Economic Growth
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is a useful measure in Living Standards?
real GDP per person - correlates with life expectancy, infant health, and literacy
Compound Interest
pays interest on the original deposit and all previously accumulated interest
differences in interest rates matter
Growth Rates in GDP per capita
have the same effect as interest rates
relatively small growth has a very large effect over a long period
in the long run, the growth rate of an economy matters
What does Real Output per person depend on?
How much each worker can produce
The percentage of the population that is working
What determines a Nation’s Economic Growth Rate?
In the long run, increases in output per person arise primarily from increases in average labour productivity
Real GDP per person Formula
Y = real GDP
N = number of employed workers
POP = total population
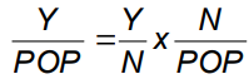
GDP per capita increases when…
Output per worker (Y/N) increases OR
The share of the population employed (N/POP) increases
In the Long Run, Increases in Average Labour Productivity cause..
increases in output per person and hence living standards
6 Determinants of Average Labour Productivity
Human capital
Physical capital
Land and other natural resources
Technology
Entrepreneurship and management
Political and legal environment
What does Human Capital Consist of?
the talents, education, training, and skills of workers
How does Human Capital affect Productivity?
increases worker productivity and innovation, leading to higher output and economic prosperity
How does Cost-Benefit Principle apply to Human Capital?
investing in education and skills brings long-term economic benefits, outweighing the initial costs
What is One Economic Benefit of acquiring Human Capital?
skilled workers receive a premium (higher wages) for their expertise
What is Physical Capital?
More and better capital (machinery, equipment, buildings, infrastructure) increases worker productivity and raises quality
Diminishing Returns to Capital
If the amount of labour and other inputs employed is held constant, then the greater the amount of capital already in use, the less an additional unit of capital adds to production
Assumption: all inputs except capital are held constant
Result: output increases at a decreasing rate
What are the Implications of Diminishing Returns to Capital?
output and labour productivity still increase, but at a decreasing rate
Does Increasing Capital always Lead to Growth?
yes, it contributes positively to growth, but with diminishing marginal returns
What limits Productivity Gains from Capital Investment?
diminishing marginal returns - the benefit of each additional unit of capital decreases over time
How is Average Labour Productivity typically measured?
real GDP per worker
What is the Relationship between Physical Capital and Labour Productivity?
countries with more capital per worker tend to have higher average labour productivity
How does Physical Capital affect Production?
increases efficiency, lower costs, and enables the creation of new products and services
What are some benefits of improved Physical Capital?
higher productivity (more goods with fewer workers), innovation and enhanced infrastructure
How does Infrastructure contribute to Productivity?
systems like transportation, communication and power grids support efficient economic activity
How do Natural Resources contribute to the Economy?
increase worker productivity, create jobs, generate revenue, and support sustained economic growth
How can Countries benefit from Natural Resources?
the extraction and processing of them creates jobs, generates income and can drive innovation and technological advancement
natural attractions like landscapes and wildlife can attract international visitors and generate revenue
land is also important for agriculture - producing food and raw materials, supporting other industries and exports
How does Technology improve Productivity?
increases output using the same input, improves efficiency, and lowers production costs
How has Globalisation been influenced by Technology?
it enables easier access to global markets for both selling products and sourcing inputs
What do Entrepreneurs do?
create new economic enterprises and identify business opportunities
crucial to a dynamic, healthy and growing society
increase competition and drive improvements in efficiency, quality, and customer service
What kinds of policies support Productive Entrepreneurship?
favourable taxation, effective regulation, and policies that foster value innovation
Why is the Political and Legal Environment important for the Economy?
encourages people to be economically productive and supports sustainable growth
What are Property Rights and why are they Essential?
define who owns what and how assets can be used, essential for encouraging investment
How does Political Stability affect Economic Growth?
attracts investment and supports a healthy business environment
what is the Rule of Law and why is it Important?
a fair, predictable legal framework that supports business operations and economic growth
What role does Effective Regulation Play in the Economy
protects consumers, promotes competition, and provides a stable environment for businesses
The Solow Growth Model
starts by postulating a relationship between the quantities of inputs used in the production process and the economy’s total output (Y)
assume there are only 2 inputs:
Physical capital, denoted as K
Labour, denoted as N
Physical Capital (Solow Growth Model)
consists of the machines and buildings used in the production of the economy’s GDP
Labour (Solow Growth Model)
the number of workers used in the production of goods and services
Solow Growth Model Production Function
Y = F(K,N)
output is a function of the quantities of capital and labour used in the production process
Constant Returns to Scale (CRS)
if the labour and capital inputs are both increased by equal proportions, then total output increases by the same proportion
CRS Production Function
zY = F(zK, zN)
where z is any positive number, assume z = 1/N
simplifies to y = f(k)
The Marginal Product
△Y = the change in output
△K = the change in the amount of capital
Holding the labour input constant, it is defined as:
assumed to be decreasing
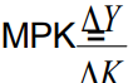
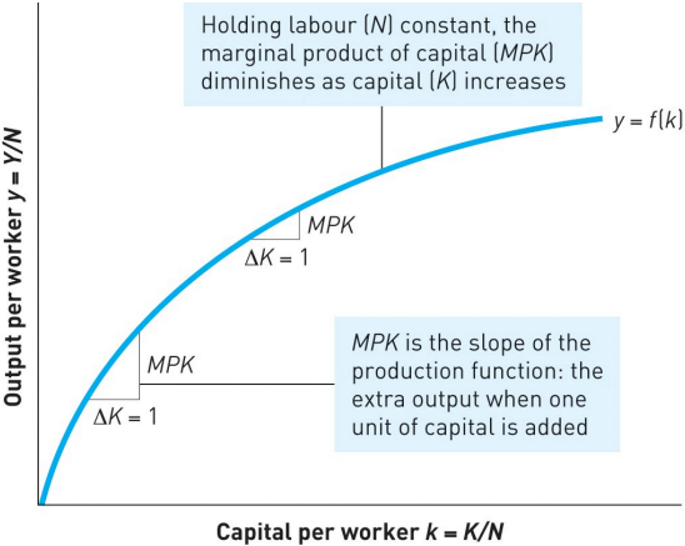
Production Function
the curve y=f(k) shows how average labour productivity increases with the capital–labour ratio k=K/N
with a constant labour force, the slope represents the marginal product of capital (MPK), which declines as k rises due to diminishing returns—making the curve flatten at higher capital level
in the Solow Growth Model, how is Investment Financed?
saving
Formula for Solow Growth Model, Investment and Saving
I = S = sY
I = investment in physical capital
S = total saving
s = the saving rate
Y = income
Per Capital Formula for Solow Growth Model, Investment and Saving
i = s * f(k)
i = investment per worker
s = savings rate
k = capita per worker
What factors determine the amount of Investment needed to keep the Capital-Labour Ratio Constant?
depreciation rate d
population growth rate n
What is Depreciation in the Solow Model?
the portion of capital that wears out or becomes less productive each period
How much Investment is needed to offset Depreciation alone?
dk, where d is the depreciation rate and k is capital per worker
How does Population Growth affect Investment Needs?
it requires additional investment of nk to maintain the capital-labour ratio
n = population (labour force) growth rate
What is the Total Investment Per Worker needed to keep the Capital-Labour Ratio constant?
(d + n)k
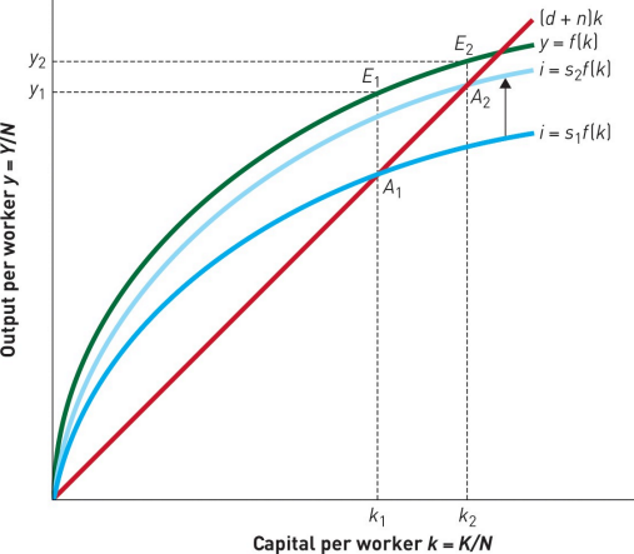
An Increase in the Saving Rate
An increase from s1 to s2 raises investment, shifting the curve upward. This leads to a higher capital–labour ratio (k1 to k2) and increased labour productivity (y1 to y2). During the transition from E1 to E2, productivity rises and output grows faster than the population. At the new equilibrium (E2), productivity stabilizes at y2 and output growth matches population growth (n)
Solow Model Implications for explaining Economic Growth
Average labour productivity depends on the amount of physical capital per head in the workforce
The more available, the higher the level of both labour productivity and income per head of the population
In the long run, the economy’s steady state growth rate should equal the rate of population growth
Technical Progress in the Solow Model
An improvement in knowledge that enables a higher output to be produced from existing resources
To add it, we make a change to the production function
Rewrite as: y = Af(k),
Where A denotes technology
If technology improves by ‘g’% per year then A = (1+g)
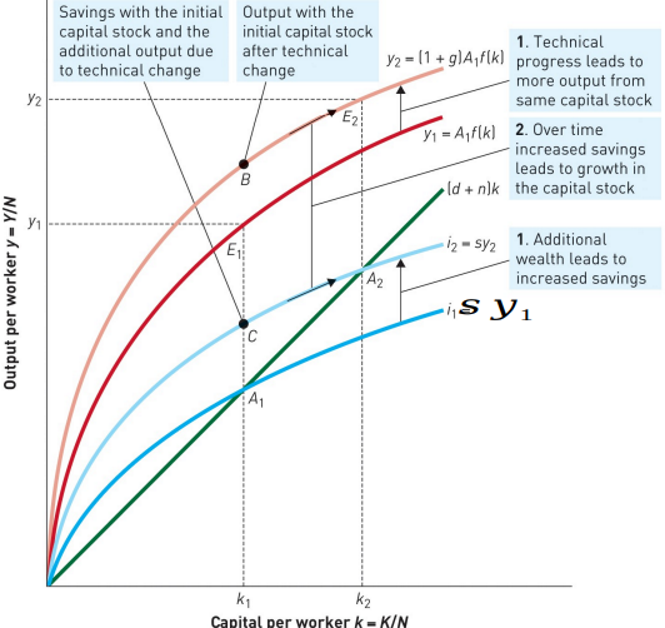
Is it possible that average Labour Productivity can Increase, even if the Capital-Labour Ratio is constant?
yes
Total Factor Productivity
entrepreneurship and management skills
the political and legal environment
Human Capital in the Solow Model
The accumulation of skills, experience and knowledge by the workforce
Workers with a large stock of it are more productive than workers with less training
Let ‘H’ denote it: Y = AF(K,N,H)
Democracy
Rule of the people; a way of governing which depends on the will of the people
How does Democracy indirectly contribute to Economic Growth?
through higher human capital accumulation, lower inflation, reduced political instability, and increased economic freedom
Opportunity Costs of Producing more Capital Goods
Fewer consumer goods
People may be willing to forego present consumption to have more in the future
Reduced leisure time
Possible risks of health and safety from rapid capital production
The cost of research and development (R&D) to improve technology
The cost of education to develop and use new capital
Why does the Government Pay for Public Education?
A democracy works better with educated voters
Progressive taxes capture some of the higher income
Increases chances of technical innovation
Poor families could not pay
How does the Government Promote Growth with Savings and Interest?
Policies can encourage new capital formation and saving in the private sector
Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) are an incentive for individuals to save
Periodically offers investment tax credits
Can invest directly in capital formation
Construction of infrastructure such as roads, bridges, airports, and dams
U.S. interstate highway system reduced costs of transporting goods, making markets more efficient
Why does the Government Promote Growth with Research and Development Support?
It promotes innovation
Some types of research, such as basic science, create externalities that a private firm cannot capture
Silicon chip
Fund basic science with National Science Foundation (NSF) and other government grants
Government sponsors research for military and space applications
Government owns GPS satellites
Maintain political and legal framework to support growth
Why do most Countries need institutions to support Growth?
Corruption creates uncertainty about property rights and drains financial resources out of the country
Regulation discourages entrepreneurship
Taxes discourage risk-taking
Markets do not function efficiently
Lack of political stability discourages foreign investment
How do Markets respond to increasing Scarcity of Resources?
high prices trigger innovation, substitution, and conservation