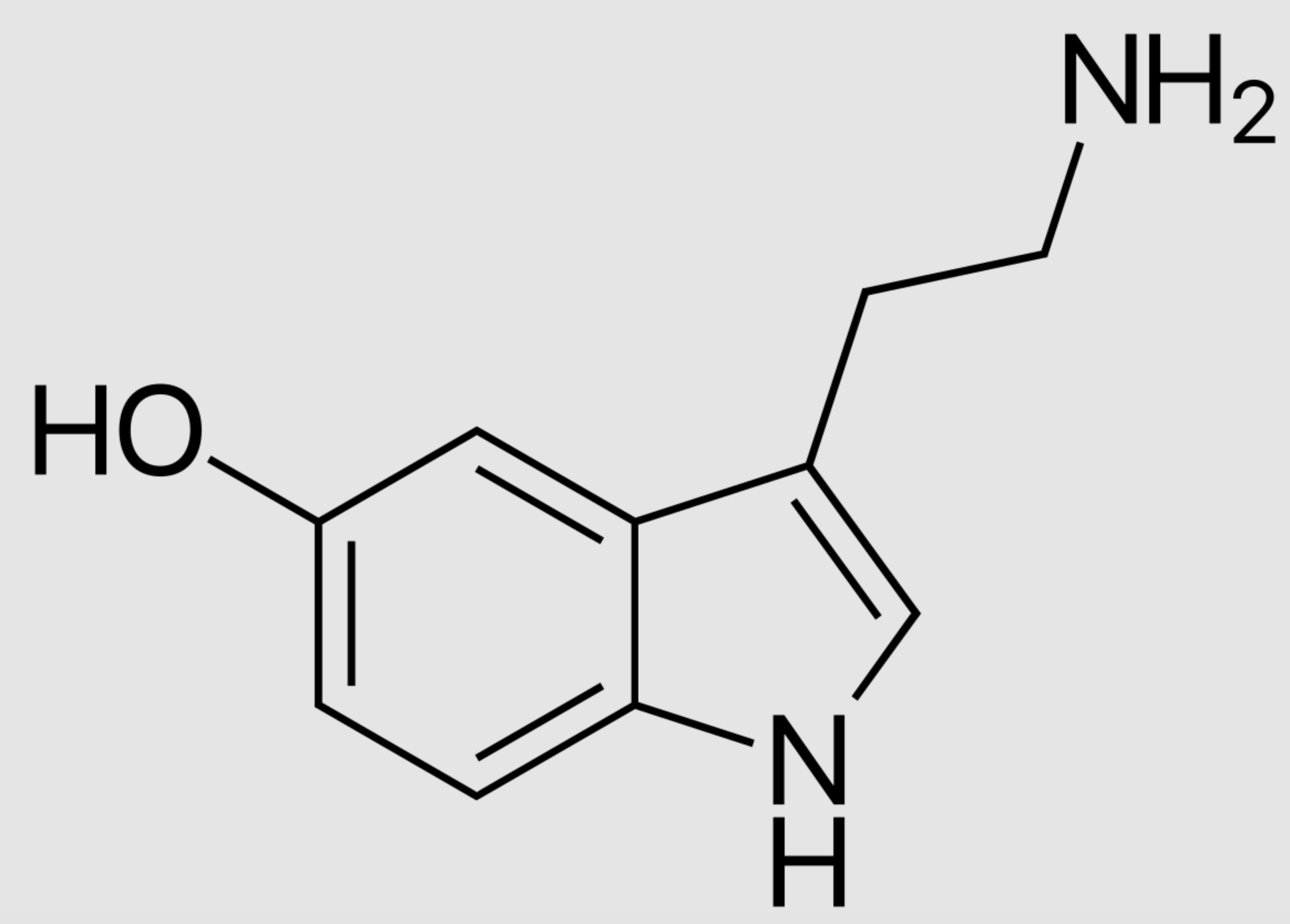
tryptophan
who dis?
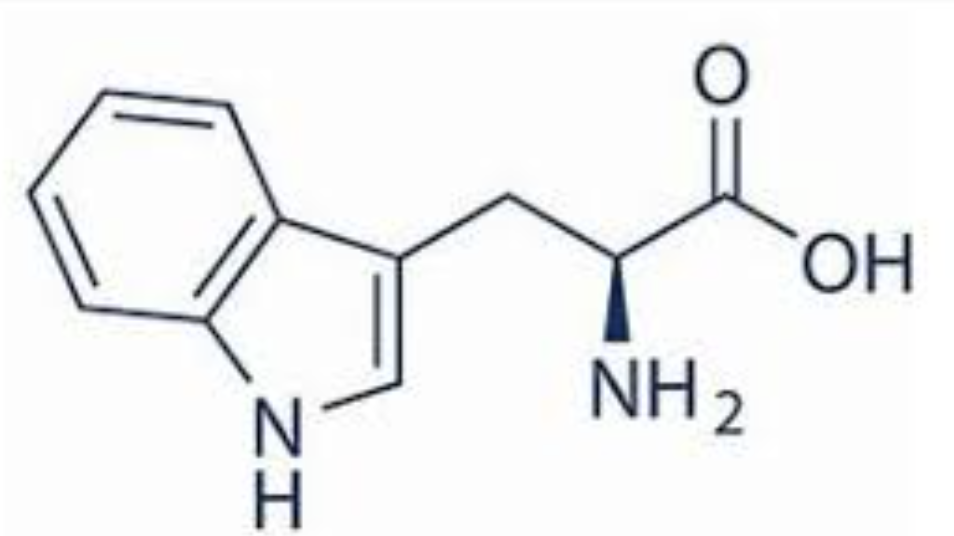
PLP
cofactor for transaminations and decarboxylations?
monoamine oxidase
enzyme in first step of oxidative deamination?
FAD required, H2O2 produced
inhibitory
GABA is a _ NT
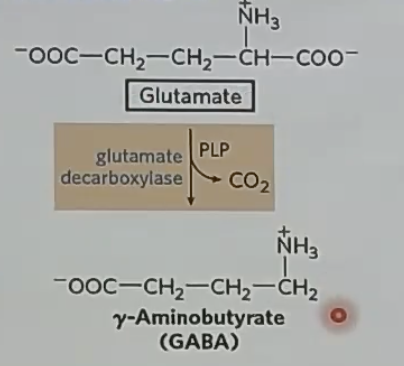
stimulatory
Glutamate is a _ NT
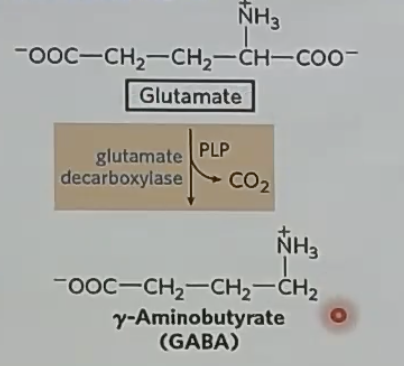
decarboxylation
histidine to histamine is a _
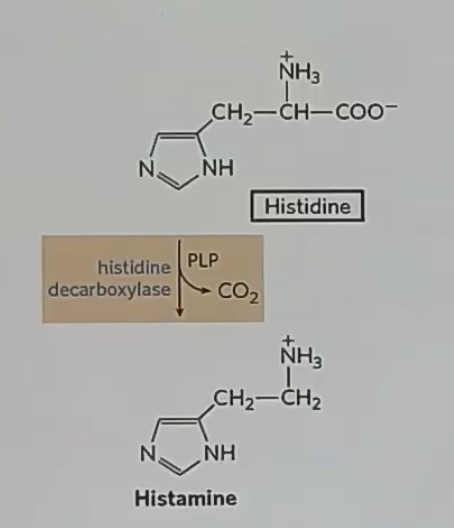
oki
Draw Trp to Serotonin!
MAOI
after serotonin reuptake, can be destroyed by _ --> blood --> kidneys --> urine
monoamine oxidase
_ turns dopamine amine into a carboxylic acid (DOPAC)
increase
blocking MAO with MAOI can _ monoamines
dopamine
norepinephrine
serotonin
name the three monoamines
VGLUT
(vesicular glutamate)
Eat glutamate from diet, use as NT, pack into vesicle using _.
Then depolarization occurs, Ca2+ release triggers exocytosis of NTs.
kainate, AMPA, NMDA
glutamate receptors (3) …