A&P Chapter 4,5,6,7
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
Ciliated epithelium
Sweeps dust and pathogens from the trachea
Synovial fluid
Prevents friction in joints
Goblets cells that secrete mucus
What does the lining of the trachea have?
Dermis
bottom layer of skin
sebum
What is secreted by the sebaceous gland?
touch and pressure
The nerve ending encapsulated receptors in the skin are for?
synergistic
Muscles with same or similar functions
muscle tone
State of slight contraction that depends upon nerve impulses
circulatory
System transports oxygen to the muscles and takes carbon dioxide
Antagonists
Muscle with the opposite functions
manubrium, body, and xiphoid process
_____, _____, and _____ make up the sternum
no
Is ossification complete at Birth
Goblet cells
Secrete mucus in the respiratory tract
Epidermis
top layer of skin
Keratin
What prevents entry of water and pathogens and loss of water?
drying
Sebum protects the skin from ________.
Hair shaft
1
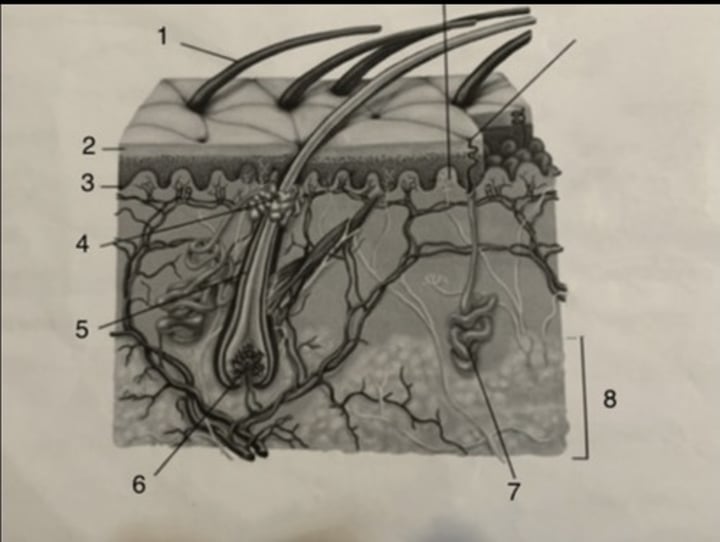
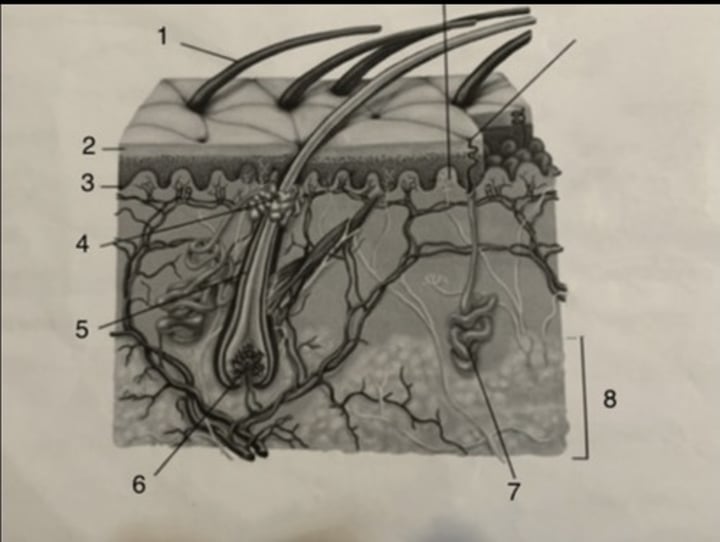
sweat gland
7
muscle sense
having a mental picture where your muscles are
they have the same function
two muscles are called synergists if
Diffusion of gas
Simple squamous epithelium causes _____ in the lungs?
Cilia
Opens the airway in the trachea
Transitional epithelium
Lines the urinary bladder and undergoes cell formation changes
Stratified squamous epithelium
The oral cavity and the esophagus is aligned with what?
Fibrous connective tissue
Forms strong tendons
Brown adipose
Heat generating tissue
Mucous
Lines all body cavities
Microvilli
Increases surface area for absorption in the small intestine
Peristalsis
Waves of contraction in smooth muscles of the small intestine
Spleen
May destroy older blood cells
Bone Marrow
Produces white blood cells
No
Is skin a major nerve tissue?
Dendrites
Carry impulses towards the cell body
Axon
Carries impulses away from the cell body
Cell body
Contains the nucleus and is essential for life in a neuron
Cartilage
What type of tissue keeps the trachea's airway open and provides a smooth surface in joints.
Cuboidal epithelial tissue
Kidney tubes are part of this type of tissue
Bones
Support the body
Capillaries
Nourish the surrounding bone in joints with cartilage
Keratin
What type of molecule makes the skin waterproof?
melanin
UV rays stimulate the production of?
melanocytes
melanin cells are called
Epidermis
What prevents entry of pathogens?
dermis
What layer of the skin contain sweat glands and sensory receptors?
subcutaneous tissue
what part of the skin connects skin to muscle?
no
Does the integumentary allow water to enter our body?
collagen
What gives strength to the dermis?
produces more skin
What is the function of the stratum germinativum?
langerhans
WBC and ________ are defensive cells.
Dehydration
What is the consequence of sweating to much?
no
Are sweat glands only activated by heat?
expand
What do arterioles do when body is warm?
constrict
What do arterioles do when body is cold?
stratum corneum
2
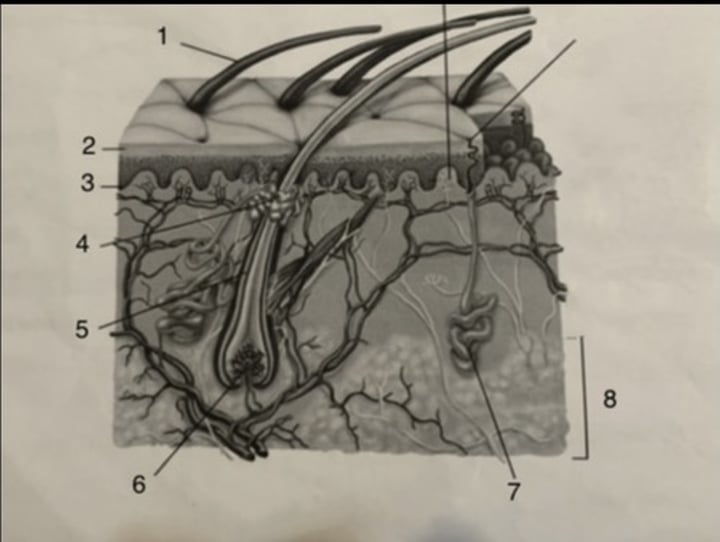
stratum germinativum
3
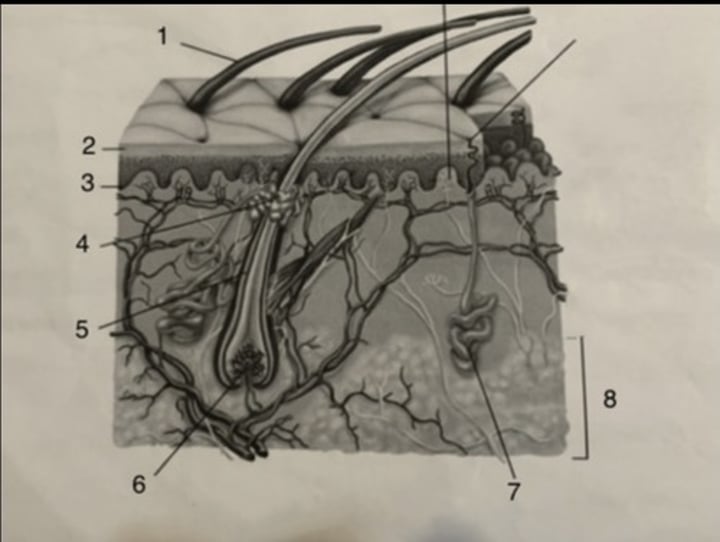
hair follicle
5
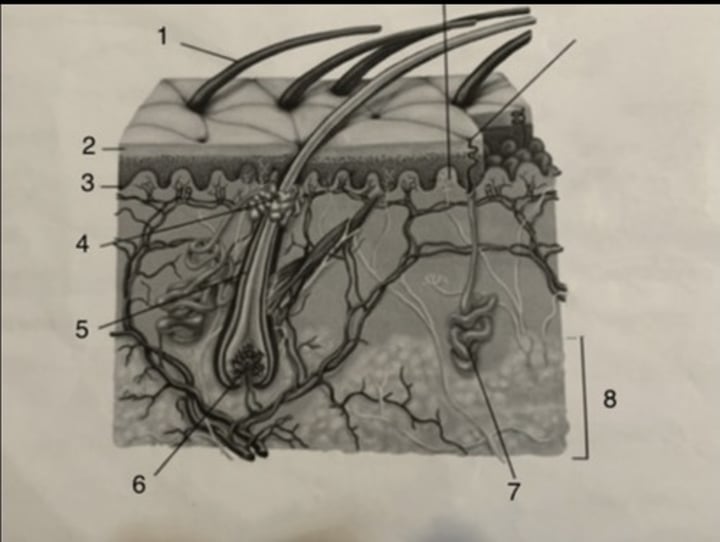
subcutaneous tissue
8
antagonistic muscles
Muscles with opposite functions
muscle tone
About 25% of the bodies heat is at rest is produced by the ________ _______ of a skeletal muscle
Digestive
System that's not necessary for the function of the muscular system
skeletal system
System that forms framework and is moved by the muscles
nervous
System that transmits impulses to the muscle to cause contraction
False, they are pulled
True or false? Bones of the skeletal system are pushed by the muscles
Adduction
Moves closer to the mid line
isometric
Type of exercise involves contraction without movement
ATP
Direct energy source for muscle contraction
True
True or false? Extension of the muscle increases the angle of the joint
glycogen
Most abundant energy source for muscle contraction
orbicularis oculi
Muscle around the eye that is closes it
orbicularis oris
Muscle around the mouth that puckers the lips
Masseter
Muscle that raises that mandible for chewing
trapezius
Muscle raises lowers and adducts shoulder
Gluteus Maximus
Most abundant energy source for muscle contraction
Synergists
Muscle with the same function
Tendon
Structure that connects muscle to bone
Tendons and muscle
Fibrous connective tissue make up ________ and are attached to the fascia of a ________
Spongy bone and red bone marrow
What type of bone marrow is found in flat and regular bones?
cervical spine
The vertebrae in the neck are called
24
How many vertebrates are there?
Osteoblasts
What cells make a new bone matrix?
Fontanels
An infant's skull may be compressed slightly during birth without harming the brain because of the presence of?
True ribs
The seven pairs of ribs that articulate directly with the sternum are called?
Ball and Joint
What is the shoulder joint formed by?
Cartilage
In the embryo the bones in the skull are first made of?
Saddle joint
Carpal and metacarpal are examples of ______ joint
Neck and wrist
_______ and _______ are examples of a pivot joint
shoulder and hip joints
examples of a ball and socket joint are
7, 3, 2
The numbers of pairs for each type of rib-true, false and floating are ___, ____, ____
7 and Neck
There are ____ cervical vertebrae which are found in the ______
Thoracic
There are 12 ______ vertebrae which the ribs articulate
Sacrum
There are 5 Lumbar vertebrae which the ______ articulate
Vertebral column
What provides direct attachment for the hip bones, Supports the trunk and head, Protects the spinal cord from mechanical injury
osteon or haversian system
found in compact bones, contain osteocytes in rings of bone matrix and have a good blood supply
Red bone marrow
All RBCs are produced by and found in flat bones is
Yellow bone marrow
What kind of bone marrow is mostly adipose tissue
cartilage
cranial bones are first form as _____
fibroblasts
Osteoblast differentiate from ______
growth
What occurs when cartilage replaces bone on the diaphysis side
Bone grow in length
Cartilage production on the epithesis side makes what grow
When the cartilage has been replaced
When does growth stop in epiphyseal discs of long bones?