Photosynthesis: Part 3
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
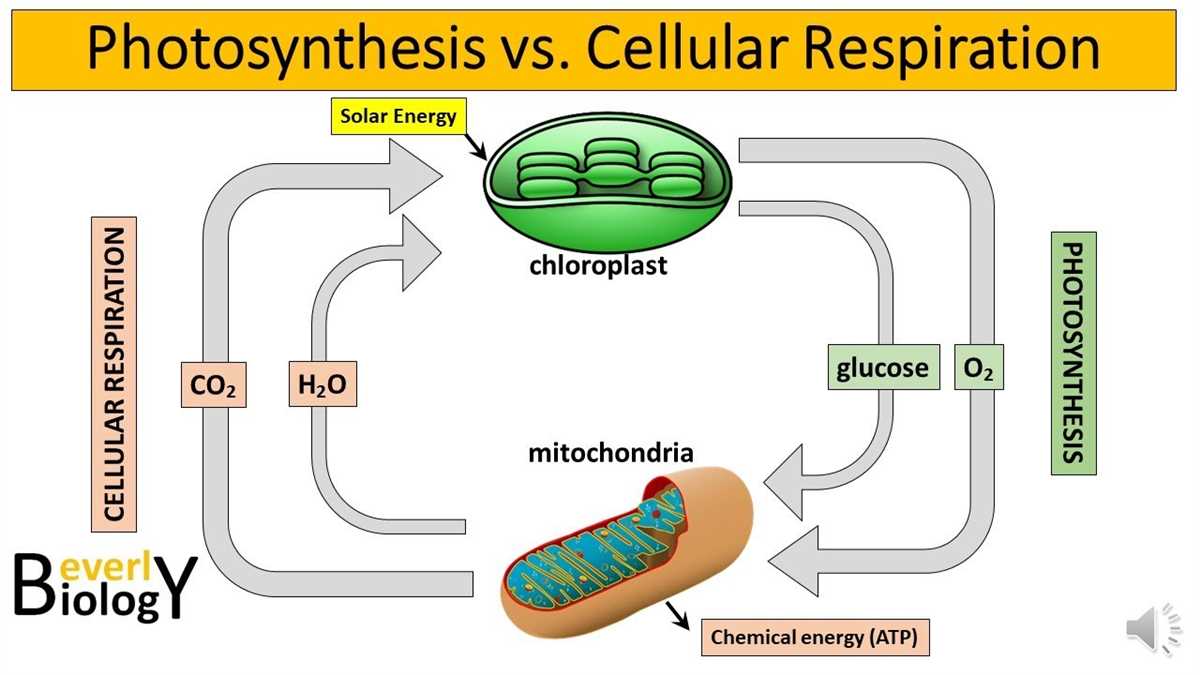
What are the “two separate reactions happening simultaneously” for both cellular respiration and photosynthesis?
Glucose Breakdown → Glycolysis, Pyruvate Processing, Citric Acid Cycle,
Light capture → Chlorophyll and other molecules in the Chloroplast split water to create electrons, hydrogen ions, NADPH, and Oxygen gas
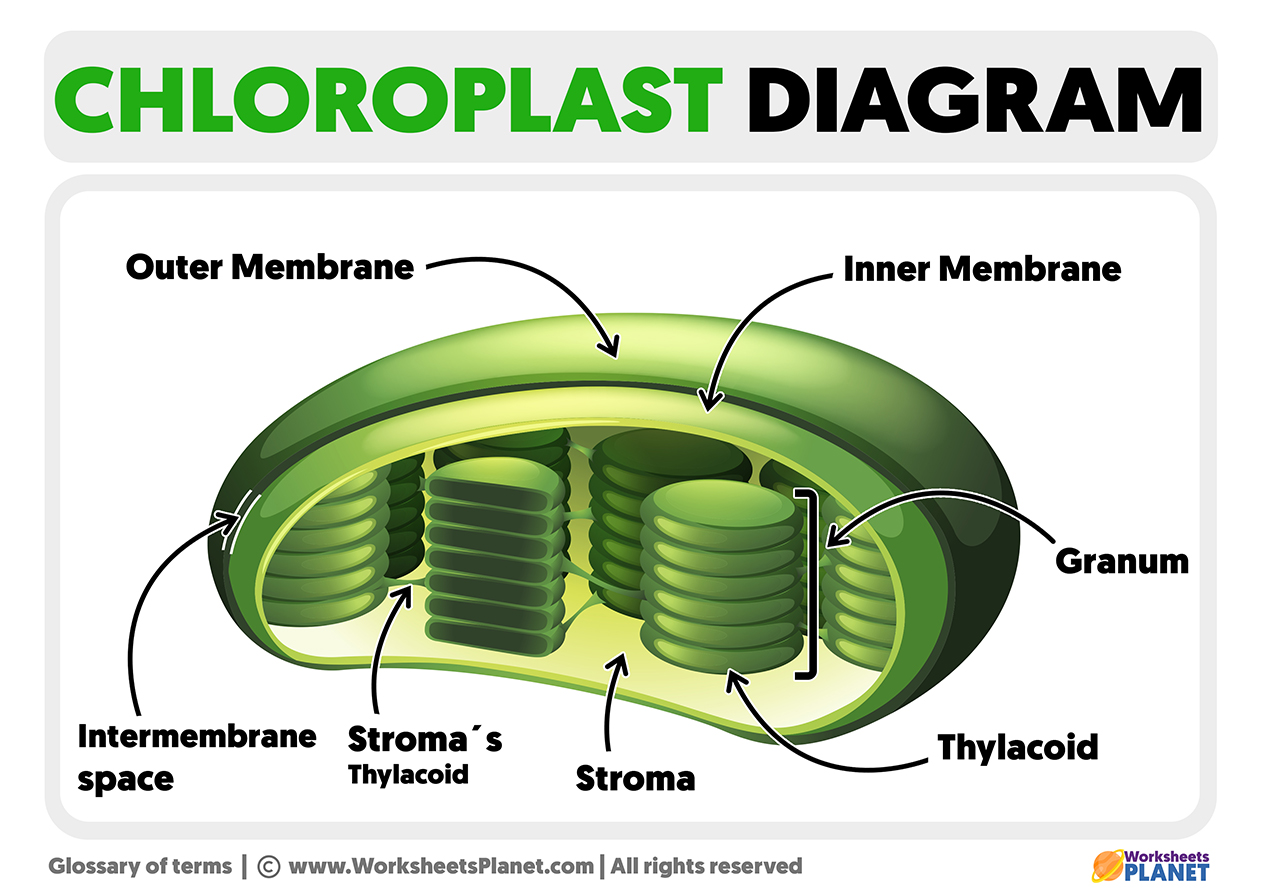
What are the basic structures and parts of a chloroplast?
Double Membrane
Inner Membrane
Outer Membrane
Stroma (water-based interior)
Thylakoids (folded, flattened sacs of membrane inside the stroma)
Thylakoid lumen (the space inside the thylakoid)
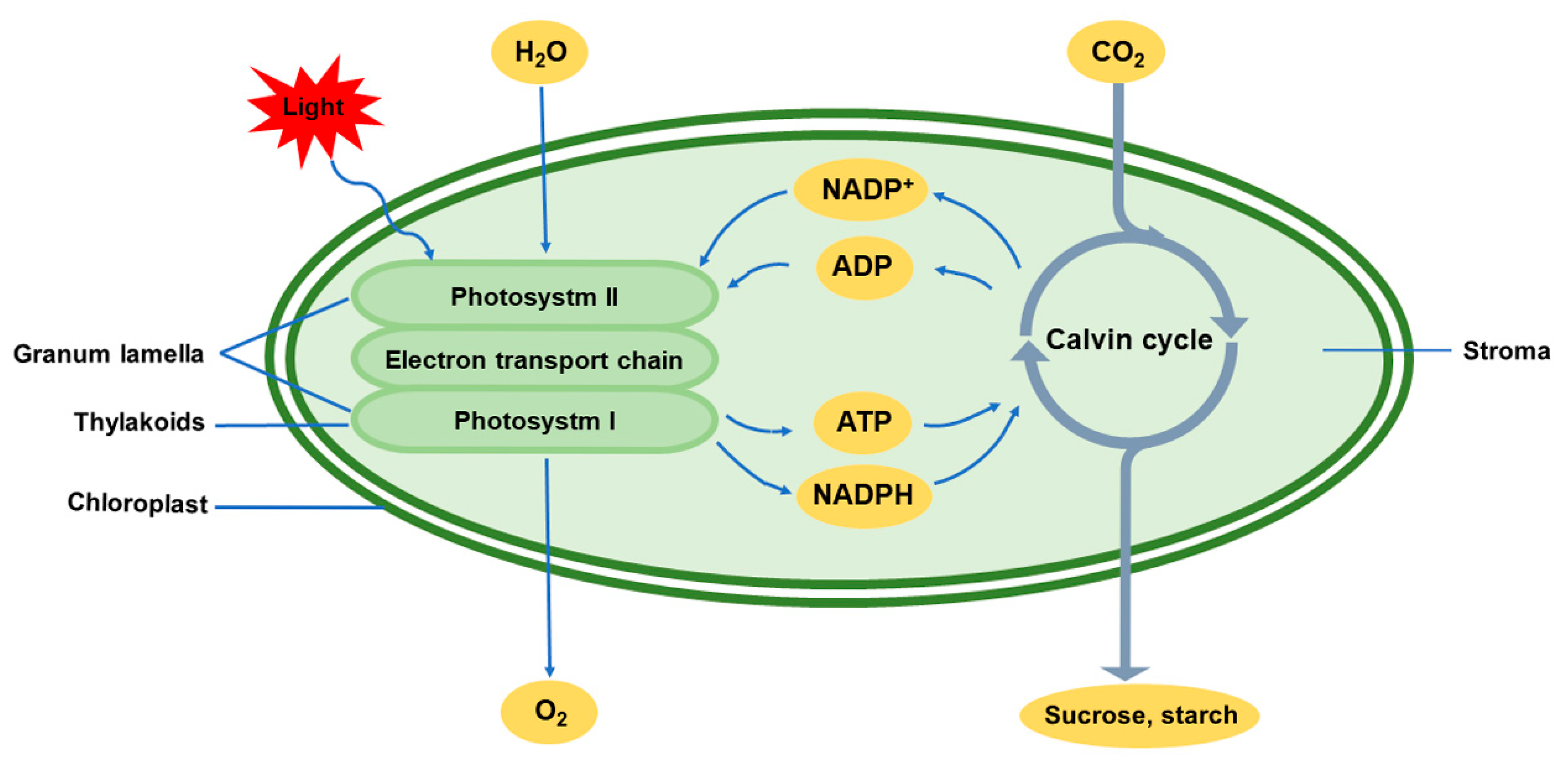
What are the two photosystems of photosynthesis and where are they located in a chloroplast?
Photosystem 2 and Photosystem 1 are both located in the Thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts
Photosystem 2 performs the first steps of light capture, not Photosystem 1
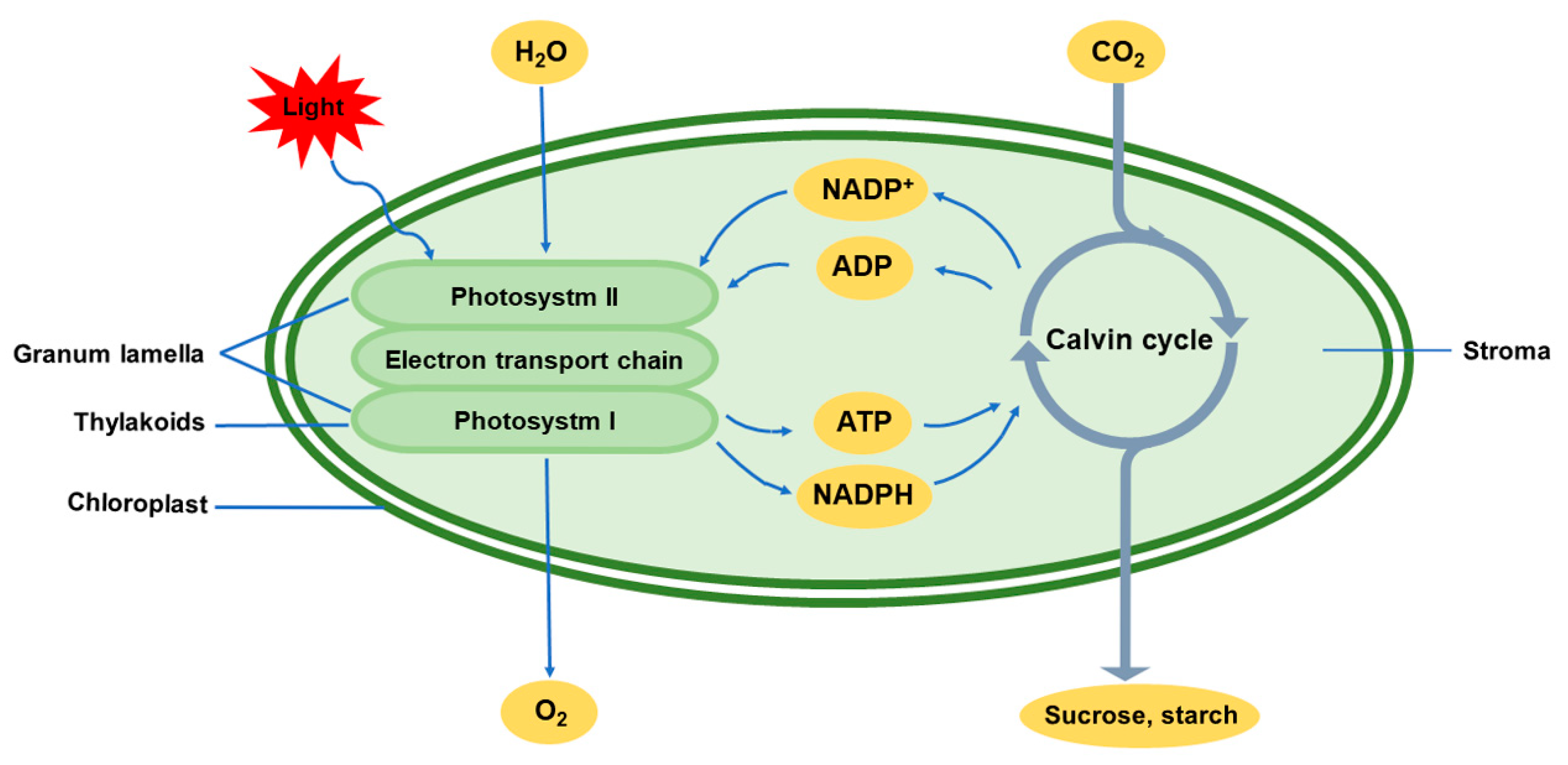
What kind of pigments do the two photosystems of photosynthesis use and what do those pigments do?
They both use chlorophyll pigments
These pigments contain electrons that can be energized when struck by photons of light
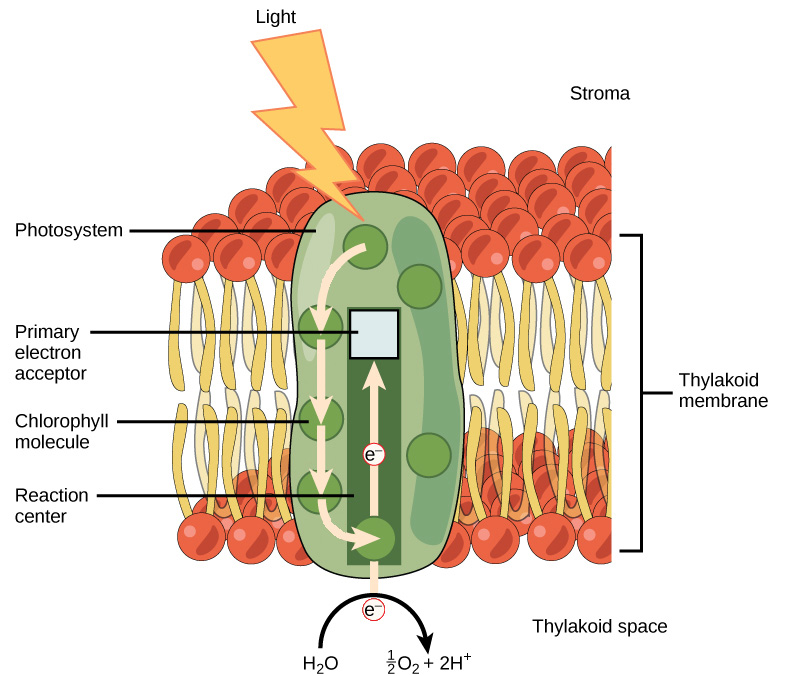
What is the 7 step process of photosystem 2?
Light energy is caught when it hits the light harvesting complex
Light harvesting complex transfers the energy to a chlorophyll-containing region called the reaction center
Electrons in the reaction center are energized by the transferred energy
Pheophytin molecule removes energized electrons from the reaction center
Pheophytin passes electrons into the Photosynthetic Electron Transport Chain (pETC)
The electrons are transferred through the Thylakoid membrane, which creates the proton gradient which is in the Thylakoid lumen
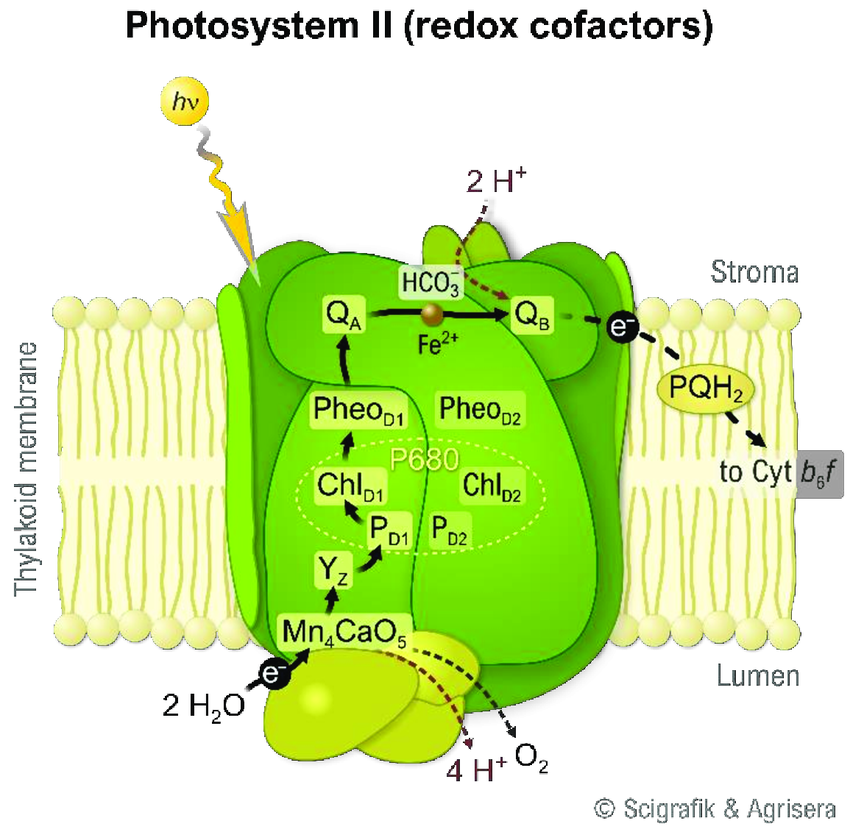
What are the names and functions of all relevant parts of the photosystem 2 process?
Light harvesting complex → Harvests light energy
Reaction center → Energizes electrons
Pheophytin → Removes energized electrons from the reaction center
Photosynthetic ETC → Transports electrons through the Thylakoid membrane
ATP synthase → Diffuses hydrogen down its concentration gradient, makes ATP
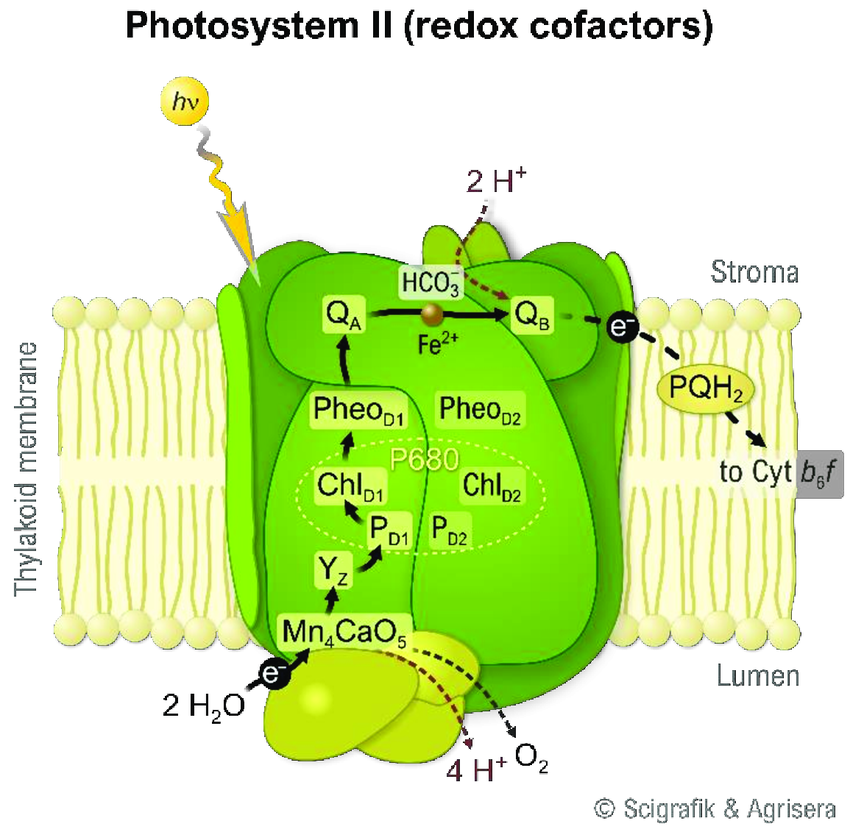
Where does each step of the process of photosystem 2 occur?
Light harvesting complex → Thylakoid membrane
Reaction center → Core of Photosystem 2
Pheophytin → Photosystem 2 reaction center
Photosynthetic ETC → Thylakoid Membrane
ATP synthase → Thylakoid Membrane (separate from Photosystem 2)
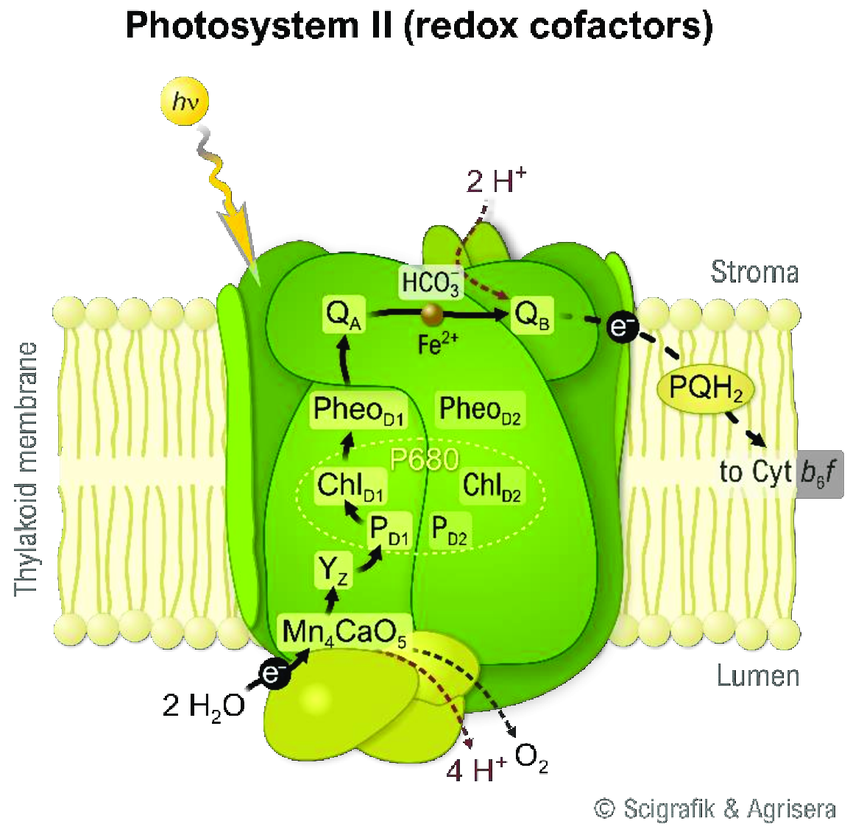
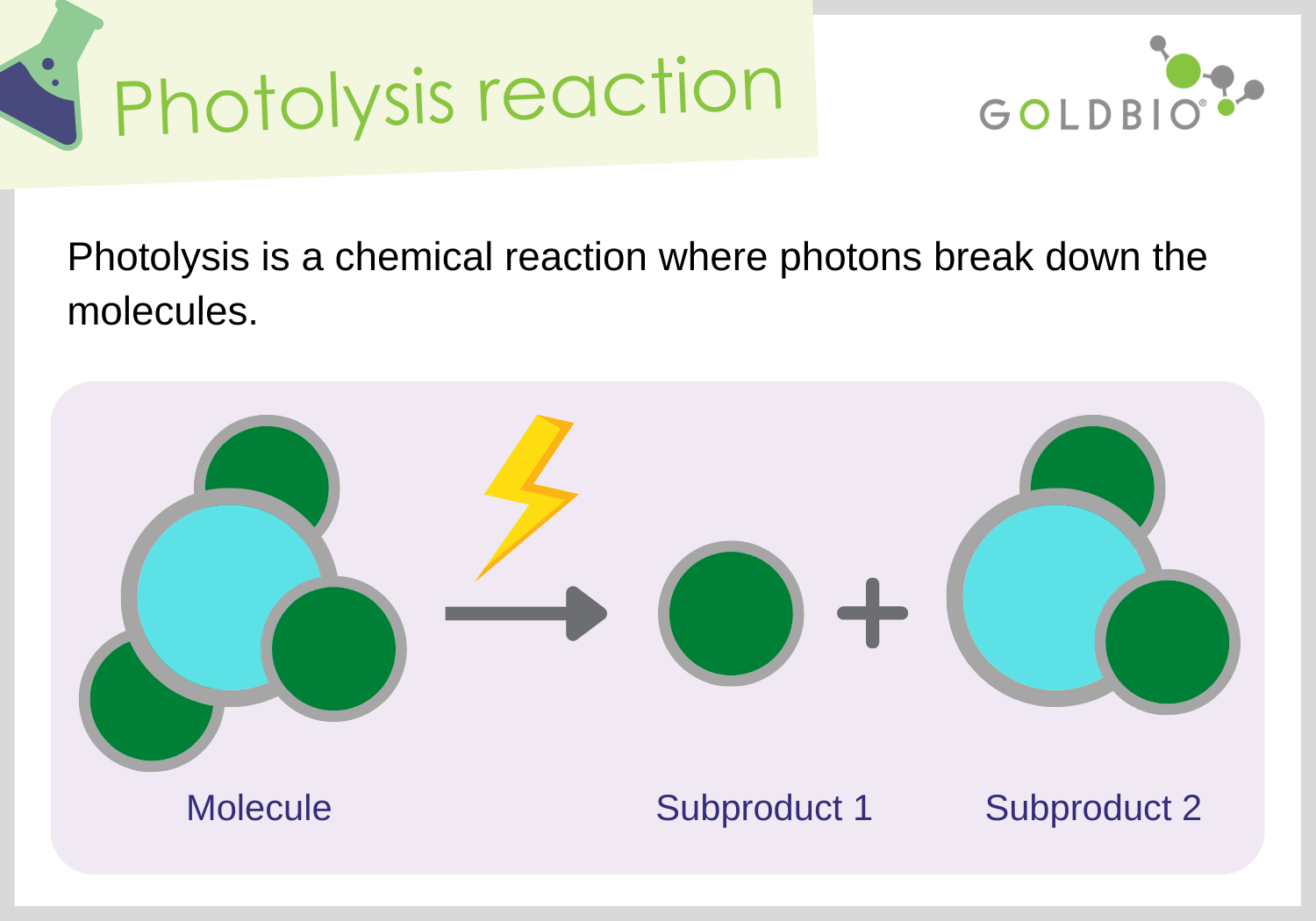
What is photolysis? What are the outputs of its chemical reaction?
The water-splitting reaction that Photosystem 2 performs that creates:
2 electrons, go to Photosystem 2
2 hydrogens ions, used to make NADPH
Oxygen Gas (O2)
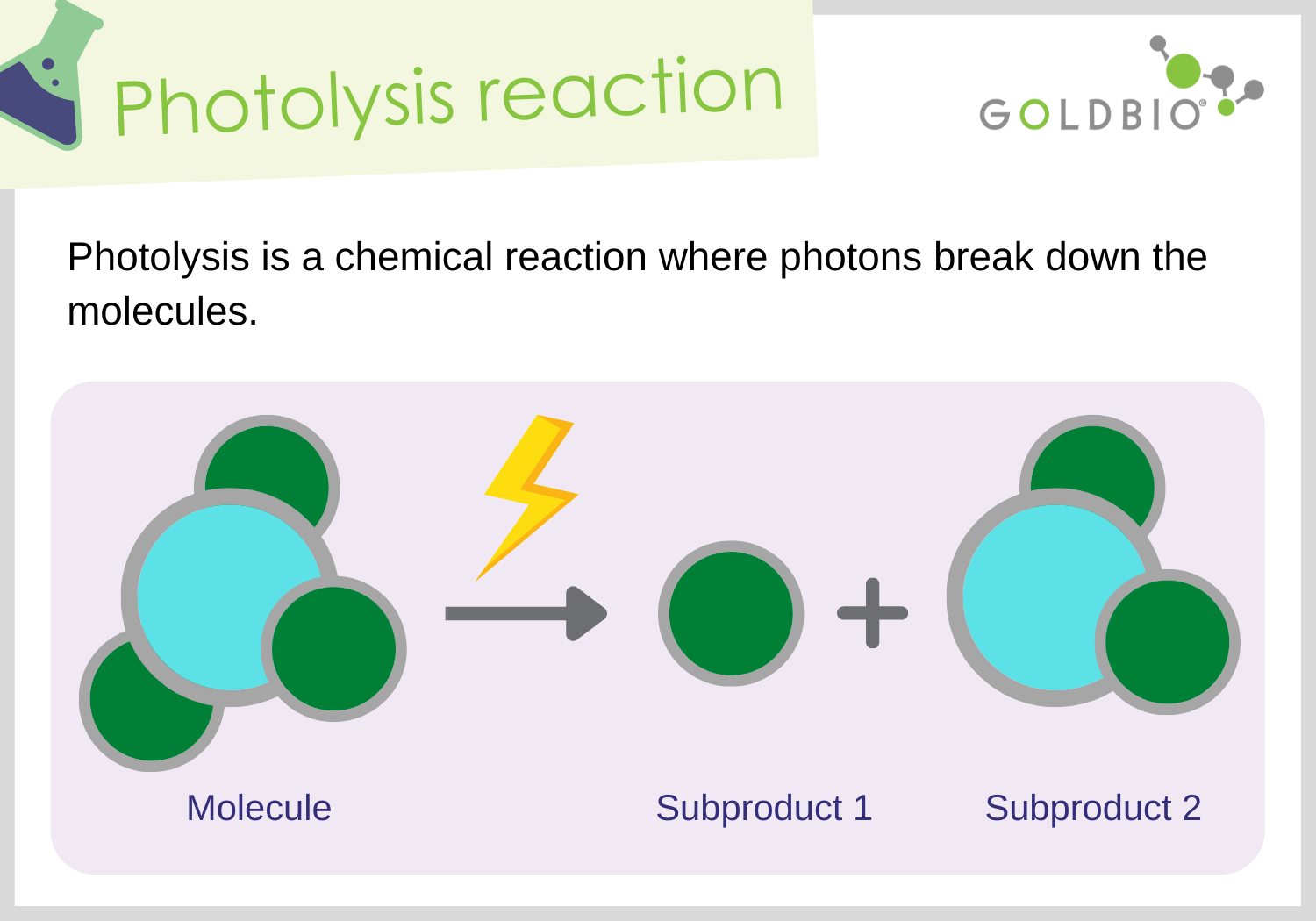
Why is photolysis necessary?
The electrons that Pheophytin took from Photosystem 2 need to be replaced
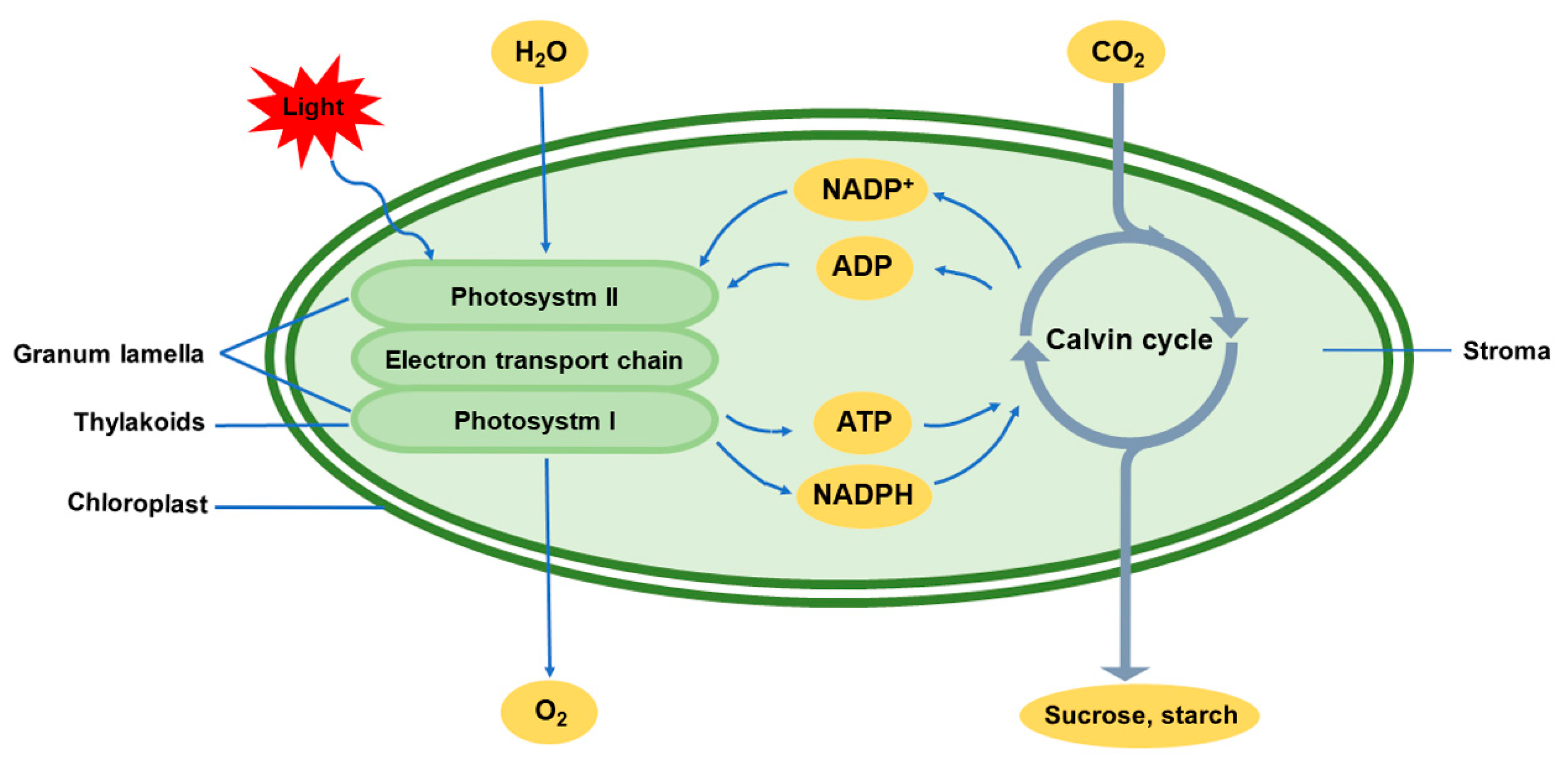
Where is photosystem 1 in the chloroplast?
Thylakoid membrane
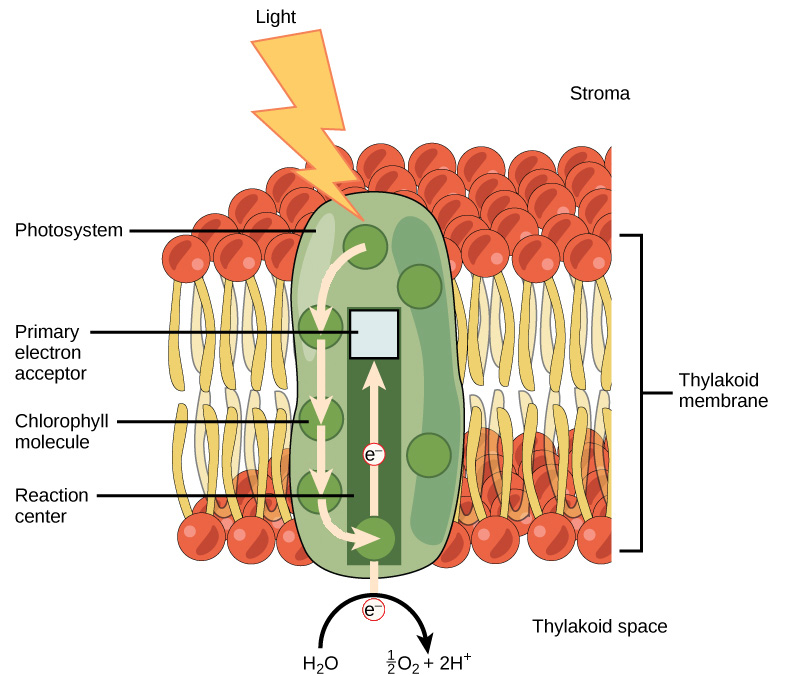
What are the names and functions of relevant parts of photosystem 1?
Plastocyanin → Electron carrier
Light harvesting complex → Captures photons, transfers them to Photosystem 1 reaction center
Reaction center → Chlorophyll donates an electron to PSI
Ferredoxin → Accepts electrons from PSI and transfers them to NADP+ to form NADPH
What are the two chemical pathways for energized electrons in photosystem 1?
Cyclic Electron Flow
Non-Cyclic Electron Flow
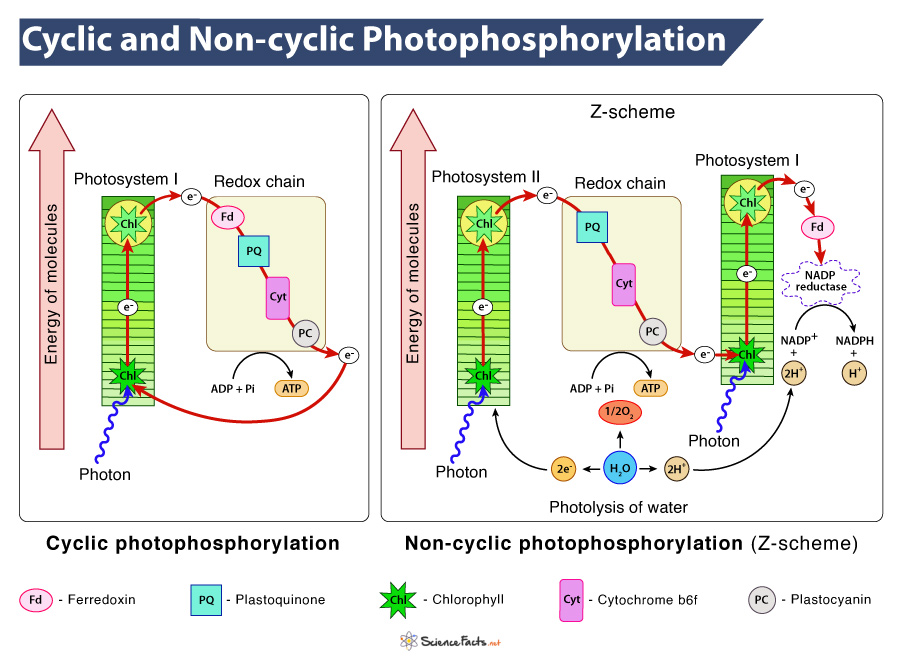
What are the names and functions of the relevant parts of the chemical pathways of photosystem 1?
Photosynthetic ETC → Transfers electrons from photosystem 2 to photosystem 1 and then to NADP+
NADP+ reductase → Catalyzes the final steps of the light reactions
What are the similarities between NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH?
Nad+/NADH
NAD+ is the form of NADH that is not carrying electrons. Used to carry energy that forms catabolic reactions (reactions that break down molecules)
NADP+/NADPH
NADP+ is the form of NADPH that is not carrying electrons. Used to carry energy that forms anabolic reactions (reactions that build molecules)
Why does the cell use both NAD and NADP even though they are similar molecules with a nearly identical function?
Because the cell needs to preform both catabolic and anabolic reactions at the same time
So, the cell keeps two different pools of electrons for each type of reaction