(6,7,8) Software Construction Quiz 3
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Slides 6,7, 8
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
CRC Cards
Contains information of class, responsibility (knows or does), potential collaborators (other class used to get information or perform action)
May contain superclasses/subclasses, description and attributes on back.

Advantages of CRC Cards
Portable, Anthropomorphic, involvement increase, useful, serves as input/starting point, eases transition from process to objects, general size bound
CRC Process
Exploratory phase - find classes, determine responsibilities, collaborators
Analysis phase - collect into subsystems (group classes)
Properties of good class
Clear/recognizable name, uppercase letter singular noun, has responsibilities, participates in system
Class Responsibilities
Public services provided to other objects and system
Knowledge and Action
Knowing - private encapsulated data, related objects, things derived
Doing - creating an object, initiating/controlling action/activities in other objects
Identifying Responsibilities
Verb-phrase identification - identify verbs
Scenarios and role play - walk-through where people play classes
Class enumeration - create initial set of responsibilities and designate them to enumerated classes
Class relationship examination - examine how class relationships fulfill responsibilities
Collaboration
Request from one object to another in order to fulfill a responsibility.
“Is-part-of” Relationship between classes
Imply responsibilities for maintaining information OR fulfill responsibilities by delegating them. (Composition and Aggregation) (students as part of school)
“Has-knowledge-of” Relationship
May know other classes that are not in part-of relationships (associations in UML) (teacher has knowledge of subject)
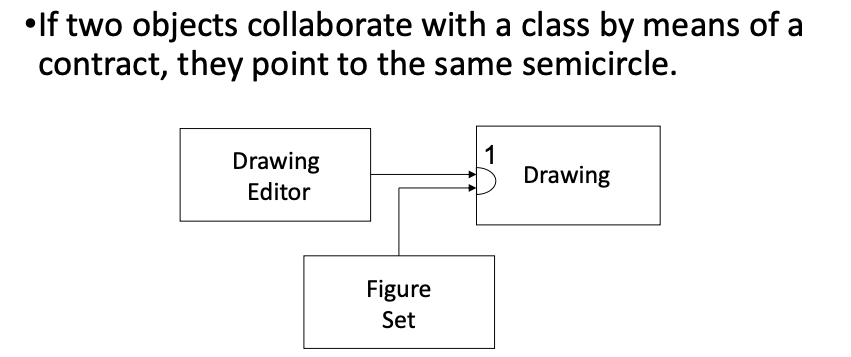
Collaboration Graph
Arrows point from client(class) to contract(semi-circle).
Exploratory Phase
Identify preliminary list of classes, responsibilities, collaborations. (all identified classes are probably concrete and few may have been identified as abstract)
Analysis Phase
Obtain global understanding of design using Hierarchy graphs, Venn diagrams, Contracts
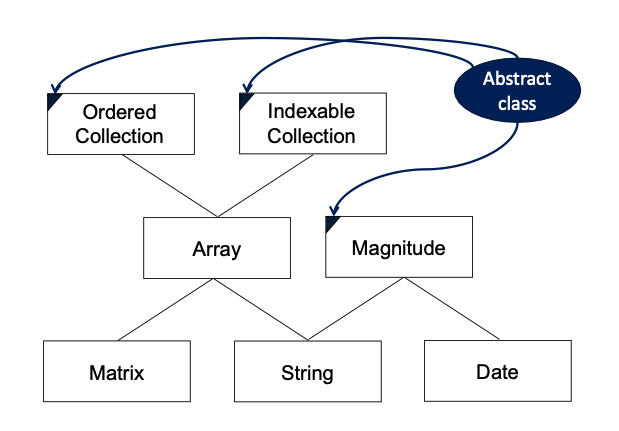
Hierarchy Graph
Tree representation of inheritance, parents are superclasses, children are subclasses, arcs represent abstract class.
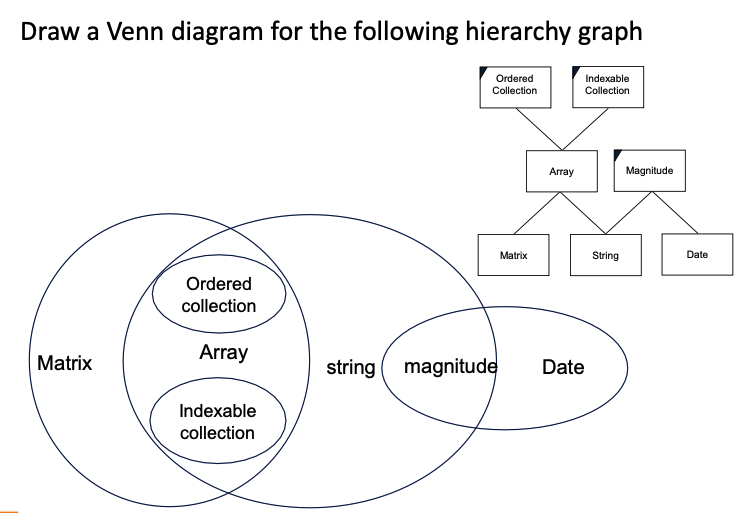
Venn Diagram
Views class as set of responsibilities. (Ordered and Indexable are properties of all Matrix,Array, and String)
If B supports only a part of the responsibilities for A, make a new abstract class C and have both A and B extend from them.
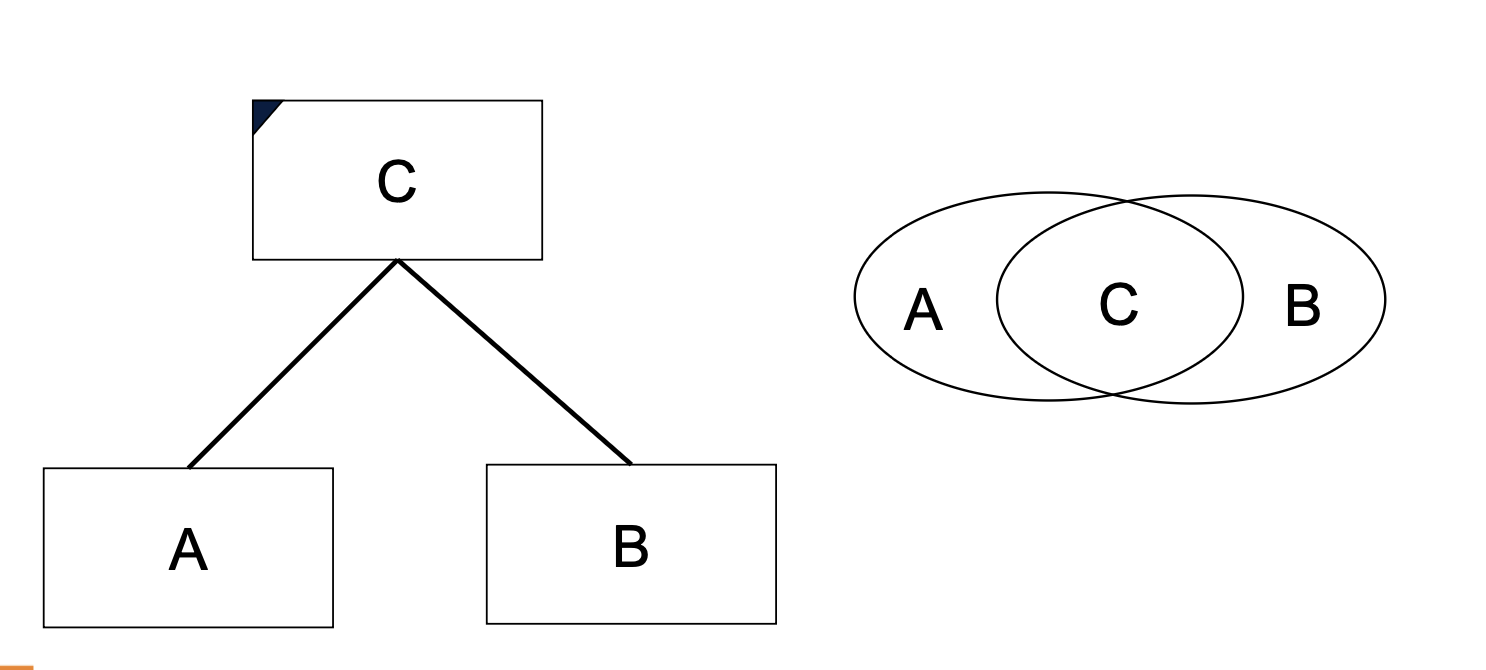
It only takes one responsibility to create an abstract class.
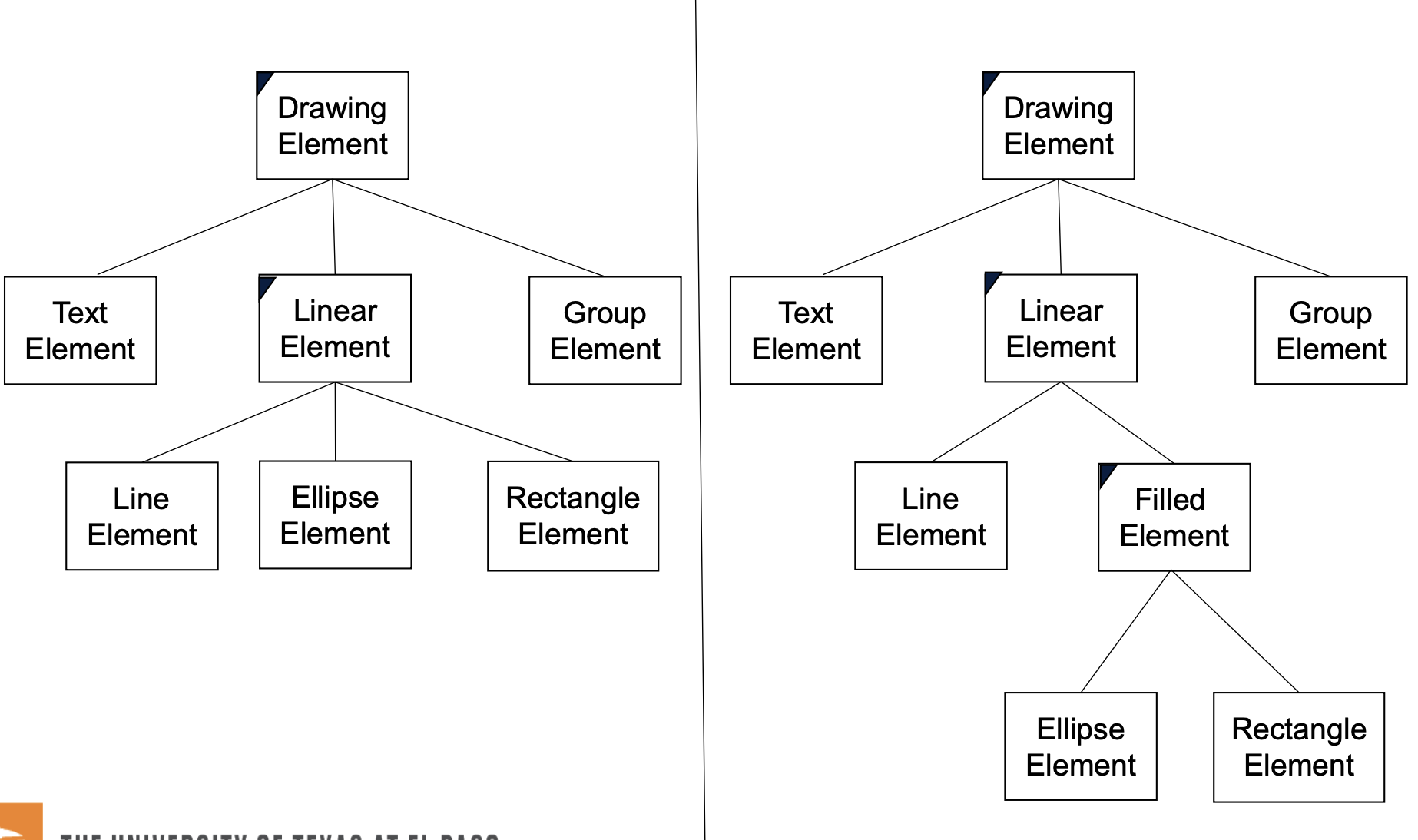
Ellipse and Rectangle are both Filled, so Filled Element is created as an abstract class.
Contract
Set of cohesive responsibilities that a client can depend on. (Defines set of requests client make to server, server is guaranteed to respond). An abstraction analysis technique for refining hierarchy and identifying subsystems.
True Or False: Responsibilities are the basis for determining contracts.
True
True or False: A class can support any number of contracts.
True
True or False: All responsibilites will be part of contract.
False (private responsibilities)
True or False: A responsibility may only be a part of at most one contract.
True (cannot have same responsibility in different contracts)
True or False: Contracts are used in a collaboration
True
Contract Documentation
A contract is a set of responsibilities.

Guideline 1 for Defining Contract
Group responsibilities used by same clients
Guideline 2 for Defining Contract
Maximize cohesiveness of classes
Guideline 3 for Defining Contract
Minimize coupling of classes by reducing the number of contracts
(provide general interface, use polymorphism, look for similar responsibilities to generalize, define classes for classes at the top of hierarchy, add new contracts only for subclasses that add new functionality.