Starting Small, Getting Bigger, Body Plans, & Natural Histories
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What are the main things that categorize something as an organism?
reproduce without host, metabolism, and grow
Lateral/Horizontal Gene Transfer
the transfer of genetic information from one individual to another
Virus
cooperating biological units, cannot grow, no metabolism, cannot reproduce without host, evolves
Are viruses organisms?
mixed opinions
Bacterium
single cells, cooperating biological units, grow, metabolism, reproduce without host, evolve
Is bacterium organisms?
yes
Jellyfish
multicellular, cooperating biological unit, grow, metabolism, reproduce without host, evolve
Are jellyfish organisms?
yes
Siphonophore
colony of individuals, cooperating biological units, grow, metabolism, reproduce without host, evolve
Are siphonophores organisms?
yes if whole colony
Eukaryota
eukaryotic; variable size range; some single cells, some colonies, some multicellular
Archaea
prokaryotic; small (a few μm); single cells, some colonies
Bacteria
prokaryotic; small (a few μm); single cells, some colonies
What are the 3 Domains?
Eukaryota, Archaea, Bacteria
What is the environment dominated by?
viscous-based forces
Viscous
resistant to flow
Diffusion
passive; moves materials within cell and in/out cells
What is moved in/out of cells with diffusion?
supply for metabolic demands, metabolic wastes, chemical signals
What does diffusion depend on?
distance; surface area; difference in concentration; “Diffusion Coefficient”
The larger the distance between two points, the _____ diffusion will take
longer
What is the time required for a particle to move via diffusion?
x²; x = distance
More Surface Area, _____ rate of diffusion
faster
Bigger difference in concentration, ______ rate of diffusion
faster
What can organisms not modify in Fick’s Law?
diffusion coefficient
Fick’s Law
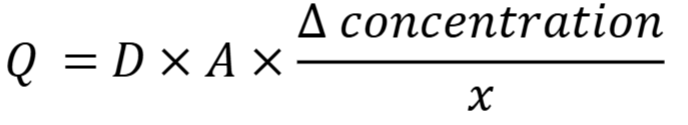
What are the benefits to increasing size?
more room for larger genome; more room for internal processes; bigger cells can engulf smaller cells
Moore room for larger genome allows for
more complex gene networks
More room for internal processes leads to
greater specialization and stability
Predation
bigger cells digest smaller cells when they engulf them
Endosymbiosis
bigger cells do not digest smaller cells when they engulf them
How did eukaryotes arise?
from endosymbiotic event between archaea and bacteria
What is a reason why endosymbiosis occurred?
mitochondria bc they have their own genome
Reynolds Numbers
dimensionless number that describes how an object or organism moves through a fluid (water or air)
Low Rynolds Numbers
Re < 10
What does a Reynold Number <10 mean?
small objects/organisms and/or slow movement; forces dominated by viscosity & flow is orderly and reversible
High Reynolds Numbers
Re > 100
What does Reynolds number > 100 mean?
larger objects/organisms and/or fast movement; forces dominated by velocity & flow is disordered
Volume
Demand; energy/resources needed
Surface Area
supply; area where diffusion can occur
Which grows much faster: supply/demand?
demand
How to overcome problem of size?
modify supply and demand
Increase supply by
changing overall shape to increase surface area : volume ratio; spheres have lowest SA:V
Decrease Demand
slow down metabolic processes, etc.; but leads to slower growth and reproduction
Multicellularity allows for ____ & __ that would be faced by single large cells, or by groups of un-connected cells
larger size & relief from some of the constraints of diffusion
True or False: Multiple Cells is not the same as Multicellular.
True
How can multicellularity happen?
aggregation & clonal development
Aggregation
cells come together (adhere); less common (slime molds, etc.)
Clonal Development
serial division without separation of cells; more common
Body Plan
the general structure of an organism; cooperating entities at different levels are arranged in
Cooperating biological Units
proteins, nucleic acids, some organelles
Life History
the lifetime pattern of growth, reproduction, and survivial for an average individual
Photosynthetic organisms
obtain energy from sunlight; need chloroplasts
Heterotrophic
obtain energy and nutrients from pre-formed, external source
Multicellularity Hierarchy Order
cells → tissues → organs → systems → individuals
convergent evolution
have similar morphological features but evolved independently; probably from similar external pressures
Somatic cells
body cells; all genetically identical
Housekeeping genes
essential genes no matter the cell specialization; all cells express
Tissues
made up of cells; common developmental line, morphology, and function; cell-cell connections
Organs
groups of tissues that work together for a common goal/function
Organ systems
groups of tissues and organs that work together for a common goal/function
Hypertrophy
an increase in cell size
Hyperplasia
increase in cell number by mitosis
Meristem cells
undifferentiated cells; with hyperplasia can contribute to normal growth in plants and algae
Stem Cells
undifferentiated cells; with hyperplasia can contribute to normal growth in animals
How do plant cells connect?
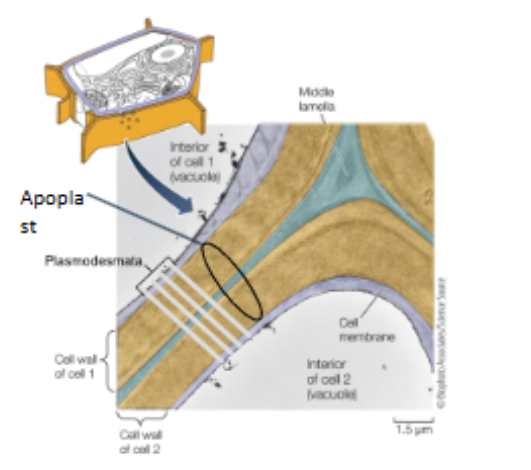
hemicellulose fibers (structure & flexibility) and pectin (glue) in apoplast
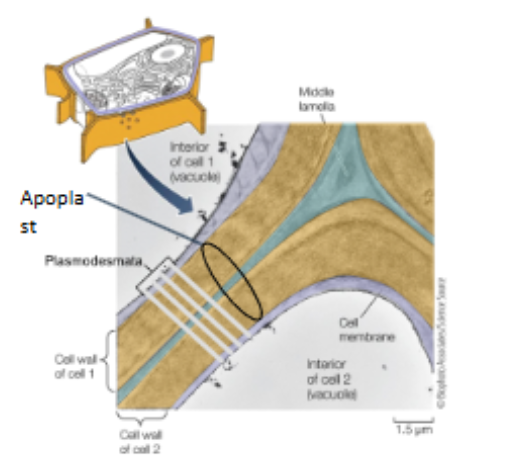
How do plants communicate?
via the plasmodesmata
Adherens junctions & Desmosomes
connect cells to each other or the extracellular matrix
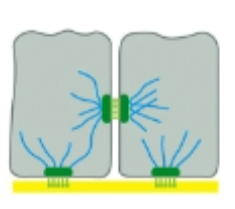
Tight Junctions
close adherence between two cells, prevents most movement from one side of cell sheet to another
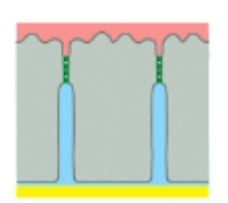
Gap junctions
channels allow communication between cells
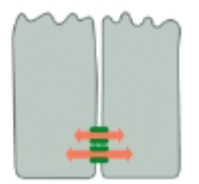
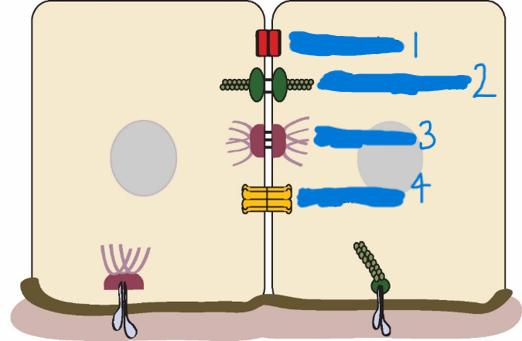
Which is a tight junction?
1
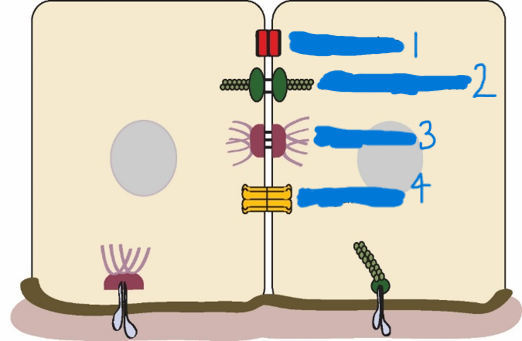
Which is a adherens junction?
2
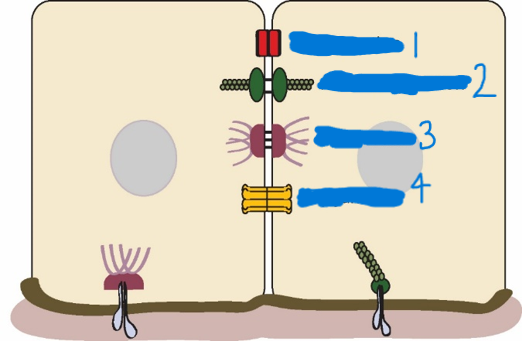
Which is a desmosome?
3
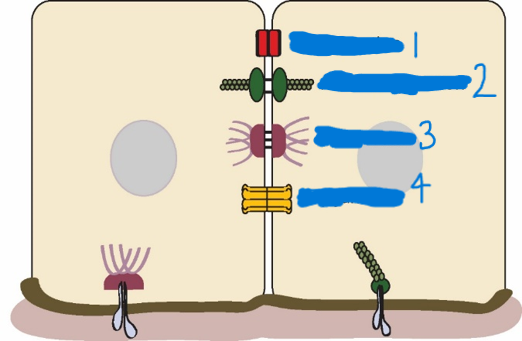
Which is a Gap junction?
4
Dermal Tissue
surface of body, protection, regulates exchange with enviornment
Ground Tissue
bulk of body, photosynthesis, storage
Vascular Tissue
plants only; bulk flow
Hyphae
branching tubular strands of fungal cells
mycelium
hyphae joined together; body of multicellular fungus
Epithelial tissue
surface of body, protection, regulate exchange with environment
Contractile tissue
muscles, cells get shorter
nervous tissue
neurons and glial cells, electrical signaling
connective tissue
support tissues, fibrous tissues, blood and adipose tissue, characterized by extensive extracellular matrix