Design of Goods and Services
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Goods and Services Selection
Organizations exist to provide goods or services to society
Great products are the key to success
Top organizations typically focus on core products
Customers buy satisfaction, not just a physical good or particular service
Fundamental to an organization's strategy with implications throughout the operations function
Goods or services are the basis for an organization's existence
Limited and predicable life cycles requires constantly looking for, designing, and developing new products
New products generate substantial revenue
Product Decision
The objective of the product decision is to develop and implement a product strategy that meets the demands of the marketplace with a competitive advantage
Product Strategy Options
Differentiation
Shouldice Hospital
Low cost
Taco Bell
Rapid response
Toyota
Product Life Cycles
May be any length from a few days to decades
The operations function must be able to introduce new products successfully
Product Life Cycle and Strategy - Introductory Phase
Fine tuning may warrant unusual expenses for
Research
Product development
Process modification and enhancement
Supplier development
Product Life Cycle and Strategy - Growth Phase
Product design begins to stabilize
Effective forecasting of capacity becomes necessary
Adding or enhancing capacity may be necessary
Product Life Cycle and Strategy - Maturity Phase
Competitors now established
High volume, innovative production may be needed
Improved cost control, reduction in options, paring down of product line
Product Life Cycle and Strategy - Decline Phase
Unless product makes a special contribution to the organization, must plan to terminate offering
Generating New Products
Understanding the customer
Economic change
Sociological and demographic change
Technological change
Political and legal change
Market practice, professional standards, suppliers, distributors
Product Development Stages
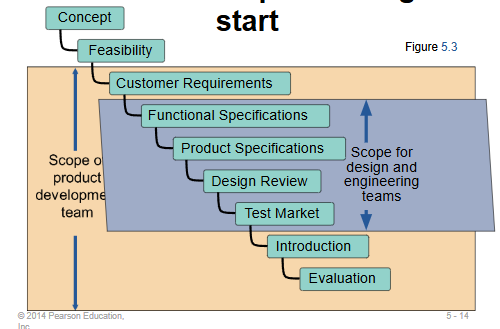
Quality Function Deployment
Identify customer wants
Identify how the good/service will satisfy customer wants
Relate customer wants to product hows
Identify relationships between the firm’s hows
Develop customer importance ratings
Evaluate competing products
Compare performance to desirable technical attributes
Organizing for Product Development - Traditionally
distinct departments
Duties and responsibilities are defined
Difficult to foster forward thinking
Organizing for Product Development - Champion
Product manager drives the product through the product development system and related organizations
Organizing for Product Development - Team Approach
Cross functional – representatives from all disciplines or functions
Product development teams, design for manufacturability teams, value engineering teams
Organizing for Product Development - Japanese “whole organization” approach
No organizational divisions
Manufacturability and Value Engineering
Benefits:
Reduced complexity of the product
Reduction of environmental impact
Additional standardization of components
Improvement of functional aspects of the product
Improved job design and job safety
Improved maintainability (serviceability) of the product
Robust design
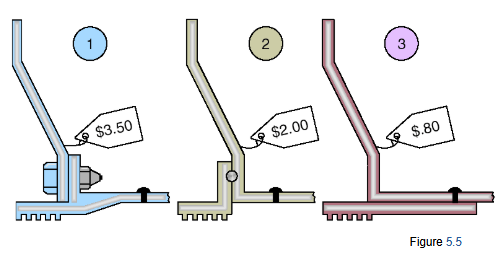
Cost Reduction of a Bracket via Value Engineering
Issues for Product Design
Robust design
Modular design
Computer-aided design (CAD)
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM)
Virtual reality technology
Value analysis
Sustainability and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Robust Design
Product is designed so that small variations in production or assembly do not adversely affect the product
Typically results in lower cost and higher quality
Modular Design
Products designed in easily segmented components
Adds flexibility to both production and marketing
Improved ability to satisfy customer requirements
Computer Aided Design (CAD)
Using computers to design products and prepare engineering documentation
Shorter development cycles, improved accuracy, lower cost
Information and designs can be deployed worldwide
Extensions of CAD
Design for Manufacturing and Assembly (DFMA)
Solve manufacturing problems during the design stage
3-D Object Modeling
Small prototype development
CAD through the internet
International data exchange through STEP
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
Utilizing specialized computers and program to control manufacturing equipment
Often driven by the CAD system (CAD/CAM)
Benefits of CAD/CAM
Product quality
Shorter design time
Production cost reductions
Database availability
New range of capabilities
Virtual Reality Technology
Computer technology used to develop an interactive, 3-D model of a product from the basic CAD data
Allows people to ‘see’ the finished design before a physical model is built
Very effective in large-scale designs such as plant layout
Value Analysis
Focuses on design improvement during production
Seeks improvements leading either to a better product or a product which can be produced more economically with less environmental impact
Sustainability and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA)
Sustainability means meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs
LCA is a formal evaluation of the environmental impact of a product