Design and Manufacturing Lab Exam (copy)
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
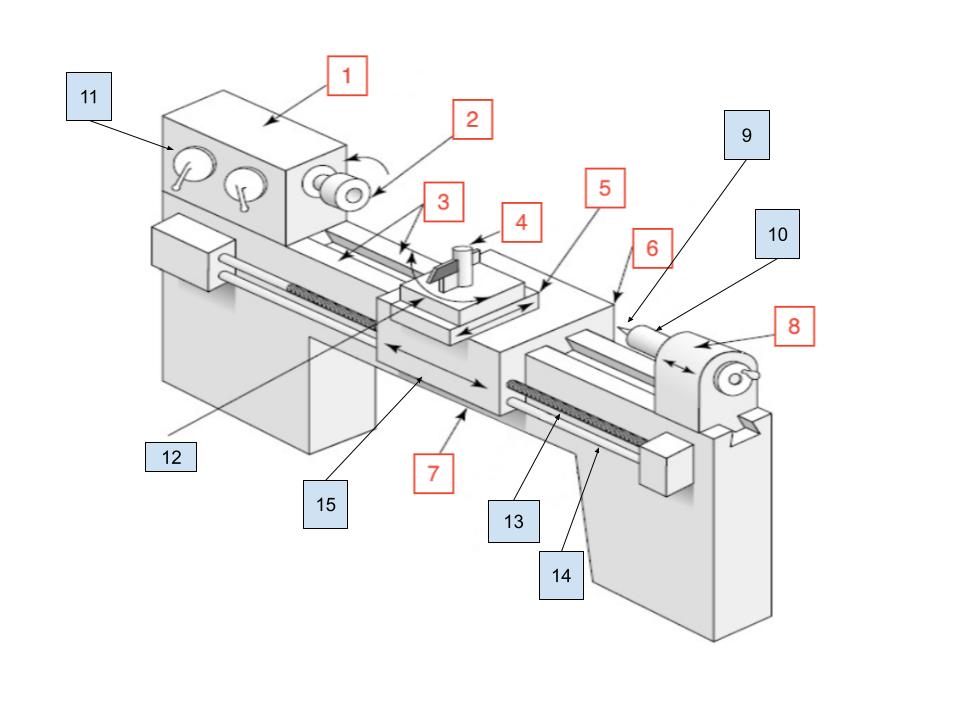
Headstock
1
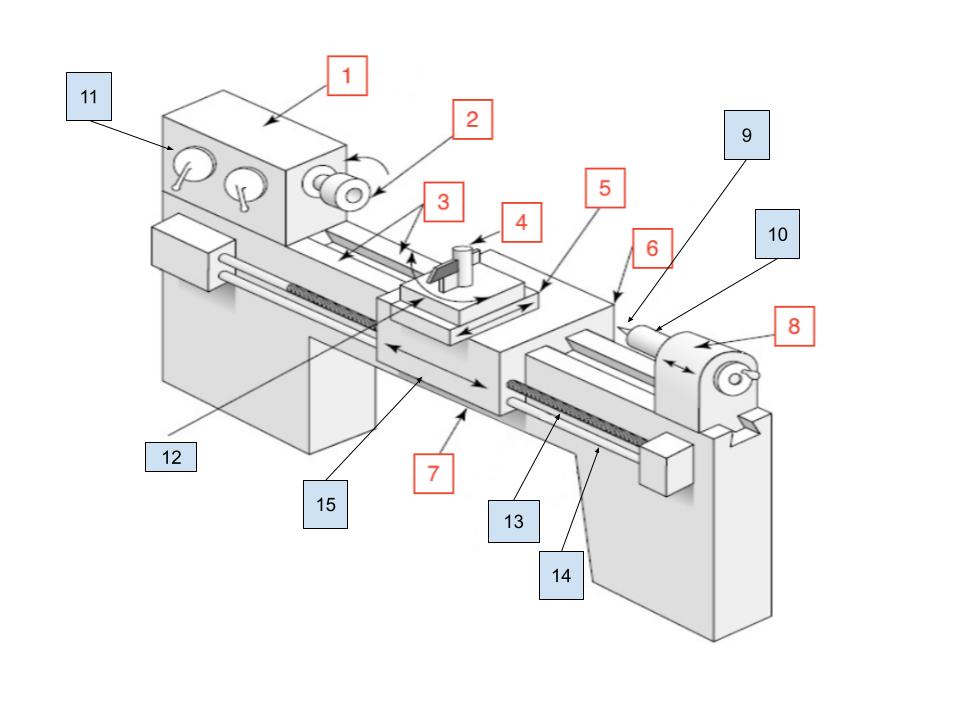
Spindle
2
Ways
3
Toolpost
4
Cross Slide
5
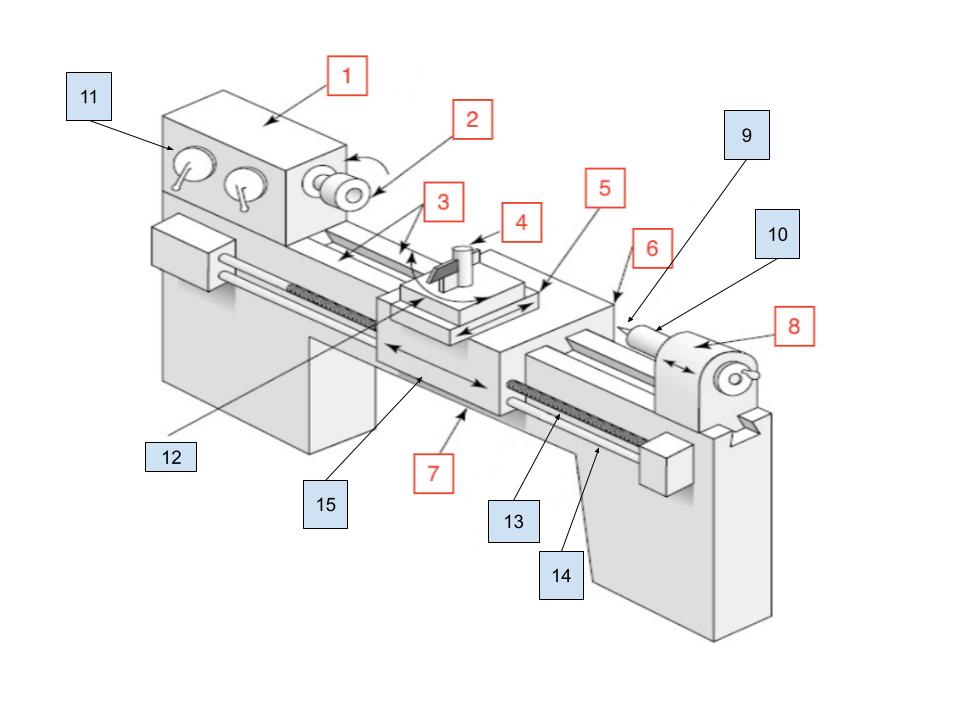
Carraige
6
Bed
7
Tailstock
8
Center
9
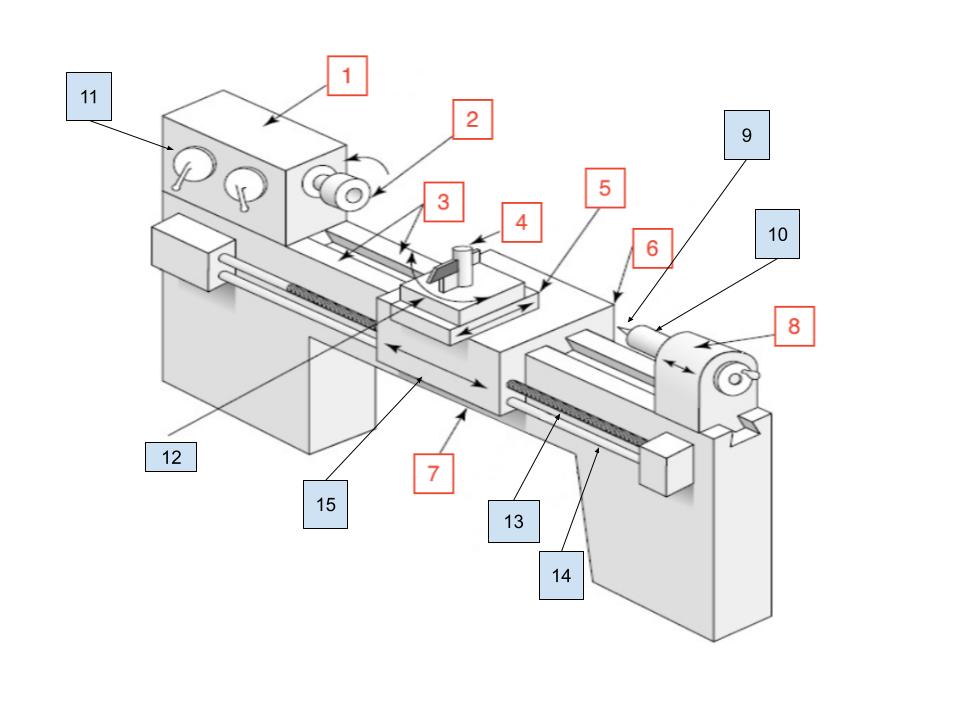
Tailstock Quill
10
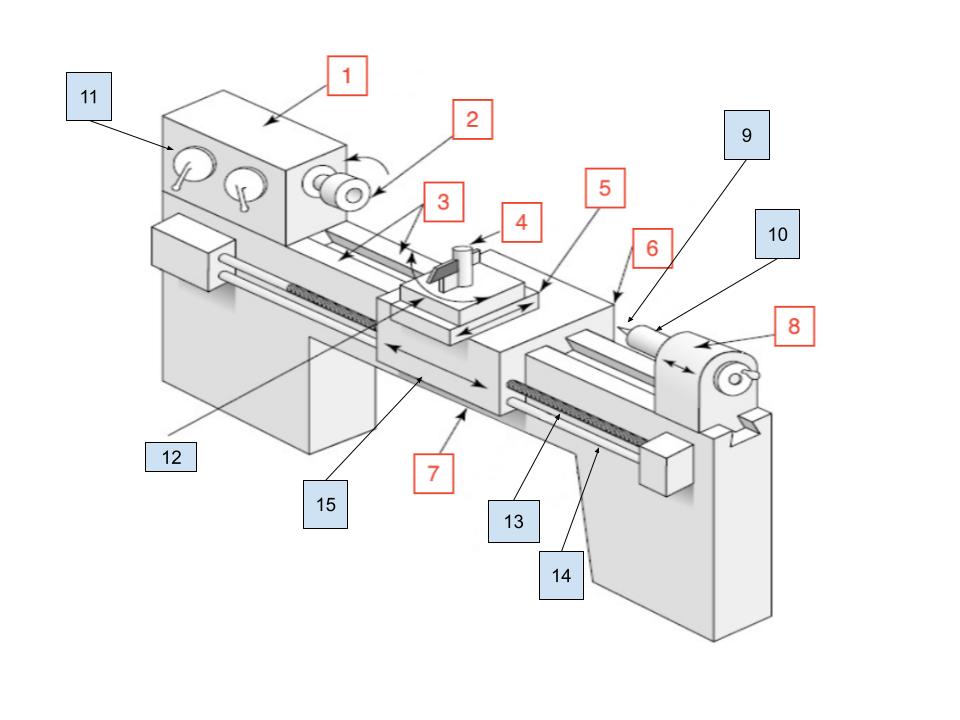
Spindle Speed Selector
11
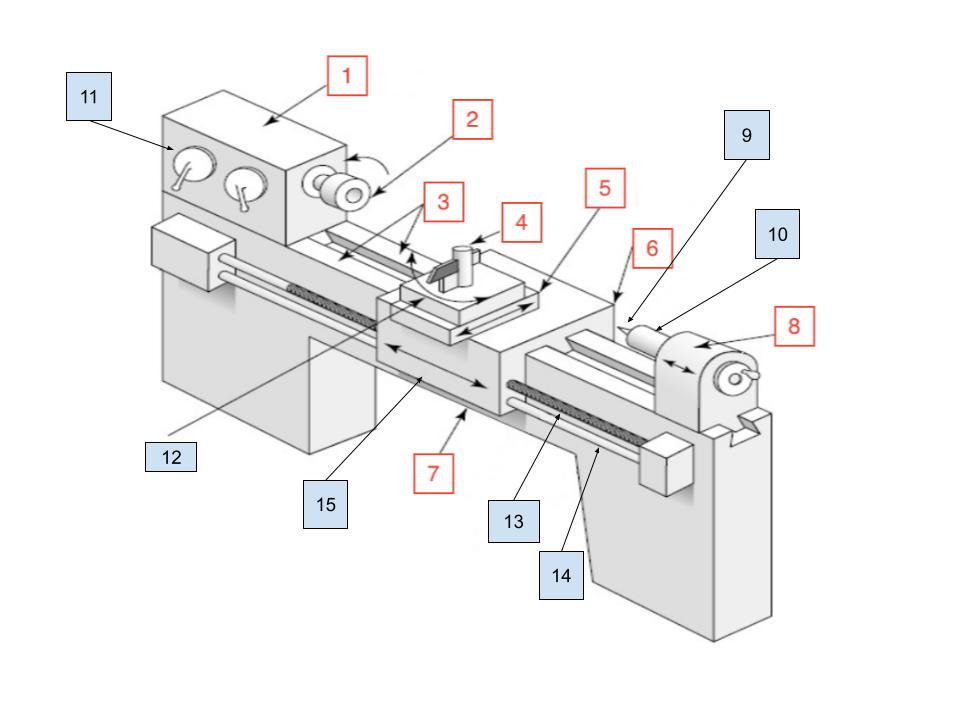
Compound Rest
12
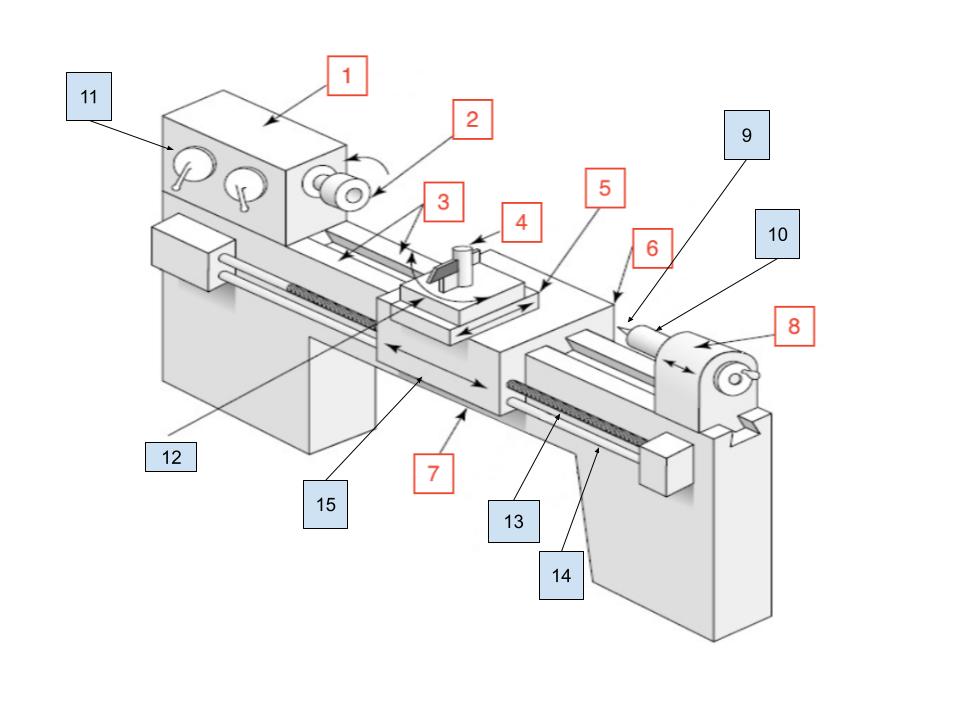
Lead Screw
13
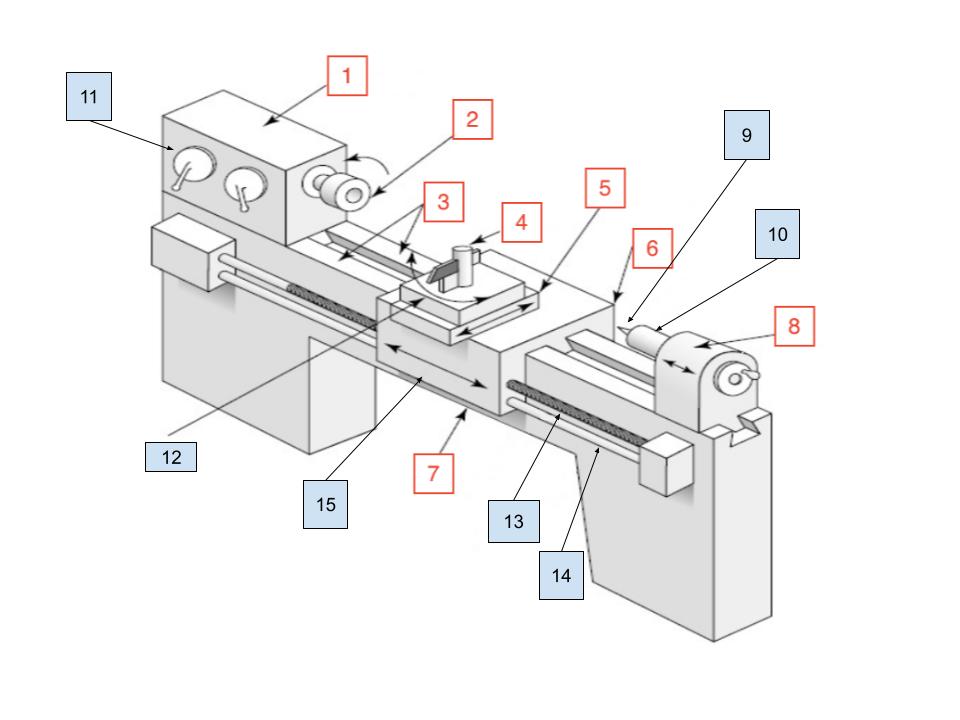
Feed Rod
14
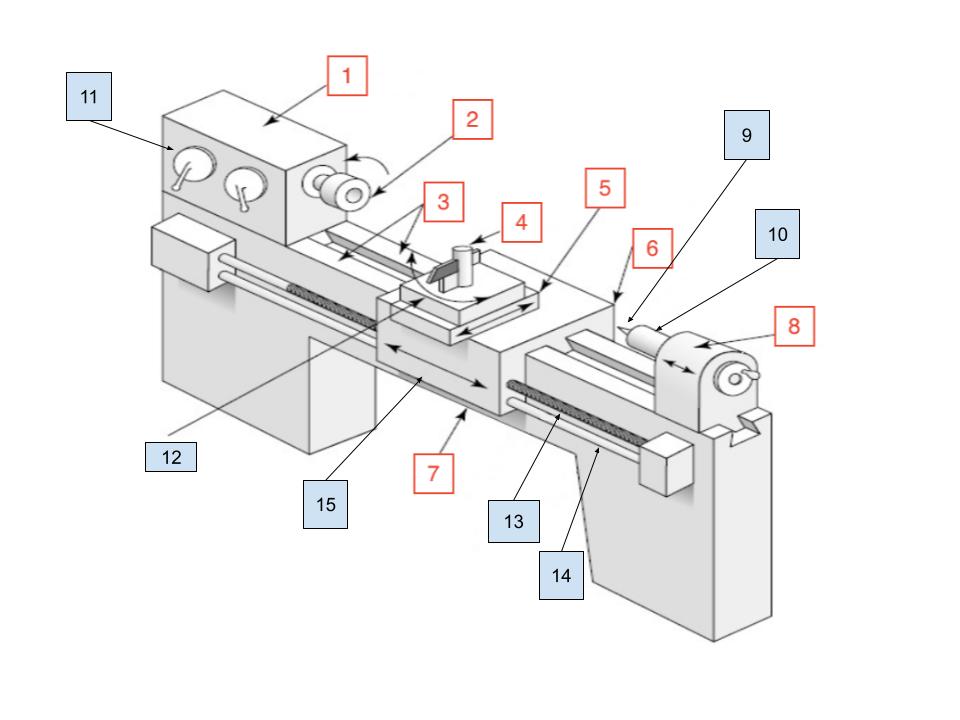
Apron
15
X Axis
Lathe axis that moves “in and out”, parallel to face of part
Z Axis
Lathe axis that moves “left and right”, parallel to axis of part
Recognize the problem/need
Design Process Step 1
Define your problem, and quantify it if possible
Design Process Step 2
Gather information
Design Process Step 3
Generate concepts based on constraints such as deadlines, strength, cost, etc.
Design Process Step 4
Out of the proposed concepts, select the best one using a decision matrix
Design Process Step 5
Communicate the design
Design Process Step 6
Detailed Design and Analysis using CAD
Design Process Step 7
Prototype Development and Testing
Design Process Step 8
Manufacturing
Design Process Step 9
Life Cycle Maintenance
Design Process Step 10
Bilateral Tolerance
A nominal measurement with a tolerance in both directions
Unilateral tolerance
A nominal measurement with a tolerance in one direction
Limit tolerance
A dimension with no nominal measurement, just an upper and lower bound
End Mill
Used for milling the sides of a workpiece. Used for profiling, contouring
Face Mill
Used for milling, creating a smooth, flat surface.
Collet
Used to hold tools in a mill or lathe
Clockwise
Direction mill should rotate
Counter-Clockwise
Direction lathe should rotate
Tap
A tool used to cut threads into a workpiece
Tap guide
A tool used to align the tap to ensure it’s going straight into the workpiece
Tap handle
The tool that rotates the tap when creating threads
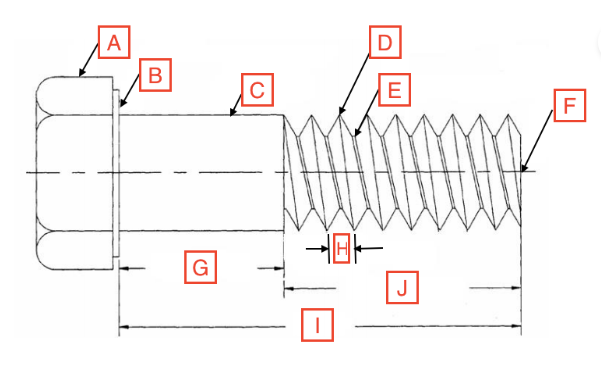
Grip Length/Shoulder
G
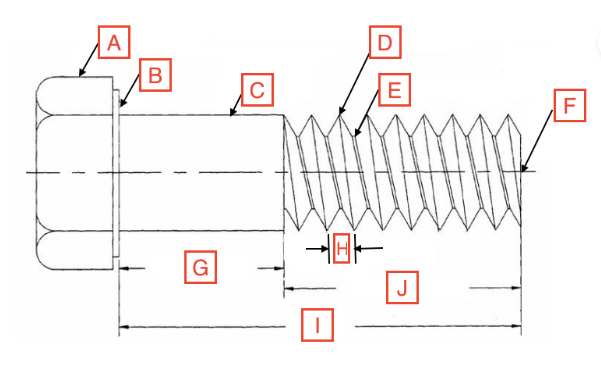
Thread Root
E
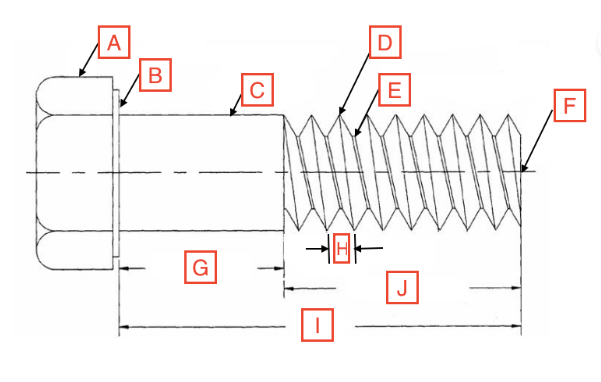
Head
A
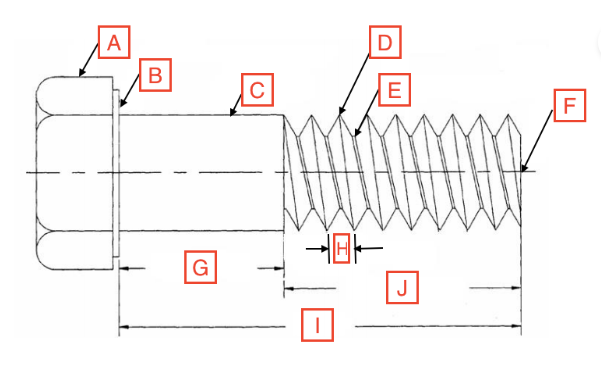
Drive
The spot on the fastener where the screwdriver goes
Point
F
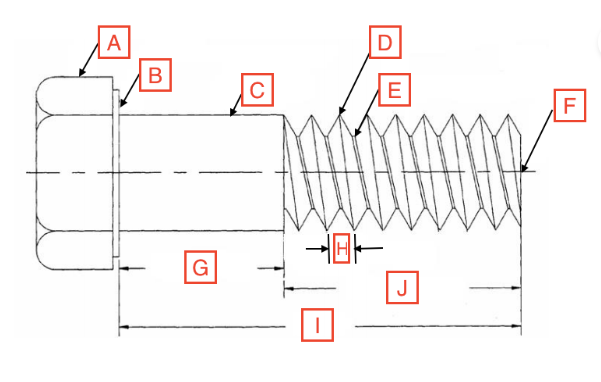
Length
I
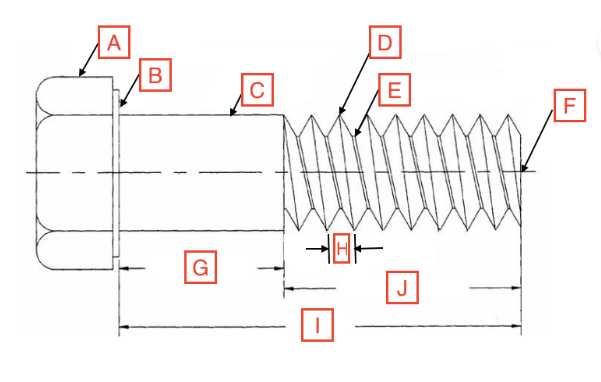
Thread Length
J
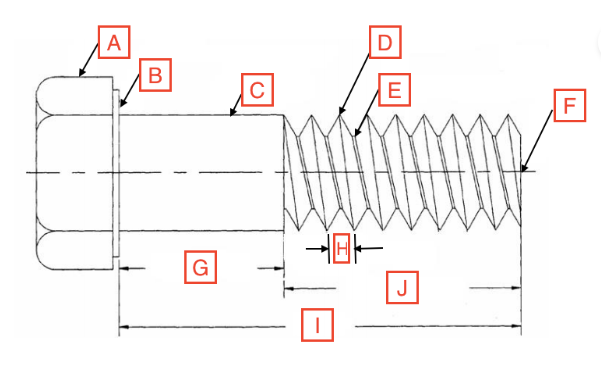
Shank
C
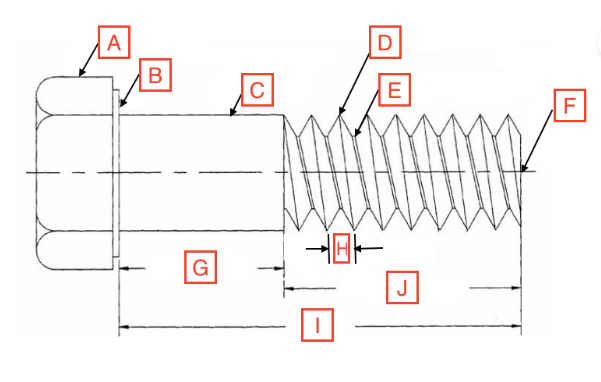
Bearing Surface
B
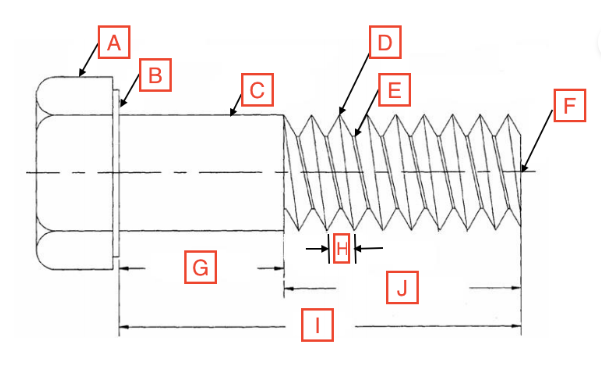
Pitch
H
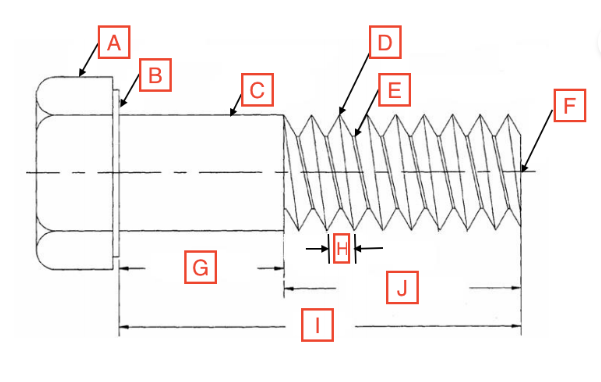
Thread Crest
D
Coarse threads - female threads are most likely to fail via shear at the major diameter, so more area in contact is better.
The larger size thread, better for stronger screws into weak materials. Why is it better?
Fine threads - male threads are more likely to fail from tensile loading at the thread root, so a larger minor diameter is better.
The smaller size thread, better for weaker screw, stronger material
Rolled —> Threads are made by being pushed in so the grains are compressed, rather than removed.
The threads on all quality fasteners are made by being _______. What does this mean?
Shear - the threaded portion has a slightly smaller diameter, the threaded portion has less surface area, and the thread will move and act as a file, removing material.
What force should threaded regions not be put under (use dowel pins or shoulders instead here). Why?
Tensile stress, torque
What two things keep a fastener secure
The point of the smallest diameter
Where do fasteners most commonly fail?
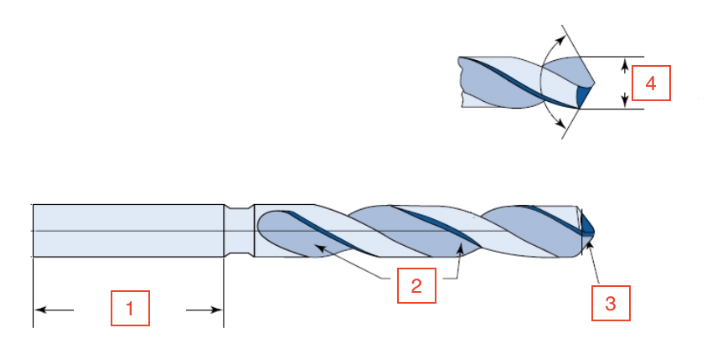
Shank Length
1
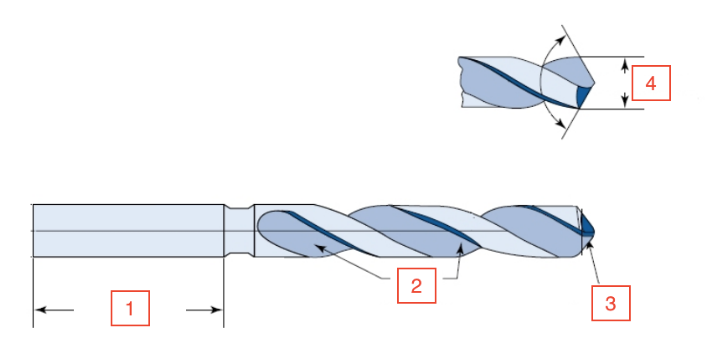
Flutes
2
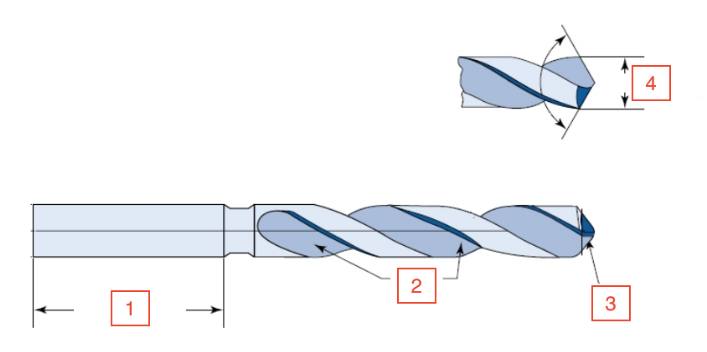
Lip
3
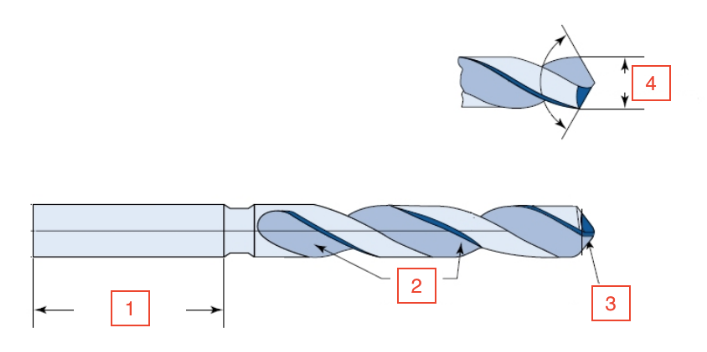
Drill diameter
4
Motor
1
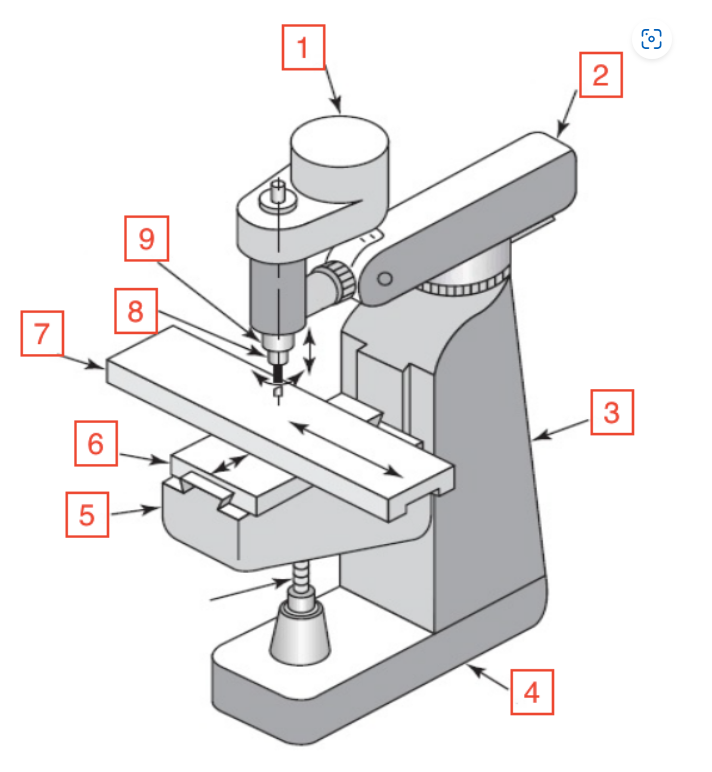
Overarm
2
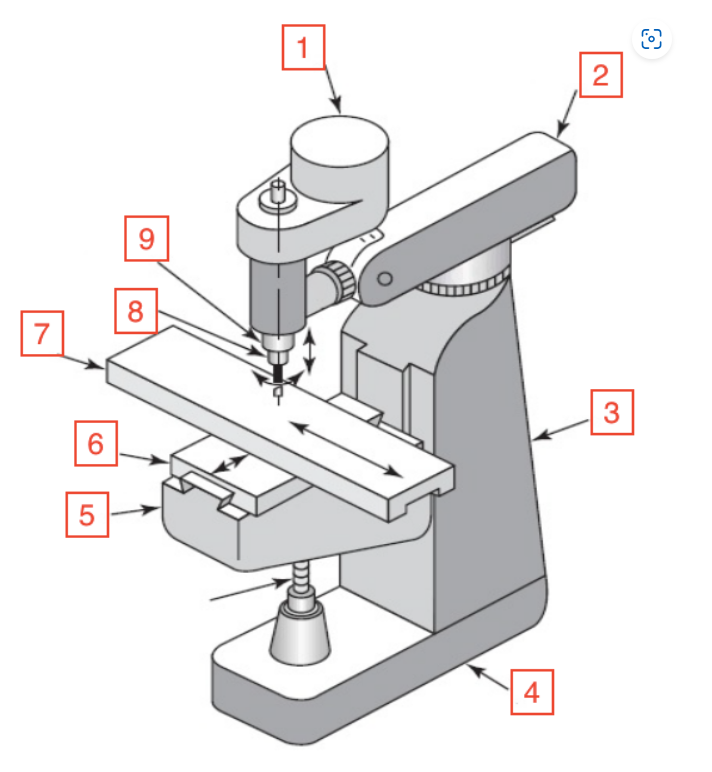
Column
3
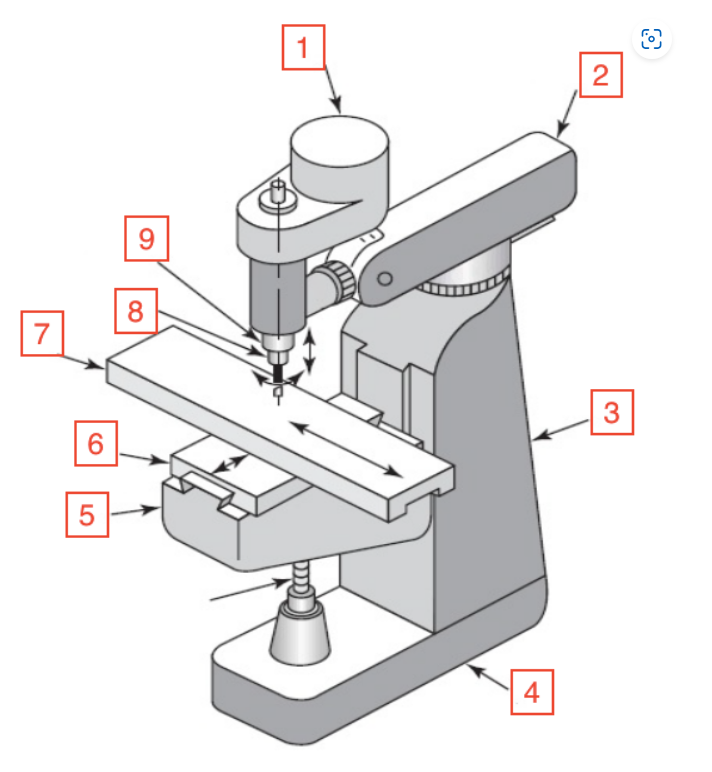
Base
4
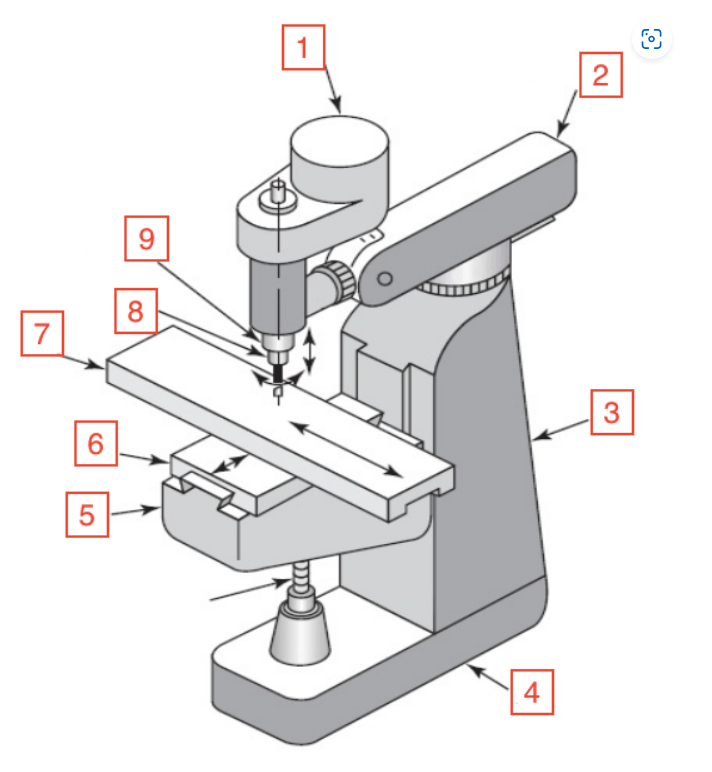
Knee
5
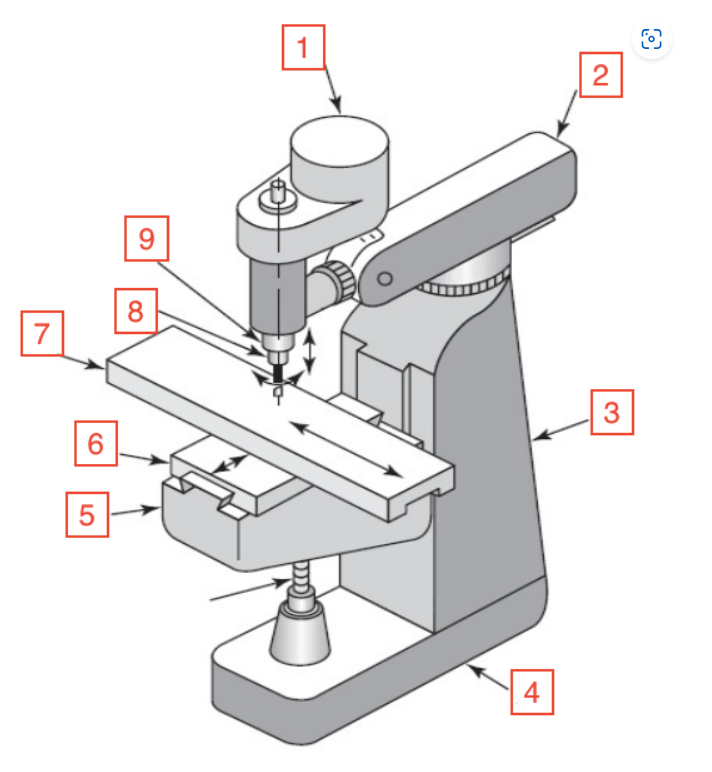
Saddle
6
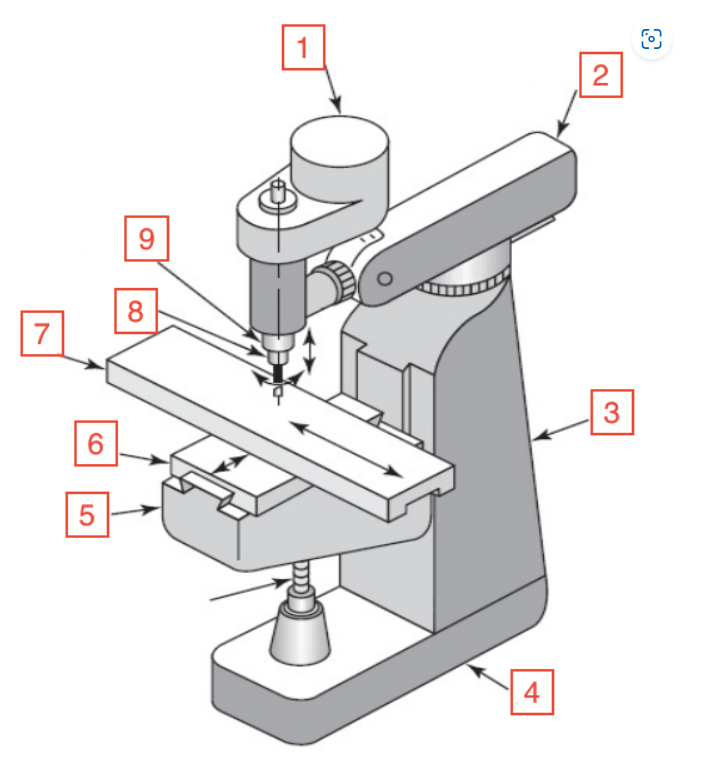
Table
7
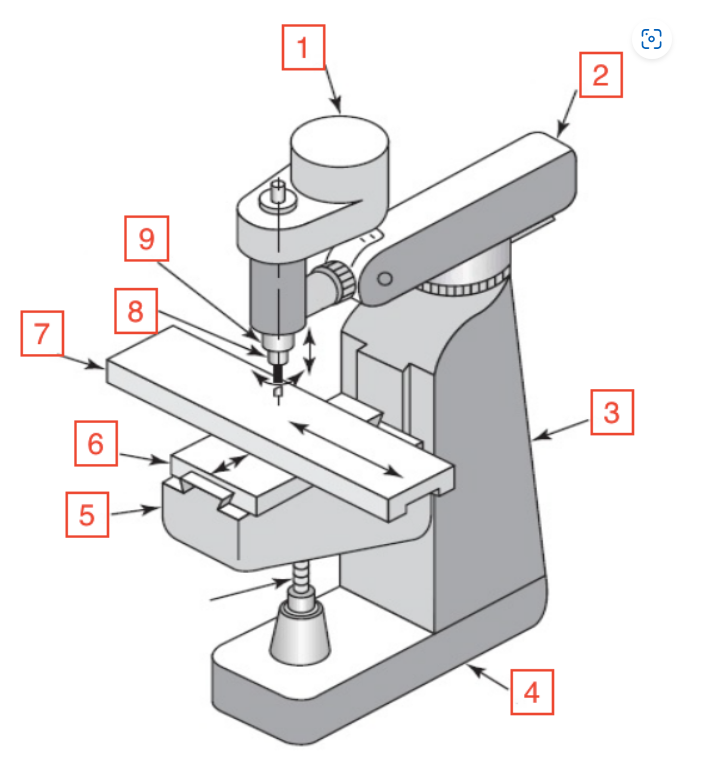
Spindle
8
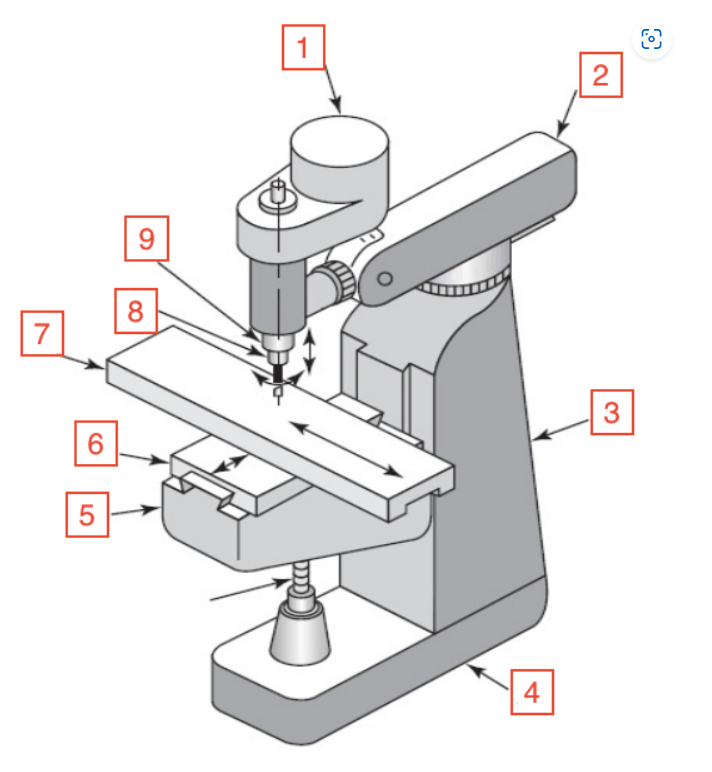
Quill
9
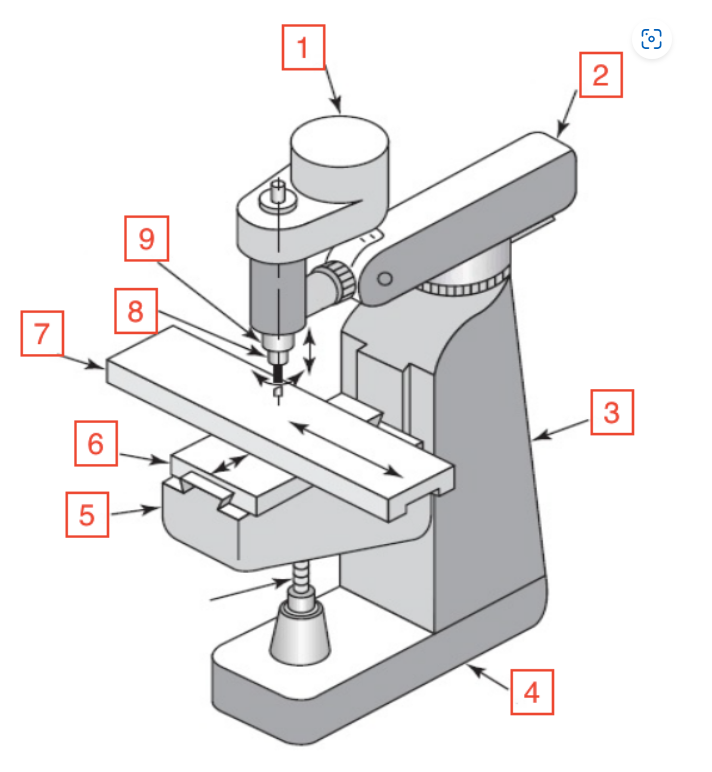
Quill handle
Bar used to move quill up and down on mill
Tap handle, used to twist the tap into the hole
What is this tool and what is its use?

Tap, creates threads in material
What is this tool and what is its use?

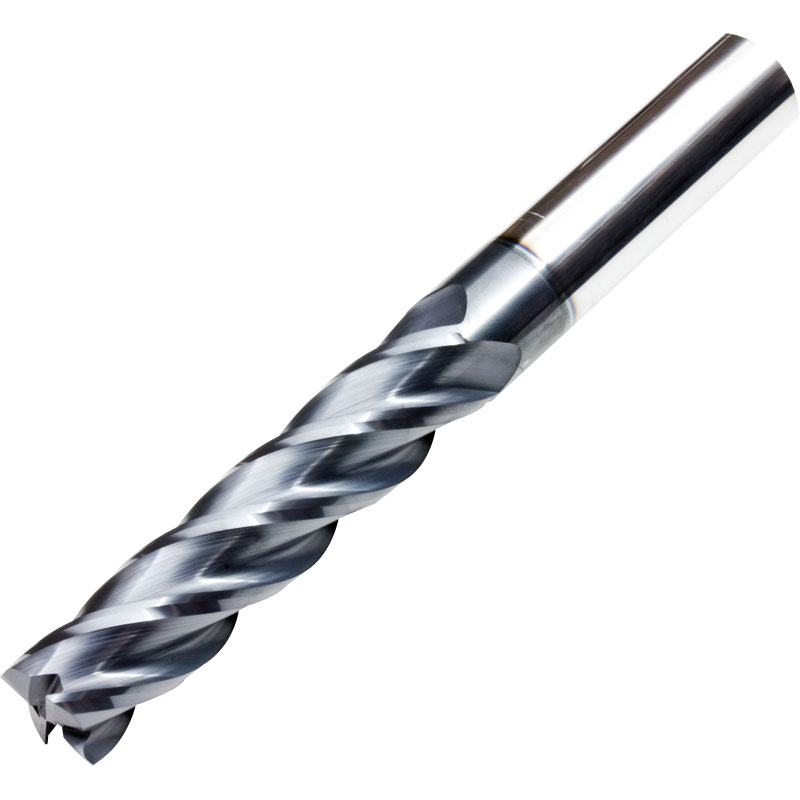
End mill, used to cut off larger amounts of material than face mills
What is this tool and what is its use?

Face mill, used to smooth surfaces and make surface level cuts
What is this tool and what is its use?

Reamer, used to make the diameter of holes very precise after they’ve been drilled
What is this tool and what is its use?

Collet, used to hold tools in the mill or lathe
What is this tool and what is its use?

Tool holder, used to hold lathe tools in place
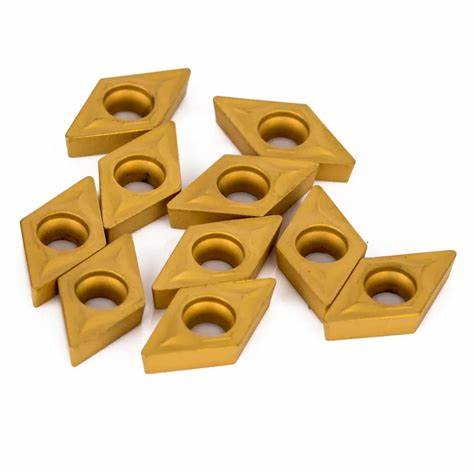
What is this tool and what is its use?

Insert - used to cut material on the lathe
What is this tool and what is its use?

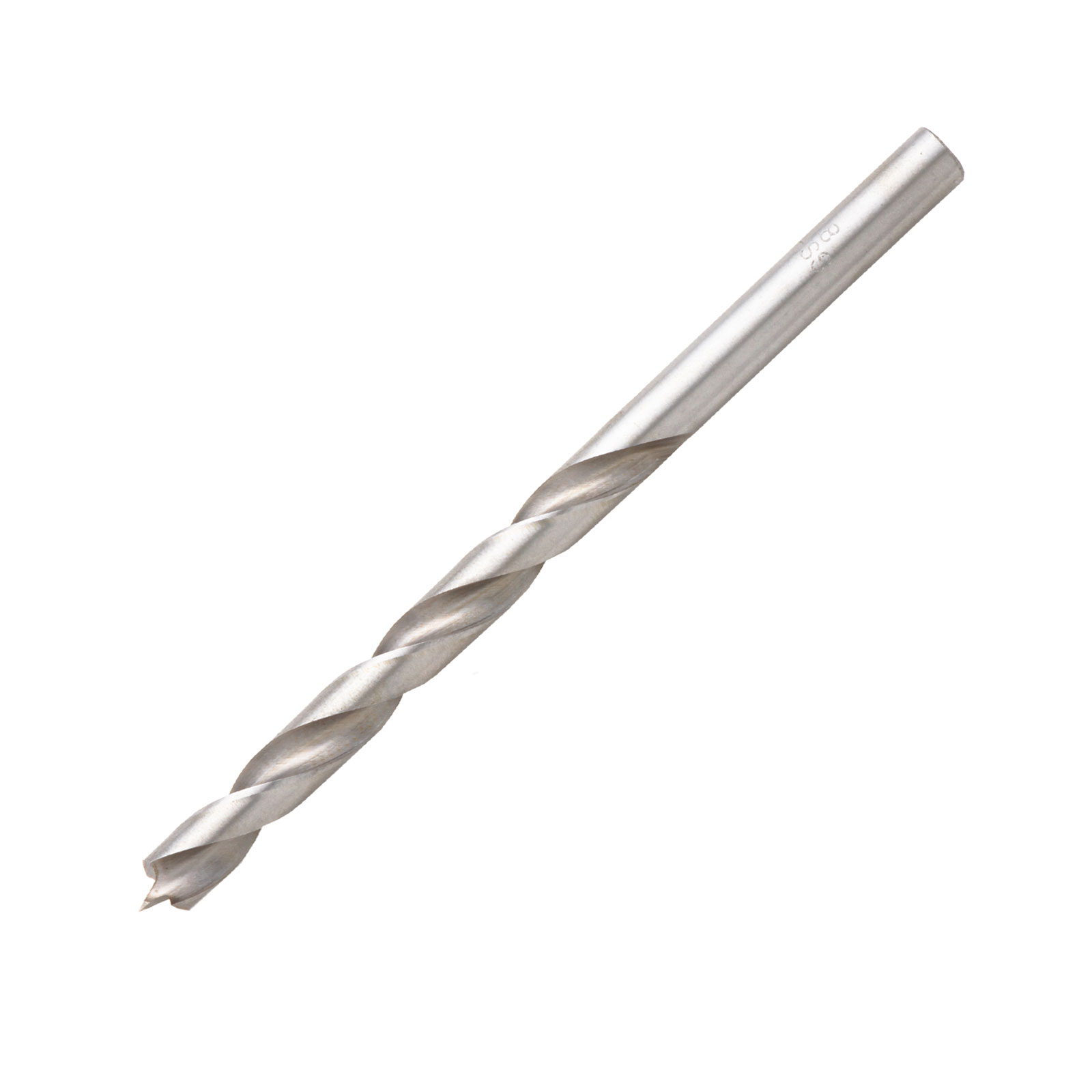
Drill bit - used to drill holes into material
What is this tool and what is its use?

Center drill - used to drill a leading hole into a material to ensure the drill bit is fully aligned when it goes through
What is this tool and what is its use?

Edge finder, used to take a non-destructive zero on the milling machine
What is this tool and what is its use

Drilling
In the "_______" process, a hole is produced by feeding a drill into a rotating workpiece along its axis.
Threading
During a "______" operation, external or internal threads are achieved by feeding a pointed tool linearly across the outside or inside surface of a rotating part.
Knurling
In an operation known as "________," a regular cross-hatched pattern is produced in work surfaces through metal forming.
Boring
A single point tool is fed linearly and parallel to the axis of a workpiece to enlarge a hole made by a previous process in the operation known as "_______."
Facing
Surfaces are typically positioned perpendicular to the axis of the workpiece in the "______" operation. This operation is dominated by radial feed.
Parting
For a "______" operation, the end of a part is cut off by feeding a tool radially into a rotating workpiece at a particular location along its length.
Profiling
In a "______" operation, both modes of tool feed are simultaneously desired to create tapered and contoured surfaces.
Chamfering
For a "_____" operation, a tool cuts the corner of a cylinder at an angle.
Turning
The generation of any cylindrical surface with a single point tool is referred to as "______." In this operation, the direction of the feeding motion is predominantly axial with respect to the machine spindle.
Steel
What material always needs to be oiled when cutting it? (Steel/aluminum)
Drilling
What operation always needs oil regardless of the material or size?
Roughing
Does a roughing or facing pass always need oil with aluminum?
0.02 (20 Thou)
What is the maximum depth of cut to be considered a “facing pass”?
Y Axis
On the mill, which axis is “front to back”?
X Axis
On the mill, which axis is “left and right”?
To clamp things together
What is the ONLY purpose of fasteners?
Endmills have more flutes, drills are usually longer per diameter, and endmills have cutting edges on the side.
What are differences in geometry between endmills and drills?
Cylindrical and conical
What are the two kinds of edge finders?
Stabilizing long parts in the lathe to avoid the moment generated
What is a center finder used for?
A reamer has straight instead of helical flutes.
What is a difference in geometry between a reamer and a drill?