Churches, Mosques, Stupas, and Temples in the Eastern Mediterranean and India
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
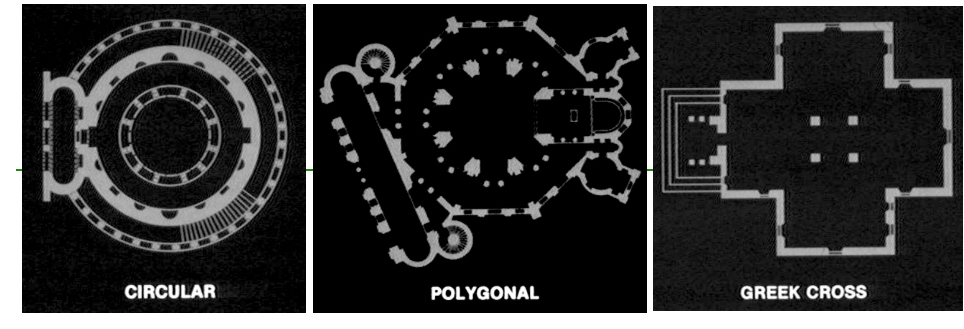
Central Plan
in architecture, a plan in which the parts of a building radiate from a central point. Types include circular, polygonal, and Greek cross plans
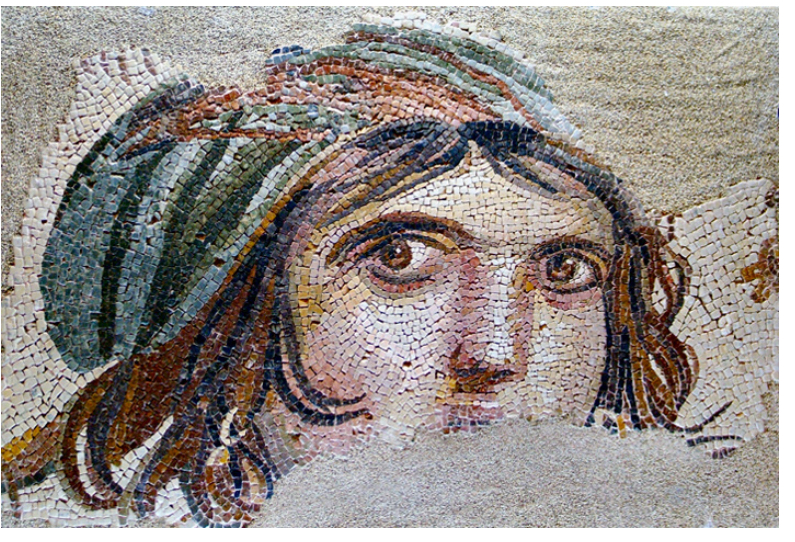
Mosaic
a medium in which small, roughly cubic pieces of colored material (usually stone or glass) are embedded in mortar to create patterns or images. The small pieces are called tesserae

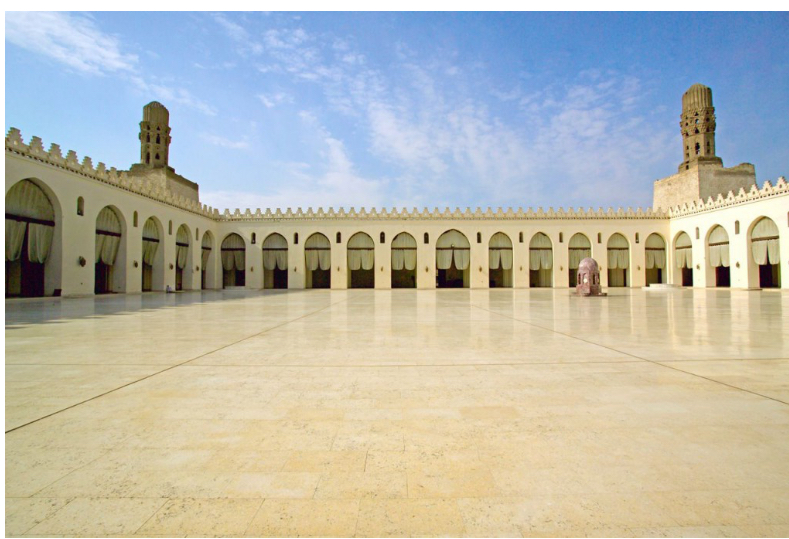
Mosque
a building used by Muslims for communal worship

Qibla
In Arabic, it means “direction.” The direction to the Kaaba in Mecca, towards which Muslims are required to pray. Most mosques contain a niche, the mihrab, that indicates the qibla.
Mihrab
In a mosque, the niche that indicates the wall oriented toward Mecca and serves as a focal point for prayer.
a niche found in a mosque, intended to indicate the direction of Mecca

Minaret
A tall slender tower, typically part of a mosque complex, with a balcony from which the Muslim congregation is called to prayer.
reminder of where muhammad stood and spoke

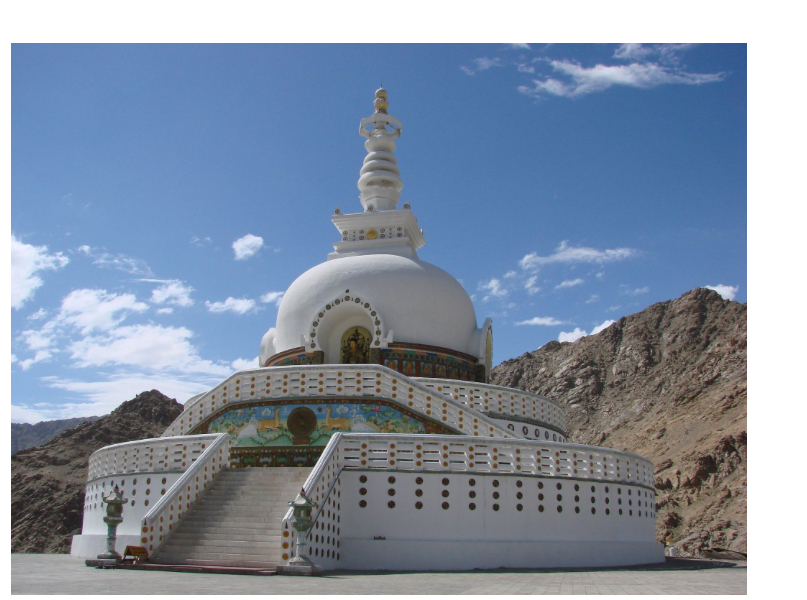
Stupa
In Buddhist architecture, a monument made of earth and/or stone and containing sacred relics
are monuments to the memory of the Buddha and are bural mounds for the relics of other important persons

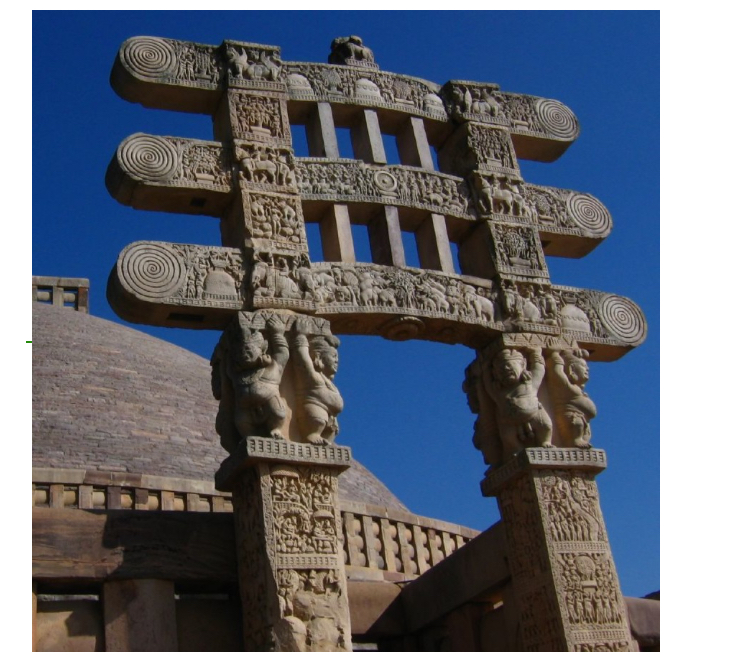
Torana
In Buddhist and Hindu architecture, an ornamented gateway leading to a temple or stupa often features intricate carvings and symbolic motifs. And symbolizes the transition between the secular and sacred realms.
gateway

Mandala
In Buddhist art, a symbolic diagram of the cosmos in a circular shape. The creation of a mandala is used as a tool for re-consecrating the earth and its inhabitants and is often associated with meditation practices.

Yakshi
In Hindu and Buddhist art, auspicious female nature spirits, symbolic of fertility and abundance. Yakshi are typically depicted as beautiful and voluptuous, with wide hips, narrow waists, and exaggerated spherical breasts.

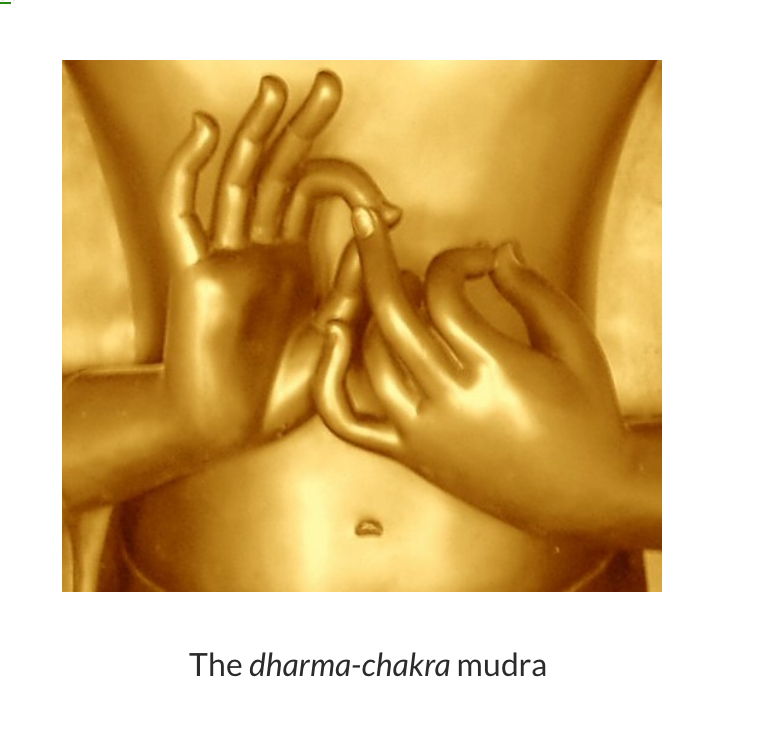
Mudra
In Hindu and Buddhist art, a hand gesture is used to express the meaning of an image of a divinity. While some mudras involve the entire body, most are performed with the hands and fingers. Mudras denote specific behaviors, actions, or states of mind

Nimbus
In Latin, nimbus=cloud. A luminous cloud appearing around a figure’s head or surrounding the entire figure, signifying holiness or divinity

Lakshana
In Buddhism, the 32 “auspicious marks” (physical traits) by which the Buddha can be recognized. The lakshanas include golden skin, long arms, a tuft of hair between the eyebrows (the urna), and a knot of hair on the top of the head (the ushnisha)

Chaitya
(definition for chaitya hall) In India, a temple or shrine, especially a Buddhist prayer hall containing a stupa at one end where devotees gather to worship and meditate, often featuring intricate architecture and sculptures.
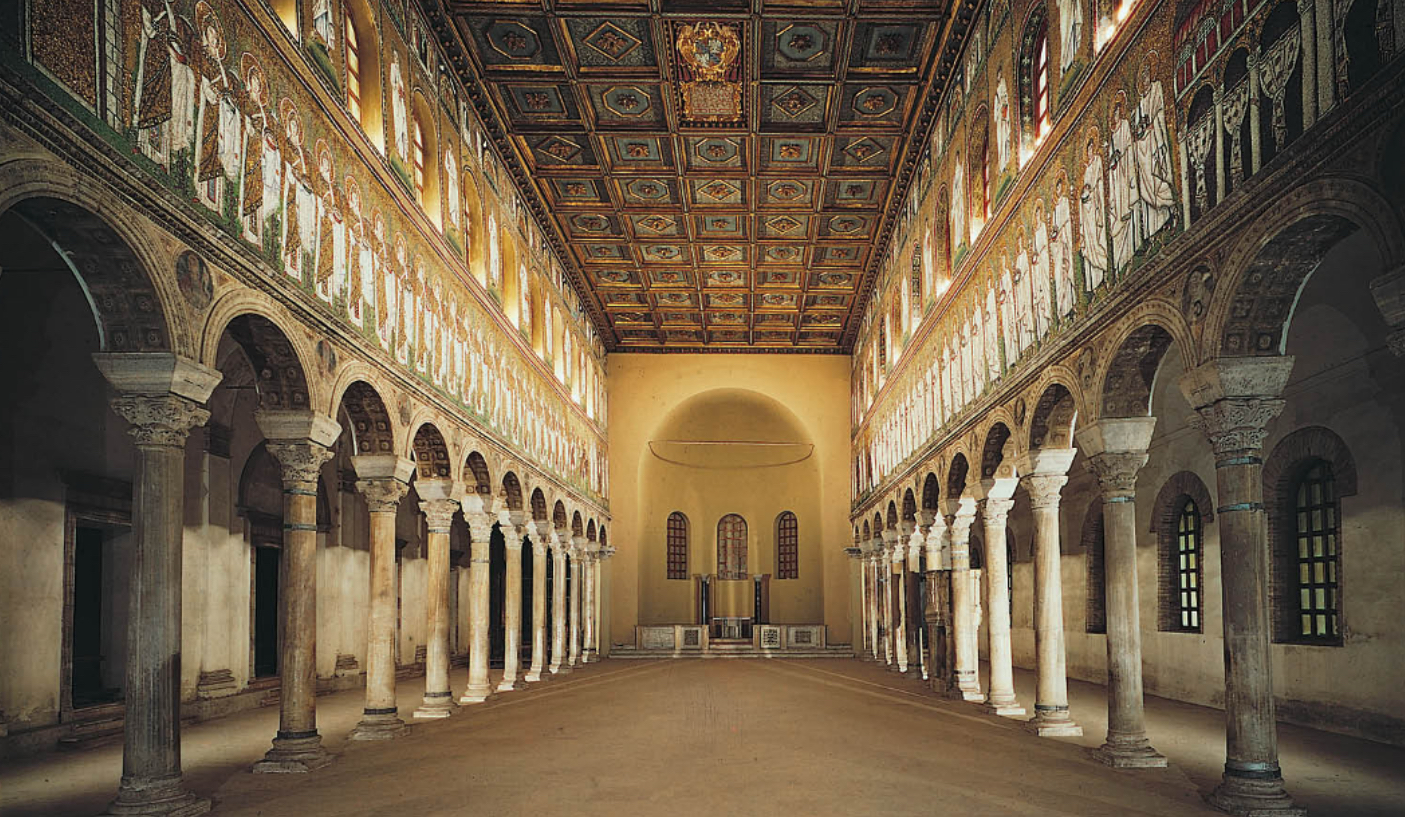


Sant’Apollinare Nuovo, Ravenna, 6th century/late 5th century (Early Byzantine)
Basilica church
mosaic of many types, but also of the life of Jesus (ex. the Last Supper)
Jesus here has a beard, which is a symbol of maturity. He’s looking like an emperor
is a notable example of Early Christian architecture, featuring ornate mosaics that depict biblical scenes, including significant events from the life of Christ.
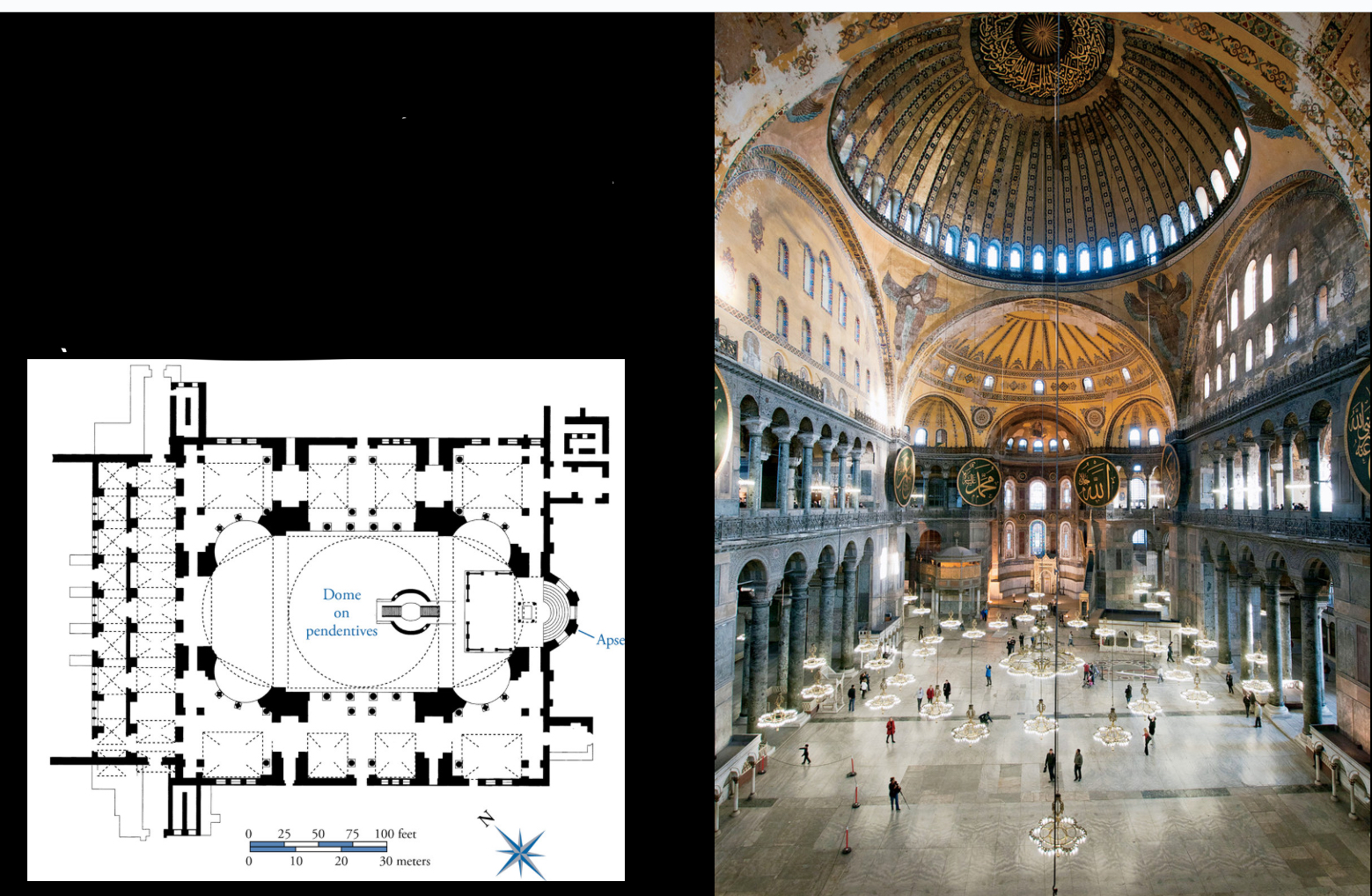

Hagia Sophia, Constantinople (Istanbul), architects: Anthemius and Isidorus, 6th century (Byzantine)
central plan church → dome central
extremely influential for later architects of Islamic mosques. Built other mosques based on this one
one of the largest interior spaces
they redorated it into a mosque
similar dome to the Pantheon
has domes and half domes
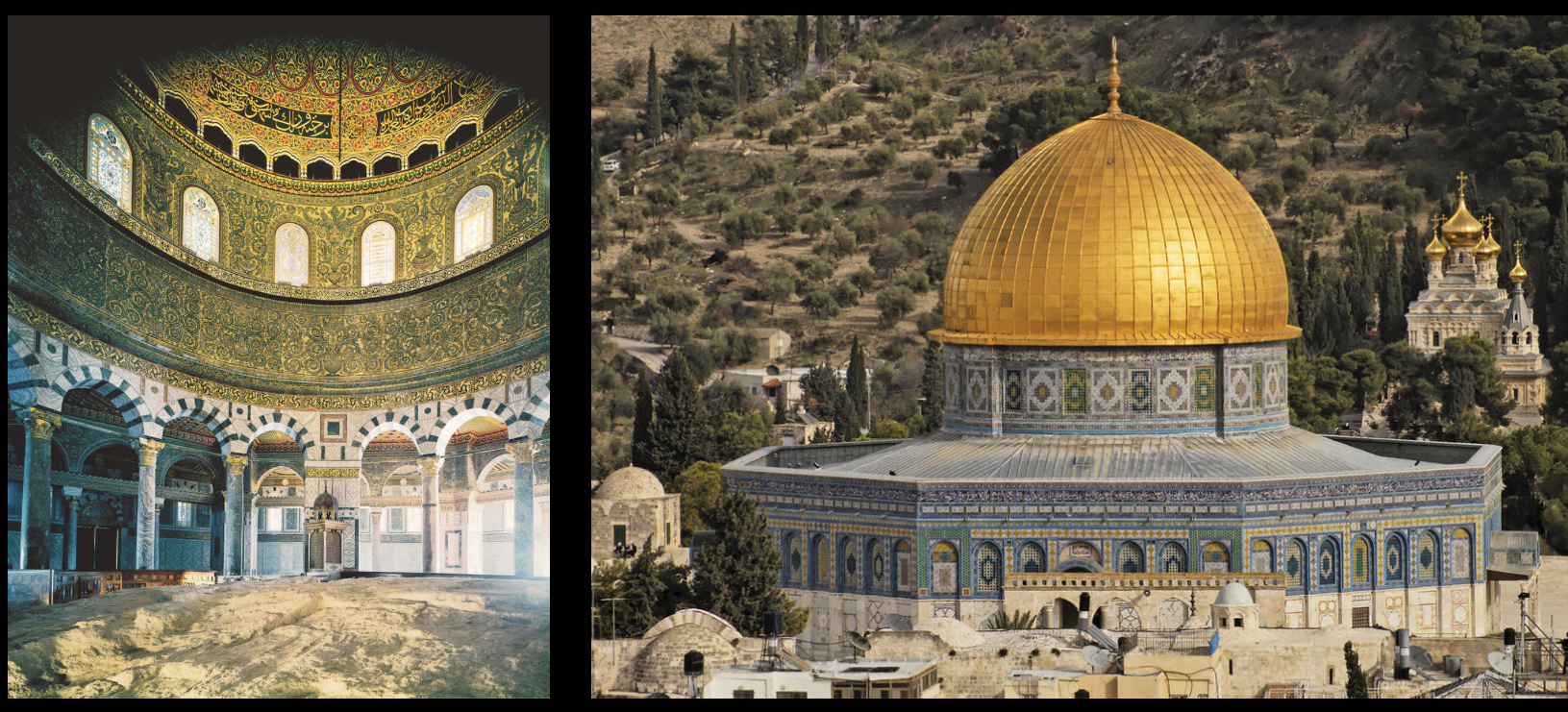

Dome of the Rock, Jerusalem, Israel, 7th century (Islamic)
is an iconic Islamic shrine featuring a gold-plated dome, built on the Temple Mount, significant in both Islamic and Jewish traditions.
earliest surviving Muslim sacred space
plays and develops using basilican structure and mosaics
more a pilgrimage site than a mosque
exterior is decorated in tiles with flower designs and the word (Arabic)
has Calligraphy
potential source is roman and Byzantine central plan building
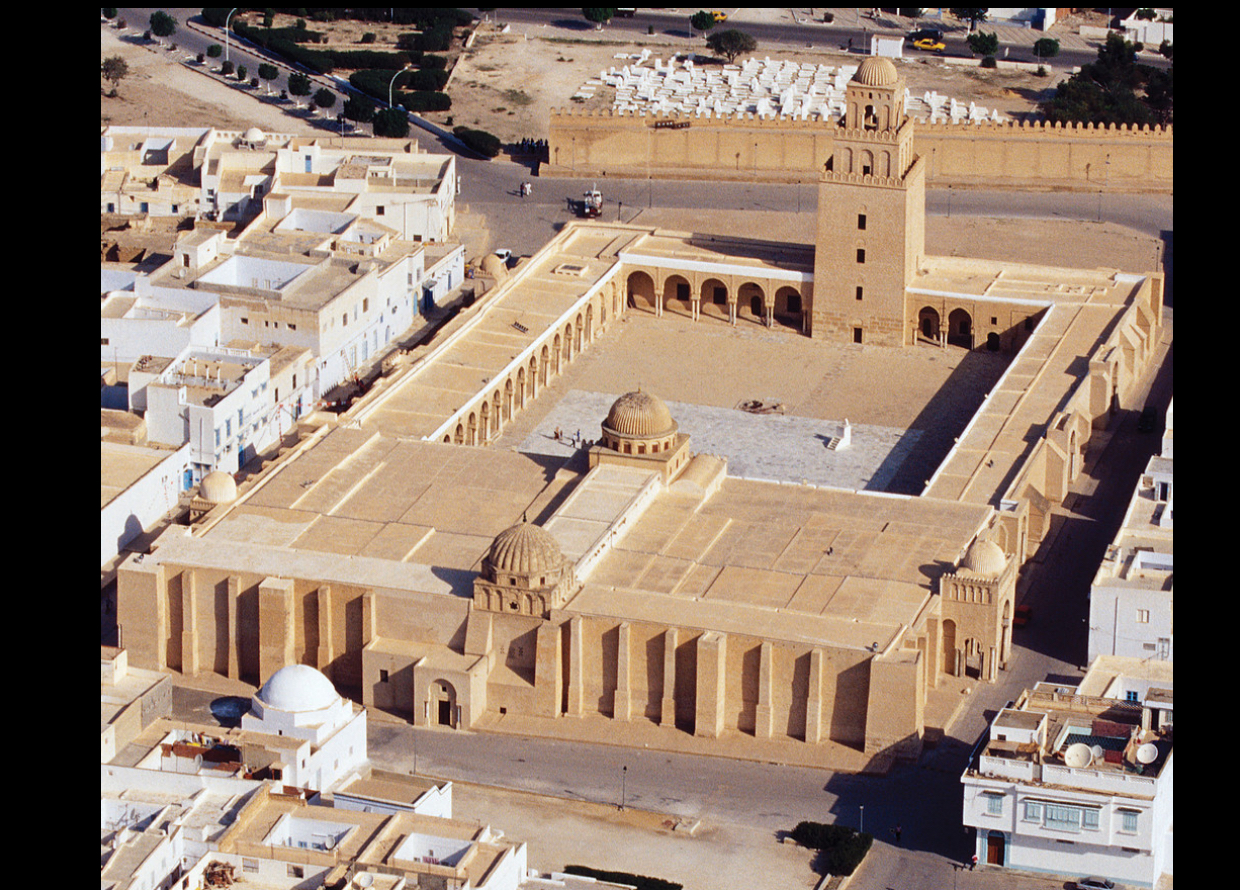

Great Mosque, Kairouan, Tunisia, 9th century (Islamic)
was based on Muhammad’s house in Medina: 7th-century, prototype for early mosques, hypothetical reconstruction
Has a
Qibla wall (it’s eastern wall in this case)
Mihrab
Hypostyle prayer hall (actual prayer with a lot of columns)
Forecourt (open space where you take off your shoes and prepare for prayer)
Minaret
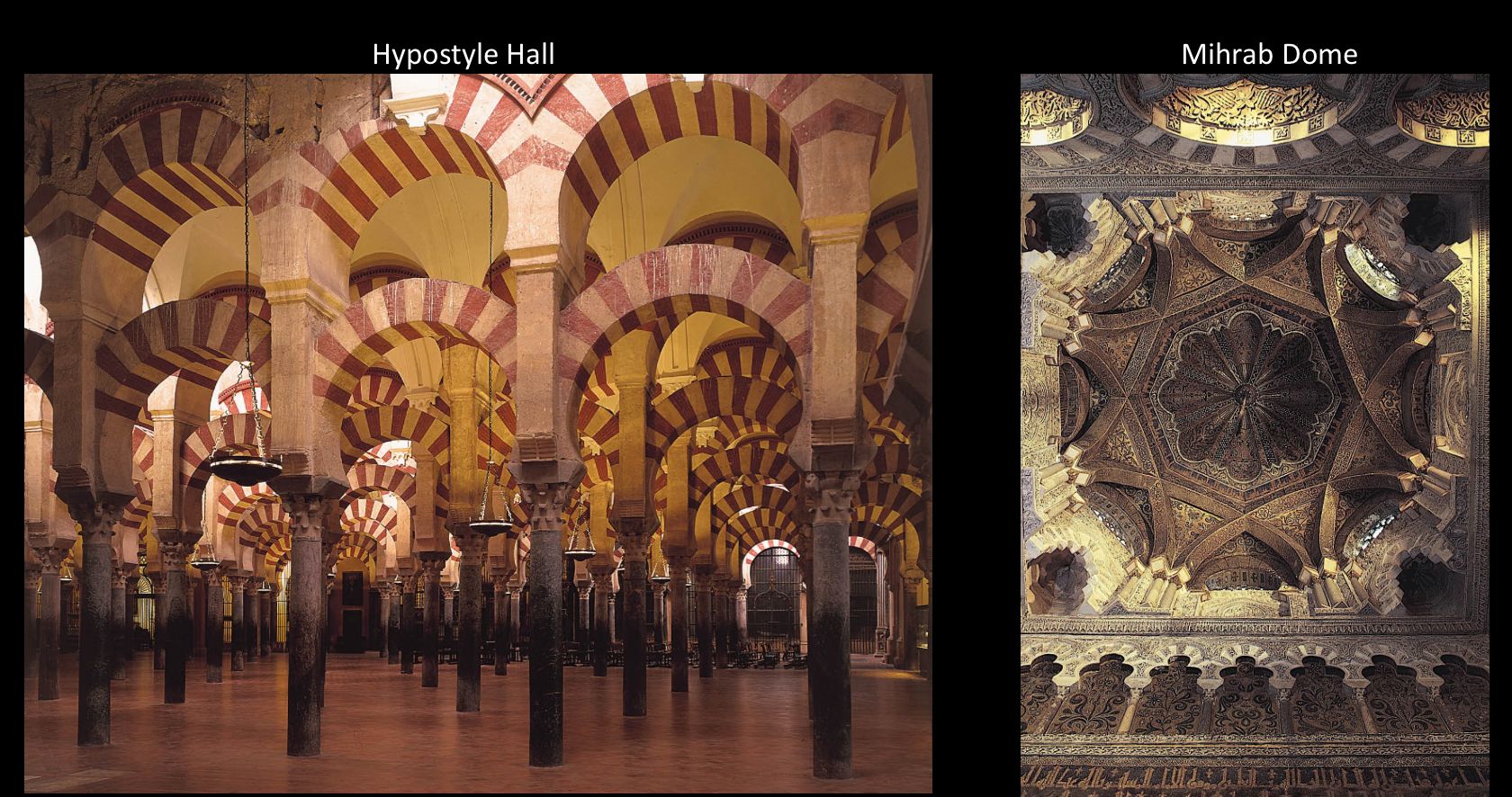

Great Mosque of Córdoba, Spain, 8th-10th centuries (Islamic Spain)
remodeled the center into a Christian church, which happened when Muslim wasn’t the dominant religion
The Mihrab wall has a horseshoe arch this time
Mihrab is a dome in this example
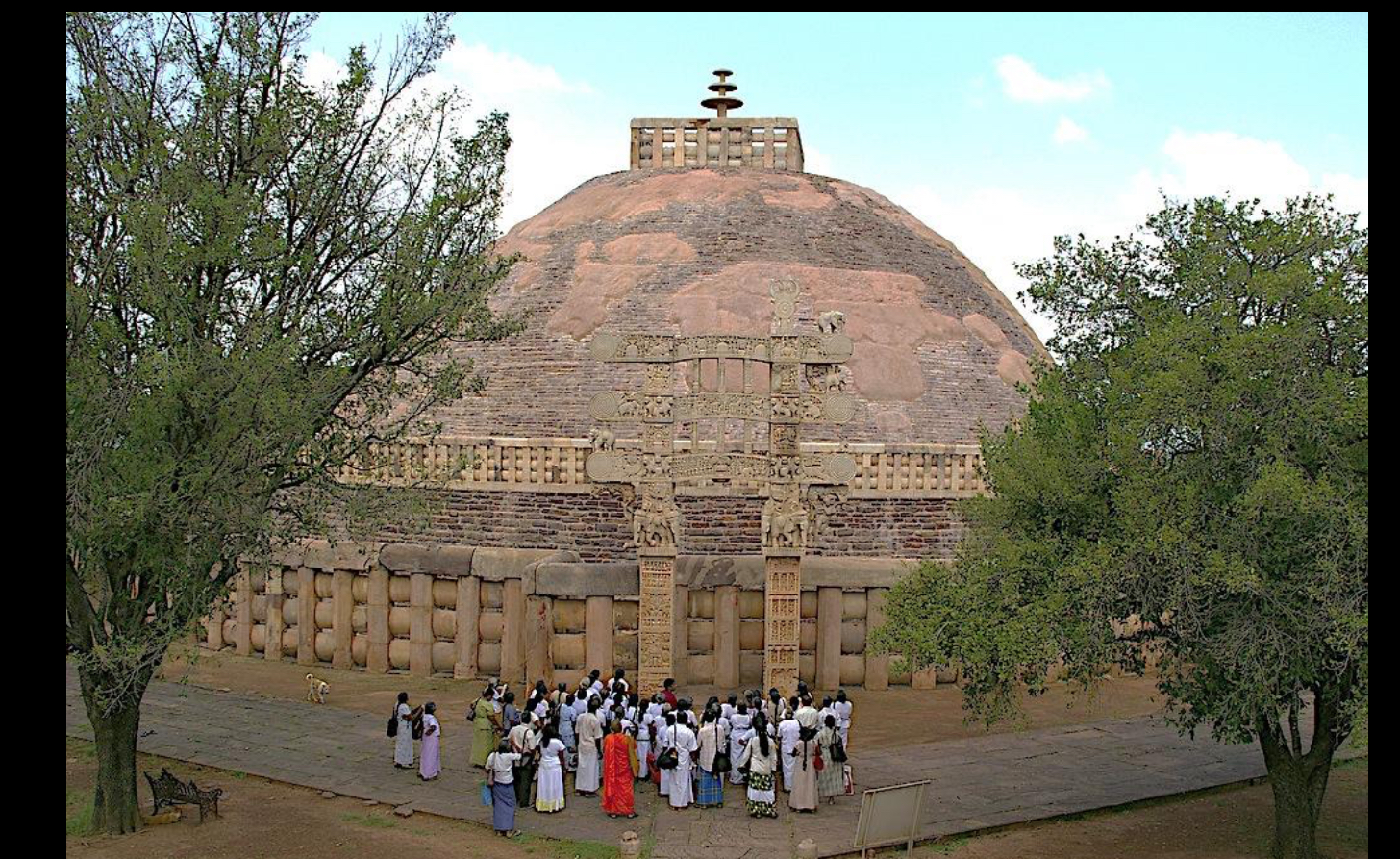

Great Stupa at Sanchi, India, 1st century BCE to 1st century CE (Early Buddhist India)
supposed to appreiciate from walking around the outside not from going inside
The stupa itself is a solid mound
thought to have some of buddha’s ashes
Has torana (gateways) at the north, east, west, and south
Has chatras an umbrella-like disk that symbolizes a heavenly paradise
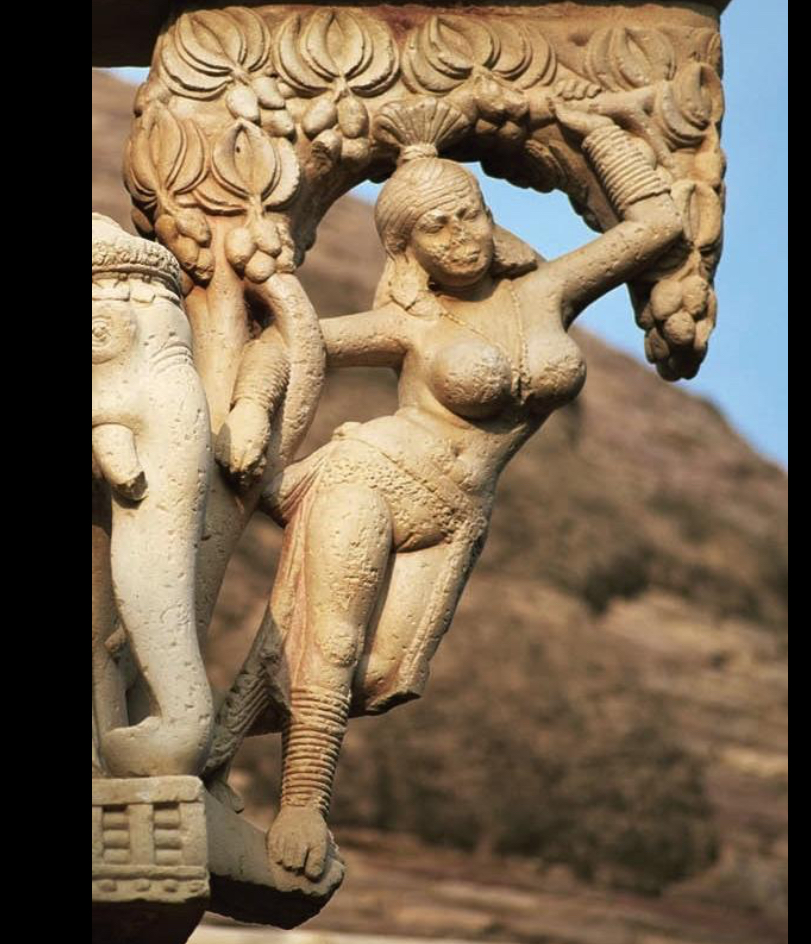

Yakshi from east torana, Great Stupa at Sanchi, India, 1st century BCE to 1st century CE (Early Buddhist India)
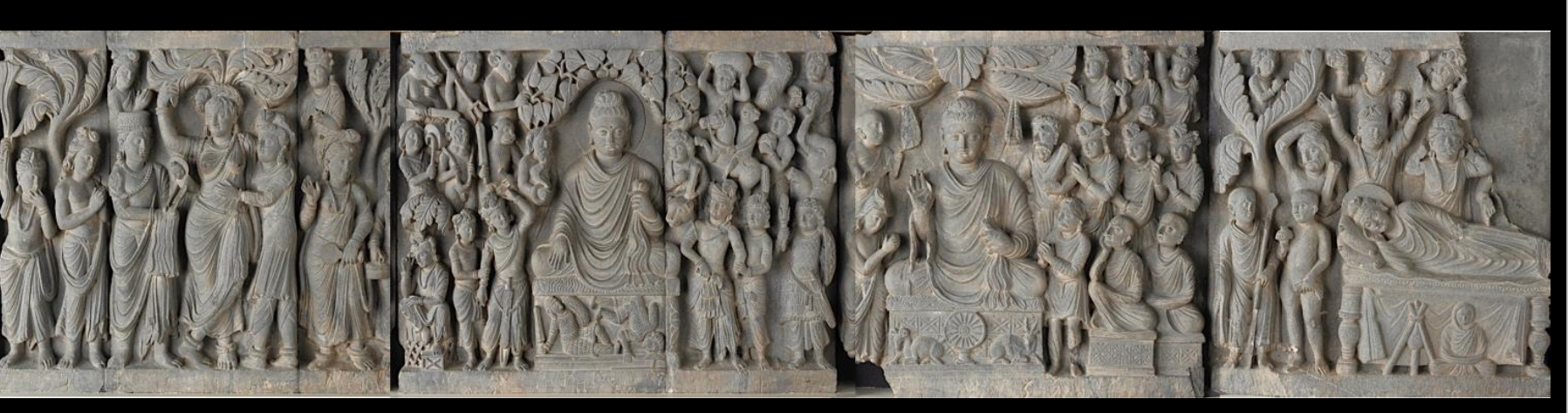

Life and Death of the Buddha, narrative frieze from Gandhara, Pakistan, 2nd century CE (Early Buddhist India)
has a symbolic nimbus (halo), lakshanas, and mudras, and other distinctive Buddhist iconography
lumbini (where he was born)
bodh gaya (where he achieved enlightenment)
sermon
death
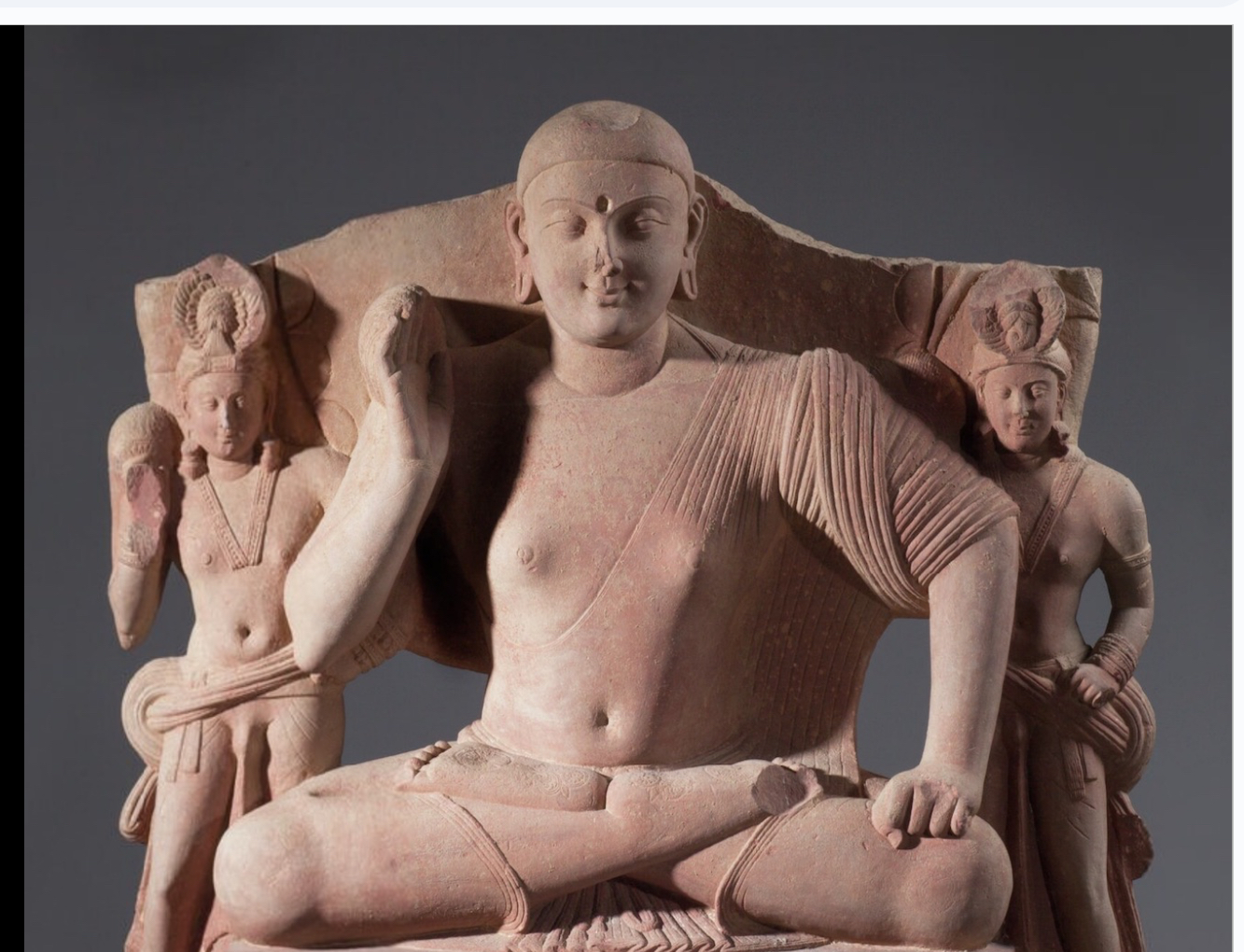


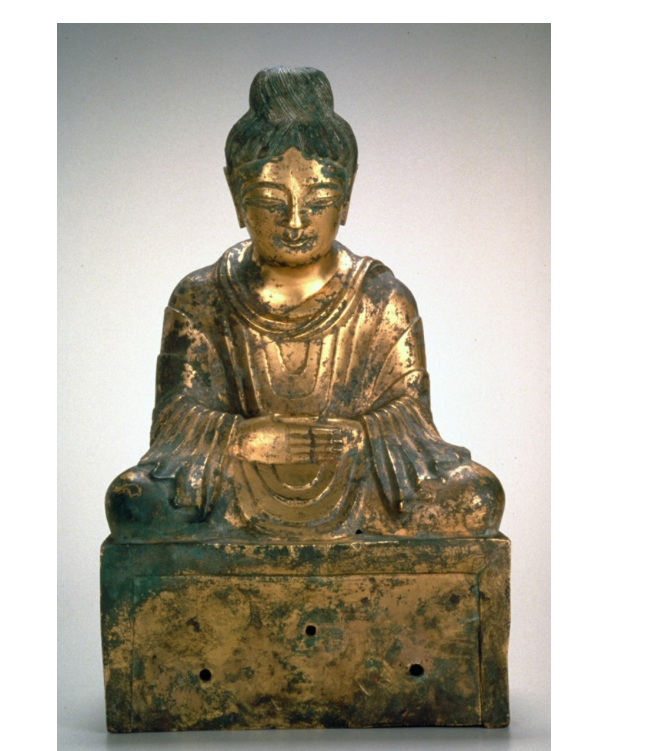
Seated Buddha from Mathura, 2nd century CE (early Buddhist India)
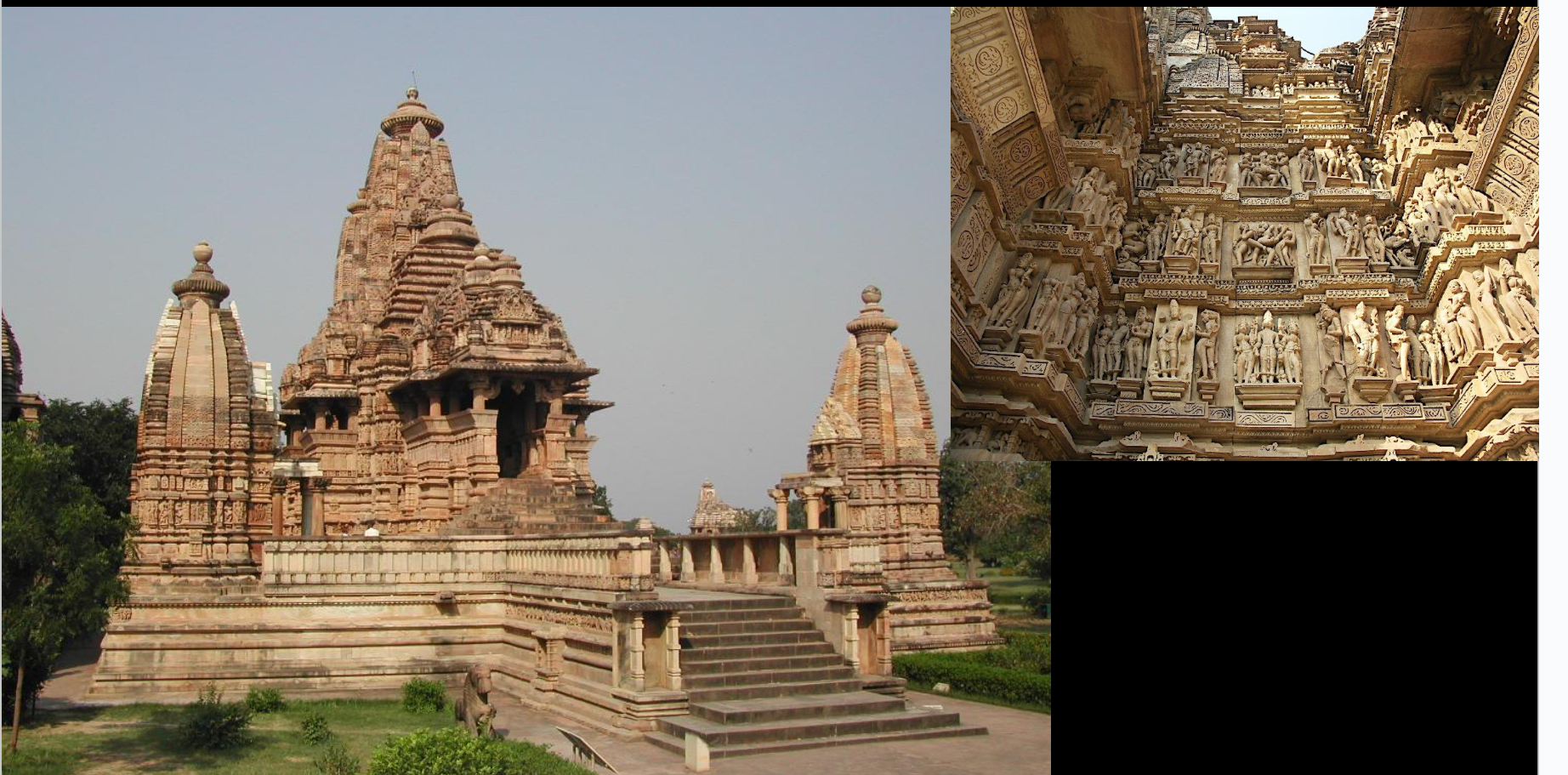

Lakshmana Temple, Khajuraho, India, 10th century CE (Hindu India)
has sculptures on outer walls
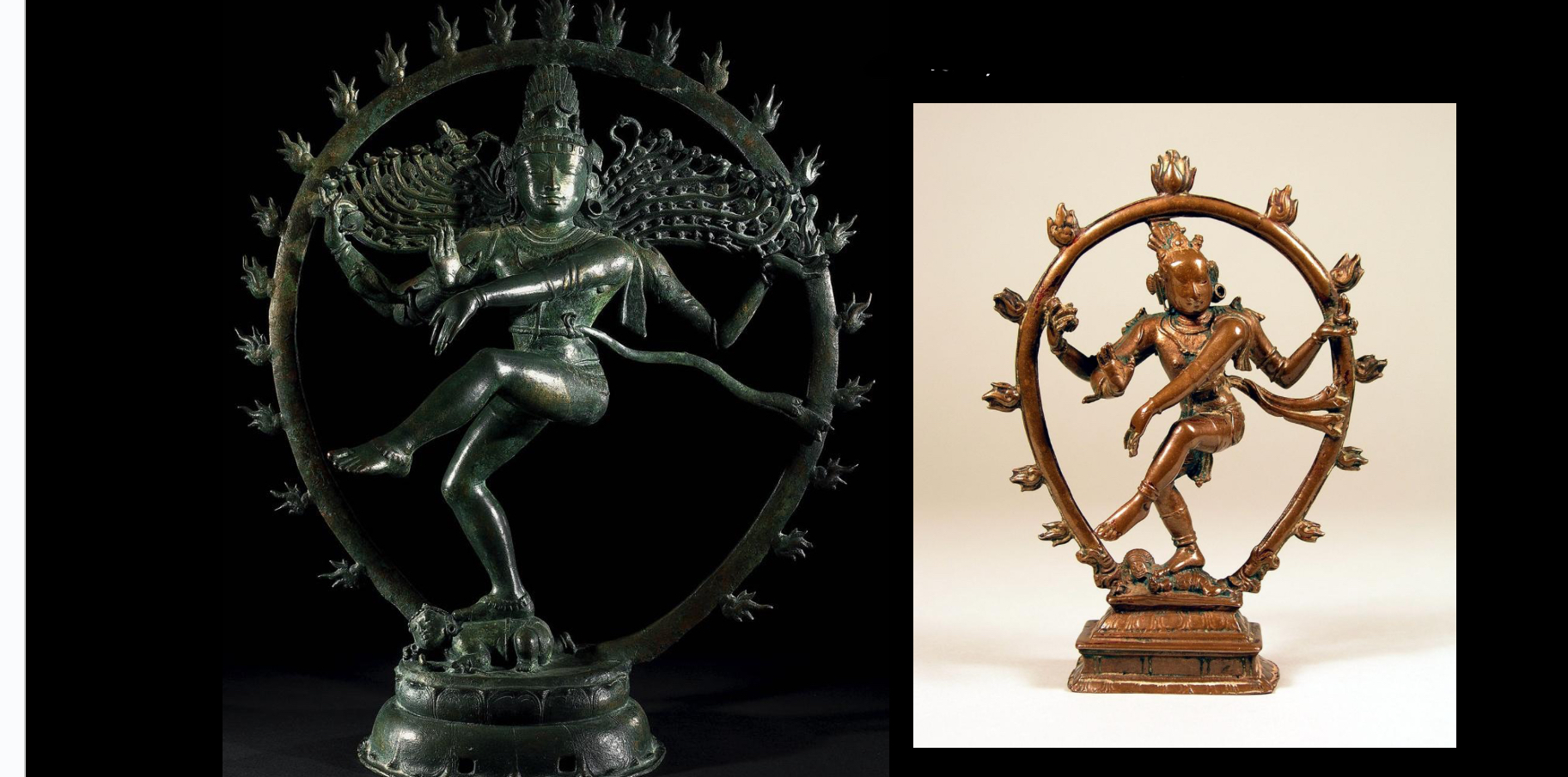

Shiva as Nataraja, India, c. 1000 CE (Hindu India)
Calligraphy
In Greek means “beautiful writing.” The art of ornamental handwriting
Compare a Qur’an Fragment from the early 8th century (Islamic) with Noah and the Rainbow, From the Vienna Genesis, 6th century (Byzantine)
Both pieces exemplify religious themes in art and literature, reflecting their respective cultural contexts and beliefs through narrative and calligraphic styles.
But the Qur’an doesn’t really have colors or pictures; it’s read from right to left, and it’s a landscape. While Noah and the rainbow have pictures, more colors, and its more vertical (hotdog) rather than landscape (hamburger)
Hypostyle prayer hall
It is a type of mosque hall that has a roof supported by many columns. (from the Greek hypo = under, style = column).
Forecourt
transitional space between outside life and sacred space inside the mosque.
It’s an open preparatory courtyard, but the real “take off your shoes” moment is right before entering the prayer hall proper.
What type of religion are Hinduism and Buddhism
Polytheistic
Indus River Valley
A historical region in present-day Pakistan and northwest India, known for the ancient Indus Valley Civilization, characterized by advanced urban planning and river-based agriculture.
Samsara
The cycle of birth, death, and rebirth in Hinduism and Buddhism, driven by karma.
reincarnation
karma
The principle of cause and effect in Hinduism and Buddhism, where one's actions (good or bad) influence future outcomes and rebirths.
is a key component in both Hinduism and Buddhism is the energy generated by a person’s actions and the ethical consequences of those actions. Karma affects a persons next existence or rebirth.
Buddhism develops in ____
Buddha means
late 6th century BCE
enlightened one
Compare Lakshmana Temple to Old St.peter’s Rome
Both are significant religious structures; Lakshmana Temple is known for its intricate carvings and representation of Hindu architecture, while Old St. Peter's Basilica reflects Renaissance and classical styles in Christianity, showcasing differing cultural and religious values.
yakshas
male, more muscular, guardian-like figures, sometimes fierce, sometimes benevolent.
Both appear in Buddhist, Jain, and Hindu art, especially early stupas (like Sanchi), where they decorate gateways as protective, auspicious beings.
iconic
in human form often representing divine beings or deities in spiritual contexts.
padmasana or lotus pose
A seated posture used in yoga, symbolizing spiritual awakening and meditation.
an advanced crossed legged yoga posture/ meditative pose
Buddha’s teachings, known as the Four Noble Truths/Dharma
Life is suffering (suffering=rebirth)
the cause of suffering is desire
the cause of desire must be overcome
when desire is overcome must be overcome more suffering (suffering=rebirth)
fundamental principles in Buddhism that outline the nature of suffering, its origin, cessation, and the path to its cessation.
early depictions of the buddha were ____ symbolic
anionic