AUBF WEEK 7: MICROSCOPIC EXAMINATION OF URINE SEDIMENT PART II
1/311
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
312 Terms
7 um (6-8 um)
Size of RBC
Crenated RBC
A hypertonic urine would affect RBC in what way?
Ghost Cell or Shadow Cell RBC
A hypotonic urine would affect RBC in what way?
Yeast Cells, Air Bubbles, Oil Droplets, WBC
Sources of error for RBCs (4)
Average number of RBC / hpf
Reporting RBC
0-2 / hpf
Normal value for RBC
Acetic Acid
What solution may remove RBC?
Microscopic Hematuria
Supposed a MT finds RBCs in a yellow-colored urine. What phenomenon is this?
RBC
Identify the microscopic particle
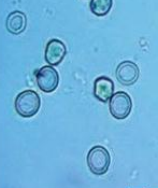
Yeast Cell
Identify the microscopic particle
Air Bubble
Identify the microscopic particle

RBC
Identify the microscopic particle

Crenated RBC
Identify the microscopic particle

Air Bubble
Identify the microscopic particle

RBC
Identify the microscopic particle
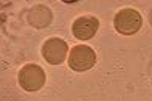
Crenated RBC
Identify the microscopic particle

Dysmorphic RBC
RBC with a protrusion or fragmentation
Renal or Glomerular Bleeding
Suppose an MT finds a number of dysmorphic RBCs in a px’s urine. What may be the cause of this?
Dysmorphic RBC
Acanthocyte with multiple protrusions
Wright’s Stain
Stain used in checking for dysmorphic RBCs characteristic traits.
Dysmorphic RBC
Identify the microscopic particle

Glomerulonephritis, Vascular Injury, Renal Calculi, Malignancy
Clinical significance of RBC (4)
Bleeding distal to the kidneys
Suppose an MT finds incomplete RBCs with casts in a px’s urine. What does this implicate?
Renal Bleeding
Suppose an MT finds incomplete RBCs with no casts in a px’s urine. What does this implicate?
Glomerular Damage or Vascular Injury
Suppose a px produced a red cloudy urine and an MT performed microanalysis and discovered an RBC amount of 125/hpf. What does this implicate?
Renal Calculi, Malignancy, or Early-stage Glomerular Disorders
Suppose a px produced a clear yellow urine and an MT performed microanalysis and discovered RBCs. What does this implicate?
Strenuous Exercise
Suppose an MT discovers RBC in a px’s urine along with hyaline and granular casts. What may be the cause of this?
Pyuria
Described as an increase numbed of WBCs in the urine.
Glitter Cells
What happens to WBC when urine is diluted and hypotonic?
Glitter Cells
Suppose an MT discovers WBCs with swelled nuclei and cytoplasmic granules exhibiting Brownian movement. What did they find out?
High pH and Hypotonic Urine
What may be the cause of WBC lysis?
WBC
Identify the microscopic structure
WBC
Identify the microscopic structure

Glitter Cell
Identify the microscopic structure
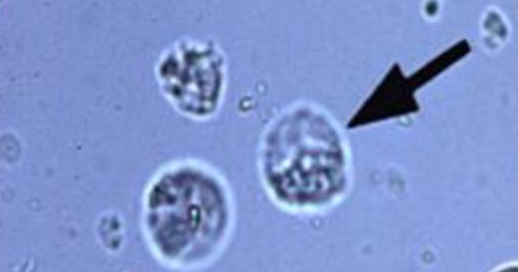
Glitter Cell
Identify the microscopic structure
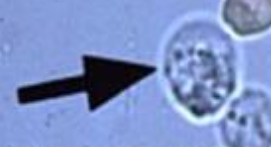
WBC
Identify the microscopic structure
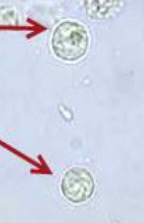
RBC
Identify the microscopic structure

WBC
Identify the microscopic structure
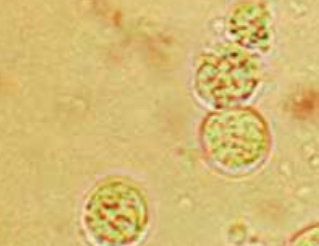
WBC
Identify the microscopic structure
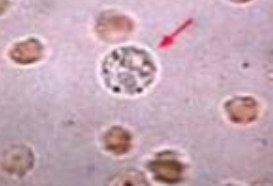
WBC
Identify the microscopic structure
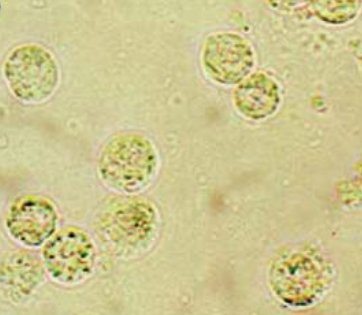
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells, RBCs
Sources of Error for WBC
Average/10 hpf
Reporting of WBC values
0-5
Normal values of WBC per hpf
Leukocyte Esterase, Nitrite, pH
An increase in the WBC values in urine would affect what parameters? (3)
Inflammation or Infection of Renal Origin
Suppose an MT counted a significant amount of WBC in urine along with WBC casts. What is the clinical significance?
Pyelonephritis, Cystitis, Prostatitis, Urethritis
Bacterial infections that produce WBC in urine (4)
Glomerulonephritis, Lupus Erythematosus, Interstitial Nephritis, Tumors
Non-bacterial infection that produce WBC in urine (4)
WBC
Identify the microscopic Structure
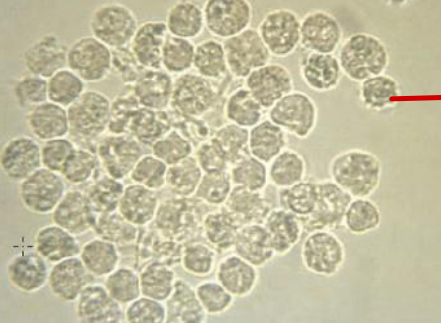
Eosinophil
WBC that is not normally seen in urine
Hansel and Wright
What stains can be used to visualize eosinophil in a urine specimen?
Uses Methylene Blue in Eosin Y
What is the mechanism of Hansel stain?
Tubulointerstitial Disease and Hypersensitivity to Dugs
Clinical significance of eosinophil in urine (2)
Squamous Epithelial Cell
Among the three epithelial cells, which is the least significant but most numerous?
Vagina, Urethra, Vulva
Sources of SEC in a female px
Distal 1/3 Urethra
Sources of SEC in a male px
Folded cells may resemble casts
Sources of error for SEC
Average per LPF
Reporting for SEC
Increased SEC
Suppose an MT is about to examine a turbid urine. What may be the findings in terms of SEC?
Gardnerella Vaginalis
Microbe associated with clue cells
Bacterial Vaginosis
Suppose an MT discovers clue cells in a px’s urine. What may this indicate?
Squamous Epithelial Cell (SEC)
Identify the microscopic particle
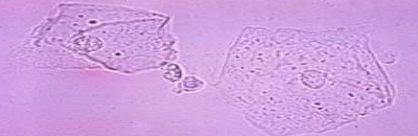
Squamous Epithelial Cell (SEC)
Identify the microscopic particle
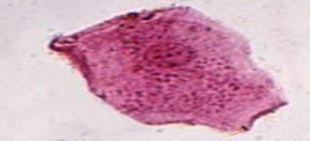
Squamous Epithelial Cell (SEC)
Identify the microscopic particle
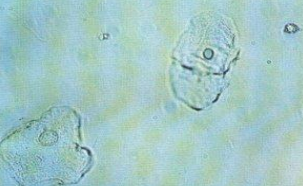
Squamous Epithelial Cell (SEC)
Identify the microscopic particle
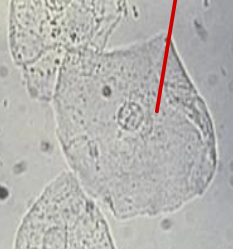
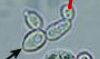
Clue Cell
Identify the microscopic particle
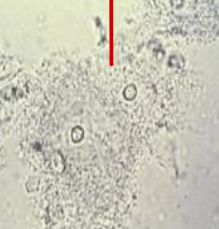
Squamous Epithelial Cell (SEC)
Identify the microscopic particle
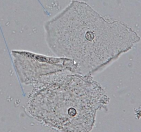
Sternheimer Malbin Stain
What stain can be used to distinguish SEC?
Upper Urethra, Ureters, Bladder, Renal Pelvis
Sources of TEC? (4)
Catheterization, Malignancy and Viral Infections
Clinical significance of TEC (2)
Transitional Cell Carcinoma
Suppose an MT discovered large clumps of TEC in a px’s urine. What can be indicated from this?
Transitional Cell Epithelium
Identify the microscopic structure
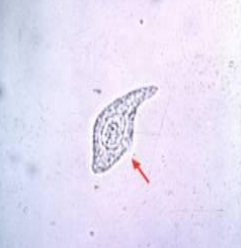
Transitional Cell Epithelium
Identify the microscopic structure
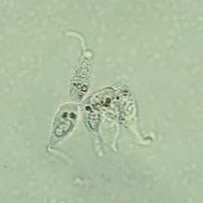
Round, Oval, Pear, Caudate, Kite
TEC may come in 5 different shapes. What are the shapes?
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
The most significant epithelial cell found in urine.
PCT, DCT, Collecting Tubules
Sources of RTEs (3)
PCT-RTE
RTE: rectangular, columnar, convoluted, coarsely granular, and may resemble cast
DCT-RTE
RTE: egg-shaped (round or oval), coarsely granulated, and eccentric nucleus
Collecting Tubule RTE
RTE: w/ one straight edge, cuboidal, polygonal, eccentric nucleus, high NC ratio
0-2/hpf
Normal values of RTEs
Drug and Heavy Metal Poisoning, Pyelonephritis, CMV Infection, Allergic Reaction, Acute Allogenic Transplant Rejection
Possible causes of tubular necrosis (5)
Severe Tubular Injury
Suppose an MT discovers renal fragments in a px’s urine. What does this indicate?
Salicylate Poisoning
Suppose an MT discovers single, cuboidal cells in a px’s urine. What does this indicate?
PCT-RTE
Identify the microscopic particle
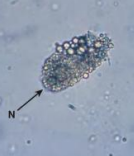
DCT-RTE
Identify the microscopic particle
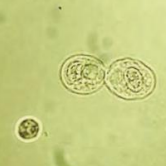
Collecting Tubules RTE
Identify the microscopic particle
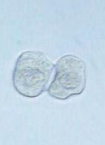
DCT-RTE
Identify the microscopic particle
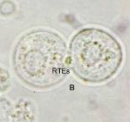
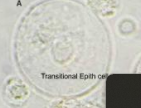
Transitional Epithelial Cells
Identify the microscopic particle
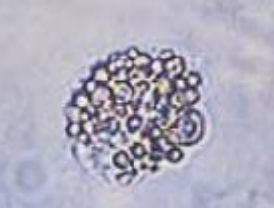
Oval Fat Bodies
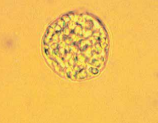
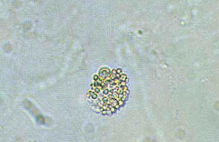
Lipid-containing RTEs, are highly vacuolated, and seen with free-floating fat droplets.
Nephrotic Syndrome
Suppose an MT discovers oval fat bodies within a px’s urine. What may this indicate?
Sudan III or Oil Red O
Stains used in distinguishing oval fat bodies
Maltese Cross Fornation
Specific trait of oval bodies under polarized microscopy
Oval Fat Bodies
Identify the microscopic particle
Oval Fat Bodies
Identify the microscopic particle
Oval Fat Bodies
Identify the microscopic particle
Bubble Cells
Vacuolated, non-lipid containing RTEs
Acute Tubular Necrosis
Suppose an MT discovers bubble cells within a px’s urine. What may this indicate?
Vaginal, Urethral, External Genitalia Contamination
Suppose an MT discovers a few bacteria in a px’s urine. What may this indicate?
Gram (-) Enterobacteriaceae E. coli, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus
Bacteria associated with UTI
UTI
Suppose an MT discovers bacteria and WBC in a px’s urine. What may this indicate?
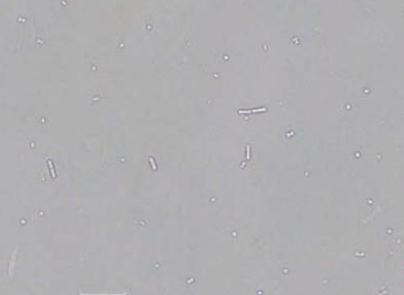
Bacteria
Identify the microscopic particle