BME 70A - Lecture 3 - Engineering Design Process and Project Management
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Provide a general definition of design.
It is an open-ended process where more than one feasible solution may exist. The goal of a design is to meet a set of pre-determined specifications.
Provide a technical definition of design.
Engineering design integrates mathematics, basic sciences, engineering sciences and complementary studies in developing elements, systems and processes to meet specific needs. It is a creative, iterative, and often open-ended process subject to constraints which may be governed by standards or legislation to varying degrees depending upon the discipline. These constraints may relate to economic, health, safety, environmental, social, or other pertinent factors.
What is the role of the customer during the design process?
The customer sets the goals and requirements
How does the customer and design synthesis coincide?
Design synthesis which includes the functional specs, design specs, and model and prototypes is shown to the customer while the customer drives the design synthesis using customer, functional, and performance requirements.
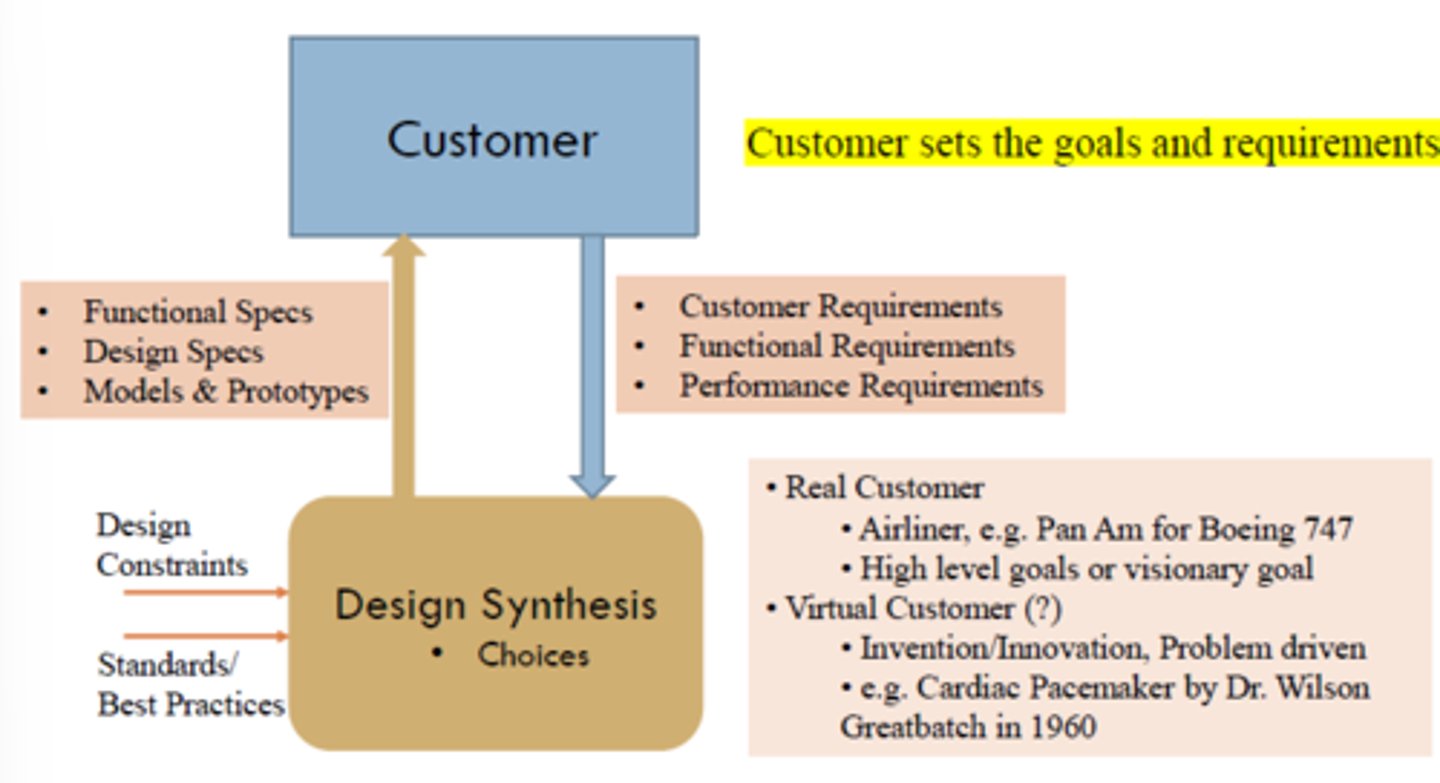
What is the role of the customer during the design process?
List the three design types?
1. Evolutionary design
2. Innovative design
3. Evolutionary + Innovative design
What is innovative design?
Original idea, a novel way of solving a problem. It is an invention.
Define invention.
The realization of a new and useful product, process, or system. Result of applying innovation to technology
Provide an example of innovative design.
Cellular network in the early 70's
Define evolutionary design (re-design).
Is an improvement to an existing design.
Provide an example of evolutionary design.
Passenger cars have come a long way from Henry Ford's Model T, yet the basic functions remain same: propulsion, steering, braking, seating, and others.
Define competitive analysis.
Comparing with similar design or product. Helps with establishing design criteria.
Define benchmarking.
It is the process of determining how well a function is performed, usually for later competitive analysis.
Define reverse engineering.
It is the process of decomposing an existing solution to understand how it has been constructed and where its design limitations are
Evolution + Innovation Design
Much complex design involves a combination of re-engineering and innovative design
Provide an example of evolution and innovation design.
Generational evolution of Cellular network, smart phone era
What are the seven steps of the waterfall model design process.
1. Needs assessment
2. Synthesis
3. Design analysis
4. Implementation
5. Testing and validation
6. Recommendation
7. Construction and Manufacturing
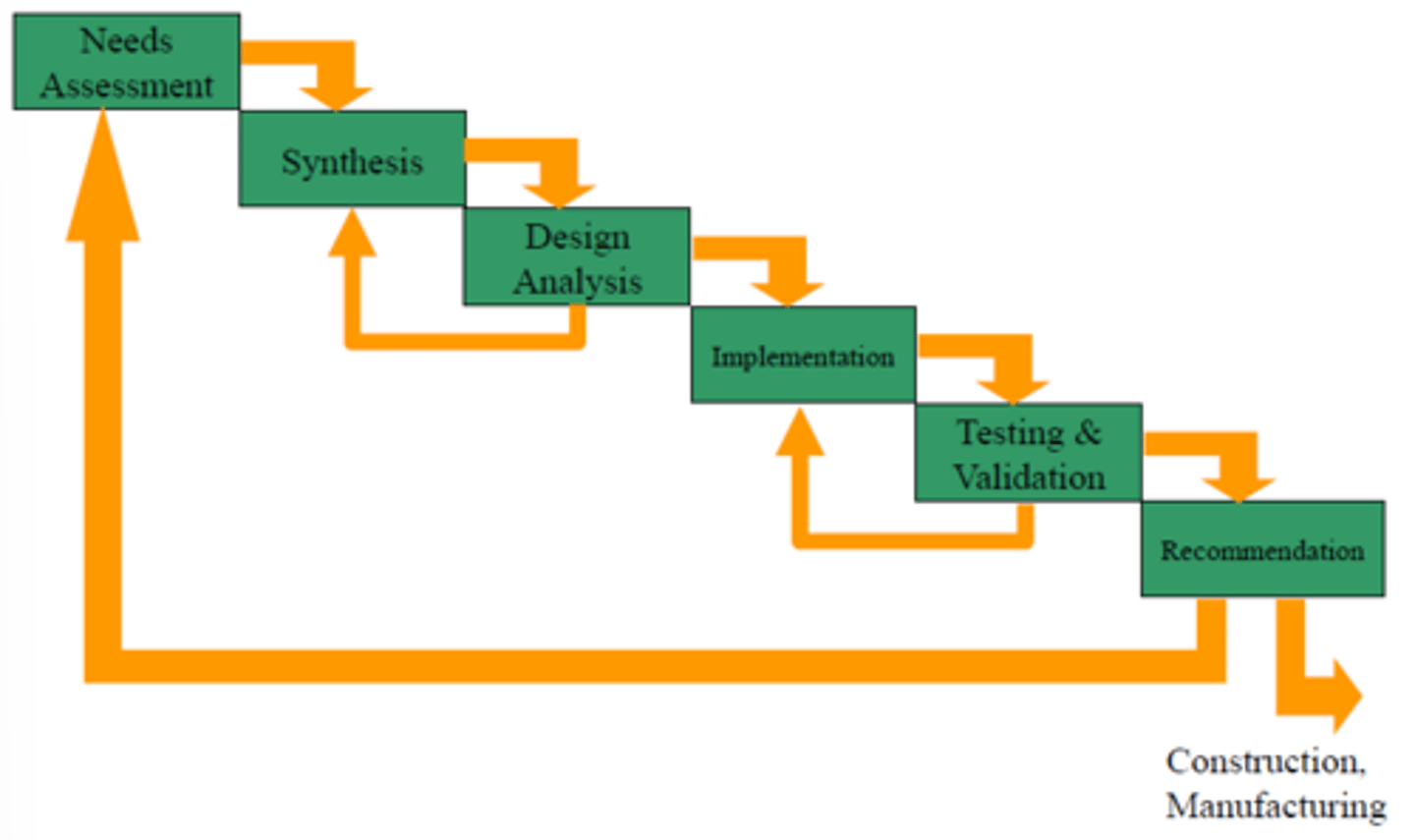
What occurs during the needs assessment step?
Determine the problem, stake holders, existing solutions and their suitability, requirements, constraints, additional criteria
What are four specific customer requirements that should be considered during the design process?
1. Performance
2. Time
3. Cost
4. Quality
In what six ways can the quality of customer requirements be determined during the design process?
1. Performance
2. Features
3. Reliability
4. Durability
5. Serviceablity
6. Conformance
What are the four customer requirement classifications?
1. Expecters
2. Spoken
3. Unspoken
4. Exciters
What occurs during the synthesis assessment step?
Ideas for solving the problem, creative ways of addressing limitations, solution alternatives and their priority
What occurs during the design analysis assessment step?
Whether design idea is feasible, whether it incorporates best practice, predicted performance
What occurs during the design implementation assessment step?
How to build the solution? Prototype or simulation for testing the solution
What occurs during the testing and validation implementation assessment step?
Evaluation process or steps, test measures, acceptable outcomes
What occurs during the recommendation implementation assessment step?
Whether design specification for manufacturing can be generated, or it needs further improvements
Diagram of the engineering design cycle.
What are design skills?
1. Clearly defining the problem with requirements
2. Generating solutions
What are the three steps of solution generation?
1. Explain the problem
2. Brainstorming
3. Assumption smashing
What are the three phases of formal brainstorming?
Phase 1: Idea generation phase
Phase 2: Idea trigger phase -> tension and relaxation technique
Phase 3: Compilation phase
What are the parts of a prototype?
1. Fidelity
2. Functionality
What defines the fidelity of a prototype?
How it conveys the look-and-feel of the final product
What defines the functionality of a prototype?
Sample or model of a product built to test a concept or process or to act as a visual prop to be replicated
What are the 8 general factors that define good design?
1. Requirements
2. Constraints
3. Identify users and their tasks
4. Identify effects on the environments
5. Generate multiple solutions
6. Select optimal solutions
7. Defensible decisions
8. Best practice
What is the most important requirement for a product?
The function and the performance. "It should work and perform one or more functions."
Define the constraints of a design.
Maximum and Minimum limitations on performance of specific functions or sub-functions. Specific limitations regarding size, shape, materials, or manufacturing processes
What is an example of a constraint for a design?
The product must not exceed certain budget.
What is an example of a requirement for a design?
The sports car must cruise at 200 kmph
What are defensible decisions?
Complex process of selling ideas to the customer. Multiple stakeholders are involved, ex. team, marketing team etc.
What six areas of engineering design need to be documented for good engineering design?
1. Project plan and milestones
2. Project budget
3. Functional specifications
4. Design specifications
5. Test and validation plan
6. Design reviews, design logbook, progress reports, final reports
What should be included in functional specifications?
States functions in quantitative terms and in the order of priority
What should be included in design specifications?
Detailed blueprint of the design solution (ex. Block diagram). Form of the discipline (ex. diagrams for H1 and entity-relationship for SW)
What is the Charles De Gaulle Airport Terminal 2E collapse?
Inaugurated in May 2004, portion of roof in Terminal 2E fell. 1475 ft (450 mt) tube of concrete rings. Fallen due to lack of detailed feasibility analysis.
What issues did the Charles De Gaulle roof have?
- Lack of redundant supports
- Poorly placed reinforcing steel
- Weak outer steel struts
- Weak concrete support beams
- Low resistance to temperature fluctuations
Example of testing failure in Hartford Civic Centre.
Built in the mid-1970's,, innovative design, instead of conventional I-beam structure, used frame structure of interconnected trusses and joints to form visually appealing pattern. But ignored derating factors at structural joints to account for slight changes in layout
Example of software failure in engineering (Continental Distribution Networking outage)
- Major websites were down -Amazon, Spotify, Airbnb etc.
- Nick Rockwell, Fastly's senior vice president of engineering, said the hour-long outage happened because a customer pushed a configuration change that triggered the undiscovered software bug (https://www.fastly.com/blog/summary-of-june-8-outage).
- Rockwell doesn't explain what exactly happened, other than saying that on May 12, the company deployed a software update that "introduced a bug that could be triggered by a specific customer configuration under specific circumstances."
- Then yesterday, June 8, a customer pushed a configuration change that met the conditions to trigger the bug, which caused 85% of its network to return errors. End users visiting affected sites saw the "Error 503 Service Unavailable" error message in browsers.
McDonald operates restaurants in ______ locations in ___countries across the globe
37000; 120
Describe the digital acceleration project in Jan 2017.
CEO wanted to use digital technology for completely overhauling the customer delivery experience and achieve this change within a year
What is the CEO's vision?
"I have absolutely no doubt that our industry will get disrupted by technology," he warned. "Our discussions within McDonald's are 'Why don't we be the ones to disrupt ourselves rather than wait to be disrupted?' You have a choice to either be the disrupter or the disrupted."
Explain the McDonald's digital acceleration project.
Launched in January 2017
Completion Time Target: Less than a year
Budget: $155 million
Scope: Deployment in 20,000 stores in USA, Canada, UK, France, Australia, China and Hong Kong
Objective: Custom mobile ordering and payment platform that lets customers order meals via in-store kiosks or a mobile app and pick up their orders as soon as they arrive at the restaurant. The system uses geofencing technology to direct orders to the proper restaurant based on customer's location that reduces the delivery time by giving a lead time for food preparation.
Risks: Pace to complete the project on a short time and Change that overhauls the order and delivery process
What is the global project management office (PMO)?
Previous global projects had siloed plans for each market that slowed progress and prevented consistent communication and delivery with a centralized governance
What is the global management office (PMO) provide through a centralized governance?
- ensures same level of quality and reliability in deployment
- accelerated delivery with short release cycle
- allows for local customization
What is the change control board (CCB)?
Prioritize stakeholder demands, provide a firewall for developers and mitigate the risk of scope creep. The board approved no changes unless they met a valid business purpose, aligned with the strategic vision and had a defined budget
What is robust change management?
Local franchise owners need to roll out training for staff to learn new technology and delivery process, make counter-design changes, create space to install kiosks and adapt parking lots for curb side pickup. Experts were brought to counsel stakeholders how to plan changes and deployment, and communicate the value of transformation. Held technology demonstrations, set strict deadlines and captured learning lessons
What has McDonald's achieved?
- 20,000 deployment in Nov. 2017
- 1 month ahead of schedule, nearly $10 million under budget
What does the platform (McDonald's) allow customers to do?
To place orders, access special offers and pay
through their devices. To pick up their food at the
counter, in the drive through, or at the curbside
What are some reasons why projects fail so often?
- Unrealistic or unarticulated project goals
- Inaccurate estimates of needed resources
- Badly defined system requirements
- Poor reporting of the project's status
- Unmanaged risks
- Poor communication among customers, developers, and users
- Use of immature technology
- Inability to handle the project's complexity
- Sloppy development practices
- Poor project management
- Stakeholder politics
0 Commercial pressures
Define project.
A temporary endeavor undertaken to produce a unique product, service or result -PMI definition. Combination of human and non-human resources pulled together in a temporary (specified start and end time) organization to achieve a specified purpose
What do features do?
- Definable purpose with established goals
- Project Requirements -Performance, Cost, Time and Scope (PCTS) targets
- One-time activity (defined start and end time) -a repetitive activity is not a project
- Temporary activity
- Multiple resources across organizational lines
- Element of risk
- Process of phases/project life cycle
Diagram showing process approach to PM.
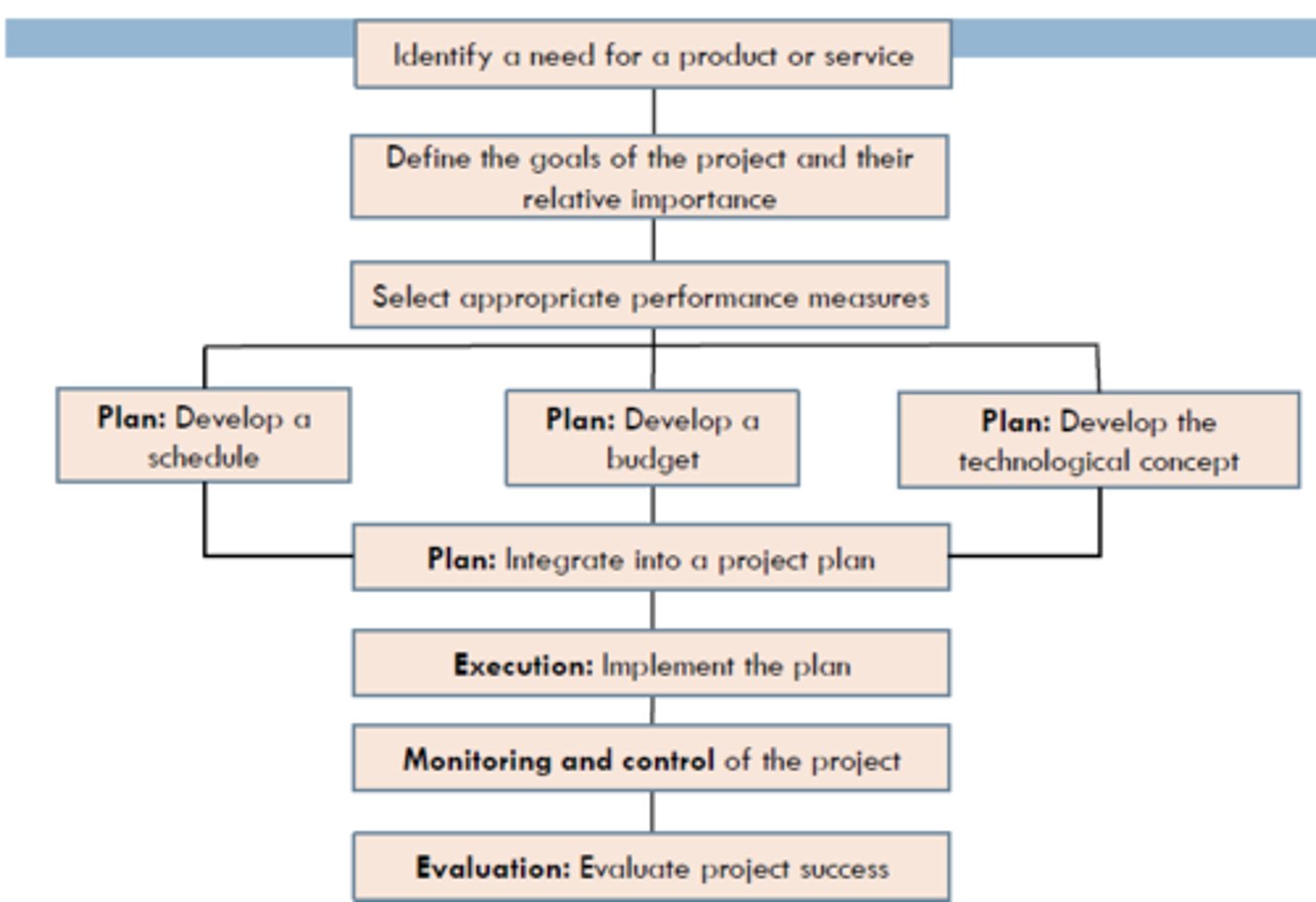
List the six steps of the project lifecycle.
1. Conceiving and defining the project
2. Planning the project
3. Implementing the plan
4. Completing and evaluating the project
5. Operating and maintaining the project
6. Life-cycle Model -Project phases
Diagram of software system Waterfall model.
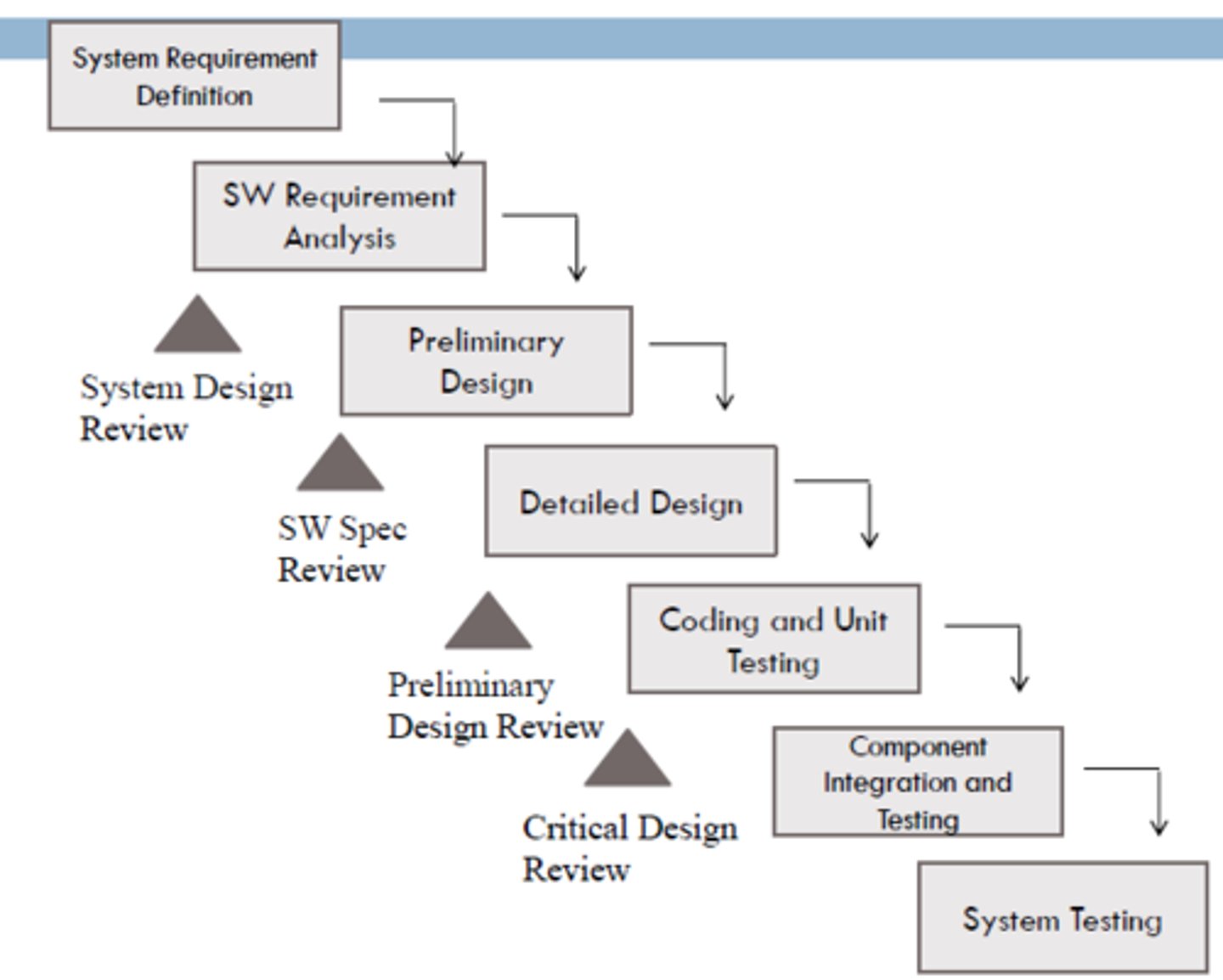
Diagram of resource distribution.
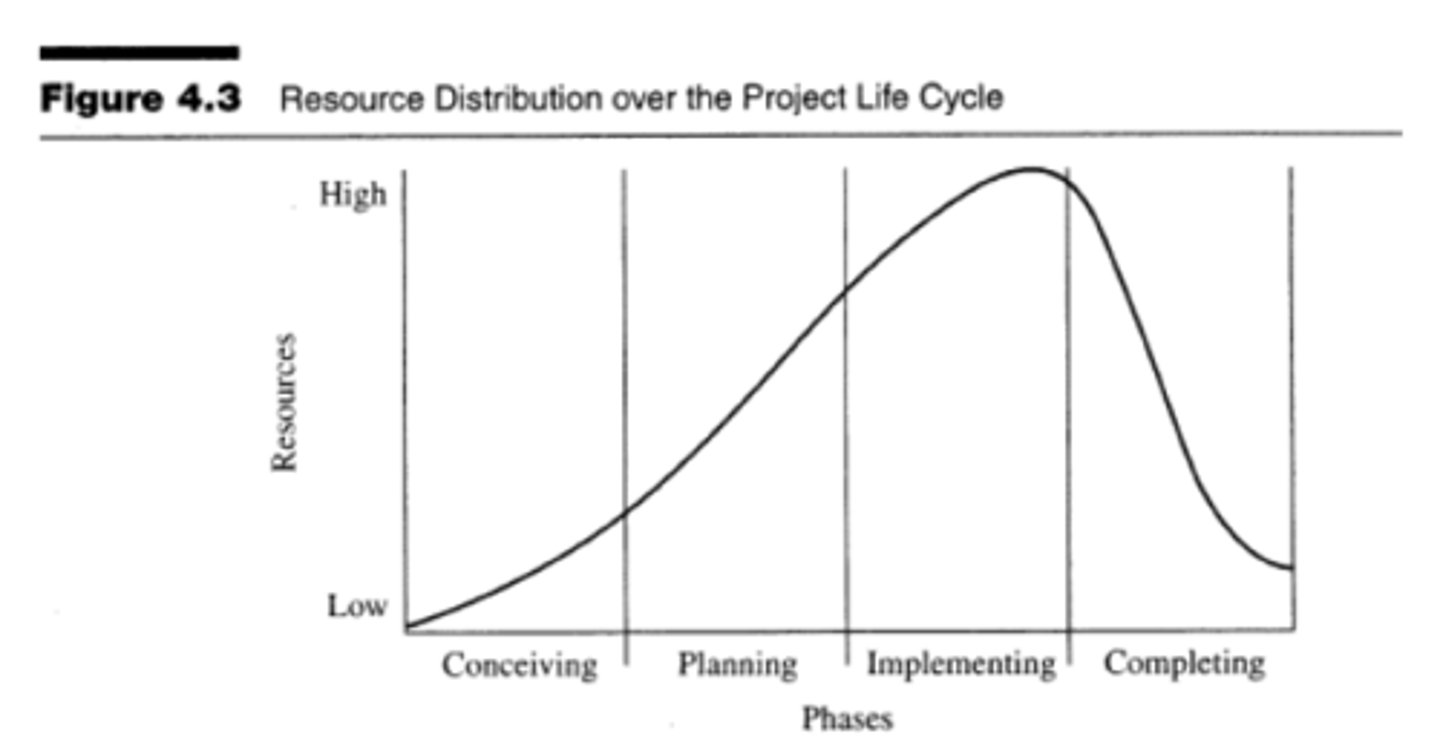
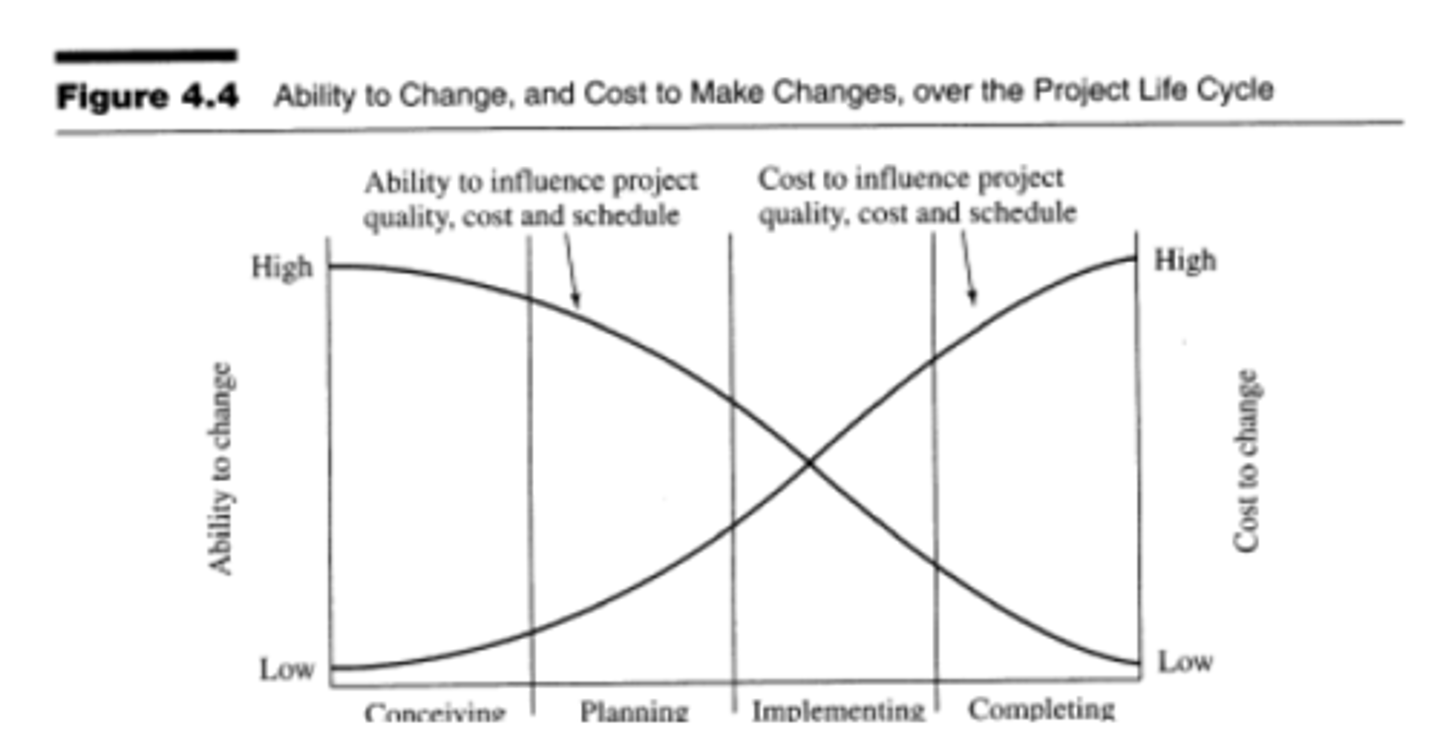
Diagram of ability and cost of changes.
What nine aspects does project planning consist of?
1. Overview: brief description of project, deliverables, and milestones
2. Objectives: detailed description of project deliverables
3. General approach
4. Contractual aspects: reporting requirements, technical specifications, project review dates
5. Schedules: outlines of schedules, milestones, tools
6. Resource requirements
7. Personnel: necessary skills and training
8. Evaluation methods: standards, benchmarks, testing
9. Potential problems
What five roles do project managers need to engage in?
1. Planning
2. Organization
3. Staffing
4. Directing
5. Controlling
Explain the organizing role of project managers?
- Develop WBS (Work Breakdown Structure)
- Scheduling, Budgeting, and distribution of responsibilities
Explain the directing role of a project manager.
Coordinating project components, investigating potential problems and taking steps to resolve them including allocation/reallocation of resources
Explain the controlling role of a project manager.
Communicating with team members; measuring project performance; planning, monitoring progress of and completing milestones; convening and documenting meetings
A project manager needs both _________ and ________ skills : management skill to administer above tasks and leadership skill to get the staff do the work on their own will
Management; leadership;
What are the five characteristics of an effective team?
1. Positive interdependence
2. Individual and group accountability
3. Promotive interaction
4. Teamwork skills
5. Group processing
What is positive interdependence?
Team is focused on a common goal. Team goals are as important as individual goals.
What is individual and group accountability?
The team understand the goals and is committed to achieving them. Each person takes responsibility to the success of the team. Each person delivers on commitments
What is a promotive interaction?
Trust replaces fears and people feel comfortable taking risks. Respect, collaboration and open-mindedness are prevalent
What are teamwork skills?
Each member has the skill for and practices effective communication, decision making, problem solving, conflict management, and leadership. Team members adopt tools to effectively manage teamwork
What is group processing?
The team reflects on its processing, celebrates its achievements and take correctional steps in case of problems.
What are eight individual essentials of teamwork?
1. Energy
2. Enthusiasm
3. Passion
4. Punctuality
5. Integrity
6. Good behavior
7. Understanding
8. Respect
What are the five team dynamic stages?
1. Orientation of forming
2. Dissatisfaction or storming
3. Resolution or norming
4. Production or performing
5. Termination or adjourning
What is dissatisfaction or storming?
Challenges of forming a cohesive team. Differences in personalities, working and learning styles and habits, logistics etc.
What is resolution or norming?
The team establishes group norms to guide the process, resolve conflicts and focus on common goals
What is production or performing?
The team is working co-operatively with few disruptions. Effective project planning and project management is a major reason for team's performance, e.g. missing or tight deadlines cause tension within the team.
What is termination or adjourning?
Joint reflection and evaluation of team performance, and celebration
What are the basics of communication ?
1. Listening and Speaking
2. Honesty and Fairness
3. Respect
4. Say What You Mean and Mean What You Say
How should meetings be conducted?
1. Plan, Inform, Prepare, Structure and Control, Summarize and Recall
2. Hold at least one meeting every week
3. Record the minutes in a logbook
What does PIP SCS R stand for?
1. Plan, Inform, Prepare, Structure and Control, Summarize and Recall
Define conflict.
The situation in which an action of one person prevents, obstructs, or interferes with the actions of another
What are seven ways to manage conflict?
1. Withdrawal or Avoiding
2. Forcing
3. Smoothing
4. Compromise
5. Confrontation
6. Competing
7. Collaborating
What are five ways to build collaboration?
1. Manage Your Feelings
2. Create a Supportive Climate
3. Focus on the Facts -data driven approach
4. Describe the Goals
5. Create Solutions -solution oriented approach
In what two ways can someone create a supportive climate?
1. Coming together on mutual ground
2. Having a sense of openness
What are the four steps of the decision making process?
1. Frame
2. Gather intelligence
3. Come to conclusions
4. Learn from experience
What happens during the framing process of the decision making process?
Decide (define) what you are going to decide and what you are not going to decide
What happens during the gathering of intelligence decision making process?
Gather real intelligences, not just information that will support your biases
What happens during the come to conclusions during the decision making process?
Determine how your team will act on the intelligence it gathers
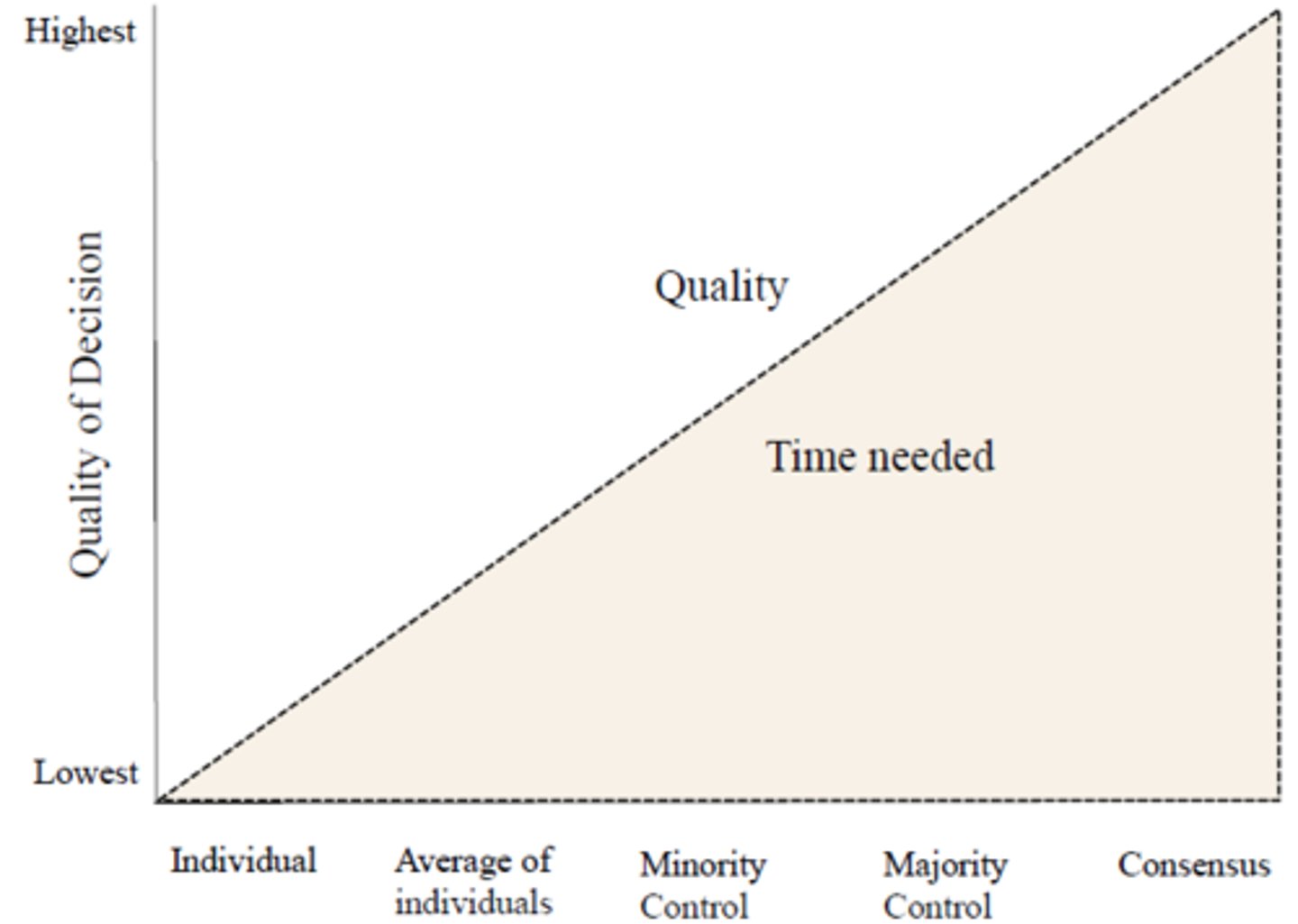
What are the seven types of decision making?
1. Authority without discussion
2. Expert member
3. Average of member's opinion
4. Authority offer discussion
5. Minority in control
6. Majority in control
7. Consensus
Time and quality graph
What are the four aspects of leadership?
1. Plan
2. Organize
3. Control
4. Lead
Define lead.
Show innovation and open-mindedness
Define the engineering leader.
Is Proactive, Has Vision, Creates Alignment, Promotes Growth, Promotes Continuous Improvement, Prevents or Put Out Fires, Leads by Example
Define the engineering manager.
Is Responsive, Stays Focused and Maintains Control, Provides Resources, Manages the Firehouse
Case study: WSB Team of X-Network
